(Pixel2PixelGANs)Image-to-Image translation with conditional adversarial networks
Introduction
1. develop a common framework for all problems that are the task of predicting pixels from pixels.
2. CNNs learn to minimize a loss function -an objective that scores the quality of results-- and although the learning process is automatic, a lot of manual effort still goes into designing effective losses.
3.the CNN to minimize Euclidean distance(欧式距离L2) between predicted and ground truth pixels, it will tend to produce blurry results.
why? because the L2 distance is minimized by averaging all plausible outputs, which cause blurring.
4.GANs learn a loss that tries to classify if the output image is real of fake , blurry images will not be tolerated since they obviously fake!
5. they apply cGANs suitable for image-to-image translation tasks, where we condition on input image and generate a corresponding output image.
Releted work
1.image-to-image translation problems are formulated as per-pixel(逐个像素的)classfication or regression.but these formulations treat the output space as “unstructured” ,each output pixel is considered conditionally independent from all others given the input image.(独立性!)
2. conditional GANs learn a structured loss.
3. cGANs is different in that the loss is learned(损失可以学习), in theory, penalize any possible structure that differs between output and target.(条件GAN的不同之处在于,损失是可以习得的,理论上,它可以惩罚产出和目标之间可能存在差异的任何结构。)
4. the choices for generator and discriminator achitecture:
for G: using 'U-Net '
for D: using PatchGAN classifier penalizes structure at the scale of image patches.
The purpose of PatchGAN aim to capure local style statistics.(用于捕获本地样式统计信息)
Method
1. The whole of framwork is that conditional GANs learn a mapping from observed image x and random noise vector z, to y. $G:{x,z}\rightarrow y(ground-truth)$ .
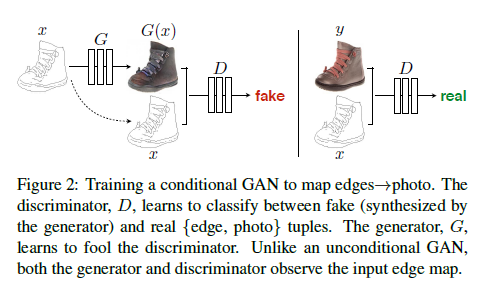
2. Unlike an unconditional GAN, both the generator and discriminator observe the input edge map.
3. objective function:
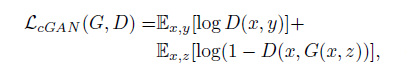
G try to minimize this objective against an adversarial D that try to maximize it.
4. they test the importence of conditioning the disctiminator, the discriminator dose not oberve x(edge map):
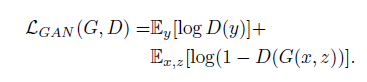
5. it's beneficial to mix GAN objective with a more traditional loss, such as L2-distance.
6. G is tasked to not only fool the discriminator but also to be near the ground truth output in an L2 sense.
7. L1 distance is applied into the additional loss rather than L2 as L1 encourages less blurring(remeber it!).
8.
final objective
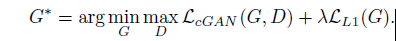
9. without $z$ (random noise vector), the net still learn a mapping from $x$ to $y$, but would produce deterministic output, therefore fail to match any distribution other than a delta function.(因此无法匹配除函数之外的任何分布)
10. towords $z$, Gaussian noise often is used in the past, but authors find this strategy ineffective, the G simply learned to ignore the noise. Finally, in the form of dropout is provided.but we observe only minor stochasticity in the output of our nets.
Network Architecture
1. The whole of generator and discriminator architectures from DCGANs.
For G: U-Net;DCGAN; encoder- decoder; bottleneck; shuttle the information;
The job:
1.mapping a high resolution grid to a high resolution output grid.
2. although the input and output differ in surface appearance, but both are rendering of same underlying structure.
The character:
structure in the input is roughly aligned with structure in the output.
The previous measures:
1.encoder-decoder network is applied.
2.until a bottleneck layer, downsample is changed to upsample.
