《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.15
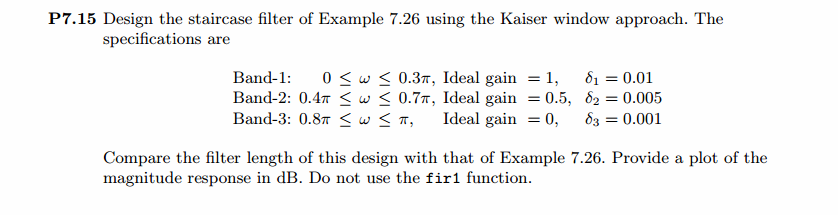
用Kaiser窗方法设计一个台阶状滤波器。
代码:
%% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
%% Output Info about this m-file
fprintf('\n***********************************************************\n');
fprintf(' <DSP using MATLAB> Problem 7.15 \n\n'); banner();
%% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ % staircase bandpass 3-Band
w1 = 0; w2 = 0.3*pi; delta1 = 0.01;
w3 = 0.4*pi; w4 = 0.7*pi; delta2 = 0.005;
w5 = 0.8*pi; w6 = pi; delta3 = 0.001; tr_width = min(w3-w2, w5-w3); f = [0 w2 w3 w4 w5 w6]/pi;
m = [1 1 0.5 0.5 0 0]; [Rp1, As1] = delta2db(delta1, delta3);
[Rp2, As2] = delta2db(delta2, delta3);
As = min(As1, As2) M = ceil((As-7.95)/(2.285*tr_width)) + 1; % Kaiser Window Length if As > 21 || As < 50
beta = 0.5842*(As-21)^0.4 + 0.07886*(As-21);
else
beta = 0.1102*(As-8.7);
end fprintf('\nKaiser Window method, Filter Length: M = %d. beta = %.4f\n', M, beta); n = [0:1:M-1]; wc1 = (w2+w3)/2; wc2 = (w4+w5)/2; %wc = (ws + wp)/2, % ideal LPF cutoff frequency hd = ideal_lp(wc1, M) + 0.5*(ideal_lp(wc2, M) - ideal_lp(wc1, M));
w_kai = (kaiser(M, beta))'; h = hd .* w_kai;
[db, mag, pha, grd, w] = freqz_m(h, [1]); delta_w = 2*pi/1000;
[Hr,ww,P,L] = ampl_res(h); Rp1 = -(min(db(1 :1: w2/delta_w+1))); % Actual Passband Ripple
fprintf('\nActual Passband Ripple1 is %.4f dB.\n', Rp1); Rp2 = -(min(db(w3/delta_w+1 :1: w4/delta_w+1))); % Actual Passband Ripple
fprintf('\nActual Passband Ripple2 is %.4f dB.\n', Rp2); As = -round(max(db(floor(w5/delta_w)+1 : 1 : floor(w6/delta_w)+1 ))); % Min Stopband attenuation
fprintf('\nMin Stopband attenuation is %.4f dB.\n', As); [delta1, delta3] = db2delta(Rp1, As)
[delta2, delta3] = db2delta(Rp2, As) % Plot figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 7.15 ideal_lp Method')
set(gcf,'Color','white'); subplot(2,2,1); stem(n, hd); axis([0 M-1 -0.3 0.5]); grid on;
xlabel('n'); ylabel('hd(n)'); title('Ideal Impulse Response'); subplot(2,2,2); stem(n, w_kai); axis([0 M-1 0 1.1]); grid on;
xlabel('n'); ylabel('w(n)'); title('Kaiser Window'); subplot(2,2,3); stem(n, h); axis([0 M-1 -0.3 0.5]); grid on;
xlabel('n'); ylabel('h(n)'); title('Actual Impulse Response'); subplot(2,2,4); plot(w/pi, db); axis([0 1 -120 10]); grid on;
set(gca,'YTickMode','manual','YTick',[-90,-65,-6,0]);
