如何将tensorflow1.x代码改写为pytorch代码(以图注意力网络(GAT)为例)
之前讲解了图注意力网络的官方tensorflow版的实现,由于自己更了解pytorch,所以打算将其改写为pytorch版本的。
对于图注意力网络还不了解的可以先去看看tensorflow版本的代码,之前讲解的地址:
非稀疏矩阵版:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiximayou/p/13622283.html
稀疏矩阵版:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiximayou/p/13623989.html
以下改写后的代码我已经上传到gihub上,地址为:
https://github.com/taishan1994/pytorch_gat
图注意力网络的官方代码使用的是tensorflow1.x版本的,地址为:
https://github.com/Diego999/pyGAT
下面开始进入正题了。
1、tensorflow1.x的一般建模过程:
- 定义好训练的数据
- 定义计算图(包含占位)
- 定义训练主函数、损失函数计算、优化器
- 定义Session,参数初始化以及实际的前向传播和反向传播计算都是在Session中
2、将tensorflow转换为pytorch代码
其他数据处理的代码都是一致的,主要是一些需要改变的地方:
2.1 数据的读取
在tensorflow中,标签是要经过onehot编码的,而在pytorch中确是不用的,在load_data中:
def load_data(dataset_str): # {'pubmed', 'citeseer', 'cora'}
"""Load data."""
names = ['x', 'y', 'tx', 'ty', 'allx', 'ally', 'graph']
objects = []
for i in range(len(names)):
with open("data/ind.{}.{}".format(dataset_str, names[i]), 'rb') as f:
if sys.version_info > (3, 0):
objects.append(pkl.load(f, encoding='latin1'))
else:
objects.append(pkl.load(f))
x, y, tx, ty, allx, ally, graph = tuple(objects)
test_idx_reorder = parse_index_file("data/ind.{}.test.index".format(dataset_str))
test_idx_range = np.sort(test_idx_reorder)
if dataset_str == 'citeseer':
# Fix citeseer dataset (there are some isolated nodes in the graph)
# Find isolated nodes, add them as zero-vecs into the right position
test_idx_range_full = range(min(test_idx_reorder), max(test_idx_reorder)+1)
tx_extended = sp.lil_matrix((len(test_idx_range_full), x.shape[1]))
tx_extended[test_idx_range-min(test_idx_range), :] = tx
tx = tx_extended
ty_extended = np.zeros((len(test_idx_range_full), y.shape[1]))
ty_extended[test_idx_range-min(test_idx_range), :] = ty
ty = ty_extended
features = sp.vstack((allx, tx)).tolil()
features[test_idx_reorder, :] = features[test_idx_range, :]
adj = nx.adjacency_matrix(nx.from_dict_of_lists(graph))
labels = np.vstack((ally, ty))
labels[test_idx_reorder, :] = labels[test_idx_range, :]
#pytorch的标签不需要进行one-hot编码
my_labels = np.where(labels==1)[1]
idx_test = test_idx_range.tolist()
idx_train = range(len(y))
idx_val = range(len(y), len(y)+500)
train_my_labels_mask = sample_mask(idx_train, my_labels.shape[0])
val_my_labels_mask = sample_mask(idx_val, my_labels.shape[0])
test_my_labels_mask = sample_mask(idx_test, my_labels.shape[0])
train_my_labels = my_labels[train_my_labels_mask]
val_my_labels = my_labels[val_my_labels_mask]
test_my_labels = my_labels[test_my_labels_mask]
train_mask = sample_mask(idx_train, labels.shape[0])
val_mask = sample_mask(idx_val, labels.shape[0])
test_mask = sample_mask(idx_test, labels.shape[0])
y_train = np.zeros(labels.shape)
y_val = np.zeros(labels.shape)
y_test = np.zeros(labels.shape)
y_train[train_mask, :] = labels[train_mask, :]
y_val[val_mask, :] = labels[val_mask, :]
y_test[test_mask, :] = labels[test_mask, :]
print(adj.shape)
print(features.shape)
data_dict = {
'adj': adj,
'features': features,
