《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 8.21
代码:
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------
%% Output Info about this m-file
fprintf('\n***********************************************************\n');
fprintf(' <DSP using MATLAB> Problem 8.21 \n\n'); banner();
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Fp = 3.2; % analog passband freq in kHz
Fs = 3.8; % analog stopband freq in kHz
fs = 8; % sampling rate in kHz % -------------------------------
% ω = ΩT = 2πF/fs
% Digital Filter Specifications:
% -------------------------------
%wp = 2*pi*Fp/fs; % digital passband freq in rad/sec
wp = Fp;
%ws = 2*pi*Fs/fs; % digital stopband freq in rad/sec
ws = Fs;
Rp = 0.5; % passband ripple in dB
As = 45; % stopband attenuation in dB Ripple = 10 ^ (-Rp/20) % passband ripple in absolute
Attn = 10 ^ (-As/20) % stopband attenuation in absolute % Analog prototype specifications: Inverse Mapping for frequencies
T = 1; % set T = 1
OmegaP = wp/T; % prototype passband freq
OmegaS = ws/T; % prototype stopband freq % Analog Chebyshev-1 Prototype Filter Calculation:
[cs, ds] = afd_chb1(OmegaP, OmegaS, Rp, As); % Calculation of second-order sections:
fprintf('\n***** Cascade-form in s-plane: START *****\n');
[CS, BS, AS] = sdir2cas(cs, ds)
fprintf('\n***** Cascade-form in s-plane: END *****\n'); % Calculation of Frequency Response:
[db_s, mag_s, pha_s, ww_s] = freqs_m(cs, ds, 8); % Calculation of Impulse Response:
[ha, x, t] = impulse(cs, ds); % Impulse Invariance Transformation:
[b, a] = imp_invr(cs, ds, T); [C, B, A] = dir2par(b, a) % Calculation of Frequency Response:
[db, mag, pha, grd, ww] = freqz_m(b, a); %% -----------------------------------------------------------------
%% Plot
%% -----------------------------------------------------------------
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.21 Analog Chebyshev-I lowpass')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
M = 1.0; % Omega max subplot(2,2,1); plot(ww_s, mag_s/T); grid on; %axis([-10, 10, 0, 1.2]);
