android五种布局模式
Android布局是应用界面开发的重要一环,在Android中,共有五种布局方式,分别是:LinearLayout (线性布局),FrameLayout(框架布
局),AbsoluteLayout(绝对布局),RelativeLayout(相对布局),TableLayout(表格布局)。
在windows下有预览功能,可以在xml中查看布局的样式,在linux中无。
一、LinearLayout
线性布局,这个东西,从外框上可以理解为一个div,他首先是一个一个从上往下罗列在屏幕上。每一个LinearLayout里面又可分为垂直布局
(android:orientation="vertical")和水平布局(android:orientation="horizontal"
)。当垂直布局时,每一行就只有一个元素,多个元素依次垂直往下;水平布局时,只有一行,每一个元素依次向右排列。
linearLayout中有一个重要的属性 android:layout_weight="1",这个weight在垂直布局时,代表行距;水平的时候代表列宽;weight值越大就越大。
线形布局中预览和真机中完全一样。
TextView占一定的空间,没有赋值也有一定的宽高,要特别注意。
二、FrameLayout
FrameLayout是最简单的一个布局对象。它被定制为你屏幕上的一个空白备用区域,之后你可以在其中填充一个单一对象 —
比如,一张你要发布的图片。所有的子元素将会固定在屏幕的左上角;你不能为FrameLayout中的一个子元素指定一个位置。后一个子元素将会直接在前
一个子元素之上进行覆盖填充,把它们部份或全部挡住(除非后一个子元素是透明的)。
三、AbsoluteLayout
AbsoluteLayout 这个布局方式很简单,主要属性就两个 layout_x 和 layout_y 分别定义 这个组件的绝对位置。 即,以屏幕左上角为(0,0)的坐标轴的x,y值,当向下或向右移动时,坐标值将变大。AbsoluteLayout 没有页边框,允许元素之间互相重叠(尽管不推荐)。我们通常不推荐使用 AbsoluteLayout ,除非你有正当理由要使用它,因为它使界面代码太过刚性,以至于在不同的设备上可能不能很好地工作。
四、RelativeLayout
相对布局可以理解为某一个元素为参照物,来定位的布局方式。
android:layout_方向 = id 表示 在这个id对应的控件的方向上(上|下)
android:layout_align方向 = id 表示和这个控件的(上下左右)对齐
android: layout_to方向Of = id 表示在这个控件的 左或者右
eg:
android:layout_below="@id/la1"/>
将当前控件放置于id为la1 的控件下方。
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
使当前控件的右端和父控件的右端对齐。这里属性值只能为true或false,默认false。
android:layout_marginLeft="10dip"
使当前控件左边空出相应的空间。
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/true"
使当前控件置于id为true的控件的左边。
android:layout_alignTop="@id/ok"
使当前控件与id为ok的控件上端对齐。
五、TableLayout
表格布局类似Html里面的Table。每一个TableLayout里面有表格行TableRow,TableRow里面可以具体定义每一个元素。每
个TableRow 都会定义一个 row (事实上,你可以定义其它的子对象,这在下面会解释到)。TableLayout 容器不会显示row
、cloumns 或cell 的边框线。每个 row 拥有0个或多个的cell ;每个cell 拥有一个View
对象。表格由列和行组成许多的单元格。表格允许单元格为空。单元格不能跨列,这与HTML 中的不一样。
TabRow只论行,不论列(列自定义)。
每一个布局都有自己适合的方式,另外,这五个布局元素可以相互嵌套应用,做出美观的界面。
例子:
1 线性布局(LinearLayout)

描述:最简单布局方式,依次向下进行排列。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<Button android:text="Up"
android:id="@+id/Button03"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"></Button>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<Button android:text="left"
android:id="@+id/Button01"
android:width="120px"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"></Button>
<Button
android:text="right"
android:id="@+id/Button02"
android:width="120px"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"></Button>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
2、 表格布局(TableLayout)
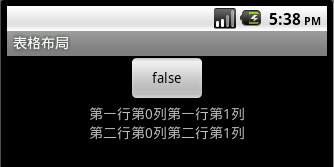
描述:类似于HTML table ,在其中间添加View 或是<TableRow></TableRow>控件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/TableLayout01"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TableRow android:gravity="center">
<Button
android:text="@+id/Button01"
android:id="@+id/Button01"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
</Button>
</TableRow>
<TableRow android:gravity="center">
<TextView android:text="第一行第0列"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"></TextView>
<TextView android:text="第一行第1列"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"></TextView>
</TableRow>
<TableRow android:gravity="center">
<TextView android:text="第二行第0列"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"></TextView>
<TextView android:text="第二行第1列"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"></TextView>
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
3、 单帧布局(FrameLayout)

描述:类似于HTML层叠
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/ImageView01"
android:src="@drawable/circle_blue"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
</ImageView>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/ImageView02"
android:src="@drawable/circle_green"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
</ImageView>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/ImageView03"