'y_train': y_train,
'y_val': y_val,
'y_test': y_test,
'train_mask': train_mask,
'val_mask': val_mask,
'test_mask': test_mask,
'train_my_labels': train_my_labels,
'val_my_labels': val_my_labels,
'test_my_labels': test_my_labels,
'my_labels': my_labels
}
return data_dict
我们要使用np.where()函数,将每一个ont-hot编码中值为1的索引(也就是标签)取出来,然后在对其进行划分训练标签、验证标签和测试标签。
顺便提一下,当我们要返回的值很多的时候,可以用一个字典包装起来,最后返回该字典就行了,这符合python的编码规范。
2.2 注意力层的搭建
在tensorflow中:
conv1d = tf.layers.conv1d def attn_head(seq, out_sz, bias_mat, activation, in_drop=0.0, coef_drop=0.0, residual=False):
with tf.name_scope('my_attn'):
if in_drop != 0.0:
seq = tf.nn.dropout(seq, 1.0 - in_drop) seq_fts = tf.layers.conv1d(seq, out_sz, 1, use_bias=False) # simplest self-attention possible
f_1 = tf.layers.conv1d(seq_fts, 1, 1)
f_2 = tf.layers.conv1d(seq_fts, 1, 1)
logits = f_1 + tf.transpose(f_2, [0, 2, 1])
coefs = tf.nn.softmax(tf.nn.leaky_relu(logits) + bias_mat) if coef_drop != 0.0:
coefs = tf.nn.dropout(coefs, 1.0 - coef_drop)
if in_drop != 0.0:
seq_fts = tf.nn.dropout(seq_fts, 1.0 - in_drop) vals = tf.matmul(coefs, seq_fts)
ret = tf.contrib.layers.bias_add(vals) # residual connection
if residual:
if seq.shape[-1] != ret.shape[-1]:
ret = ret + conv1d(seq, ret.shape[-1], 1) # activation
else:
ret = ret + seq return activation(ret) # activation
直接就可以使用相关api进行计算,但是在pytorch中,无论是定义自己的层还是模型,都需要先建立,然后再使用(一般是这样)。改写后的代码如下:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn class Attn_head(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
in_channel,
out_sz,
bias_mat,
in_drop=0.0,
coef_drop=0.0,
activation=None,
residual=False):
super(Attn_head, self).__init__()
self.in_channel = in_channel
self.out_sz = out_sz
self.bias_mat = bias_mat
self.in_drop = in_drop
self.coef_drop = coef_drop
self.activation = activation
self.residual = residual self.conv1 = nn.Conv1d(self.in_channel, self.out_sz, 1)
self.conv2_1 = nn.Conv1d(self.out_sz, 1, 1)
self.conv2_2 = nn.Conv1d(self.out_sz, 1, 1)
self.leakyrelu = nn.LeakyReLU()
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
#pytorch中dropout的参数p表示每个神经元一定概率失活
self.in_dropout = nn.Dropout()
self.coef_dropout = nn.Dropout()
self.res_conv = nn.Conv1d(self.in_channel, self.out_sz, 1) def forward(self,x):
seq = x
if self.in_drop != 0.0:
seq = self.in_dropout(x)
seq_fts = self.conv1(seq)
f_1 = self.conv2_1(seq_fts)
f_2 = self.conv2_2(seq_fts)
logits = f_1 + torch.transpose(f_2, 2, 1)
logits = self.leakyrelu(logits)
coefs = self.softmax(logits + self.bias_mat)
if self.coef_drop !=0.0:
coefs = self.coef_dropout(coefs)
if self.in_dropout !=0.0:
seq_fts = self.in_dropout(seq_fts)
ret = torch.matmul(coefs, torch.transpose(seq_fts, 2, 1))
ret = torch.transpose(ret, 2, 1)
if self.residual:
if seq.shape[1] != ret.shape[1]:
ret = ret + self.res_conv(seq)
else:
ret = ret + seq
return self.activation(ret)
要继承nn.Module类,然后在__init__中初始化相关参数以及对应的层,在forward中进行前向传播计算。
2.3 搭建模型
有了注意力层之后,就可以搭建模型了,tensorflow的代码:
def inference(inputs, nb_classes, nb_nodes, training, attn_drop, ffd_drop,
