Python3之时间模块time & datetime & calendar
一. 简介
python 提供很多方式处理日期与时间,转换日期格式是一个常见的功能。
时间元组:很多python函数用一个元组装起来的9组数字处理时间。
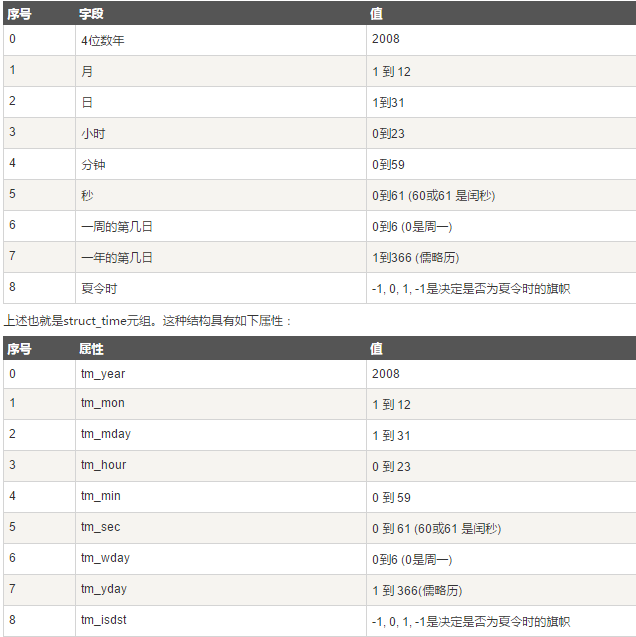
python中时间日期格式化符号:
%y 两位数的年份表示(00-99)
%Y 四位数的年份表示(000-9999)
%m 月份(01-12)
%d 月内中的一天(0-31)
%H 24小时制小时数(0-23)
%I 12小时制小时数(01-12)
%M 分钟数(00=59)
%S 秒(00-59)
%a 本地简化星期名称
%A 本地完整星期名称
%b 本地简化的月份名称
%B 本地完整的月份名称
%c 本地相应的日期表示和时间表示
%j 年内的一天(001-366)
%p 本地A.M.或P.M.的等价符
%U 一年中的星期数(00-53)星期天为星期的开始
%w 星期(0-6),星期天为星期的开始
%W 一年中的星期数(00-53)星期一为星期的开始
%x 本地相应的日期表示
%X 本地相应的时间表示
%Z 当前时区的名称
%% %号本身
二. time模块
时间相关操作,时间有三种表示方式:
- 时间戳 1970年1月1日之后的秒,即:time.time()
- 格式化的字符串 2014-11-11 11:11, 即:time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
- 结构化时间 元组包含了:年、日、星期等... time.struct_time 即:time.localtime()
time.time()
返回当前时间的时间戳(1970纪元后经过的浮点秒数)。
时间戳单位最适于做日期运算。但是1970年之前的日期就无法以此表示了。太遥远的日期也不行,UNIX和Windows只支持到2038年。
>>> import time
>>> print(time.time())
1459999336.1963577
time.mktime(tupletime)
接受时间元组并返回时间辍(1970纪元后经过的浮点秒数)。
Python time.mktime() 函数执行与gmtime(), localtime()相反的操作,它接收struct_time对象作为参数,返回用秒数来表示时间的浮点数。
如果输入的值不是一个合法的时间,将触发 OverflowError 或 ValueError。
#!/usr/bin/python3
import time t = (2016, 2, 17, 17, 3, 38, 1, 48, 0)
secs = time.mktime( t )
print ("time.mktime(t) : %f" % secs)
print ("asctime(localtime(secs)): %s" % time.asctime(time.localtime(secs))) 以上实例输出结果为:
time.mktime(t) : 1455699818.000000
asctime(localtime(secs)): Wed Feb 17 17:03:38 2016
time.gmtime([secs])
接收时间辍(1970纪元后经过的浮点秒数)并返回格林威治天文时间下的时间元组t。注:t.tm_isdst始终为0
>>> import time
>>> print ("gmtime :", time.gmtime(1455508609.34375))
gmtime : time.struct_time(tm_year=2016, tm_mon=2, tm_mday=15, tm_hour=3, tm_min=56, tm_sec=49, tm_wday=0, tm_yday=46, tm_isdst=0)
time.localtime([secs])
接收时间辍(1970纪元后经过的浮点秒数)并返回当地时间下的时间元组t(t.tm_isdst可取0或1,取决于当地当时是不是夏令时)。
>>> import time
>>> print ("localtime(): ", time.localtime(1455508609.34375))
localtime(): time.struct_time(tm_year=2016, tm_mon=2, tm_mday=15, tm_hour=11, tm_min=56, tm_sec=49, tm_wday=0, tm_yday=46, tm_isdst=0)
time.mktime(tupletime)
接受时间元组并返回时间辍(1970纪元后经过的浮点秒数)。
