【Android开发学习笔记之一】5大布局方式详解
Android中常用的5大布局方式有以下几种:
- 线性布局(LinearLayout):按照垂直或者水平方向布局的组件。
- 帧布局(FrameLayout):组件从屏幕左上方布局组件。
- 表格布局(TableLayout):按照行列方式布局组件。
- 相对布局(RelativeLayout):相对其它组件的布局方式。
- 绝对布局(AbsoluteLayout):按照绝对坐标来布局组件。
1. 线性布局
线性布局是Android开发中最常见的一种布局方式,它是按照垂直或者水平方向来布局,通过“android:orientation”属性可以设置线性布局的方向。属性值有垂直(vertical)和水平(horizontal)两种。
常用的属性:
android:orientation:可以设置布局的方向
android:gravity:用来控制组件的对齐方式
layout_weight:控制各个组件在布局中的相对大小
第一个实例
①效果图:
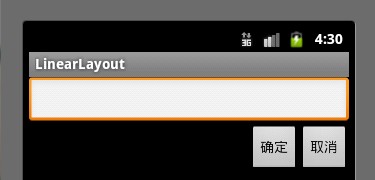
②核心代码如下:
main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
>
<EditText
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:gravity="right"
>
<!-- android:gravity="right"表示Button组件向右对齐 -->
<Button
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="确定"
/>
<Button
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="取消"
/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
第二个实例
①效果图:
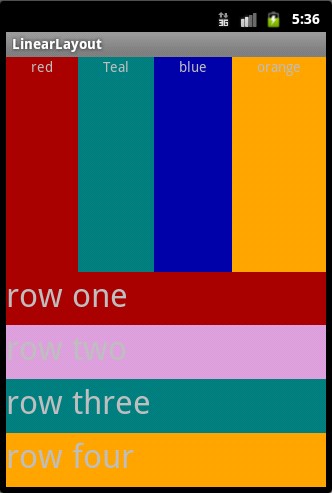
②核心代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"> <TextView
android:text="red"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:background="#aa0000"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
<!--android:gravity="center_horizontal"水平居中 -->
<!--layout_weight属性以控制各个控件在布局中的相对大小。layout_weight属性是一个非负整数值。
线性布局会根据该控件layout_weight值与其所处布局中所有控件layout_weight值之和的比值为该控件分配占用的区域。
例如,在水平布局的LinearLayout中有两个Button,这两个Button的layout_weight属性值都为1,
那么这两个按钮都会被拉伸到整个屏幕宽度的一半。如果layout_weight指为0,控件会按原大小显示,不会被拉伸;
对于其余layout_weight属性值大于0的控件,系统将会减去layout_weight属性值为0的控件的宽度或者高度,
再用剩余的宽度或高度按相应的比例来分配每一个控件显示的宽度或高度-->
<TextView
android:text="Teal"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:background="#008080"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"/> <TextView
android:text="blue"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:background="#0000aa"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
/> <TextView
android:text="orange"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:background="#FFA500"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
/> </LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"> <TextView
android:text="row one"
android:textSize="15pt"
android:background="#aa0000"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
<!-- -->
<TextView
android:text="row two"
android:textSize="15pt"
android:background="#DDA0DD"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
/> <TextView
android:text="row three"
android:textSize="15pt"
android:background="#008080"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
<TextView
android:text="row four"
android:textSize="15pt"
android:background="#FFA500"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
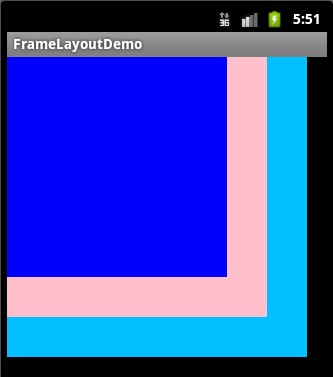
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:background="#00BFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="260dp"
android:layout_height="260dp"
android:background="#FFC0CB"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="220dp"
android:layout_height="220dp"
android:background="#0000FF"
/>
</FrameLayout>
android:shrinkColumns:收缩指定的列以适合屏幕,不会挤出屏幕
android:stretchColumns:尽量把指定的列填充空白部分
android:layout_column:控件放在指定的列
android:layout_span:该控件所跨越的列数
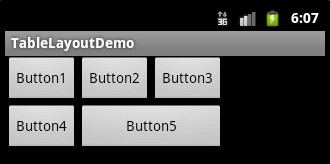
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TableRow>
<Button
android:text="Button1"
/>
<Button
android:text="Button2"
/>
<Button
android:text="Button3"
/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<Button
android:text="Button4"
/>
<Button
android:layout_span="2"
android:text="Button5"
/>
</TableRow> </TableLayout>
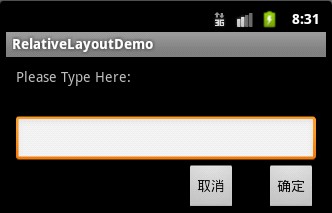
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="10px"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tev1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="30dp"
android:text="Please Type Here:"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/tx1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/tev1"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/tx1"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:text="确定"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/tx1"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/btn1"
android:layout_marginRight="30dp"
android:text="取消"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
【Android开发学习笔记之一】5大布局方式详解的更多相关文章
- 【转】Android开发学习笔记:5大布局方式详解
Android中常用的5大布局方式有以下几种: 线性布局(LinearLayout):按照垂直或者水平方向布局的组件. 帧布局(FrameLayout):组件从屏幕左上方布局组件. 表格布局(Tabl ...