bias_mat, hid_units, n_heads, activation=tf.nn.elu, residual=False):
attns = []
for _ in range(n_heads[0]):
attns.append(layers.attn_head(inputs, bias_mat=bias_mat,
out_sz=hid_units[0], activation=activation,
in_drop=ffd_drop, coef_drop=attn_drop, residual=False))
h_1 = tf.concat(attns, axis=-1)
for i in range(1, len(hid_units)):
h_old = h_1
attns = []
for _ in range(n_heads[i]):
attns.append(layers.attn_head(h_1, bias_mat=bias_mat,
out_sz=hid_units[i], activation=activation,
in_drop=ffd_drop, coef_drop=attn_drop, residual=residual))
h_1 = tf.concat(attns, axis=-1)
out = []
for i in range(n_heads[-1]):
out.append(layers.attn_head(h_1, bias_mat=bias_mat,
out_sz=nb_classes, activation=lambda x: x,
in_drop=ffd_drop, coef_drop=attn_drop, residual=False))
logits = tf.add_n(out) / n_heads[-1] return logits
改写之后的pytorch代码:
import numpy as np
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
from layer import * class GAT(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
nb_classes,
nb_nodes,
attn_drop,
ffd_drop,
bias_mat,
hid_units,
n_heads,
residual=False):
super(GAT, self).__init__()
self.nb_classes = nb_classes
self.nb_nodes = nb_nodes
self.attn_drop = attn_drop
self.ffd_drop = ffd_drop
self.bias_mat = bias_mat
self.hid_units = hid_units
self.n_heads = n_heads
self.residual = residual self.attn1 = Attn_head(in_channel=1433, out_sz=self.hid_units[0],
bias_mat=self.bias_mat, in_drop=self.ffd_drop,
coef_drop=self.attn_drop, activation=nn.ELU(),
residual=self.residual)
self.attn2 = Attn_head(in_channel=64, out_sz=self.nb_classes,
bias_mat=self.bias_mat, in_drop=self.ffd_drop,
coef_drop=self.attn_drop, activation=nn.ELU(),
residual=self.residual)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1) def forward(self, x):
attns = []
for _ in range(self.n_heads[0]):
attns.append(self.attn1(x))
h_1 = torch.cat(attns, dim=1)
out = self.attn2(h_1)
logits = torch.transpose(out.view(self.nb_classes,-1), 1, 0)
logits = self.softmax(logits)
return logits
和tensorflow代码不同的是,这里我们仅仅定义了两层注意力。还需要注意的是,我们在__init__中定义相关层的时候,对于输入和输出的维度我们是要预先知道的,并填充进去,如果在forward中实际的值与预先定义的维度不同,那么就会报错。
2.4 进行训练、验证和测试
首先还是来看一下tensorflow是怎么定义的:
with tf.Graph().as_default():
with tf.name_scope('input'):
ftr_in = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=(batch_size, nb_nodes, ft_size))
bias_in = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=(batch_size, nb_nodes, nb_nodes))
lbl_in = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.int32, shape=(batch_size, nb_nodes, nb_classes))
msk_in = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.int32, shape=(batch_size, nb_nodes))
attn_drop = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=())
ffd_drop = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=())
is_train = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.bool, shape=()) logits = model.inference(ftr_in, nb_classes, nb_nodes, is_train,
attn_drop, ffd_drop,
bias_mat=bias_in,
hid_units=hid_units, n_heads=n_heads,