Python time mktime() 函数执行与gmtime(), localtime()相反的操作,它接收struct_time对象作为参数,返回用秒数来表示时间的浮点数。
如果输入的值不是一个合法的时间,将触发 OverflowError 或 ValueError。
#!/usr/bin/python3
import time t = (2016, 2, 17, 17, 3, 38, 1, 48, 0)
secs = time.mktime( t )
print ("time.mktime(t) : %f" % secs)
print ("asctime(localtime(secs)): %s" % time.asctime(time.localtime(secs))) 以上实例输出结果为:
time.mktime(t) : 1455699818.000000
asctime(localtime(secs)): Wed Feb 17 17:03:38 2016
time.strftime(fmt[,tupletime])
接收以时间元组,并返回以可读字符串表示的当地时间,格式由fmt决定。 >>> import time
>>> print (time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime()))
2016-04-07 11:18:05
time.strptime(str,fmt='%a %b %d %H:%M:%S %Y')
根据fmt的格式把一个时间字符串解析为时间元组。
>>> import time
>>> struct_time = time.strptime("30 Nov 00", "%d %b %y")
>>> print ("返回元组: ", struct_time)
返回元组: time.struct_time(tm_year=2000, tm_mon=11, tm_mday=30, tm_hour=0, tm_min=0, tm_sec=0, tm_wday=3, tm_yday=335, tm_isdst=-1)
time.altzone
返回格林威治西部的夏令时地区的偏移秒数。如果该地区在格林威治东部会返回负值(如西欧,包括英国)。对夏令时启用地区才能使用。
>>> import time
>>> print ("time.altzone %d " % time.altzone)
time.altzone -28800
time.asctime([tupletime])
接受时间元组并返回一个可读的形式为"Tue Dec 11 18:07:14 2008"(2008年12月11日 周二18时07分14秒)的24个字符的字符串。
>>> import time
>>> t = time.localtime()
>>> print ("time.asctime(t): %s " % time.asctime(t))
time.asctime(t): Thu Apr 7 10:36:20 2016
time.clock()
用以浮点数计算的秒数返回当前的CPU时间。用来衡量不同程序的耗时,比time.time()更有用。
#!/usr/bin/python3
import time def procedure():
time.sleep(2.5) # time.clock
t0 = time.clock()
procedure()
print (time.clock() - t0) # time.time
t0 = time.time()
procedure()
print (time.time() - t0)
以上实例输出结果为:
5.000000000000143e-05
2.5020556449890137
time.ctime([secs])
作用相当于asctime(localtime(secs)),未给参数相当于asctime()
>>> import time
>>> print ("time.ctime() : %s" % time.ctime())
time.ctime() : Thu Apr 7 10:51:58 2016
time.sleep(secs)
推迟调用线程的运行,secs指秒数。
#!/usr/bin/python3
import time print ("Start : %s" % time.ctime())
time.sleep( 5 )
print ("End : %s" % time.ctime())
time.tzset()
根据环境变量TZ重新初始化时间相关设置。
标准TZ环境变量格式:
std offset [dst [offset [,start[/time], end[/time]]]] 参数:
std 和 dst:三个或者多个时间的缩写字母。传递给 time.tzname.
