2.mysql-库表行管理
1.数据库管理
1.1 SQL语句
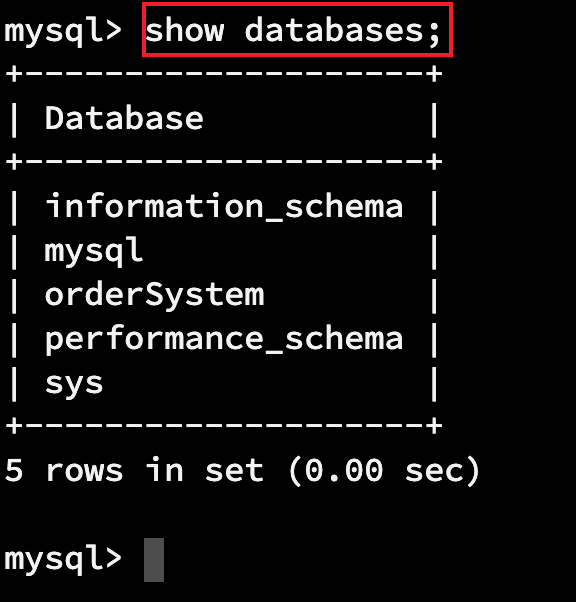
1.1.1 查看当前所有的数据库
show databases;
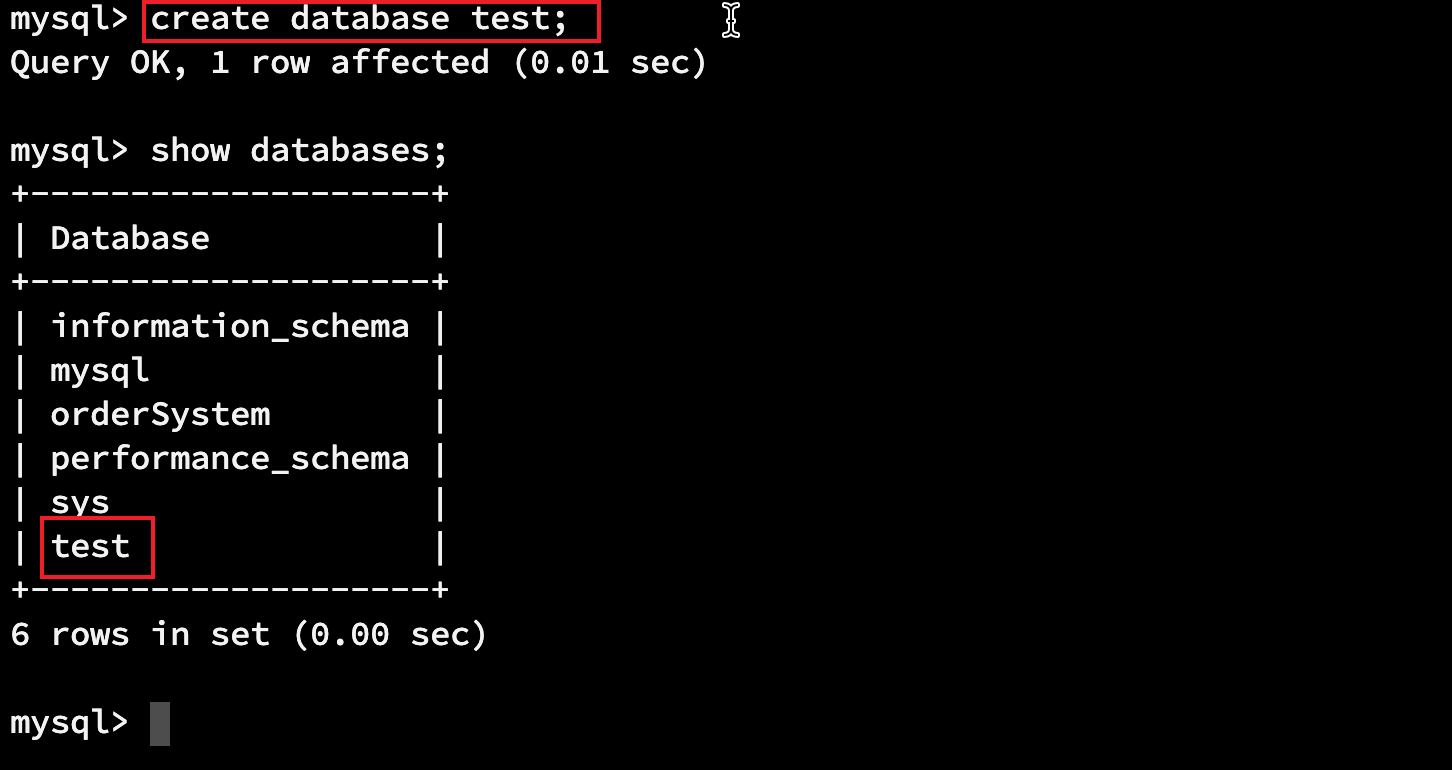
1.1.2 创建数据库
create database 数据库名;
create databse 数据库名 default charset utf8 # 支持中文
8.0版本默认就是utf编码
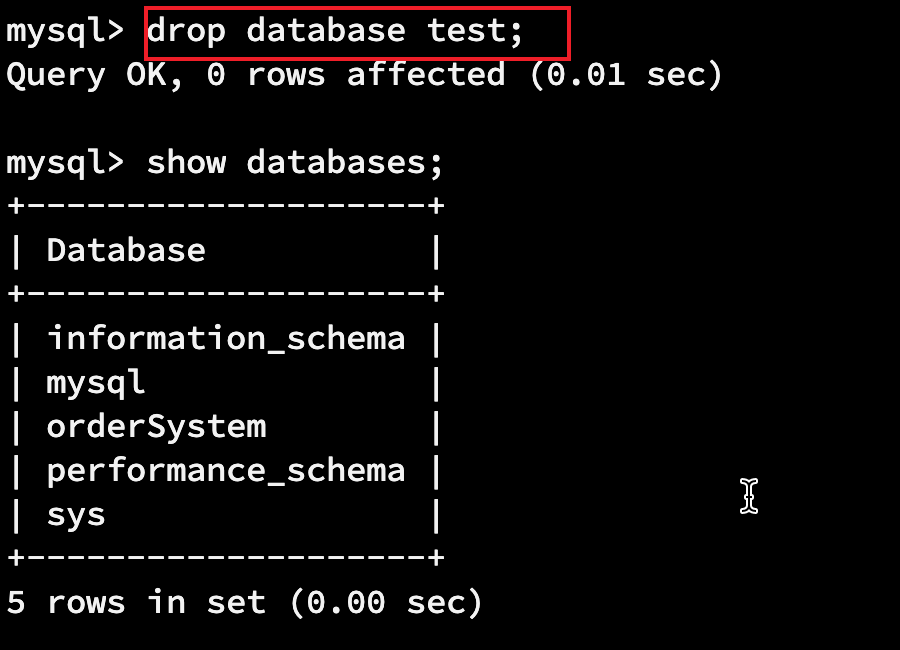
1.1.3 删除数据库
drop database 数据库;
1.1.4 进入数据库
只有进入某一个数据库,才能对指定数据库里面的数据表或者数据行操作
use 数据库名

1.2 python操作
无论通过何种方式取链接mysql,本质上发送的指令是相同的,只是链接的方式和操作形式不同而已
要想通过python操作mysql,我们需要导入第三方模块
pip install pymysql

# encoding:utf-8
# author:kunmzhao
# email:1102669474@qq.com import pymysql # 1.连接数据库
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', password='root', charset='utf8')
cursor = conn.cursor() # 2. 查看数据库
cursor.execute("show databases")
print(cursor.fetchall()) # 3.创建数据库
cursor.execute('create database test2 default charset utf8')
conn.commit() cursor.execute("show databases")
print(cursor.fetchall()) # 4.删除数据库
cursor.execute('drop database test2')
conn.commit() cursor.execute("show databases")
print(cursor.fetchall()) # 5.进入数据库
cursor.execute('use mysql')