Q:
1. A great deal of low-level information shared between the input and output, shuttling this information directly across the net is desirable.例如,在图像着色的情况下,输入和输出共享突出边缘的位置。
END:
To give the generator a means to circumvent(绕过) the bottleneck for information like this, adding skip connections is adopted, this architecture called 'U-Net'

The results of different loss function:
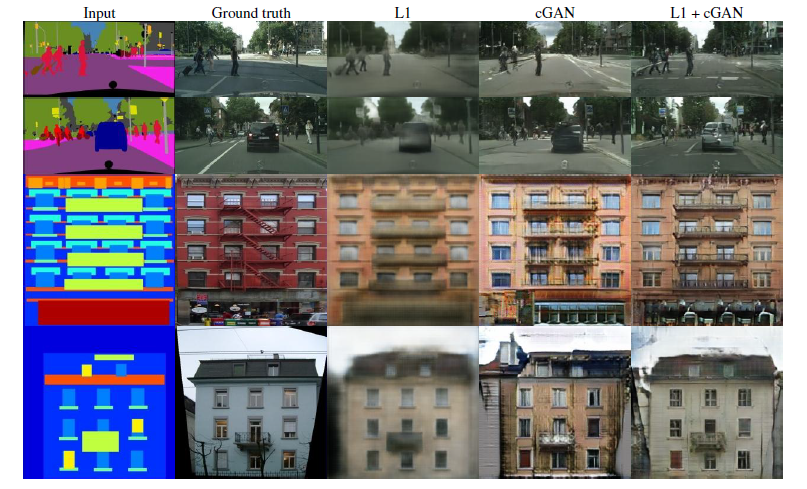

L1 loss or L2 loss produce the blurry results on image generation problems.
For D:
1. both L1 and L2 produce blurry results on image generation problems.
2. L1 and L2 fail to encourage high frequency crispness(锐度),nonetheless(仍然) accurately capture the low frequencies.
3.in order to model high-frequencies , we pay attention to the structure in local image patches.
4.This discriminator tries to classify if each patch in an N*N image is real or fake. We run this discriminator convolutationally across the image, averaging all responses to provide the ultimate output of D.(这个鉴别器试图分类一个N*N图像中的每个补丁是真还是假。我们用这个判别器对图像进行卷积,对所有响应进行平均,得到D的最终输出).
5. N can be much smaller than full size of image and still produce high quality results. smaller pathGAN have mang advantages.
6. D effectively models the image as Markov random field, PatchGAN cn be understand as a form of texture/ style loss!
For Optimization.
1. slows down D relative to G.(此外,在优化D时,我们将目标除以2,这减慢了D相对于G的学习速度)
2.当批大小设置为1时,这种批处理规范化方法被称为实例规范化,并被证明在图像生成任务中是有效的,
batchsize is setted into 1 to 10
3. Instance normalization(IN) and batch normalization(BN), the strategy of IN is adopted in this paper because IN has been demonstrated to be effective at image generation task.
BN 是一个batch 里面的所有图片的均值和标准差,IN 是对一张图片求均值和标准差,shuffle的存在让batch 不稳定, 本来就相当于引入了noise, in the task of image generation, IN outperforms compared with BN, 因为这类生成式任务自己的风格较为独立不应该与batch中的其他样本产生较大的联系,相反在图像和视频的task of classification, BN outperforms IN .
For Experiments
1. removing conditioning for D have very poor performance because the loss does not penalize mismatch between the input and output; it only cares
that the output look realistic.
2. L1 + CGANs create realistic rendersings(渲染), L1 penalize the distance between ground truth outputs, which correctly match the input and synthesized outputs.
3.An advantage of the PatchGAN is that a fixed-size patch discriminator can be applied to arbitrarily large images.
4.
(Pixel2PixelGANs)Image-to-Image translation with conditional adversarial networks的更多相关文章
- image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks文献笔记
Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks (基于条件gan的图像转图像) 作者:Phillip Isola, J ...
- 《Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks》论文笔记
出处 CVPR2017 Motivation 尝试用条件GAN网络来做image translation,让网络自己学习图片到图片的映射函数,而不需要人工定制特征. Introduction 作者从不 ...