residual=residual, activation=nonlinearity)
log_resh = tf.reshape(logits, [-1, nb_classes])
lab_resh = tf.reshape(lbl_in, [-1, nb_classes])
msk_resh = tf.reshape(msk_in, [-1])
loss = model.masked_softmax_cross_entropy(log_resh, lab_resh, msk_resh)
accuracy = model.masked_accuracy(log_resh, lab_resh, msk_resh) train_op = model.training(loss, lr, l2_coef) saver = tf.train.Saver() init_op = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(), tf.local_variables_initializer()) vlss_mn = np.inf
vacc_mx = 0.0
curr_step = 0 with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op) train_loss_avg = 0
train_acc_avg = 0
val_loss_avg = 0
val_acc_avg = 0 for epoch in range(nb_epochs):
print("epoch: ",epoch)
tr_step = 0
tr_size = features.shape[0] while tr_step * batch_size < tr_size:
_, loss_value_tr, acc_tr = sess.run([train_op, loss, accuracy],
feed_dict={
ftr_in: features[tr_step*batch_size:(tr_step+1)*batch_size],
bias_in: biases[tr_step*batch_size:(tr_step+1)*batch_size],
lbl_in: y_train[tr_step*batch_size:(tr_step+1)*batch_size],
msk_in: train_mask[tr_step*batch_size:(tr_step+1)*batch_size],
is_train: True,
attn_drop: 0.6, ffd_drop: 0.6})
train_loss_avg += loss_value_tr
train_acc_avg += acc_tr
tr_step += 1 vl_step = 0
vl_size = features.shape[0] while vl_step * batch_size < vl_size:
loss_value_vl, acc_vl = sess.run([loss, accuracy],
feed_dict={
ftr_in: features[vl_step*batch_size:(vl_step+1)*batch_size],
bias_in: biases[vl_step*batch_size:(vl_step+1)*batch_size],
lbl_in: y_val[vl_step*batch_size:(vl_step+1)*batch_size],
msk_in: val_mask[vl_step*batch_size:(vl_step+1)*batch_size],
is_train: False,
attn_drop: 0.0, ffd_drop: 0.0})
val_loss_avg += loss_value_vl
val_acc_avg += acc_vl
vl_step += 1 print('Training: loss = %.5f, acc = %.5f | Val: loss = %.5f, acc = %.5f' %
(train_loss_avg/tr_step, train_acc_avg/tr_step,
val_loss_avg/vl_step, val_acc_avg/vl_step)) if val_acc_avg/vl_step >= vacc_mx or val_loss_avg/vl_step <= vlss_mn:
if val_acc_avg/vl_step >= vacc_mx and val_loss_avg/vl_step <= vlss_mn:
vacc_early_model = val_acc_avg/vl_step
vlss_early_model = val_loss_avg/vl_step
saver.save(sess, checkpt_file)
vacc_mx = np.max((val_acc_avg/vl_step, vacc_mx))
vlss_mn = np.min((val_loss_avg/vl_step, vlss_mn))
curr_step = 0
else:
curr_step += 1
if curr_step == patience:
print('Early stop! Min loss: ', vlss_mn, ', Max accuracy: ', vacc_mx)
print('Early stop model validation loss: ', vlss_early_model, ', accuracy: ', vacc_early_model)
break train_loss_avg = 0
train_acc_avg = 0
val_loss_avg = 0
val_acc_avg = 0 saver.restore(sess, checkpt_file) ts_size = features.shape[0]
ts_step = 0
ts_loss = 0.0
ts_acc = 0.0 while ts_step * batch_size < ts_size:
loss_value_ts, acc_ts = sess.run([loss, accuracy],
feed_dict={
ftr_in: features[ts_step*batch_size:(ts_step+1)*batch_size],
bias_in: biases[ts_step*batch_size:(ts_step+1)*batch_size],
lbl_in: y_test[ts_step*batch_size:(ts_step+1)*batch_size],
msk_in: test_mask[ts_step*batch_size:(ts_step+1)*batch_size],