cursor.execute('show tables;')
print(cursor.fetchall()) cursor.close()
conn.close()
2.数据表管理
2.1 SQL语句
在操作数据表的时候首先需要进入对应的数据库
use 数据库名;
2.1.1 查看当前所有的表
show tables;

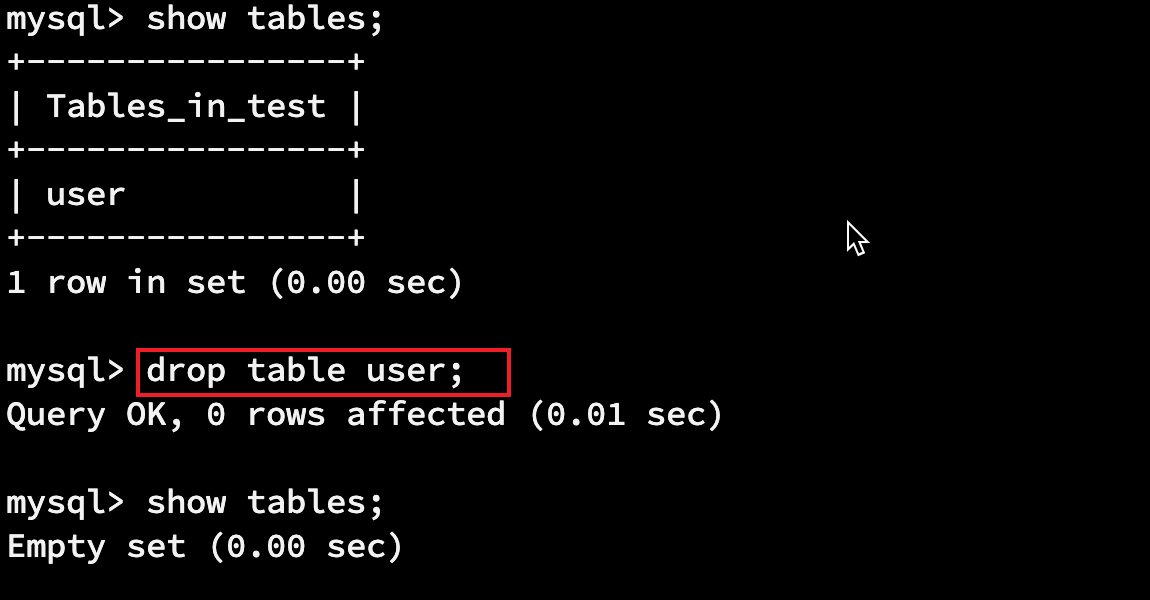
2.1.2 删除表
drop table 表名;
2.1.3 清空表
delete from 表名;

2.1.4 创建表
创建表必须要指定表名,列名称,列类型
create table 表名(
列名字 类型,
列名字 类型,
列名字 类型,
); create table user(
id int primary key, -- 主键(不允许为空且唯一)
name varchar(16) not null, -- 不能为空
age int default 18 -- 默认值为18
);
主键:一张表一般都有一个主键,primary key指定
是否为空:代表以后该数据是否可以为空,默认为允许为空,not null指定不可为空
默认值:代表着以后不主动添加该字段数据,设置为默认值, default指定
常见的列类型
int[(m)][unsigned][zerofill]int 表示有符号,取值范围:-2147483648 ~ 2147483647
int unsigned 表示无符号,取值范围:0 ~ 4294967295
int(5)zerofill 仅用于显示,当不满足5位时,按照左边补0,例如:00002;满足时,正常显示。tinyint[(m)] [unsigned] [zerofill]有符号,取值范围:-128 ~ 127.
无符号,取值范围:0 ~ 255bigint[(m)][unsigned][zerofill]有符号,取值范围:-9223372036854775808 ~ 9223372036854775807
无符号,取值范围:0 ~ 18446744073709551615decimal[(m[,d])] [unsigned] [zerofill]准确的小数值,m是数字总个数(负号不算),d是小数点后个数。 m最大值为65,d最大值为30。
char(m)定长字符串,m代表字符串的长度,最多可容纳255个字符。