offset: 距UTC的偏移,格式: [+|-]hh[:mm[:ss]] {h=0-23, m/s=0-59}。
start[/time], end[/time]: DST 开始生效时的日期。格式为 m.w.d — 代表日期的月份、周数和日期。w=1 指月份中的第一周,而 w=5 指月份的最后一周。'start' 和 'end' 可以是以下格式之一:
Jn: 儒略日 n (1 <= n <= 365)。闰年日(2月29)不计算在内。
n: 儒略日 (0 <= n <= 365)。 闰年日(2月29)计算在内
Mm.n.d: 日期的月份、周数和日期。w=1 指月份中的第一周,而 w=5 指月份的最后一周。
time:(可选)DST 开始生效时的时间(24 小时制)。默认值为 02:00(指定时区的本地时间)。 #!/usr/bin/python3
import time
import os os.environ['TZ'] = 'EST+05EDT,M4.1.0,M10.5.0'
time.tzset()
print (time.strftime('%X %x %Z')) os.environ['TZ'] = 'AEST-10AEDT-11,M10.5.0,M3.5.0'
time.tzset()
print (time.strftime('%X %x %Z'))
以上实例输出结果为:
23:25:45 04/06/16 EDT
13:25:45 04/07/16 AEST
time.timezone
属性time.timezone是当地时区(未启动夏令时)距离格林威治的偏移秒数(>0,美洲;<=0大部分欧洲,亚洲,非洲)。
time.tzname
属性time.tzname包含一对根据情况的不同而不同的字符串,分别是带夏令时的本地时区名称,和不带的。
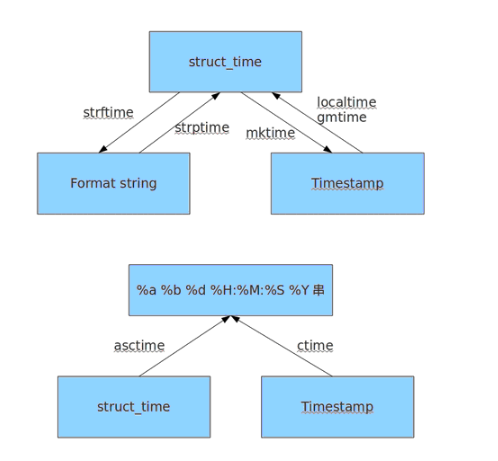
时间装换图:
三. datetime模块
print(datetime.now()) # 获取当前时间 2015-03-29 16:23:20.618564
print(datetime.date.fromtimestamp(time.time()-864400) ) #2016-01-16 将时间戳转成日期格式
current_time = datetime.datetime.now() #
print(current_time) #输出2016-01-26 19:04:30.335935
print(current_time.timetuple()) #返回struct_time格式 #datetime.replace([year[, month[, day[, hour[, minute[, second[, microsecond[, tzinfo]]]]]]]])
print(current_time.replace(2014,9,12)) #输出2014-09-12 19:06:24.074900,返回当前时间,但指定的值将被替换 str_to_date = datetime.datetime.strptime("21/11/06 16:30", "%d/%m/%y %H:%M") #将字符串转换成日期格式
new_date = datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(days=10) #比现在加10天
new_date = datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(days=-10) #比现在减10天
new_date = datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(hours=-10) #比现在减10小时
new_date = datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(seconds=120) #比现在+120s
print(new_date)
datetime转换为timestamp
>>>from datetime import datetime
>>> dt = datetime(2017,3,29,12,20) # 用指定日期创建datetime
>>> dt.timestamp() # 把datetime转换为timestamp
1490761200.0
在Python中的时间戳是一个浮点小数,如果有小数位,小数位表示毫秒数。其他如Java和JavaScript中的时间戳使用整数表示毫秒数,这种情况下只需要将时间戳除以1000就可以得到和Python一样的浮点表示法。
timestamp 转换为 datetime
>>> from datetime import datetime
>>> t = 1490761200.0
>>> print(datetime.fromtimestamp(t)) # 本地时间转换
2017-03-29 12:20:00
>>> print(datetime.utcfromtimestamp(t)) # UTC时间转换
2017-03-29 04:20:00
str转换为datetime
>>> from datetime import datetime
>>> cday = datetime.strptime('2016-01-03 16:15:56', '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
>>> print(cday)
2016-01-03 16:15:56
datetime转换为str
>>> from datetime import datetime
>>> now = datetime.now()
>>> print(now.strftime('%a, %b %d %H:%M'))
Wed, Mar 29 16:18
四. calendar模块
此模块的函数都是日历相关,星期一是每周的第一天,星期天是最后一天。
calendar.calendar(year,w=2,l=1,c=6)
返回一个多行字符串格式的year年年历,3个月一行,间隔距离为c。 每日宽度间隔为w字符。每行长度为21* W+18+2* C。l是每星期行数。
calendar.firstweekday( )
返回当前每周起始日期的设置。默认情况下,首次载入caendar模块时返回0,即星期一。
calendar.isleap(year)
是闰年返回True,否则为false。
calendar.leapdays(y1,y2)
返回在Y1,Y2两年之间的闰年总数。
calendar.month(year,month,w=2,l=1)
返回一个多行字符串格式的year年month月日历,两行标题,一周一行。每日宽度间隔为w字符。每行的长度为7* w+6。l是每星期的行数。
calendar.monthcalendar(year,month)
返回一个整数的单层嵌套列表。每个子列表装载代表一个星期的整数。Year年month月外的日期都设为0;范围内的日子都由该月第几日表示,从1开始。
calendar.monthrange(year,month)
返回两个整数。第一个是该月的星期几的日期码,第二个是该月的日期码。日从0(星期一)到6(星期日);月从1到12。
calendar.prcal(year,w=2,l=1,c=6)
相当于 print calendar.calendar(year,w,l,c).