set(gca,'YTickLabelMode','manual','YTickLabel',['90';'65';' 6';' 0']);
set(gca,'XTickMode','manual','XTick',[f]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Decibels'); title('Magnitude Response in dB'); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 7.15 h(n) ideal_lp Method')
set(gcf,'Color','white'); subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi, db); grid on; axis([0 2 -120 10]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Decibels'); title('Magnitude Response in dB');
set(gca,'YTickMode','manual','YTick',[-90,-65,-6,0])
set(gca,'YTickLabelMode','manual','YTickLabel',['90';'65';' 6';' 0']);
set(gca,'XTickMode','manual','XTick',[f,1+f(2:6)]); subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, mag); grid on; %axis([0 2 -100 10]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Absolute'); title('Magnitude Response in absolute');
set(gca,'XTickMode','manual','XTick',[f,1+f(2:6)]);
set(gca,'YTickMode','manual','YTick',[0,0.5, 1]) subplot(2,2,2); plot(w/pi, pha); grid on; %axis([0 1 -100 10]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Rad'); title('Phase Response in Radians');
subplot(2,2,4); plot(w/pi, grd*pi/180); grid on; %axis([0 1 -100 10]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Rad'); title('Group Delay'); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 7.15 Amp Res of h(n)')
set(gcf,'Color','white'); plot(ww/pi, Hr); grid on; %axis([0 1 -100 10]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Hr'); title('Amplitude Response');
set(gca,'YTickMode','manual','YTick',[-delta3,0,delta3,0.5-0.005, 0.5+0.005,1-delta1,1,1+delta1])
%set(gca,'YTickLabelMode','manual','YTickLabel',['90';'45';' 0']);
set(gca,'XTickMode','manual','XTick',[f,2]); %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
%% fir2 function method
%% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
f = [w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6]/pi;
m = [1 1 0.5 0.5 0 0];
ripple = [0.01 0.005 0.001]; fprintf('\n--------- use fir2 function ---------\n'); h_check = fir2(M-1, f, m, kaiser(M, beta)); [db, mag, pha, grd, w] = freqz_m(h_check, [1]);
%[Hr,ww,P,L] = ampl_res(h_check);
[Hr,ww,P,L] = Hr_Type2(h_check); %% -------------------------------------------
%% plot
%% -------------------------------------------