定长的体现:即使内容长度小于m,也会占用m长度varchar(m)变长字符串,m代表字符串的长度,最多可容纳65535个字节。
texttext数据类型用于保存变长的大字符串,可以组多到65535 (2**16 − 1)个字符。
一般情况下,长文本会用text类型。例如:文章、新闻等。longtextA TEXT column with a maximum length of 4,294,967,295 or 4GB (2**32 − 1)
datetimeYYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS(1000-01-01 00:00:00/9999-12-31 23:59:59)
dateYYYY-MM-DD(1000-01-01/9999-12-31)
timeHH:MM:SS('-838:59:59'/'838:59:59')
timestampYYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS(1970-01-01 00:00:00/2037年)
MySQL还有很多其他的数据类型,例如:*set、enum、TinyBlob、Blob、MediumBlob、LongBlob 等*,详细见官方文档:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/data-types.html
查看表结构
desc 表名

2.1.5 修改表
添加列
alter table 表名 add 列名 类型;
alter table 表名 add 列名 类型 DEFAULT 默认值;
alter table 表名 add 列名 类型 not null default 默认值;
alter table 表名 add 列名 类型 not null primary key auto_increment;删除列
alter table 表名 drop column 列名;
修改列 类型 + 名称
alter table 表名 change 原列名 新列名 新类型;
修改列 默认值
alter table 表名 alter 列名 set default 1000;
删除列 默认值
alter table 表名 alter 列名 drop default;
添加主键
alter table 表名 add primary key(列名);
删除主键
alter table 表名 drop primary key;
