Hibernate学习笔记三:对象关系映射(一对一,一对多,多对一,多对多)
如需转载,请说明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/gudu1/p/6895610.html
Hibernate通过关系映射来表示数据库中表与表之间的关系,关系映射可以通过两种方式:配置文件映射和注解映射,本文主要讲解配置文件映射。
关系映射:
1.单向关联关系,表示只有一方维护关系,而另一方并不知道有这种关系,在解除和删除关联关系的时候也要在有外键方进行,否则会抛出异常,因为有外键的约束。
2.双向关联关系。双方都维护关系,无论在哪一方解除和删除关联关系,Hibernate都能够获知,都能够正确的进行操作。
关系映射中,即使你在类中添加了属性(即相关联的类对象),通过配置inverse属性,也可以设置它是否维护关系,默认为true,可以设置为false表示不维护
一:单向关联
单向多对一:
单向(many-to-one)是最常见的单向关联关系:
<class name="Department" table="department">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" column="uname" type="string" length="20"></property>
</class> <class name="Employee" table="employee">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" type="string" length="20" column="uname"></property>
<many-to-one name="department" class="Department" column="department_id"></many-to-one>
</class>
下面是对应数据库表

单向一对多:
基于外键关联的单向一对多关联是一种很少见的情况,不推荐使用它。
<class name="Department" table="department">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" column="uname" type="string" length="20"></property>
<set name="employeeSet">
<key column="employee_id"></key>
<one-to-many class="Employee" />
</set>
</class> <class name="Employee" table="employee">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" type="string" length="20" column="uname"></property>
</class>
下面是对应数据库表,可以看出跟上面是一样的

单向一对一:
基于外键关联的单向一对一关联和单向多对一关联几乎是一样的。唯一的不同就是单向一对一关联中的外键字段具有唯一性约束(unique)。
<class name="Department" table="department">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" column="uname" type="string" length="20"></property>
</class> <class name="Employee" table="employee">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" type="string" length="20" column="uname"></property>
<many-to-one name="department" column="department_id" class="Department" unique="true"></many-to-one>
</class>
看图好像和(一对多|多对一)结构一样,确实是一样的,你可以插几条数据试一下,因为是一对一关系,有可能会出错的哦!

二:使用连接表单向关联
单向一对多:
基于连接表的单向一对多关联 应该优先被采用。请注意,通过指定unique="true",我们可以把多样性从多对多改变为一对多。
<class name="Department" table="department">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" column="uname" type="string" length="20"></property>
<set name="employeeSet" table="empl_depa">
<key column="department_id"></key>
<many-to-many column="employee_id" class="Employee" unique="true"></many-to-many>
</set>
</class> <class name="Employee" table="employee">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" type="string" length="20" column="uname"></property>
</class>

单向多对一:
基于连接表的单向多对一关联在关联关系可选的情况下应用也很普遍。
<class name="Employee" table="employee">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" type="string" length="20" column="uname"></property>
<join table="emplo_depa">
<key column="employee_id"></key>
<many-to-one name="department" class="Department" column="department_id"></many-to-one>
</join>
</class> <class name="Department" table="department">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" column="uname" type="string" length="20"></property> </class>

单向一对一:
基于连接表的单向一对一关联也是可行的,但非常少见。
<class name="Department" table="department">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" column="uname" type="string" length="20"></property>
</class> <class name="Employee" table="employee">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" type="string" length="20" column="uname"></property>
<join table="emplo_depa">
<key column="employee_id"></key>
<many-to-one name="department" class="Department" column="department_id" unique="true"></many-to-one>
</join>
</class>