is_train: False,
attn_drop: 0.0, ffd_drop: 0.0})
ts_loss += loss_value_ts
ts_acc += acc_ts
ts_step += 1 print('Test loss:', ts_loss/ts_step, '; Test accuracy:', ts_acc/ts_step) sess.close()
就是建立图、然后在Session中执行。
这里需要注意的是,features的维度是(2708,1433),无论是tensorflow还是pytorch,都需要对其扩充一个维度:(1,2708,1433),其余数据也同样。在计算损失的时候,网络输出的值的维度注意是:(2708,7),就没有了之前的那个维度了。在pytorch中,输入的形状和tensorflow也不大一样,它的输入是:(1,1433,2708),第二位是特征的维度,第三位才是节点的数目,这是和tensorflow主要的区别之一。
接下来看下pytorch中是怎么做的:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import numpy as np
from utils import *
from model import * np.random.seed(1)
torch.manual_seed(1)
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(1) torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") data = load_data("cora")
adj = data['adj']
features = data['features']
y_train = data['y_train']
y_val = data['y_val']
y_test = data['y_test']
train_mask = data['train_mask']
val_mask = data['val_mask']
test_mask = data['test_mask']
train_my_labels = data['train_my_labels']
val_my_labels = data['val_my_labels']
test_my_labels = data['test_my_labels']
my_labels = data['my_labels'] features, spars = preprocess_features(features) #节点数目
nb_nodes = features.shape[0]
#特征维度
ft_sizes = features.shape[1]
#类别数目
nb_classes = my_labels.shape[0] #将邻接矩阵的稀疏形式转换为原始矩阵
adj = adj.todense() #新增加一个维度
adj = adj[np.newaxis]
features = features[np.newaxis]
y_train = y_train[np.newaxis]
y_val = y_val[np.newaxis]
y_test = y_test[np.newaxis]
#train_mask = train_mask[np.newaxis]
#val_mask = val_mask[np.newaxis]
#test_mask = test_mask[np.newaxis] biases = torch.from_numpy(adj_to_bias(adj, [nb_nodes], nhood=1)).float().to(device) features = torch.from_numpy(features)
#pytorch输入的特征:[batch, features,nodes],第二位是特征维度
#而tensorflow的输入是:[batch, nodes, features]
features = torch.transpose(features,2,1).to(device) #定义相关变量
hid_units=[8]
n_heads=[8, 1]
epochs = 5000
lr = 0.01 #定义模型
gat = GAT(nb_classes=nb_classes,
nb_nodes=nb_nodes,
attn_drop=0.0,
ffd_drop=0.0,
bias_mat=biases,
hid_units=hid_units,
n_heads=n_heads,
residual=False).to(device) criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(params=gat.parameters(),lr=lr,betas=(0.9, 0.99)) #y_train = torch.from_numpy(np.where(y_train==1)[2])
#y_val = torch.from_numpy(np.where(y_val==1)[2])
#y_test = torch.from_numpy(np.where(y_test==1)[2])
train_my_labels = torch.from_numpy(train_my_labels).long().to(device)
val_my_labels = torch.from_numpy(val_my_labels).long().to(device)
test_my_labels = torch.from_numpy(test_my_labels).long().to(device) train_mask = np.where(train_mask == 1)[0]
val_mask = np.where(val_mask == 1)[0]
test_mask = np.where(test_mask == 1)[0]
train_mask = torch.from_numpy(train_mask).to(device)
val_mask = torch.from_numpy(val_mask).to(device)
test_mask = torch.from_numpy(test_mask).to(device) print("训练节点个数:", len(train_my_labels))
print("验证节点个数:", len(val_my_labels))
print("测试节点个数:", len(test_my_labels)) def train():
gat.train()
correct = 0