- Android开发5大布局方式详解
Android中常用的5大布局方式有以下几种: 线性布局(LinearLayout):按照垂直或者水平方向布局的组件. 帧布局(FrameLayout):组件从屏幕左上方布局组件. 表格布局(Tabl ...
- Android开发之5大布局方式详解
Android中常用的5大布局方式有以下几种: 线性布局(LinearLayout):按照垂直或者水平方向布局的组件. 帧布局(FrameLayout):组件从屏幕左上方布局组件. 表格布局(Tabl ...
- android开发学习笔记000
使用书籍:<疯狂android讲义>——李刚著,2011年7月出版 虽然现在已2014,可我挑来跳去,还是以这本书开始我的android之旅吧. “疯狂源自梦想,技术成就辉煌.” 让我这个 ...
- Linux防火墙iptables学习笔记(三)iptables命令详解和举例[转载]
Linux防火墙iptables学习笔记(三)iptables命令详解和举例 2008-10-16 23:45:46 转载 网上看到这个配置讲解得还比较易懂,就转过来了,大家一起看下,希望对您工作能 ...
- (转)live555学习笔记10-h264 RTP传输详解(2)
参考: 1,live555学习笔记10-h264 RTP传输详解(2) http://blog.csdn.net/niu_gao/article/details/6936108 2,H264 sps ...
- 【Android开发学习笔记】【第八课】五大布局-下
概念 五大布局上一篇文章已经介绍了 LinearLayout RelativeLayout 这一篇我们介绍剩下的三种布局 FrameLayout 五种布局中最佳单的一种布局.在这个布局在整个界面被当成 ...
- 【Android开发学习笔记】【第七课】五大布局-上
概念 Android程序各式各样,依靠的就是布局,先来看看布局都是怎么来的: 白色部分就是我们经常用的几种布局,主要说说介绍下面五大布局 FrameLayout AbsoluteLayout Line ...
- 【转】Android开发学习笔记(一)——初识Android
对于一名程序员来说,“自顶向下”虽然是一种最普通不过的分析问题和解决问题的方式,但其却是简单且较为有效的一种.所以,将其应用到Android的学习中来,不至于将自己的冲动演变为一种盲目和不知所措. 根 ...
随机推荐
- [js高手之路] 设计模式系列课程 - jQuery的extend插件机制
这里在之前的文章[js高手之路] 设计模式系列课程 - jQuery的链式调用与灵活的构造函数基础上增加一个extend浅拷贝,可以为对象方便的扩展属性和方法, jquery的插件扩展机制,大致就是这 ...
- win10 uwp 通知列表
经常看到小伙伴问,问已经绑定列表,在进行修改时,不会通知界面添加或删除.这时问题就在,一般使用的列表不会在添加时通知界面,因为他们没有通知. 本文:知道什么是通知的列表,如何去写一个通知列表 在 C# ...
- 基于FFMPEG的跨平台播放器实现(二)
基于FFMPEG的跨平台播放器实现(二) 上一节讲到了在Android平台下采用FFmpeg+surface组合打造播放器的方法,这一节讲一下Windows平台FFmpeg + D3D.Linux平台 ...
- 【ASP.NET MVC 学习笔记】- 20 ASP.NET Web API
本文参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/willick/p/3441432.html 1.ASP.NET Web API(本文简称Web API),是基于ASP.NET平台构建REST ...
- .NET程序集引用COM组件MSScriptControl所遇到的问题
问题描述:为了在C#中执行js脚本,在一个目标平台编译为Any Cpu的.NET程序集中引用了MSScriptControl组件,在winform程序中,调用这个程序集中的执行js的方法,没有任何问题 ...
- Yii2之AR类的坑与总结
本文主要记录本人从学习yii2到使用yii2开发项目过程中遇到的一些问题以及解决方法和知识点总结. 1. AR类关联哪个数据表? 默认情况下,AR类会根据类名称关联和类名相关的数据表,如:类名为Cou ...
- hadoop2.6环境中部署hive1.2.2的错误
1.hive配置遇到的问题( Relative path in absolute URI: ${system:java.io.tmpdir%7D/$%7Bsystem:user.name%7D) 解决 ...
- MFC属性表单修改“应用”键名并对其响应
1.重载CPropertySheet的虚函数OnInitDialog(),添加如下代码 BOOL DialogInputData::OnInitDialog() { BOOL bResult = CP ...
- ssh分发秘钥时出现错误“Permission denied (publickey,gssapi-keyex,gssapi-with-mic)”
因为公司的服务器连接是通过xshell公钥和密码连接的,今天在ssh分发秘钥的时候出现了,下面的错误: [root@iZ2ze97cumk8opqm28h8Z .ssh]# ssh-copy-id - ...
- css中单位px和em,rem的区别[转载]
PX特点 1. IE无法调整那些使用px作为单位的字体大小: 2. 国外的大部分网站能够调整的原因在于其使用了em或rem作为字体单位: 3. Firefox能够调整px和em,rem,但是96%以上 ...