2.2 python操作
import pymysql # 连接MySQL
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='root123', charset="utf8")
cursor = conn.cursor() # 1. 创建数据库
"""
cursor.execute("create database db4 default charset utf8 collate utf8_general_ci")
conn.commit()
""" # 2. 进入数据库、查看数据表
"""
cursor.execute("use db4")
cursor.execute("show tables")
result = cursor.fetchall()
print(result)
""" # 3. 进入数据库创建表
cursor.execute("use db4")
sql = """
create table L4(
id int not null primary key auto_increment,
title varchar(128),
content text,
ctime datetime
)default charset=utf8;
"""
cursor.execute(sql)
conn.commit() # 4. 查看数据库中的表
"""
cursor.execute("show tables")
result = cursor.fetchall()
print(result)
""" # 5. 其他 drop table... 略过 # 关闭连接
cursor.close()
conn.close()
3.数据行管理
数据行操作就是对数据表的内容进行增删改查,是学习mysql的重头戏,先简单学习,后续再深入学习
3.1 SQL语句
3.1.1 新增数据
insert into 表名(列名,列名,列名) values(对应值,对应值,对应值);
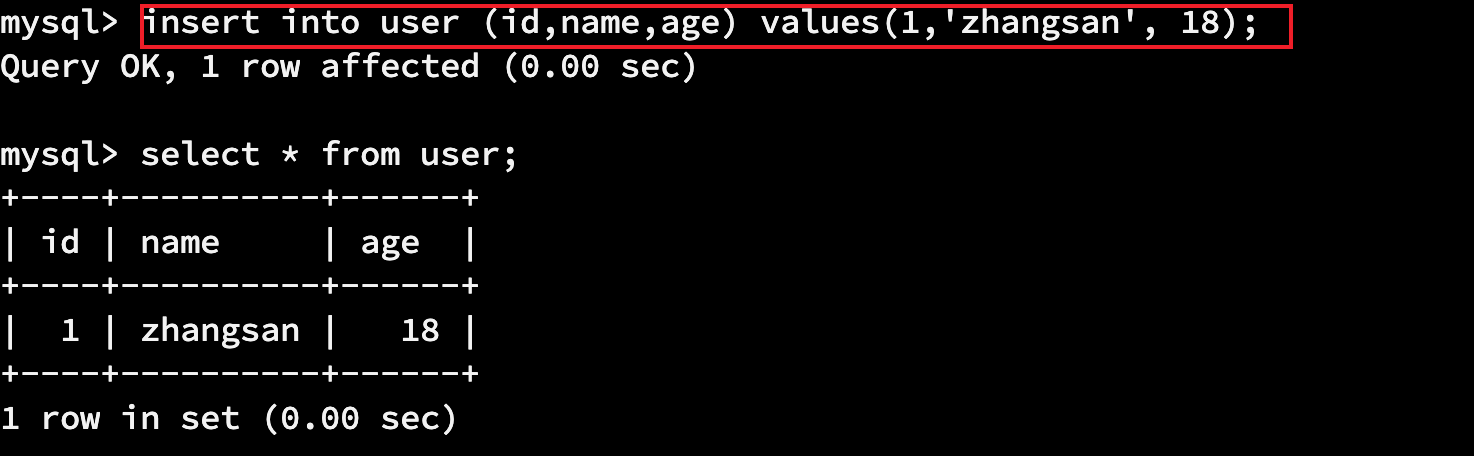
# 插入一条数据
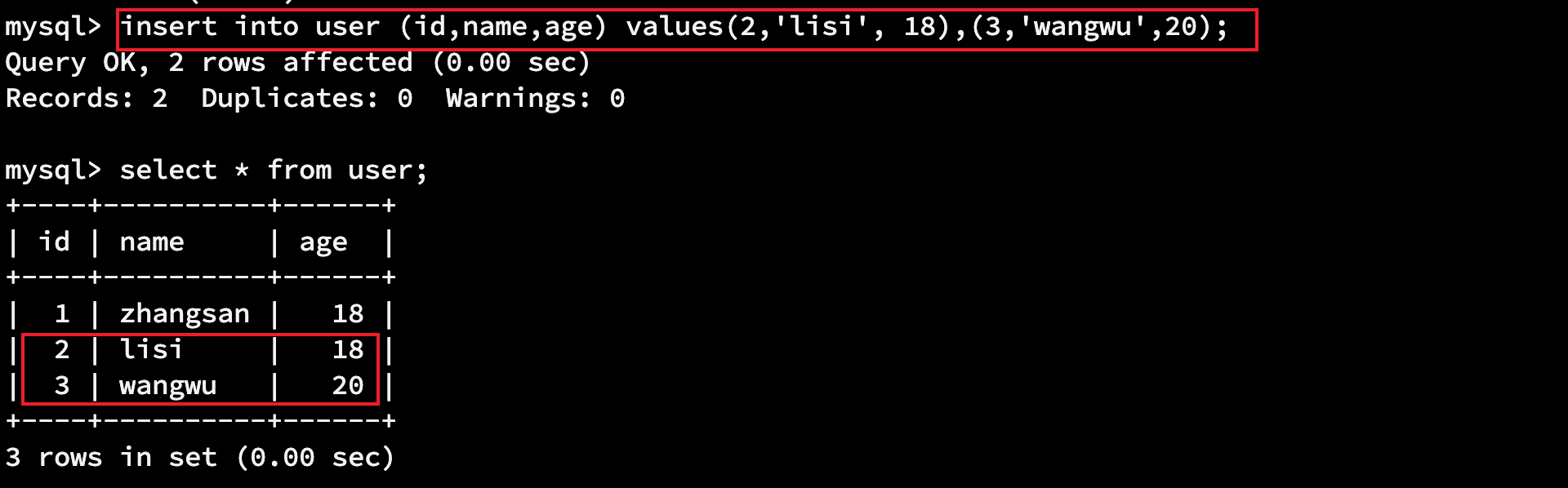
insert into user (id,name,age) values(1,'zhangsan', 18); # 插入多条数据