xlabel(' Analog frequency in kHz units'); ylabel('|H|'); title('Magnitude in Absolute');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [-8, -3.8, -3.2, 0, 3.2, 3.8, 8]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0, 0.006, 0.94, 1]); subplot(2,2,2); plot(ww_s, db_s); grid on; %axis([0, M, -50, 10]);
xlabel('Analog frequency in kHz units'); ylabel('Decibels'); title('Magnitude in dB ');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [-8, -3.8, 0, 3.2, 3.8, 8]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [-45, -1, 0]);
set(gca,'YTickLabelMode','manual','YTickLabel',['45';' 1';' 0']); subplot(2,2,3); plot(ww_s, pha_s/pi); grid on; axis([-10, 10, -1.2, 1.2]);
xlabel('Analog frequency in kHz nuits'); ylabel('radians'); title('Phase Response');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [-8, -3.8, 0, 3.2, 3.8, 8]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [-1:0.5:1]); subplot(2,2,4); plot(t, ha); grid on; %axis([0, 30, -0.05, 0.25]);
xlabel('time in seconds'); ylabel('ha(t)'); title('Impulse Response'); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.21 Digital Chebyshev-I lowpass')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
M = 2; % Omega max subplot(2,2,1); plot(ww/pi, mag); axis([0, M, 0, 1.2]); grid on;
xlabel(' frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('|H|'); title('Magnitude Response');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.8, 0.95, M]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0, 0.0056, 0.9441, 1]); subplot(2,2,2); plot(ww/pi, pha/pi); axis([0, M, -1.1, 1.1]); grid on;
xlabel('frequency in \pi nuits'); ylabel('radians in \pi units'); title('Phase Response');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.8, 0.95, M]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [-1:1:1]); subplot(2,2,3); plot(ww/pi, db); axis([0, M, -30, 10]); grid on;
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Decibels'); title('Magnitude in dB ');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.8, 0.95, M]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [-60, -45, -1, 0]);