android:src="@drawable/circle_red"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
</ImageView>
</FrameLayout>
4、 相对布局(RelativeLayout)

描述:取决于对参照控件进行布局,父控件和子控件均可
常用属性:android:layout_centerInParent=”true/false”
android:layout_above, android:layout_below
android:layout_alignleft, android:layout_alignright.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnmiddle"
android:text="MiddleButton"
android:layout_width="200px"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true">
</Button>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnup"
android:text="UpButton"
android:layout_width="100px"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_above="@id/btnmiddle"
android:layout_alignLeft="@id/btnmiddle">
</Button>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btndown"
android:text="downButton"
android:layout_width="100px"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/btnmiddle"
android:layout_alignRight="@id/btnmiddle">
</Button>
</RelativeLayout>
5、 坐标布局(AbsoluteLayout)
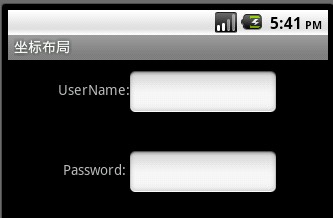
描述:对其控件进行直接定位,增加灵活性。
常用属性:android:layout_x,android:layout_y.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<AbsoluteLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="UserName:"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/tvName"
android:layout_y="20dip"
android:layout_x="50dip">
</TextView>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="Password:"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/tvPassword"
android:layout_y="100dip"
android:layout_x="55dip">
</TextView>
<EditText
android:layout_width="150px"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/tvPassword"
android:layout_y="10dip"
android:layout_x="120dip">
</EditText>
<EditText
android:layout_width="150px"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/tvPassword"
android:layout_y="90dip"
android:layout_x="120dip">
</EditText>
</AbsoluteLayout>
MyLayout.java
package com.jay.Layout; import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button; public class MyLayout extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
private Button btnLinearlayout; private Button btnTablayout; private Button btnRelativelayout; private Button btnFramelayout; private Button btnAbsolutelayout; OnClickListener listener; @Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
CreateControl(); listener = new OnClickListener() { @Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.btnlinearlayout:
setTitle("线性布局");
setContentView(R.layout.linearlayout);
break;
case R.id.btntableayout:
setTitle("表格布局");
setContentView(R.layout.tablelayout);
break;
case R.id.btnrelativelayout:
setTitle("相对布局");
setContentView(R.layout.relativelayout);
break;
case R.id.btnfreamelayout:
setTitle("单帧布局");
setContentView(R.layout.framelayout);
break;
case R.id.btnabsolutelayout:
setTitle("坐标布局");
setContentView(R.layout.absolutelayout);
break;
}
}
};
btnLinearlayout.setOnClickListener(listener);
btnTablayout.setOnClickListener(listener);
btnRelativelayout.setOnClickListener(listener);
btnFramelayout.setOnClickListener(listener);
btnAbsolutelayout.setOnClickListener(listener);
} private void CreateControl() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
btnLinearlayout = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btnlinearlayout);
btnTablayout = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btntableayout);
btnRelativelayout = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btnrelativelayout);
btnFramelayout = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btnfreamelayout);
btnAbsolutelayout = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btnabsolutelayout);
}
}
摘自:http://www.cnblogs.com/chiao/archive/2011/08/24/2152435.html
android五种布局模式的更多相关文章
- 【Android 复习】:Android五种布局的使用方法
---恢复内容开始--- 在Android布局中,有五种常用的布局,下面我们就来学习一下这几种布局的使用方式 1) 线性布局:LinearLayout 2) 帧布局: FrameLayout 3) ...