insert into user (id,name,age) values(2,'lisi', 18),(3,'wangwu',20);
3.1.2 删除数据
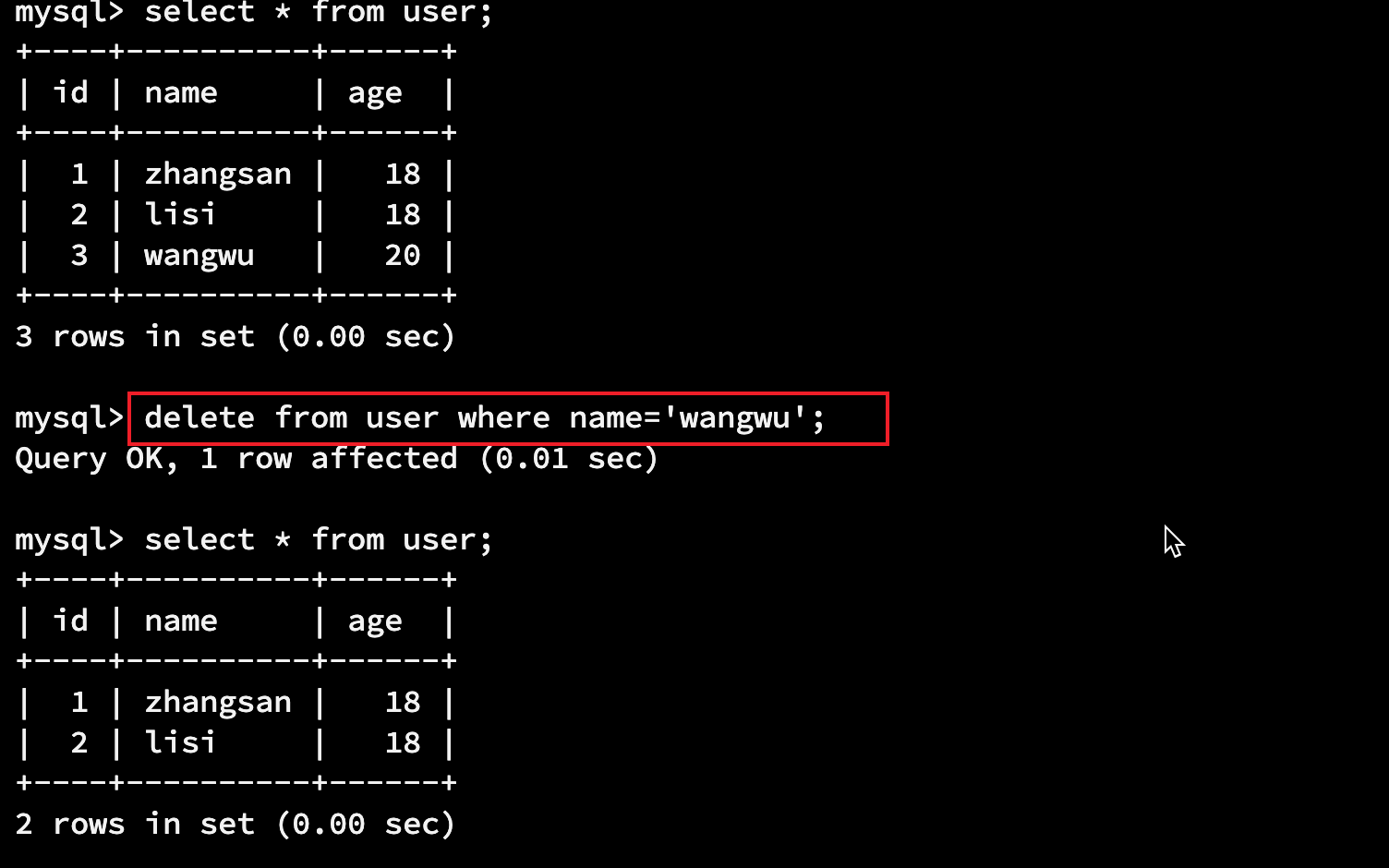
delete from 表名 where 条件;
delete from user where name='zhangsan';
delete from user where id > 9;
delete from user where name='zhangsan' and id < 6;
delete from user where name='zhangsan' or id = 1;
3.1.3 修改数据
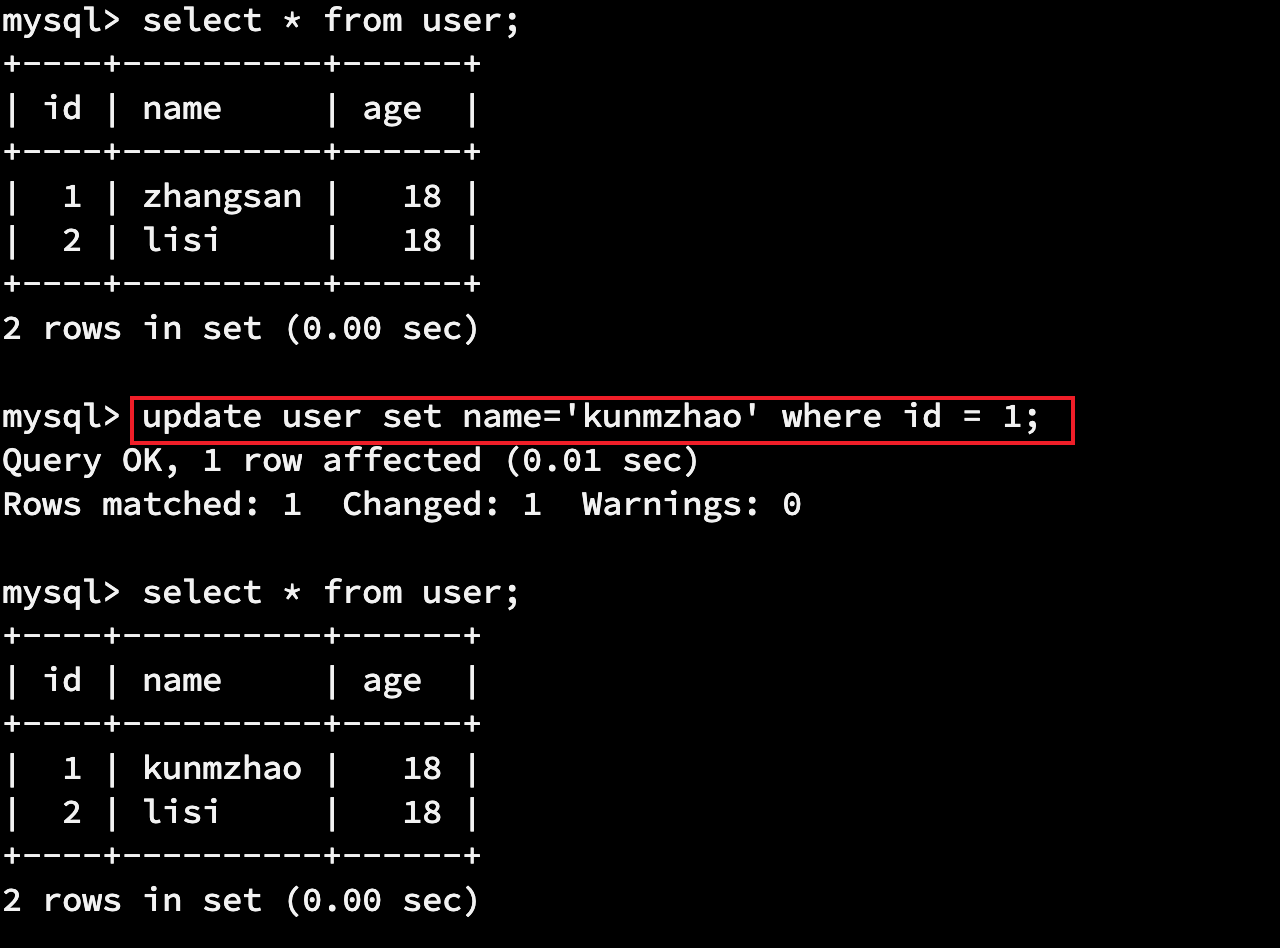
update 表名 set 列名=值 where 条件;
update user set name='kunmzhao' where id = 1;
3.1.4查询数据
select * from 表名;
select 列名,列名,列名 from 表名;
select 列名 as 别名,列名,列名 from 表名;
select 列名,列名,列名 from 表名 where 条件;
select * from user;
select id as ID, name as 姓名 from user where id =1;
3.2 python操作
import pymysql # 连接MySQL,自动执行 use userdb; -- 进入数据库
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='root123', charset="utf8", db='userdb')
cursor = conn.cursor() # 1.新增(需commit)
cursor.execute("insert into tb1(name,password) values('武沛齐','123123')")
conn.commit() # 2.删除(需commit) cursor.execute("delete from tb1 where id=1")
conn.commit() # 3.修改(需commit) cursor.execute("update tb1 set name='xx' where id=1")
