cf437D The Child and Zoo
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Of course our child likes walking in a zoo. The zoo has n areas, that are numbered from 1 to n.
The i-th area contains ai animals
in it. Also there are m roads in the zoo, and each road connects two distinct areas. Naturally the zoo is connected, so you can reach any area of the zoo
from any other area using the roads.
Our child is very smart. Imagine the child want to go from area p to area q.
Firstly he considers all the simple routes from p to q.
For each route the child writes down the number, that is equal to the minimum number of animals among the route areas. Let's denote the largest of the written numbers as f(p, q).
Finally, the child chooses one of the routes for which he writes down the value f(p, q).
After the child has visited the zoo, he thinks about the question: what is the average value of f(p, q) for all pairs p, q (p ≠ q)?
Can you answer his question?
The first line contains two integers n and m (2 ≤ n ≤ 105; 0 ≤ m ≤ 105).
The second line contains n integers: a1, a2, ..., an (0 ≤ ai ≤ 105).
Then follow m lines, each line contains two integers xi and yi (1 ≤ xi, yi ≤ n; xi ≠ yi),
denoting the road between areas xi and yi.
All roads are bidirectional, each pair of areas is connected by at most one road.
Output a real number — the value of 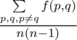 .
.
The answer will be considered correct if its relative or absolute error doesn't exceed 10 - 4.
4 3
10 20 30 40
1 3
2 3
4 3
16.666667
3 3
10 20 30
1 2
2 3
3 1
13.333333
7 8
40 20 10 30 20 50 40
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
1 4
5 7
18.571429
Consider the first sample. There are 12 possible situations:
- p = 1, q = 3, f(p, q) = 10.
- p = 2, q = 3, f(p, q) = 20.
- p = 4, q = 3, f(p, q) = 30.
- p = 1, q = 2, f(p, q) = 10.
- p = 2, q = 4, f(p, q) = 20.
- p = 4, q = 1, f(p, q) = 10.
Another 6 cases are symmetrical to the above. The average is 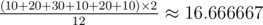 .
.
Consider the second sample. There are 6 possible situations:
- p = 1, q = 2, f(p, q) = 10.
- p = 2, q = 3, f(p, q) = 20.
- p = 1, q = 3, f(p, q) = 10.
Another 3 cases are symmetrical to the above. The average is 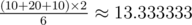 .
.
在鸿巨大的指导下才有了思路……orzlwh
首先把所有的点按权从大到小排序,然后顺序加入图中。对于一个新插入的点,可能有很多连出去的边,如果边的另一端已经在图中,就把它用并查集并起来,可以证明这些联通快之间的p就是新加入的点。然后统计答案。
黄巨大的题解:http://hzwer.com/3332.html
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
struct sth
{
int v,bh;
}p[100010];
int n,m;
int sz,to[200010],pre[200010],last[100010];
int fa[100010],sum[100010];
bool mark[100010];
double ans;
void Ins(int a,int b)
{
sz++;to[sz]=b;pre[sz]=last[a];last[a]=sz;
}
inline bool comp(sth a,sth b)
{
return a.v>b.v;
}
int getfa(int x)
{
if(fa[x]==0) return x;
return fa[x]=getfa(fa[x]);
}
int main()
{
int i,j,x,y,a,b;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&p[i].v);
p[i].bh=i;sum[i]=1;
}
for(i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
Ins(a,b);Ins(b,a);
}
sort(p+1,p+1+n,comp);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
x=p[i].bh;
for(j=last[x];j;j=pre[j])
if(mark[to[j]])
{
y=getfa(to[j]);
a=getfa(x);
if(a!=y)
{
ans+=(long long)sum[y]*sum[a]*p[i].v;
sum[y]+=sum[a];
fa[a]=y;
}
}
mark[x]=1;
}
ans/=n*1.0;
ans/=(n-1)*1.0;
ans*=2.0;
printf("%.12lf\n",ans);
return 0;
}
cf437D The Child and Zoo的更多相关文章
- CF437D(The Child and Zoo)最小生成树
题目: D. The Child and Zoo time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input sta ...
