JAVA NIO FileChannel 内存映射文件
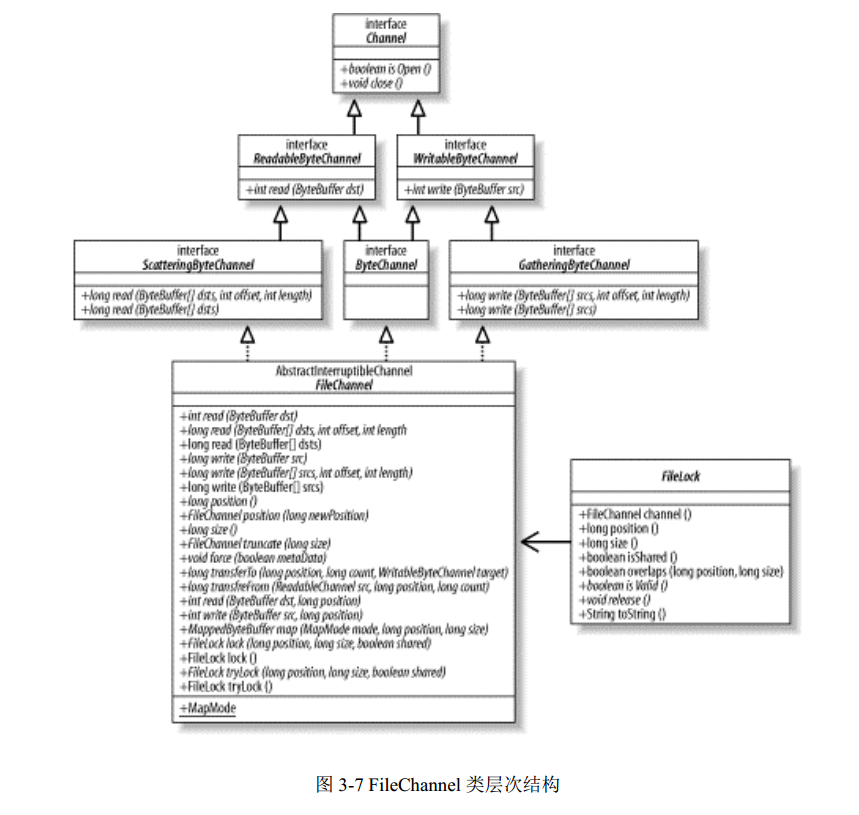
文件通道总是阻塞式的。
文件通道不能创建,只能通过(RandomAccessFile、FileInputStream、FileOutputStream)getChannel()获得,具有与File形同的访问权限。
线程安全。
文件锁:锁的对象是文件。
package org.windwant.nio; import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.MappedByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.Channel;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.channels.FileLock;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReadWriteLock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock; /**
* Created by windwant on 2016/5/13.
*/
public class NIOOpt { public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
MappedPrivateChannel();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} /**
* MapMode.PRIVATE 写时拷贝(copy-on-write)映射:通过put()修改的任何修改,会导致产生一个私有的数据
* 拷贝,宝贝中的数据只有MappedByteBuffer实例可以看到。不会对底层文件做任何修改。若缓冲区被回收,修改丢
* 失,read/write方式建立通道。
* 做修改,拷贝副本前,其它方式的映射区的修改,会反映到当前区域。映射相互的修改不可见
* 允许父子进程共享内存页
* 处理一个文件多个映射场景。
* 关闭通道,映射会保持。除非丢弃缓冲区本身。
* MappedByteBuffer 对象是直接的,占用的内存位于jvm堆栈之外。
*/
public static void MappedPrivateChannel() throws Exception {
// Create a temp file and get a channel connected to it
File tempFile = File.createTempFile ("mmaptest", null);
RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile (tempFile, "rw");
FileChannel channel = file.getChannel( );
ByteBuffer temp = ByteBuffer.allocate (100);
// Put something in the file, starting at location 0
temp.put ("This is the file content".getBytes( ));
temp.flip( );
channel.write (temp, 0);
// Put something else in the file, starting at location 8192.
// 8192 is 8 KB, almost certainly a different memory/FS page.