单向多对多:
<class name="Department" table="department">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" column="uname" type="string" length="20"></property>
<set name="employeeSet" table="emplo_depa">
<key column="department_id"></key>
<many-to-many class="Employee" column="employee_id"></many-to-many>
</set>
</class> <class name="Employee" table="employee">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" type="string" length="20" column="uname"></property>
</class>
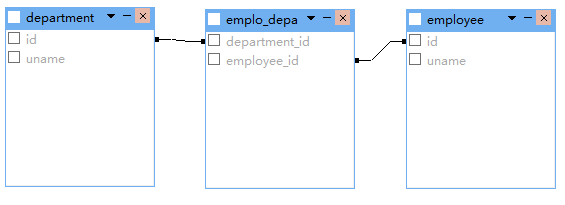
三:双向关联
一对一双向关联
<class name="Department" table="department">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" column="uname" type="string" length="20"></property>
<one-to-one name="employee" class="Employee" property-ref="department"></one-to-one>
</class> <class name="Employee" table="employee">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" type="string" length="20" column="uname"></property>
<many-to-one name="department" class="Department" unique="true"></many-to-one>
</class>
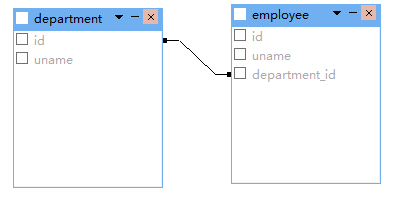
一对多双向关联
<class name="Department" table="department">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" column="uname" type="string" length="20"></property>
<set name="employeeSet">
<key column="department_id"></key>
<one-to-many class="Employee" />
</set>
</class> <class name="Employee" table="employee">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" type="string" length="20" column="uname"></property>
<many-to-one name="department" class="Department" column="department_id"></many-to-one>
</class>
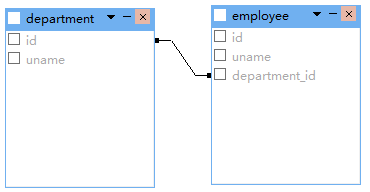
双向多对一关联把上面权限反转一下就好,这里就不贴代码了。
四:使用连接表双向关联
一对一双向关联
<class name="Department" table="department">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" column="uname" type="string" length="20"></property>
<join table="emplo_depa" inverse="true" optional="true">
<key column="department_id" unique="true"></key>
<many-to-one name="employee" unique="true" column="employee_id"></many-to-one>
</join>
</class> <class name="Employee" table="employee">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" type="string" length="20" column="uname"></property>
<join table="emplo_depa" optional="true">
<key column="employee_id" unique="true"></key>
<many-to-one name="department" unique="true" column="department_id"></many-to-one>
</join>
</class>
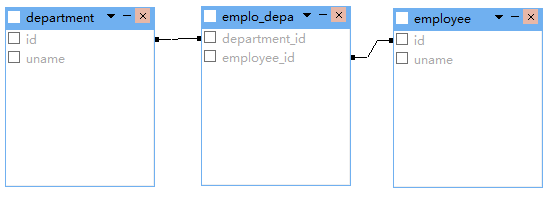
多对多双向关联
<class name="Department" table="department">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" column="uname" type="string" length="20"></property>
<set name="employeeSet" table="emplo_depa" inverse="true">
<key column="department_id"></key>
<many-to-many class="Employee" column="employee_id" ></many-to-many>
</set>
</class> <class name="Employee" table="employee">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" type="string" length="20" column="uname"></property>
<set name="departmentSet" table="emplo_depa">
<key column="employee_id"></key>
<many-to-many class="Department" column="department_id"></many-to-many>
</set>
</class>

一对多双向关联
<class name="Department" table="department">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" column="uname" type="string" length="20"></property>
<set name="employeeSet" inverse="true" table="emplo_depa">
<key column="department_id"></key>
<many-to-many unique="true" class="Employee" column="employee_id"></many-to-many>
</set>
</class> <class name="Employee" table="employee">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="uname" type="string" length="20" column="uname"></property>
<join table="emplo_depa">
<key column="employee_id"></key>
<many-to-one name="department" column="department_id" class="Department"></many-to-one>
</join>
</class>