- 《Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks》论文笔记
Code Address:https://github.com/junyanz/CycleGAN. Abstract 引出Image Translating的概念(greyscale to color ...
- Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks 阅读笔记
Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks (使用循环一致的对抗网络的非配对图像-图 ...
- Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks(使用循环一致的敌对网络进行不成对的图像到图像转换)
作者:朱俊彦,朱俊彦博士是计算机图形学领域现代机器学习应用的开拓者.他的论文可以说是第一篇用深度神经网络系统地解决自然图像合成问题的论文.因此,他的研究对这个领域产生了重大影响.他的一些科研成果,尤其 ...
- CycleGAN --- Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks
文章地址:http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ICCV_2017/papers/Zhu_Unpaired_Image-To-Image_Translation_I ...
- 语音合成论文翻译:2019_MelGAN: Generative Adversarial Networks for Conditional Waveform Synthesis
论文地址:MelGAN:条件波形合成的生成对抗网络 代码地址:https://github.com/descriptinc/melgan-neurips 音频实例:https://melgan-neu ...
- 生成对抗网络(Generative Adversarial Networks,GAN)初探
1. 从纳什均衡(Nash equilibrium)说起 我们先来看看纳什均衡的经济学定义: 所谓纳什均衡,指的是参与人的这样一种策略组合,在该策略组合上,任何参与人单独改变策略都不会得到好处.换句话 ...
- StarGAN: Unified Generative Adversarial Networks for Multi-Domain Image-to-Image Translation - 1 - 多个域间的图像翻译论文学习
Abstract 最近在两个领域上的图像翻译研究取得了显著的成果.但是在处理多于两个领域的问题上,现存的方法在尺度和鲁棒性上还是有所欠缺,因为需要为每个图像域对单独训练不同的模型.为了解决该问题,我们 ...
随机推荐
- TensorFlow之张量
张量的概念 TensorFlow中的Tensor就是张量,张量是数学对象,是对标量.向量.矩阵的泛化.我们可以直接理解成张量就是列表,就是多维数组. 张量的维数用阶来表示: 0阶张量 标量 单个值 例 ...
- 虚拟机系列 | JVM类加载机制
本文源码:GitHub·点这里 || GitEE·点这里 一.类加载简介 类的加载机制是指把编译后的.class类文件的二进制数据读取到内存中,并为之创建一个java.lang.Class对象,用来封 ...
- windows服务器添加磁盘后,提示The disk is offline because of policy set by an administrator的解决办法
操作系统:Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise 事件:存储在虚拟机上添加三块磁盘,笔者准备扩展到E盘(动态分区) 问题:存储团队添加磁盘后,OS的磁盘管理界面,看到提示, ...
- 记一次select2赋值动态数组的坑
var roles = $td.eq(3).text().split(","); var arr = []; //循环去除每个值前后的空格,否则下拉框赋值回显出错for(var i ...
- 登陆页跳出iframe
1 if(top.location.href != location.href){ 2 top.location.href = location.href; 3 }
- 一起构建Python生长土壤
环境 环境安装 1. 解释器 Python https://www.python.org/ 2. IDE Pycharm https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/downl ...
- [JZOJ]2109 清兵线 题解
## [JZOJ]2109 清兵线 题解 **FIRST 题目大意** 给你一些正整数,这些正整数为数轴上若干个点代表的数.现求:假设从原点出发,走m以内(包括m)的距离最多能够访问多少个点,输出m- ...
- const放在函数前后的区别
转载:const放在函数前后的区别 一.const修饰指针 int b = 500; 1.const int * a = & b; 2.int const * a = & b; 3.i ...
- RHSA-2017:1931-中危: bash 安全和BUG修复更新(代码执行)
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release CentOS Linux release 7.2.1511 (Core) 修复命令: 使用root账号登陆She ...
- vue的二级联动,数据是从php获取到的
1.首先,一级要有change改变事件的关键字,v-on:change="selectarr($event)" 这是created(){}函数里面的自动调用一级分类的数据 html ...