// This may cause a file hole, depending on the
// filesystem page size.
temp.clear( );
temp.put ("This is more file content".getBytes( ));
temp.flip( );
channel.write (temp, 8192);
// Create three types of mappings to the same file
MappedByteBuffer ro = channel.map (
FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, channel.size( ));
MappedByteBuffer rw = channel.map (
FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, channel.size( ));
MappedByteBuffer cow = channel.map (
FileChannel.MapMode.PRIVATE, 0, channel.size( ));
// the buffer states before any modifications
System.out.println ("Begin");
showBuffers (ro, rw, cow);
// Modify the copy-on-write buffer
cow.position (8);
cow.put ("COW".getBytes( ));
System.out.println ("Change to COW buffer");
showBuffers (ro, rw, cow);
// Modify the read/write buffer92
rw.position (9);
rw.put (" R/W ".getBytes( ));
rw.position (8194);
rw.put (" R/W ".getBytes( ));
rw.force( );
System.out.println ("Change to R/W buffer");
showBuffers (ro, rw, cow);
// Write to the file through the channel; hit both pages
temp.clear( );
temp.put ("Channel write ".getBytes( ));
temp.flip( );
channel.write (temp, 0);
temp.rewind( );
channel.write (temp, 8202);
System.out.println ("Write on channel");
showBuffers (ro, rw, cow);
// Modify the copy-on-write buffer again
cow.position (8207);
cow.put (" COW2 ".getBytes( ));
System.out.println ("Second change to COW buffer");
showBuffers (ro, rw, cow);
// Modify the read/write buffer
rw.position (0);
rw.put (" R/W2 ".getBytes( ));
rw.position (8210);
rw.put (" R/W2 ".getBytes( ));
rw.force( );
System.out.println ("Second change to R/W buffer");
showBuffers (ro, rw, cow);
// cleanup
channel.close( );
file.close( );
tempFile.delete( );
} // Show the current content of the three buffers
public static void showBuffers (ByteBuffer ro, ByteBuffer rw, ByteBuffer cow) throws Exception{
dumpBuffer ("R/O", ro);
dumpBuffer ("R/W", rw);
dumpBuffer ("COW", cow);
System.out.println ("");
}
// Dump buffer content, counting and skipping nulls
public static void dumpBuffer (String prefix, ByteBuffer buffer) throws Exception {
System.out.print (prefix + ": '");
int nulls = 0;
int limit = buffer.limit( );
for (int i = 0; i < limit; i++) {
char c = (char) buffer.get (i);
if (c == '\u0000') {
nulls++;
continue;
}
if (nulls != 0) {
System.out.print ("|[" + nulls
+ " nulls]|");
nulls = 0;
}
System.out.print (c);
}
System.out.println ("'");
} /**
* channel Gather/Scatter 矢量IO
*/
public static void channelGatherScatter(){
ByteBuffer head = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
ByteBuffer body = ByteBuffer.allocate(100);
RandomAccessFile afile = null;
RandomAccessFile bfile = null;
ReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
try {
afile = new RandomAccessFile("hello.txt", "r");
bfile = new RandomAccessFile("hehe.txt", "rw");
readWriteLock.readLock().lock();
FileChannel fileChannel = afile.getChannel();
ByteBuffer[] buffers = {head, body};
while (fileChannel.read(buffers) != -1){
}
head.flip();
body.flip();
System.out.println(new String(head.array()));
System.out.println(new String(body.array()));
readWriteLock.readLock().unlock();
fileChannel.close();
afile.close(); readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
FileChannel bfileChannel = bfile.getChannel(); while (bfileChannel.write(buffers) > 0){
} bfileChannel.position(bfileChannel.position() + 10);
bfileChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("THIS IS THE TEST TEXT!".getBytes()));
bfileChannel.truncate(3); //改变文件大小
bfileChannel.force(true); //写入磁盘文件 参数 是否更新文件元数据(所有者、访问权限等)
readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
bfileChannel.close();
bfile.close();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
} /**
* 基于MappedFileChannle的文件复制
* 文件锁
*/
public static void mappedFileChannelLock(){
RandomAccessFile afile = null;
RandomAccessFile bfile = null;
FileChannel fc = null;
FileChannel fcb = null;
try {
afile = new RandomAccessFile("hello.txt", "rw");
fc = afile.getChannel();
long length = fc.size();
FileLock fileLock = fc.tryLock(0, length, true);//true共享锁 false 独占锁 从开始 锁定全部内容 如果获取不到锁会返回null
if(null != fileLock) {