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = gat(features)
train_mask_outputs = torch.index_select(outputs, 0, train_mask)
#print("train_mask_outputs.shape:",train_mask_outputs.shape)
#print("train_my_labels.shape[0]:",train_my_labels.shape[0])
_, preds =torch.max(train_mask_outputs.data, 1)
loss = criterion(train_mask_outputs, train_my_labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
correct += torch.sum(preds == train_my_labels).to(torch.float32)
acc = correct / train_my_labels.shape[0]
return loss,acc def val():
gat.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
correct = 0
outputs = gat(features)
val_mask_outputs = torch.index_select(outputs, 0, val_mask)
#print("val_mask_outputs.shape:",val_mask_outputs.shape)
#print("val_my_labels.shape[0]:",val_my_labels.shape[0])
_, preds =torch.max(val_mask_outputs.data, 1)
loss = criterion(val_mask_outputs, val_my_labels)
correct += torch.sum(preds == val_my_labels).to(torch.float32)
acc = correct / val_my_labels.shape[0]
return loss,acc def test():
gat.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
correct = 0
outputs = gat(features)
test_mask_outputs = torch.index_select(outputs, 0, test_mask)
#print("test_mask_outputs.shape:",test_mask_outputs.shape)
#print("val_my_labels.shape[0]:",val_my_labels.shape[0])
_, preds =torch.max(test_mask_outputs.data, 1)
loss = criterion(test_mask_outputs, test_my_labels)
correct += torch.sum(preds == test_my_labels).to(torch.float32)
acc = correct / test_my_labels.shape[0]
print("TestLoss:{:.4f},TestAcc:{:.4f}".format(loss,acc))
return loss,acc,test_mask_outputs.cpu().numpy(),test_my_labels.cpu().numpy() from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def main():
train_loss_history = []
val_loss_history = []
train_acc_history = []
val_acc_history = []
for epoch in range(1,epochs+1):
train_loss,train_acc = train()
val_loss,val_acc = val()
print("epoch:{:03d},TrainLoss:{:.4f},TrainAcc:{:.4f},ValLoss:{:.4f},ValAcc:{:.4f}"
.format(epoch,train_loss,train_acc,val_loss,val_acc))
train_loss_history.append(train_loss)
train_acc_history.append(train_acc)
val_loss_history.append(val_loss)
val_acc_history.append(val_acc)
num_epochs = range(1, epochs + 1)
plt.plot(num_epochs, train_loss_history, 'b--')
plt.plot(num_epochs, val_loss_history, 'r-')
plt.title('Training and validation Loss ')
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.ylabel("Loss")
plt.legend(["train_loss", 'val_loss'])
plt.savefig("loss.png")
plt.close() plt.plot(num_epochs, train_acc_history, 'b--')
plt.plot(num_epochs, val_acc_history, 'r-')
plt.title('Training and validation Acc ')
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.ylabel("Acc")
plt.legend(['train_acc','val_acc'])
plt.savefig("acc.png")
plt.close() _, _, test_data, test_labels = test()
tsne = TSNE(perplexity=30, n_components=2, init='pca', n_iter=5000) # TSNE降维,降到2
low_dim_embs = tsne.fit_transform(test_data)
plt.title('tsne result')
plt.scatter(low_dim_embs[:,0], low_dim_embs[:,1], marker='o', c=test_labels)