除此之外,还有更多映射配置(继承映射,组件映射),本篇就不写那么多了,希望读者能够查阅文件学习。每天一小步,人生一大步。
Hibernate学习笔记三:对象关系映射(一对一,一对多,多对一,多对多)的更多相关文章
- [原创]java WEB学习笔记81:Hibernate学习之路--- 对象关系映射文件(.hbm.xml):hibernate-mapping 节点,class节点,id节点(主键生成策略),property节点,在hibernate 中 java类型 与sql类型之间的对应关系,Java 时间和日期类型的映射,Java 大对象类型 的 映射 (了解),映射组成关系
本博客的目的:①总结自己的学习过程,相当于学习笔记 ②将自己的经验分享给大家,相互学习,互相交流,不可商用 内容难免出现问题,欢迎指正,交流,探讨,可以留言,也可以通过以下方式联系. 本人互联网技术爱 ...
- Hibernate学习笔记二:常用映射配置
转载请注明原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ygj0930/p/6760895.html 一:单向一对一 常用唯一外键的方法来配置单向一对一关系. 1:实体关系 类A中有类B对象 ...
- Hibernate学习笔记三 多表
一对多|多对一 表中的表达 实体中的表达 实体代码: package com.yyb.domain; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; p ...
- JPA学习笔记(8)——映射双向一对多关联关系
双向一对多关联关系 前面的博客讲的都是单向的,而本问讲的是双向的(双向一对多 = 双向多对一) 什么是双向? 我们来对照一下单向和双向 单向/双向 User实体类中是否有List< Order& ...
- Hibernate学习笔记三
1.1.1 Hibernate的关联关系映射:(多对多) 1.1.1.1 多对多的配置: 步骤一创建实体和映射: Student: public class Student { private Int ...
- JS学习笔记 (三) 对象进阶
1.JS对象 1.1 JS对象特征 1.JS对象是基本数据数据类型之一,是一种复合值,可以看成若干属性的集合. 属性是名值对的形式(key:value) 属性名是字符串,因此可以把对象看成是字符串到值 ...
- Hibernate学习笔记三:常用数据库操作语句
转载请注明原文地址: 一:HQL 1:HQL语句格式:select from POJO类名 where 条件表达式 group by 属性 having 聚集函数 order by 属性 [其中,fr ...
- Hibernate映射--基本类映射和对象关系映射(转)
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/lovesummerforever/article/details/20901011 尊重原创,请访问原网址 回想一些我们在没有学习ssh的时候 ...
- Hibernate的核心对象关系映射
Hibernate的核心就是对象关系映射: 加载映射文件的两种方式: 第一种:<mapping resource="com/bie/lesson02/crud/po/employee. ...
随机推荐
- 3.Redis常用命令:String
字符串类型是Redis中最为基础的数据存储类型,它在Redis中是二进制安全的,这便意味着该类型可以接受任何格式的数据,如JPEG图像数据或Json对象描述信息等.在Redis中字符串类型的Value ...
- 拍照、本地图片工具类(兼容至Android7.0)
拍照.本地图片工具类:解决了4.4以上剪裁会提示"找不到文件"和6.0动态授予权限,及7.0报FileUriExposedException异常问题. package com.hb ...
- SVG如何做圆形图片
SVG如何做圆形图片 2016年5月31日17:30:48 提到圆形图片,大家首先想到的一定是border-radius,但在SVG中这些方法很难起效,下面方法适合SVG中制作任意规则与不规则的图形. ...
- 凭证(Credential)
在SQL Server中,凭证(Credential)用于把Windows用户的身份验证信息(在Windows环境下,是Windows 用户名和密码)存储在SQL Server实例中,并把该身份验证信 ...
- grunt构建一个项目
准备工作:grunt基于node环境运行,所有先安装node.js 1.安装grunt,通过node的npm的包管理工具 >npm install grunt --save-dev 2.npm ...
- Maven的下载,安装,配置,测试,初识
1:Maven官网:http://maven.apache.org/ Maven远程仓库:http://search.maven.org/ 2:Maven是一个采用纯Java编写的开源项目管理工具,M ...
- Python:字符串的分片与索引、字符串的方法
这是关于Python的第3篇文章,主要介绍下字符串的分片与索引.字符串的方法. 字符串的分片与索引: 字符串可以用过string[X]来分片与索引.分片,简言之,就是从字符串总拿出一部分,储存在另一个 ...
- Elasticsearch 默认配置 IK 及 Java AnalyzeRequestBuilder 使用
摘要: 原创出处 www.bysocket.com 「泥瓦匠BYSocket 」欢迎转载,保留摘要,谢谢! 『 春夏秋冬失去了你,我怎么过一年四季- 民谣歌词 』 本文提纲 一.什么是 Ela ...
- hdu1054最小顶点覆盖
最小定点覆盖是指这样一种情况: 图G的顶点覆盖是一个顶点集合V,使得G中的每一条边都接触V中的至少一个顶点.我们称集合V覆盖了G的边.最小顶点覆盖是用最少的顶点来覆盖所有的边.顶点覆盖数是最小顶点覆盖 ...
- arcgis属性选取like用法
查询对象为ArcInfo coverage,shapefile, INFO table,dBASE table,ArcSDE data,ArcIMS 要素类,或者 ArcIMS image servi ...