calendar.prmonth(year,month,w=2,l=1)
相当于 print calendar.calendar(year,w,l,c)。
calendar.setfirstweekday(weekday)
设置每周的起始日期码。0(星期一)到6(星期日)。
calendar.timegm(tupletime)
和time.gmtime相反:接受一个时间元组形式,返回该时刻的时间辍(1970纪元后经过的浮点秒数)。
calendar.weekday(year,month,day)
返回给定日期的日期码。0(星期一)到6(星期日)。月份为 1(一月) 到 12(12月)。
Python3之时间模块time & datetime & calendar的更多相关文章
- python 时间模块(time ,datetime,calendar)
Python中提供了时间相关的内置模块,我们主要用的是:time模块.datetime模块和calendar模块 ⽇期格式化的标准: %y 两位数的年份表示(00-99) %Y 四位数的年份表示(00 ...
- Python3之时间模块详述
Python3之时间模块 time & datetime & calendar 一. 概述 python 提供很多方式处理日期与时间,转换日期格式是一个常见的功能. 时间元组:很多p ...
- Python模块 - time,datetime,calendar
time模块 localtime 当前时间的struct_time形式 >>> time.localtime() time.struct_time(tm_year=2015, tm_ ...
- Day 16 : Python 时间模块[time,]datetime[]及第三方模块的下载与安装
在进行python程序开发时,除了可以使用python内置的标准模块外,还右许多第三方模块使用,可以在python官网找到. 在使用第三方模块时,需要下载并安装此模块,然后就可以使用标准模块一样导入并 ...
- python3中time模块与datetime模块的简单用法
__author__ = "JentZhang" import time # Timestamp 时间戳 print("Timestamp 时间戳:") pri ...
- Python3对时间模块的操作
python中使用time和datetime来进行时间操作 import time import datetime # 获取时间戳 time.time() # 1544601181.549864 # ...
- Python时间模块datetime用法
时间模块datetime是python内置模块,datetime是Python处理日期和时间的标准库. 1,导入时间模块 from datetime import datetime 2,实例 from ...
- python 学习笔记 13 -- 经常使用的时间模块之time
Python 没有包括相应日期和时间的内置类型.只是提供了3个相应的模块,能够採用多种表示管理日期和时间值: * time 模块由底层C库提供与时间相关的函数.它包括一些函数用于获取时钟时间和处 ...
- 【转】Python3 日期时间 相关模块(time(时间) / datatime(日期时间) / calendar(日历))
Python3 日期时间 相关模块(time(时间) / datatime(日期时间) / calendar(日历)) 本文由 Luzhuo 编写,转发请保留该信息. 原文: http://blog. ...
随机推荐
- 开启mysql远程访问
一.登陆mysql以后执行以下命令: GRANT ALL ON *.* TO username@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'password' WITH GRANT OPTION; FLUS ...
- Python将两个数组合并成一个数组,多维数组变成一维数组
1.extend方法 c1 = ["Red","Green","Blue"] c2 = ["Orange"," ...
- Unity抗锯齿的设置
[Unity抗锯齿的设置] "Edit"->"Project Settings"->"Quality",可以质量设置Inspec ...
- Physics Material
[Physics Material] 1. The Physics Material is used to adjust friction and bouncing effects of collid ...
- 【原创】10. MYSQL++ 之 DbDriver
1. 综述 DbDriver只是对于MYSQL C API的一个非常简单的封装,作者原句是This class does as little as possible to adapt between ...
- zlib编程
一.简介 zlib是提供数据压缩用的函式库,使用DEFLATE算法,最初是为libpng函式库所写的,后来普遍为许多软件所使用,今天,zlib是一种事实上的业界标准. 二.基本信息 数据头(hea ...
- 15.select into
select into SELECT INTO 语句从一个表中选取数据,然后把数据插入另一个表中. SELECT INTO 语句常用于创建表的备份复件或者用于对记录进行存档. CREATE TABLE ...
- jquery表单数据反序列化为字典
.前台代码 <%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeBehind="WebForm1 ...
- 7. Smali基础语法总结
最近在学习Android 移动安全逆向方面,逆向首先要看懂代码,Android4.4之前一直使用的是 Dalivk虚拟机,而Smali是用于Dalivk的反汇编程序的实现. Smali 支持注解,调试 ...
- Requests接口测试(五)
使用python+requests编写接口测试用例 好了,有了前几章的的基础,写下来我把前面的基础整合一下,来一个实际的接口测试练习吧. 接口测试流程 1.拿到接口的URL地址 2.查看接口是用什么方 ...