MappedByteBuffer mbb = fc.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, length);
byte[] fbo = new byte[(int) length];
mbb.get(fbo);
System.out.println(new String(fbo, "UTF-8"));
fileLock.release();
bfile = new RandomAccessFile("hehe.txt", "rw");
fcb = bfile.getChannel();
fileLock = fcb.tryLock(0, length, false);
MappedByteBuffer mbbb = fcb.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, length); for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
mbbb.put(i, fbo[i]);
}
mbbb.flip();
mbbb.force();
fileLock.release();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
fc.close();
fcb.close();
afile.close();
bfile.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} /**
* MappedByteBuffer map(MapMode mode, long position, long size)
* size大于文件大小,文件会做扩充
* MappedByteBuffer 内存映射缓冲池
* 基于MappedFileChannle的文件复制
* 读写锁
* 直接读取,修改磁盘上的文件。
* 自动缓存内存页,比较高效。
*/
public static void mappedFileChannel(){
RandomAccessFile afile = null;
RandomAccessFile bfile = null;
FileChannel fc = null;
FileChannel fcb = null;
ReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
try {
afile = new RandomAccessFile("hello.txt", "rw");
readWriteLock.readLock().lock();
fc = afile.getChannel();
long length = fc.size();
MappedByteBuffer mbb = fc.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, length);
byte[] fbo = new byte[(int) length];
mbb.get(fbo);
System.out.println(new String(fbo));
readWriteLock.readLock().unlock();
bfile = new RandomAccessFile("hehe.txt", "rw");
readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
fcb = bfile.getChannel();
MappedByteBuffer mbbb = fcb.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, length); for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
mbbb.put(i, fbo[i]);
}
mbbb.flip();
mbbb.force();
readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
fc.close();
fcb.close();
afile.close();
bfile.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} /**
* FileChannel文件读取
*/
public static void fileChannel(){
try {
RandomAccessFile afile = new RandomAccessFile("hello.txt", "rw");
FileChannel fc = afile.getChannel();
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
int byteRead;
while ((byteRead = fc.read(bb)) != -1){//确保读完
System.out.println("read:" + byteRead);
bb.flip();//翻转为读状态
while (bb.hasRemaining()){//直到没有可读的字节
System.out.println(String.valueOf(bb.get()));
}
bb.clear();
}
fc.close();
afile.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} /**
* 基于FileChannel transferTo transferFrom 方法文件复制
*/
public static void fileTransfer(){
try {
RandomAccessFile afile = new RandomAccessFile("hello.txt", "rw");
RandomAccessFile bfile = new RandomAccessFile("hehe.txt", "rw");
FileChannel ac = afile.getChannel();
FileChannel bc = bfile.getChannel();
long position = 0;
long count = ac.size();
// bc.transferFrom(ac, position, count);
ac.transferTo(position, count, bc);
ac.close();
afile.close();
bc.close();
bfile.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} public static void fileSelector(){
try {
RandomAccessFile afile = new RandomAccessFile("hello.txt", "rw");
Channel c = afile.getChannel();
Selector s = Selector.open();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} /**
* 基于基本channel buffer的文件复制操作
*/
public static void fileTransferByNormal() {
try {
RandomAccessFile afile = new RandomAccessFile("hello.txt", "rw");
RandomAccessFile bfile = new RandomAccessFile("hehe.txt", "rw");
FileChannel ac = afile.getChannel();
FileChannel bc = bfile.getChannel(); ByteBuffer bf = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(16 * 1024);
while (ac.read(bf) != -1) {
bf.flip();
while (bf.hasRemaining()) {//确保写完
bc.write(bf);
}
bf.clear();
}
ac.close();
afile.close();
bc.close();
bfile.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
JAVA NIO FileChannel 内存映射文件的更多相关文章
- Java NIO之内存映射文件——MappedByteBuffer
大多数操作系统都可以利用虚拟内存实现将一个文件或者文件的一部分"映射"到内存中.然后,这个文件就可以当作是内存数组来访问,这比传统的文件要快得多. 内存映射文件的一个关键优势是操作 ...
- JAVA NIO之浅谈内存映射文件原理与DirectMemory
JAVA类库中的NIO包相对于IO 包来说有一个新功能是内存映射文件,日常编程中并不是经常用到,但是在处理大文件时是比较理想的提高效率的手段.本文我主要想结合操作系统中(OS)相关方面的知识介绍一下原 ...
- 内存映射文件(Memory-Mapped File)
Java Memory-Mapped File所使用的内存分配在物理内存而不是JVM堆内存,且分配在OS内核. 1: 内存映射文件及其应用 - 实现一个简单的消息队列 / 计算机程序的思维逻辑 在一般 ...