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 7.15 fir2 Method')
set(gcf,'Color','white'); subplot(2,2,1); stem(n, hd); axis([0 M-1 -0.3 0.5]); grid on;
xlabel('n'); ylabel('hd(n)'); title('Ideal Impulse Response'); subplot(2,2,2); stem(n, w_kai); axis([0 M-1 0 1.1]); grid on;
xlabel('n'); ylabel('w(n)'); title('Kaiser Window'); subplot(2,2,3); stem([0:M-1], h_check); axis([0 M -0.3 0.5]); grid on;
set(gca,'XTickMode','manual','XTick',[0 M/2 M]);
xlabel('n'); ylabel('h\_check(n)'); title('Actual Impulse Response'); subplot(2,2,4); plot(w/pi, db); axis([0 1 -120 10]); grid on;
set(gca,'YTickMode','manual','YTick',[-90,-65,-6,0]);
set(gca,'YTickLabelMode','manual','YTickLabel',['90';'65';' 6';' 0']);
set(gca,'XTickMode','manual','XTick',[f]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Decibels'); title('Magnitude Response in dB'); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 7.15 h_check(n) fir2 Method')
set(gcf,'Color','white'); subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi, db); grid on; axis([0 2 -120 10]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Decibels'); title('Magnitude Response in dB');
set(gca,'YTickMode','manual','YTick',[-90,-65,-6,0])
set(gca,'YTickLabelMode','manual','YTickLabel',['90';'65';' 6';' 0']);
set(gca,'XTickMode','manual','XTick',[f,1+f(2:6)]); subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, mag); grid on; %axis([0 2 -100 10]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Absolute'); title('Magnitude Response in absolute');
set(gca,'XTickMode','manual','XTick',[f,1+f(2:6)]);
set(gca,'YTickMode','manual','YTick',[0,0.5, 1]) subplot(2,2,2); plot(w/pi, pha); grid on; %axis([0 1 -100 10]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Rad'); title('Phase Response in Radians');
subplot(2,2,4); plot(w/pi, grd*pi/180); grid on; %axis([0 1 -100 10]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Rad'); title('Group Delay');
运行结果:
Kaiser窗长M=74,两个通带衰减分别为0.0079dB和6.0345dB,阻带最小衰减65dB>60dB,满足设计要求。

用理想低通滤波方法设计的结果,实际脉冲响应、幅度谱(dB单位)
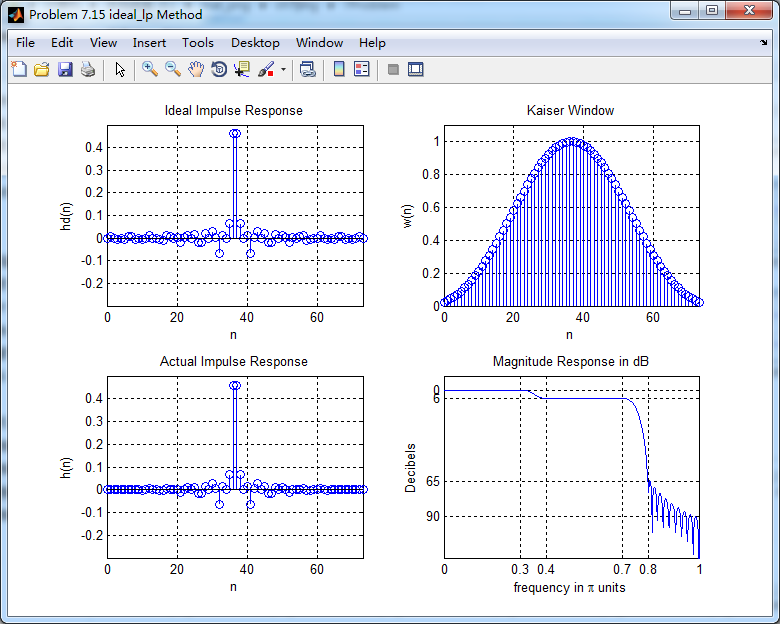
幅度谱(dB和绝对单位)、相位谱和群延迟响应

振幅响应(台阶状)
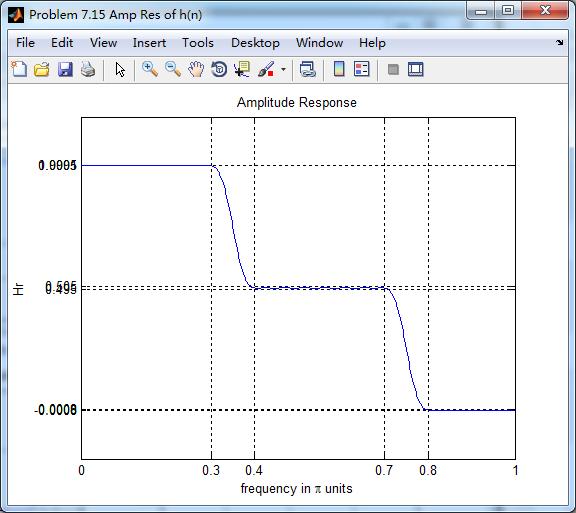
第一个台阶(通带)
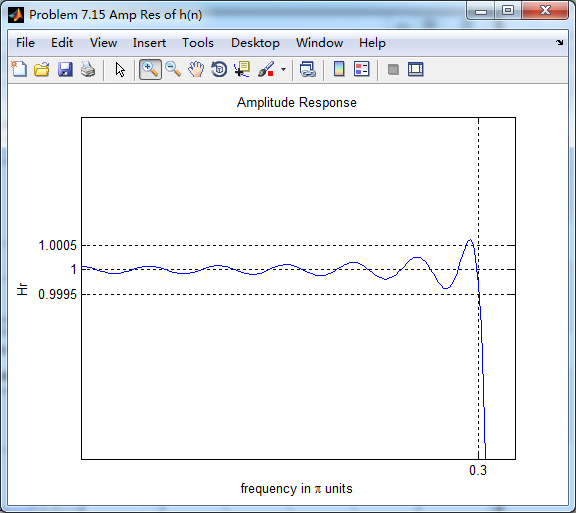
第二个台阶(通带)
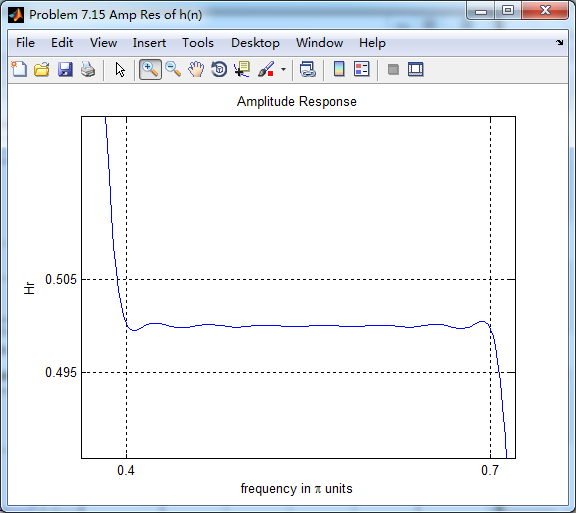
阻带

题目中暗示可以用fir1函数,但查了帮助和网上资料还是不会,只好用fir2函数的方法来设计,结果如下:

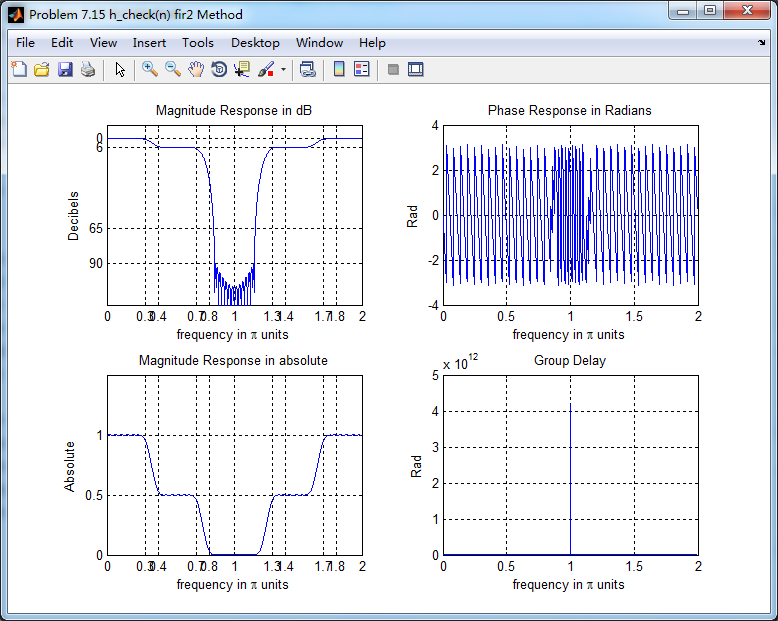
群延迟不是严格的常数了,非线性相位滤波器。
《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.15的更多相关文章
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 6.15
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 5.15
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 4.15
只会做前两个, 代码: %% ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- %% Outpu ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 2.15
代码: %% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ %% Output Info about ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 8.15
代码: %% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ %% Output Info about ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 5.38
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 5.31
第3小题: 代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Out ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 5.22
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% O ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 5.21
证明: 代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
随机推荐
- spring websocket报错:No matching message handler methods.
错误信息: [org.springframework.web.socket.messaging.WebSocketAnnotationMethodMessageHandler]-[DEBUG] No ...
- python之路-数据类型(方法)
Int i = 1 print(i.bit_length()) # 转化成二进制的最小位数. ''' 0000 0001 ''' Str class str(basestring): "&q ...
- day-02
昨天吧 需要写一个财务管理制度 很是伤脑 我发现一旦用脑过度 就会极其想吃零食 所以 昨天吃了些零食 说这个呢 无非是想说 我昨天学习python的时间很少 而且昨晚安装python软件也出现问题了 ...
- 修改VScode行号区的背景颜色
vs code是相当不错的一个编辑器,现阶段我用来编写nim程序. vs code非常丧心病狂一点就是行号区和编辑区的背景颜色都是一样, 这样会导致要看行首有没有对齐会非常吃力.这个问题让我纠结了非常 ...
- 石头的Xcode学习列表
http://www.cnblogs.com/JangoJing/tag/xcode/
- h5页面使用sessionStorage滚动到上次浏览器位置《原创》
前言: 因最近移动端开发过程中遇到一个运营提出的所谓技术难点需求,对于原生APP来说轻而易举,毕竟自己的APP用户操作指哪打哪,但是H5该怎么做?H5就实现不了么?对于一个爱研究攻克这些前端棘手问题的 ...
- java第六周作业
1 JSF请求处理生命周期的高度概述 从历史上看,Web应用程序必需的大部分开发,主要是处理Web客户端的HTTP请求.随着Web从传统的静态文档传送模型(在这种模型中,只请求静态Web页面,没有参 ...
- python3 opencv3 实现基本的人脸检测、识别功能
一言不和,先上码子(纯新手,莫嘲笑) # encoding: utf-8 #老杨的猫,环境:PYCHARM,python3.6,opencv3 import cv2,os import cv2.fac ...
- CCF CSP 201803-3 URL映射
转载自 https://blog.csdn.net/tigerisland45/article/details/81697594 /* CCF201803-3 URL映射 */ #include &l ...
- Echarts 一个开源图表设计工具
一般来说,因有所需,方有所求.最近项目中有这方面的需求,用着感觉不错.特此记录!此处仅是一个简单的demo.官网地址:http://echarts.baidu.com/,相关文档.插件都有. 1.js ...