conn.commit() # 4.查询 cursor.execute("select * from tb where id>10")
data = cursor.fetchone() # cursor.fetchall()
print(data) # 关闭连接
cursor.close()
conn.close()
3.3 查询数据进阶
3.3.1 条件
where
# 比较运算
select * from info where age > 30;
select * from info where aid != 1;
select * from info where between 2 and 4; -- id介于2-4之间 # 逻辑运算
select * from info where name='alex' and age=16;
select * from info where name='alex' or age = 16; # 成员运算
select * from info where id in (1,4,6);
select * from info where id not in (1, 4, 6);
select * from info where id in (select id from depart); # 布尔运算
# select * from depart where id=5存在则整体进行查询,否则整体为空
select * from info where exists (select * from depart where id=5);
3.3.2 通配符
一般用于模糊搜素 使用关键字like
%:多个字符
?:单个字符
#:单数字
select * from info where name like "%明%" -- 查询包含明的name
select * from info where name like "明%" -- 查询包含明且以明开头的name
select * from info where name like "%明" -- 查询包含明且以明结尾的name
3.3.3 映射
获取想要的列
select * from info; -- 获取info表的所有字段
select id,name from info; -- 获取info表的id,name字段
select id, name as 姓名 from info; -- 获取info表的id,name字段,并将name字段命名为姓名