set(gca,'YTickLabelMode','manual','YTickLabel',['60';'45';' 1';' 0']); subplot(2,2,4); plot(ww/pi, grd); grid on; %axis([0, M, 0, 35]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Samples'); title('Group Delay');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.8, 0.95, M]);
%set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0:5:35]); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.21 Pole-Zero Plot')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
zplane(b,a);
title(sprintf('Pole-Zero Plot'));
%pzplotz(b,a); % ----------------------------------------------
% Calculation of Impulse Response
% ----------------------------------------------
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.21 Imp & Freq Response')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
t = [0:0.01:60]; subplot(2,1,1); impulse(cs,ds,t); grid on; % Impulse response of the analog filter
axis([0,60,-0.5,1.0]);hold on n = [0:1:60/T]; hn = filter(b,a,impseq(0,0,60/T)); % Impulse response of the digital filter
stem(n*T,hn); xlabel('time in sec'); title (sprintf('Impulse Responses T=%2d',T));
hold off % Calculation of Frequency Response:
[dbs, mags, phas, wws] = freqs_m(cs, ds, 2*pi/T); % Analog frequency s-domain [dbz, magz, phaz, grdz, wwz] = freqz_m(b, a); % Digital z-domain %% -----------------------------------------------------------------
%% Plot
%% ----------------------------------------------------------------- subplot(2,1,2); plot(wws/(2*pi),mags/T,'b+', wwz/(2*pi*T),magz,'r'); grid on; xlabel('frequency in Hz'); title('Magnitude Responses'); ylabel('Magnitude'); text(-0.8,0.15,'Analog filter'); text(0.6,1.05,'Digital filter');
运行结果:
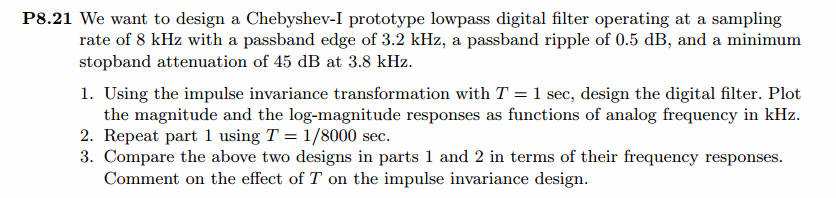
通带、阻带指标
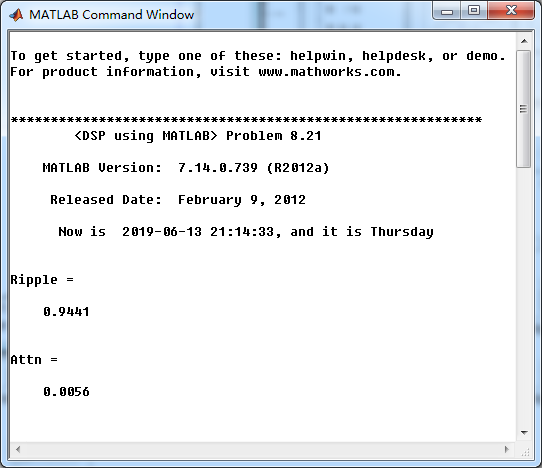
模拟Chebyshev-1型低通系统函数,串联形式系数
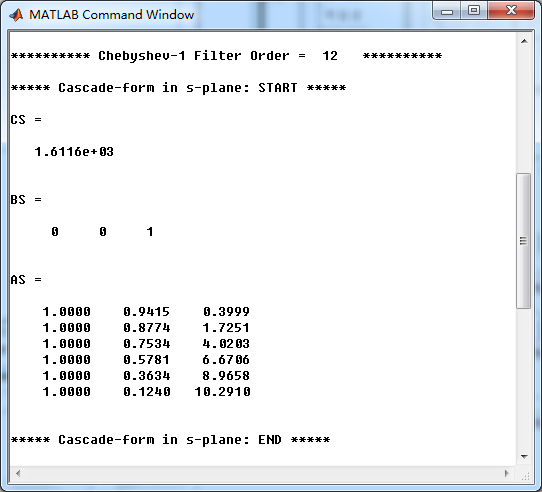
脉冲响应不变法,转换成数字低通,系统函数直接形式系数
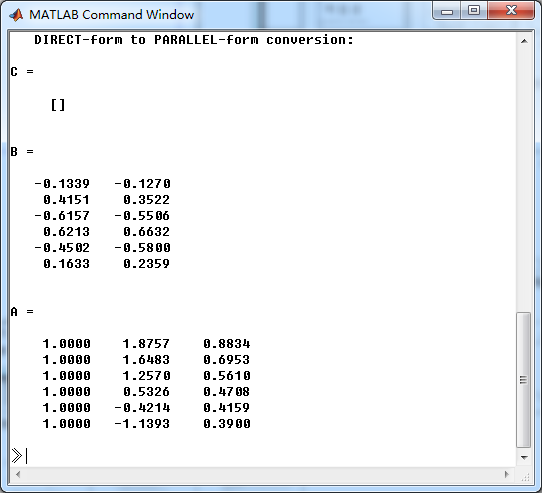
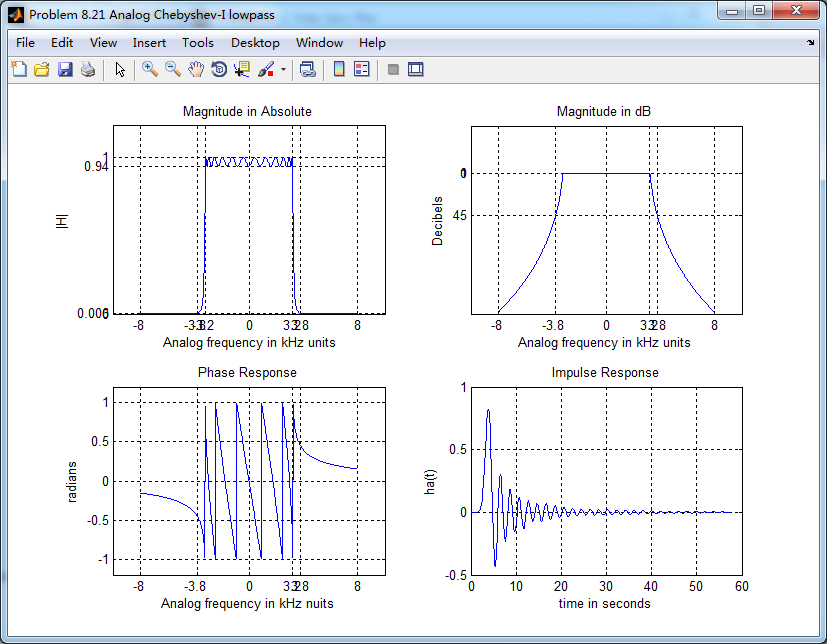
模拟Chebyshev-1型低通,幅度谱、相位谱和脉冲响应
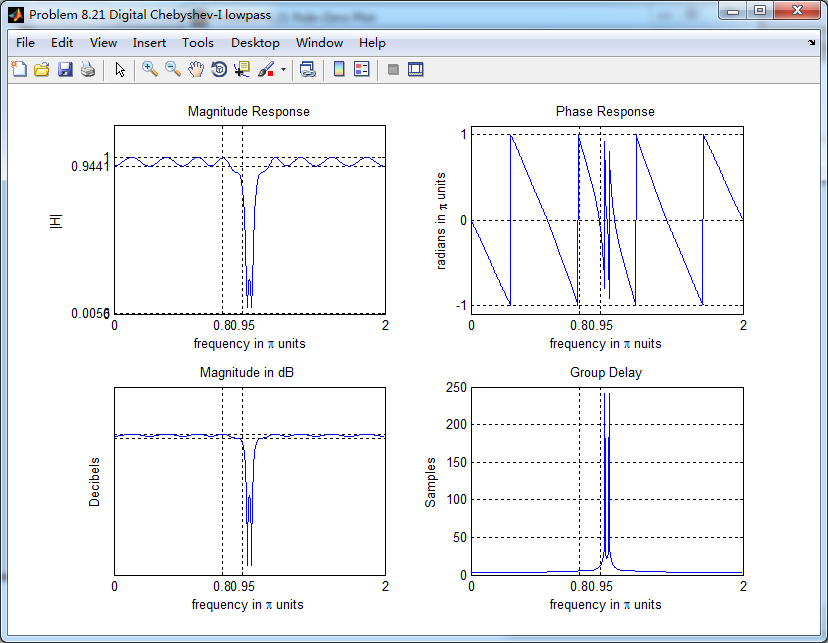
数字Chebyshev-1型低通,幅度谱、相位谱和群延迟
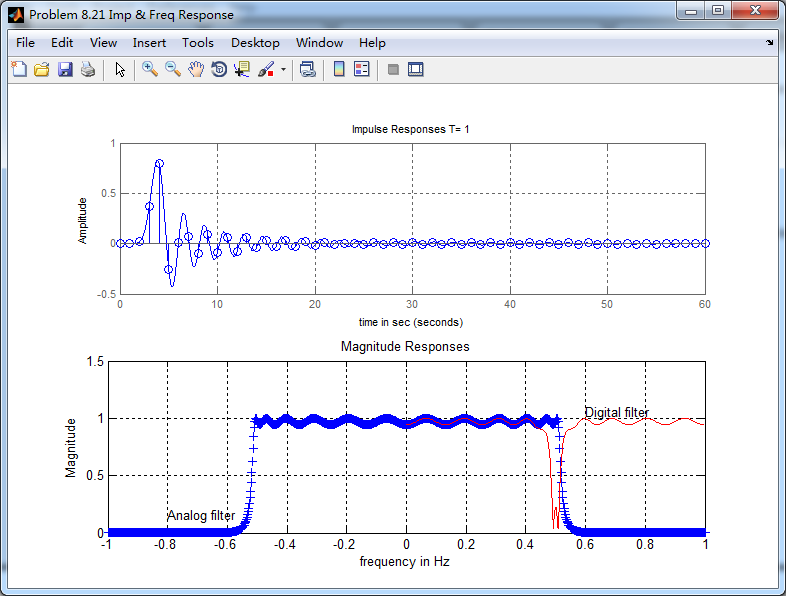
《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 8.21的更多相关文章
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 6.21