plt.savefig("tsne.png")
plt.close() main()
大体上还是很简单明了的,这里还是的注意一个问题。在pytorch中,我们首使用网络对整个图进行计算,但是我们只更新根据mask所得的节点的参数,如果直接是使用outputs[train_mask],这样是不行的,pytroch的张量是不支持根据布尔值来进行分割的,如果我们将里面的True和False转换为1和0,虽然不会报错,但是就根本没有作用,因此在一开始,我们就要找到哪些节点是需要被训练的,取得其索引值,然后使用torch.index_select()进行切割。
最后绘制了损失函数和准确率随epoch的变化情况以及降维之后测试数据的分布情况。
3、结果
官方实现:
Dataset: cora
----- Opt. hyperparams -----
lr: 0.005
l2_coef: 0.0005
----- Archi. hyperparams -----
nb. layers: 1
nb. units per layer: [8]
nb. attention heads: [8, 1]
residual: False
nonlinearity: <function elu at 0x7f1b7507af28>
model: <class 'models.gat.GAT'>
(2708, 2708)
(2708, 1433) epoch: 1
Training: loss = 1.94574, acc = 0.14286 | Val: loss = 1.93655, acc = 0.13600
epoch: 2
Training: loss = 1.94598, acc = 0.15714 | Val: loss = 1.93377, acc = 0.14800
epoch: 3
Training: loss = 1.94945, acc = 0.14286 | Val: loss = 1.93257, acc = 0.19600
epoch: 4
Training: loss = 1.93438, acc = 0.24286 | Val: loss = 1.93172, acc = 0.22800
epoch: 5
Training: loss = 1.93199, acc = 0.17143 | Val: loss = 1.93013, acc = 0.36400
。。。。。。
epoch: 674
Training: loss = 1.23833, acc = 0.49286 | Val: loss = 1.01357, acc = 0.81200
Early stop! Min loss: 1.010906457901001 , Max accuracy: 0.8219999074935913
Early stop model validation loss: 1.3742048740386963 , accuracy: 0.8219999074935913
Test loss: 1.3630210161209106 ; Test accuracy: 0.8219999074935913
自己的pytorch实现:
(2708, 2708)
(2708, 1433)
训练节点个数: 140
验证节点个数: 500
测试节点个数: 1000
epoch:001,TrainLoss:7.9040,TrainAcc:0.0000,ValLoss:7.9040,ValAcc:0.0000
epoch:002,TrainLoss:7.9040,TrainAcc:0.0000,ValLoss:7.9039,ValAcc:0.1920
epoch:003,TrainLoss:7.9039,TrainAcc:0.0714,ValLoss:7.9039,ValAcc:0.1600
epoch:004,TrainLoss:7.9038,TrainAcc:0.1000,ValLoss:7.9039,ValAcc:0.1020
。。。。。。
epoch:2396,TrainLoss:7.0191,TrainAcc:0.8929,ValLoss:7.4967,ValAcc:0.7440
epoch:2397,TrainLoss:7.0400,TrainAcc:0.8786,ValLoss:7.4969,ValAcc:0.7580
epoch:2398,TrainLoss:7.0188,TrainAcc:0.8929,ValLoss:7.4974,ValAcc:0.7580
epoch:2399,TrainLoss:7.0045,TrainAcc:0.9071,ValLoss:7.4983,ValAcc:0.7620
epoch:2400,TrainLoss:7.0402,TrainAcc:0.8714,ValLoss:7.4994,ValAcc:0.7620
TestLoss:7.4805,TestAcc:0.7700
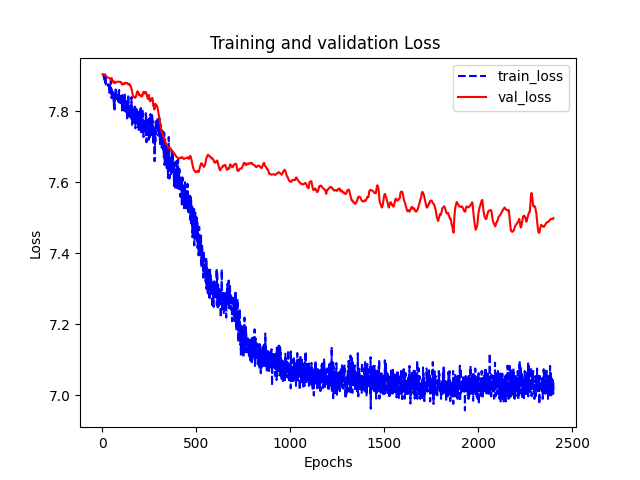
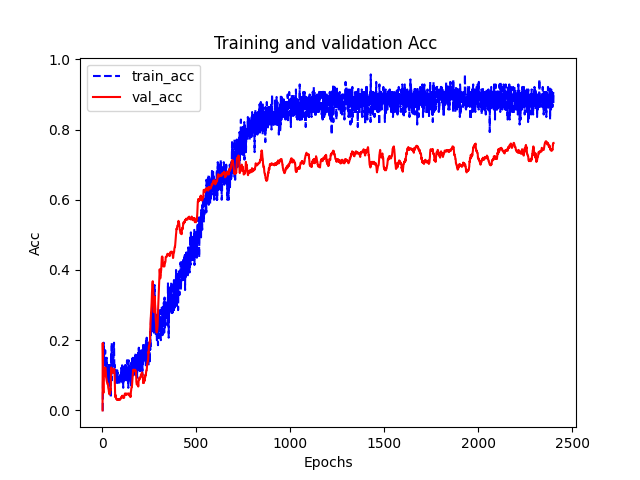
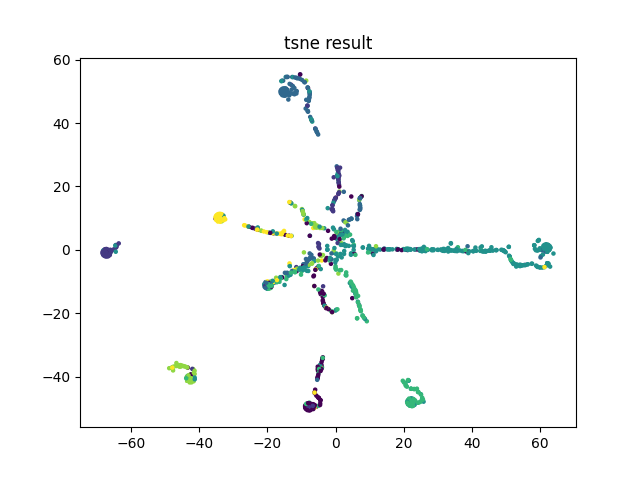
可能实现的和原始tensorflow版本的还有一些差别,自己实现的只有0.77。还有点奇怪的地方是loss比官方的大好多。。。
4、总结
关于tensorflow代码转pytorch需要注意的一些地方:
(1)输入的数据不同,比如特征,tensorflow是(1,2708,1433),pytorch的是(1,1433,2708)。
(2)标签的编码方式不同,tensorflow是onehot编码,比如[[0,0,1],[1,0,0],[0,1,0]],pytorch就是原始的类[2,0,1]。
(3)构建模型的方式不同,tensorflow直接使用,pytorch要继承nn.Module,然后在__init__建立层,在forward中进行计算。
(4)训练验证测试的不同,tensorflow要先构建计算图,然后在Session中执行计算,也就是静态图,pytorch是动态图,没有显示的定义计算图。
(5)相关的接口也不同,这是自然而然的,毕竟都有着自己的设计理念,比如tf.concat()对应torch.cat(),即使名字相同的两个类,使用的方法也可能是不同的。
总而言之,动手是最重要的。
如果哪里有问题,还请指出。
如何将tensorflow1.x代码改写为pytorch代码(以图注意力网络(GAT)为例)的更多相关文章
- (原)SphereFace及其pytorch代码
转载请注明出处: http://www.cnblogs.com/darkknightzh/p/8524937.html 论文: SphereFace: Deep Hypersphere Embeddi ...