- Java NIO 内存映射文件
Java NIO 内存映射文件 @author ixenos 文件操作的四大方法 前提:内存的访问速度比磁盘高几个数量级,但是基本的IO操作是直接调用native方法获得驱动和磁盘交互的,IO速度限制 ...
- 【JavaNIO的深入研究4】内存映射文件I/O,大文件读写操作,Java nio之MappedByteBuffer,高效文件/内存映射
内存映射文件能让你创建和修改那些因为太大而无法放入内存的文件.有了内存映射文件,你就可以认为文件已经全部读进了内存,然后把它当成一个非常大的数组来访问.这种解决办法能大大简化修改文件的代码.fileC ...
- Java编程的逻辑 (61) - 内存映射文件及其应用 - 实现一个简单的消息队列
本系列文章经补充和完善,已修订整理成书<Java编程的逻辑>,由机械工业出版社华章分社出版,于2018年1月上市热销,读者好评如潮!各大网店和书店有售,欢迎购买,京东自营链接:http:/ ...
- JAVA I/O(三)内存映射文件
<Java编程思想>中对内存映射文件有详细的介绍,此处仅做简单记录和总结.内存映射文件允许创建和修改因为太大而不能放入内存的文件. 1. 内存映射文件简单实例 import java.io ...
- NIO之通道(Channel)的原理与获取以及数据传输与内存映射文件
通道(Channel) 由java.nio.channels包定义的,Channel表示IO源与目标打开的连接,Channel类似于传统的“流”,只不过Channel本身不能直接访问数据,Channe ...
- Java 内存映射文件
import java.io.*; import java.nio.MappedByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; import jav ...
随机推荐
- 菜鸟学Struts2——HelloWorld
写在前面 自从工作后就过上了只有一个月记忆的生活,太健忘,很多学过的东西因为用得少便忘记了,第二次学习struts,为了以后便于查阅,开始自己的博客之旅.Struts的学习还是从Hello World ...
- 使用自定义 classloader 的正确姿势
详细的原理就不多说了,网上一大把, 但是, 看了很多很多, 即使看了jdk 源码, 说了罗里吧嗦, 还是不很明白: 到底如何正确自定义ClassLoader, 需要注意什么 ExtClassLoade ...
- 电容与EMC-电容不同功能时对整板EMC的作用
一般我们的pcb板的器件有很多种类,但是值得特别关注的,很多人都会说是BGA.接口.IC.晶振之类,因为这些都是layout功能模块以及设计难点.然而数量上占绝对优势的器件却是阻容器件,之前围殴阻抗时 ...
- Atitit 图像处理的心得与疑惑 attilax总结
Atitit 图像处理的心得与疑惑 attilax总结 1.1. 使用类库好不好??还是自己实现算法1 1.2. 但是,如果遇到类库体积太大,后者没有合适的算法,那就只能自己开发算法了1 1.3. 如 ...
- Android-横竖屏切换问题(转)
先附上链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoQLu/p/3324503.html 项目要求要做横竖屏,发现横屏的时候,生命周期函数会乱执行,网上找了一大堆资料. 结果如下: 只需 ...
- 解析大型.NET ERP系统核心组件 查询设计器 报表设计器 窗体设计器 工作流设计器 任务计划设计器
企业管理软件包含一些公共的组件,这些基础的组件在每个新项目立项阶段就必须考虑.核心的稳定不变功能,方便系统开发与维护,也为系统二次开发提供了诸多便利.比如通用权限管理系统,通用附件管理,通用查询等组件 ...
- ZFPlayer 源码解读
源码下载地址:https://github.com/renzifeng/ZFPlayer 之前自己实现过一个模仿百思不得姐的demo https://github.com/agelessman/FFm ...
- java笔记--笔试中极容易出错的表达式的陷阱
我相信每一个学过java的人儿们都被java表达式虐过,各种"肯定是它,我不可能错!",然后各种"尼玛,真假,怎么可能?",虽然在实际开发中很少会真的让你去使用 ...
- java netty socket库和自定义C#socket库利用protobuf进行通信完整实例
之前的文章讲述了socket通信的一些基本知识,已经本人自定义的C#版本的socket.和java netty 库的二次封装,但是没有真正的发表测试用例. 本文只是为了讲解利用protobuf 进行C ...
- Node基础篇(概要)
Node简介 客户端的JavaScript是怎样的 什么是 JavaScript? 脚本语言 运行在浏览器中 一般用来做客户端页面的交互(Interactive) JavaScript 的运行环境? ...