3.3.4 排序
select * from info order by age asc; -- 按照年龄顺序排序
select * from info order by age desc; -- 按照年龄倒序排序
select * from info order by age asc,id desc; -- 优先按照age从小到大;如果age相同则按照id从大到小。
3.3.5 取部分
获取部分数据
select * from info limit 5; -- 获取前5条数据
select * from info limit 3 offset 2; -- 从位置2开始,向后获取前3数据
3.3.6 分组
select age,max(id),min(id),count(id),sum(id),avg(id) from info group by age;
select depart_id,count(id) from info group by depart_id having count(id) > 2; -- 分组之后再进行条件筛选 select count(id) from info;
select max(id) from info;
3.3.7 连表
多个表可以连接起来进行查询
主表 left outer join 从表 on 主表.x = 从表.id
select * from info left outer join depart on info.depart_id = depart.id;
select info.id,info.name,info.email,depart.title from info left outer join depart on info.depart_id = depart.id;
到目前为止SQL执行顺序:
- join
- on
- where
- group by
- having
- order by
- limit
2.mysql-库表行管理的更多相关文章
- python 存储引擎 mysql(库,表, 行) 单表多表操作 (foreign key) sql_mode pymysql模块讲解
##################总结############### mysql 常用数据类型 整型:tinyint int(42亿条左右) bigint 小数:float double dec ...