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 1) B. The Child and Zoo 并查集
B. The Child and Zoo Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/438/ ...
- Codeforces 437D The Child and Zoo(贪心+并查集)
题目链接:Codeforces 437D The Child and Zoo 题目大意:小孩子去參观动物园,动物园分非常多个区,每一个区有若干种动物,拥有的动物种数作为该区的权值.然后有m条路,每条路 ...
- Codeforces 437 D. The Child and Zoo 并查集
题目链接:D. The Child and Zoo 题意: 题意比较难懂,是指给出n个点并给出这些点的权值,再给出m条边.每条边的权值为该条路连接的两个区中权值较小的一个.如果两个区没有直接连接,那么 ...
- Codeforces 437D The Child and Zoo - 树分治 - 贪心 - 并查集 - 最大生成树
Of course our child likes walking in a zoo. The zoo has n areas, that are numbered from 1 to n. The ...
- Codeforces D - The Child and Zoo
D - The Child and Zoo 思路: 并查集+贪心 每条边的权值可以用min(a[u],a[v])来表示,然后按边的权值从大到小排序 然后用并查集从大的边开始合并,因为你要合并的这两个联 ...
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 2) D. The Child and Zoo 并查集
D. The Child and Zoo time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standar ...
- Codeforces 437D The Child and Zoo(并查集)
Codeforces 437D The Child and Zoo 题目大意: 有一张连通图,每个点有对应的值.定义从p点走向q点的其中一条路径的花费为途径点的最小值.定义f(p,q)为从点p走向点q ...
- The Child and Zoo 题解
题目描述 Of course our child likes walking in a zoo. The zoo has n areas, that are numbered from 1 to n. ...
随机推荐
- 扒一扒ReentrantLock以及AQS实现原理
提到JAVA加锁,我们通常会想到synchronized关键字或者是Java Concurrent Util(后面简称JCU)包下面的Lock,今天就来扒一扒Lock是如何实现的,比如我们可以先提出一 ...
- poj 3182 The Grove bfs
思路:如果要围绕一圈,必须经过一条竖线上的一点,把竖线左端封住,bfs一次,枚举点,再把竖线右端封住,再bfs回起点. #include <iostream> #include <c ...
- ORA-00314,redolog 损坏,或丢失处理方法
alertsid.log报错信息: Fri Sep 27 15:18:39 2013 Started redo scan Fri Sep 27 15:18:39 2013 Errors in file ...
- Jetty监控线程使用情况的配置
Jetty监控线程使用情况配置 第一步,配置xml文件 jetty-monitor.xml 参数说明: threads: 线程池中的线程 busyThreads: 使用中的线程 idleThreads ...
- 关闭myeclipse中jsp的校验功能
window--->preference--->Myeclipse--->Validation,取消下图红框中的选中状态.
- JAXB--学习2
一.Jaxb处理java对象和xml之间转换常用的annotation有: @XmlType @XmlElement @XmlRootElement @XmlAttribute @XmlAccesso ...
- [A Top-Down Approach][第一章 计算机网络和因特网]
[A Top-Down Approach][第一章 计算机网络和因特网] 标签(空格分隔): 计算机网络 介绍基本术语和概念 查看构成网络的基本硬件和软件组件. 从网络的边缘开始,考察在网络中运行的端 ...
- Beacon浅析
作者:hongbosun 一.Beacon简介 Beacon是基于BLE技术实现的物理设备.BLE(全称Bluetooth Low Energy)是蓝牙4.0技术规范的一部分.它起源于Nokia的Wi ...
- 查看 SELinux状态及关闭SELinux
查看SELinux状态: 1./usr/sbin/sestatus -v ##如果SELinux status参数为enabled即为开启状态 SELinux status: ...
- 打开较大存储量的.sql文件时,出现SQL Server 阻止了对组件 'xp_cmdshell' 的 过程'sys.xp_cmdshell' 的访问
1. “消息 15281,级别 16,状态 1,过程 xp_cmdshell,第 1 行SQL Server 阻止了对组件 'xp_cmdshell' 的 过程'sys.xp_cmdshell' 的访 ...