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 5.21
证明: 代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 4.21
快到龙抬头,居然下雪了,天空飘起了雪花,温度下降了近20°. 代码: %% -------------------------------------------------------------- ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 3.21
模拟信号经过不同的采样率进行采样后,得到不同的数字角频率,如下: 三种Fs,采样后的信号的谱 重建模拟信号,这里只显示由第1种Fs=0.01采样后序列进行重建,采用zoh.foh和spline三种方法 ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.27
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.26
注意:高通的线性相位FIR滤波器,不能是第2类,所以其长度必须为奇数.这里取M=31,过渡带里采样值抄书上的. 代码: %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.24
又到清明时节,…… 注意:带阻滤波器不能用第2类线性相位滤波器实现,我们采用第1类,长度为基数,选M=61 代码: %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.23
%% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output Info a ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.16
使用一种固定窗函数法设计带通滤波器. 代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
随机推荐
- css布局-瀑布流的实现
一.基本思路 1.先看最终的效果图: 2.实现原理:通过position:absolute(绝对定位)来定位每一个元素的位置,并且将当前列的高度记录下来方便下一个dom位置的计算 二.代码实现 1.版 ...
- unity3D笔记の四种调用其他脚本方法
第一种,被调用脚本函数为static类型,调用时直接用 脚本名.函数名() 第二种,GameObject.Find("脚本所在的物体的名字").SendMessage(" ...
- Pod 私有仓库构建
Pod 私有仓库构建 创建`私有仓库索引库`(iOS) 添加`私有仓库索引库`到本地repo管理 创建自己的`组建库工程 上传`组建库工程`到`私有仓库索引库` App工程调用`组建库工程` 目的 私 ...
- Linux 常用命令:开发调试篇
前言 Linux常用命令中有一些命令可以在开发或调试过程中起到很好的帮助作用,有些可以帮助了解或优化我们的程序,有些可以帮我们定位疑难问题.本文将简单介绍一下这些命令. 示例程序 我们用一个小程序,来 ...
- pipenv的使用
首先,确保pip install pipenv已经安装 1.新建一个文件夹,并在地址栏输入cmd,回车. 2.输入pipenv install,等待虚拟环境搭建完毕. 3.输入pipenv shell ...
- SpringBoot 非web项目简单架构
1.截图 2.DemoService package com.github.weiwei02.springcloudtaskdemo; import org.springframework.beans ...
- Vim模糊查找与替换
例如要把 ( 1 ).( 2 ) - 全部替换成其他字符,可以用命令: :%s/(.*)/str/gn 其中,.* 表示匹配任何东西,如果只希望匹配应为字母和数字,可以用 \w\+. 有些特殊字符需要 ...
- HTML 参考手册web
{ https://www.w3school.com.cn/tags/index.asp }
- Oracle连接字符串总结
Oracle XE 标准连接 Oracle XE(或者"Oracle Database 10g Express Edition")是一个简单免费发布的版本. 以下是语法格式: Dr ...
- 锁定文件失败 打不开磁盘“D:\vms\S1\CentOS 64 位.vmdk”或它所依赖的某个快照磁盘(强制关机后引起的问题)
电脑强制关机后,centos系统启动失败,报异常:锁定文件失败 打不开磁盘“D:\vms\S1\CentOS 64 位.vmdk”或它所依赖的某个快照磁盘.解决办法:进入D:\vms\S1目录,删除下 ...