- Mysql 库表操作初识
Mysql 库表操作初识 终端登录mysql 这里只演示win下, cmd 终端. 至于怎么在win下, linux, mac安装, 感觉这是一个入门级的百度搜索问题, 安装都搞不定, 确实有点尴尬, ...
- python Mysql 库表
Mysql 库表 创建 学生信息库表 学生成绩 库表
- mysql库表优化实例
一.SQL优化 1.优化SQL一般步骤 1.1 查看SQL执行频率 SHOW STATUS LIKE 'Com_%'; Com_select:执行SELECT操作的次数,一次查询累加1.其他类似 以下 ...
- MySQL库表详细操作
昨天我们初始了MySQL,今天我们先从库表方面详细说一下具体操作 一.库操作 1.创建数据库 1.1 语法 CREATE DATABASE 数据库名 charset utf8; 1.2 数据库命名规则 ...
- MySQL的表空间管理
表空间: MySQL没有真正意义上的表空间管理. MySQL的Innodb包含两种表空间文件模式,默认的共享表空间和每个表分离的独立表空间. 一般来说,当数据量很小的时候建议使用共享表空间的管理方式. ...
- MySQL库表设计小技巧
前言: 在我们项目开发中,数据库及表的设计可以说是非常重要,我遇到过很多库表设计比较杂乱的项目,像表名.字段名命名混乱.字段类型设计混乱等等,此类数据库后续极难维护与拓展.我一直相信只有优秀的库表设计 ...
- Mysql 库表
create database student_info default character set utf8 collate utf8_general_ci; ------------------- ...
- MySQL库表状态查询
一. 查看库的各链接状态 对于一个mysql连接或者一个线程,任何时刻都有一个状态,表示其当前正在做什么.一般使用show full processlist查看. +---------+------- ...
- 二 mysql库表的详细操作
目录 1.库操作 1.创建数据库 2.数据库相关操作 2.表操作 1.存储引擎 2.表介绍 3.创建表 4.查看表结构 5.MySQL的基础数据类型 6.表的完整性约束 7.修改表 alter tab ...
随机推荐
- C#实现HTTP访问类HttpHelper
在项目开发过程中,我们经常会访问第三方接口,如我们需要接入的第三方接口是Web API,这时候我们就需要使用HttpHelper调用远程接口了.示例中的HttpHelper类使用Log4Net记录了每 ...
- 高清地图转换(xord转apollo的bin文件)
目标 将carla中的OpenDrive地图(carla\Unreal\CarlaUE4\Content\Carla\Maps\OpenDrive)转换为Apollo中可识别的地图格式(bin与txt ...
- Mac_linux_ssh防掉线
vi ~/.ssh/config 加入一条 ServerAliveInterval 60 #客户端主动向服务端请求响应的间隔
- day05-线程的应用04
7.线程的应用03 7.4坦克大战5.0版 增加功能: 我方坦克在发射的子弹消亡之后,才能发射新的子弹==>拓展:发射多颗子弹怎么办,控制一次最多只能发射5颗子弹 让敌人坦克发射的子弹消亡之后, ...
- LyScript 内存扫描与查壳实现
LyScript 中提供了多种内存特征扫描函数,每一种扫描函数用法各不相同,在使用扫描函数时应首先搞清楚他们之间的差异,如下将分别详细介绍每一种内存扫描函数是如何灵活运用的,最后将实现一个简易版内存查 ...
- Batch Norm 与 Layer Norm 比较
一.结论 Batch Norm一般用于CV领域,而Layer Norm一般用于NLP领域 Batch Norm需要计算全局平均,而Layer Norm不需要计算全局平均 二.Batch Norm Ba ...
- vue3 的 ref、isRef、toRef、toRefs、toRaw 详细介绍
ref.isRef.toRef.toRefs.toRaw 看着一堆类似的东西,一个头两个大,今天整理一篇文章详细介绍它们的功能及区别. 1.ref ref 属性除了能够获取元素外,也可以使用 ref ...
- 普通用户使用CI/CD权限使用
根据文章:授权用户访问名称空间 (https://www.cnblogs.com/sanduzxcvbnm/p/15015576.html) 进行有关操作后,普通用户点击 会报错如下信息: 解决办法: ...
- Linux实例常用内核网络参数介绍与常见问题处理---重要
文章转载自:https://help.aliyun.com/knowledge_detail/41334.html 本文主要介绍如下几点内容,您可以根据实际需要选择. 查看和修改Linux实例内核参数 ...
- logstash安装插件修改使用的gem源
gem source -l # 查看当前使用的gem源 gem source --remove https://rubygems.org/ # 移除gem源 gem source -a https:/ ...