- 页面的五种布局以及嵌套『Android系列八』
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/dazlly/article/details/7860125 因为学习比较晚,我用的相关版本为SDK4.1.eclipse4.2,而自己看的教材都是低版 ...
- Android五种数据存储方式
android 五种数据存储 :SharePreferences.SQLite.Contert Provider.File.网络存储 Android系统提供了四种存储数据方式.分别为:SharePre ...
- 转:Windows下的PHP开发环境搭建——PHP线程安全与非线程安全、Apache版本选择,及详解五种运行模式。
原文来自于:http://www.ituring.com.cn/article/128439 Windows下的PHP开发环境搭建——PHP线程安全与非线程安全.Apache版本选择,及详解五种运行模 ...
- rabbitmq的五种工作模式
abbitmq的五种工作模式
- PHP5 的五种常用模式
PHP5 的五种常用模式. 工厂模式 最初在设计模式 一书中,许多设计模式都鼓励使用松散耦合.要理解这个概念,让我们最好谈一下许多开发人员从事大型系统的艰苦历程.在更改一个代码片段时,就会发生问题,系 ...
- S-T-E-A-M Science Technology Engineering Art Mathematics 五种思维模式
S-T-E-A-M五个英文字母分别代表 Science 科学,Technology 技术,Engineering 工程,Art 艺术以及 Mathematics 数学.它们并不是简单地整合原来的分科体 ...
- RabbitMQ 五种工作模式
官网介绍:https://www.rabbitmq.com/getstarted.html 五种工作模式的主要特点 简单模式:一个生产者,一个消费者 work模式:一个生产者,多个消费者,每个消费者获 ...
- java单例五种实现模式梳理
java单例五种实现模式 饿汉式(线程安全,调用效率高,但是不能延时加载) 一上来就把单例对象创建出来了,要用的时候直接返回即可,这种可以说是单例模式中最简单的一种实现方式.但是问题也比较明显.单例在 ...
随机推荐
- [置顶] Android系统移植与调试之------->如何修改Android设备状态条上音量加减键在横竖屏的时候的切换与显示
这两天由于一个客户的要求,将MID竖屏时候的状态条上的音量键去掉.所以尝试修改了一下,成功了,分享一下经验. 先看一下修改后的效果图,如下所示 . 横屏的时候:有音量加减键 竖屏的时候:音量加减键被去 ...
- Joseph(约瑟夫环)
Joseph Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Subm ...
- Tcl学习之--语法|变量
[语法|变量] l 脚本.命令和单词 Tcl提供了大约100条命令.Tk提供了另外几十条,脚本包括一条或多条,通过换行符或分号分隔开. set a 12 set b 23 也能够写成一行: set a ...
- Android学习路线(六)为Android应用加入ActionBar
Action bar 是你可以为你的应用的Activity实现的最为重要的设计元素之中的一个.它提供了集中UI特性.而且通过提供和其它的Android应用的一致性体验让你的应用可以非常快被用户熟悉.基 ...
- js中的数组和字符串的一些方法
数组的一些方法: 1.join()和split()方法 <script type="text/javascript">var x;var a=new Array();a ...
- vtp——vlan trunk protcal
server模式——服务器模式,在该模式下可以建立vlan,删除vlan,该模式下的vlan可以下发到其他的交换机 client模式——客户端模式,被动模式.交换机可以接受从server模式下传来的v ...
- telnet测试端口号
telnet Ip 端口号 如:telnet localhost 1433 详见此链接(转) http://www.3lian.com/edu/2012/11-08/43232.html
- win7系统下连接使用mac 蓝牙键盘(Apple Wireless Keyborad)
这几天买了一个apple wireless keyborad 玩玩,主要是给孩子买了一个ipad 搭配上wireless keyborad让她玩app足够了,就当一部电脑用吧. 看起来挺精致的,可以了 ...
- 【转】Eclipse自动补全的设置方法
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/xiadasong007/archive/2009/11/11/4799715.aspx 打开 Eclipse -> Window -> P ...
- firebug如何使用
1.怎么安装firebug: a.打开火狐浏览器--------b.点击火狐浏览器的右上角这个小图标-------c.点击<获取附件组件>,在右上角的搜索框()内,输入firebug,点击 ...