- 目标检测之Faster-RCNN的pytorch代码详解(数据预处理篇)
首先贴上代码原作者的github:https://github.com/chenyuntc/simple-faster-rcnn-pytorch(非代码作者,博文只解释代码) 今天看完了simple- ...
- (转载)PyTorch代码规范最佳实践和样式指南
A PyTorch Tools, best practices & Styleguide 中文版:PyTorch代码规范最佳实践和样式指南 This is not an official st ...
- PyTorch代码调试利器: 自动print每行代码的Tensor信息
本文介绍一个用于 PyTorch 代码的实用工具 TorchSnooper.作者是TorchSnooper的作者,也是PyTorch开发者之一. GitHub 项目地址: https://github ...
- 如何把C++的源代码改写成C代码?而C改C++只需一步!
★ 如何把C++的源代码改写成C代码? C++解释器比C语言解释器占用的存储空间要大,想要在某些特定场合兼容C++代码,同时为了节省有限的存储空间,降低成本,也为了提高效率,将用C++语言写的源程序用 ...
- pointnet.pytorch代码解析
pointnet.pytorch代码解析 代码运行 Training cd utils python train_classification.py --dataset <dataset pat ...
- 残差网络resnet理解与pytorch代码实现
写在前面 深度残差网络(Deep residual network, ResNet)自提出起,一次次刷新CNN模型在ImageNet中的成绩,解决了CNN模型难训练的问题.何凯明大神的工作令人佩服 ...
- 资源分享 | PyTea:不用运行代码,静态分析pytorch模型的错误
前言 本文介绍一个Pytorch模型的静态分析器 PyTea,它不需要运行代码,即可在几秒钟之内扫描分析出模型中的张量形状错误.文末附使用方法. 本文转载自机器之心 编辑:CV技 ...
- pytorch写一个LeNet网络
我们先介绍下pytorch中的cnn网络 学过深度卷积网络的应该都非常熟悉这张demo图(LeNet): 先不管怎么训练,我们必须先构建出一个CNN网络,很快我们写了一段关于这个LeNet的代码,并进 ...
随机推荐
- BLE MESH 学习[1] - ESP32 篇
BLE MESH 学习 BLE MESH 是一种蓝牙(n:m)组网的技术. 本篇先介绍 BLE MESH 到使用 ESP32 的官方示例对其进行学习讲解. 后面会进一步学习 SIG 的 BLE MES ...
- css如何让子元素在父元素中水平垂直居中
方法一: display:flex <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta chars ...
- Orcal语法Merge into用法
Orcal语法 Merge into 1.语法介绍 MERGE语句是Oracle9i新增的语法,用来合并UPDATE和INSERT语句.通过MERGE语句,根据一张表或子查询的连接条件对另外一张表进行 ...
- 史上最全且最简洁易懂的Activity启动流程解析
Activity的启动流程是一个资深Android工程师必须掌握的内容,也是高职级面试中的高频面试知识点,无论是从事应用层开发,还是Framework开发,其重要性都无需我多言.而要真正理解它,就不可 ...
- 火题大战Vol.1 A.
火题大战Vol.1 A. 题目描述 给定两个数\(x\),\(y\),比较\(x^y\) 与\(y!\)的大小. 输入格式 第一行一个整数\(T\)表示数据组数. 接下来\(T\)行,每行两个整数\( ...
- python基础 Day5
python Day5 字典 其他数据类型的缺点 列表可以存储大量的数据,但是关联性不强. 列表的查询速度比较慢 其容器的数据类型为dict 其数据类型的分类 可变(不可哈希)的数据类型:list d ...
- Magento 2 Factory Objects
In object oriented programming, a factory method is a method that’s used to instantiate an object. F ...
- 基于go+etcd实现分布式锁
原文链接:https://www.yii-china.com/topic/detail/113 package main import ( "context" "fmt& ...
- pandas参数设置小技巧
在日常使用pandas的过程中,由于我们所分析的数据表规模.格式上的差异,使得同样的函数或方法作用在不同数据上的效果存在差异. 而pandas有着自己的一套参数设置系统,可以帮助我们在遇到不同的数据时 ...
- play ball小游戏-Alpha版本发布说明
Alpha版本发布说明 一.功能介绍 本团队所做的微信小程序是一款小球经碰撞后最终到达目的位置通关的休闲益智类游戏.Alpha版本具有的功能大体如下: 1. 闯关模式 多达12关普通竖屏关卡.4关特殊 ...
