ML 逻辑回归 Logistic Regression
逻辑回归
Logistic Regression
1 分类 Classification
首先我们来看看使用线性回归来解决分类会出现的问题。下图中,我们加入了一个训练集,产生的新的假设函数使得我们进行分类出现了错误;而且线性回归计算的结果往往会远小于0或者远大于1,这对于0,1分类变得很奇怪。可见线性回归并不适用与分类。下面介绍的逻辑回归的结果总是在[0,1],适用于分类,其实逻辑回归是一种分类算法。
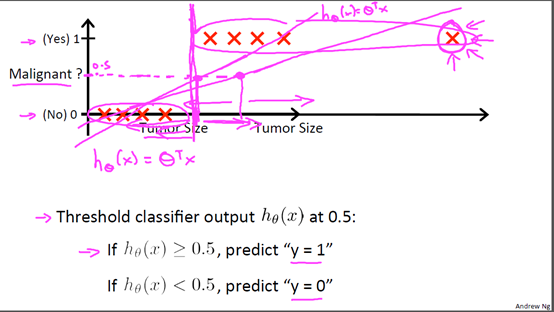

2 假设函数Hypothesis Representation
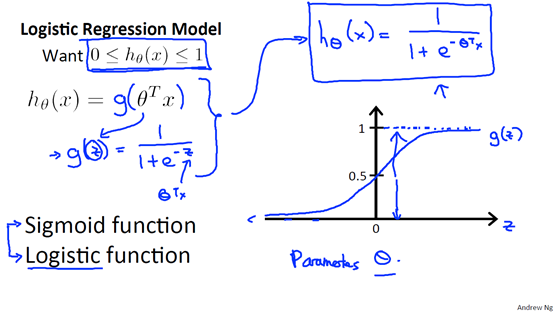
逻辑回归假设函数为:
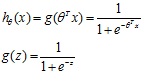
其中 是参数向量,
是参数向量, 特征向量。该函数叫做Logistic function(也叫做Sigmoid function)。函数图像如下,范围(0,1)
特征向量。该函数叫做Logistic function(也叫做Sigmoid function)。函数图像如下,范围(0,1)
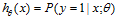
对于分类问题,它可以表示给定特征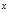 ,参数
,参数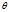 属于类别1的概率,那么属于另一类的概率自然也就是
属于类别1的概率,那么属于另一类的概率自然也就是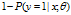 。
。

3 决策边界Decision Boundary
根据逻辑函数的特性可以看出,当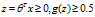 ,当
,当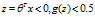

我们把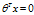 就称为决策边界(Decision Boundary)。
就称为决策边界(Decision Boundary)。
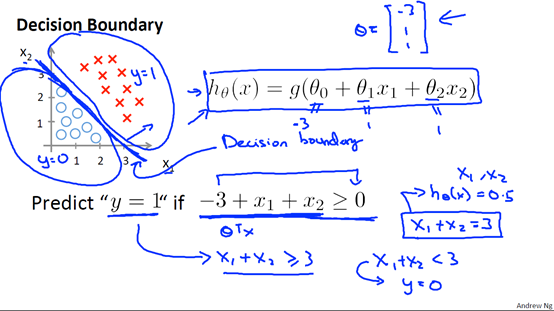
我们可以通过多项式组合来制定更加复杂的决策边界。
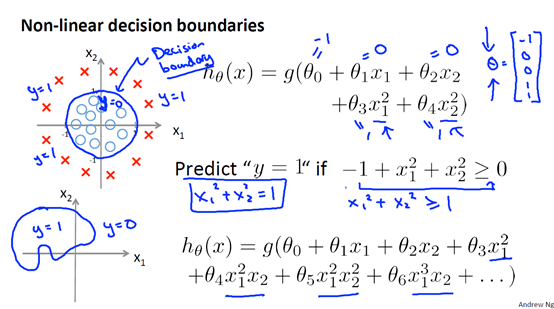
4 代价函数 Cost Function
代价函数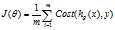 ,在线性回归中,我们的
,在线性回归中,我们的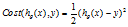 ,如果在逻辑回归中也使用这个函数,那么代价函数会是一个非凸函数,无法使用梯度下降去求解参数,所以我们要寻找一些函数使得代价函数为凸函数。
,如果在逻辑回归中也使用这个函数,那么代价函数会是一个非凸函数,无法使用梯度下降去求解参数,所以我们要寻找一些函数使得代价函数为凸函数。
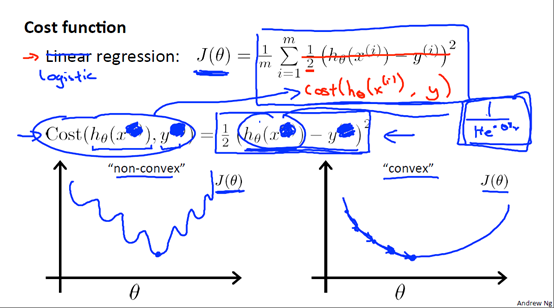
我们来看一下这个代价函数:

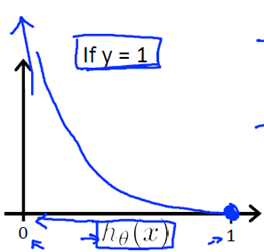
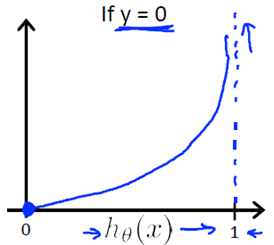
我们可以将它合并为一个公式:
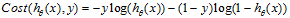
5 梯度下降 Gradient Desecent
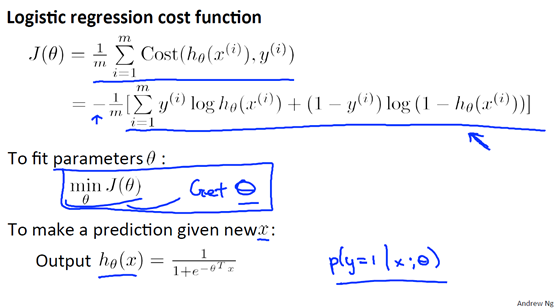
这里我们把代价函数写成这种形式是由最大似然估计得到了,当然也还有其他的形式。
梯度下降算法:
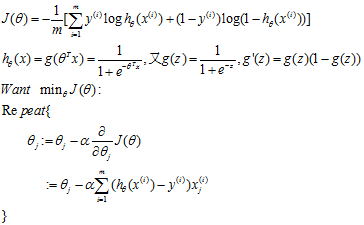
可以看到这里推导出来的公式看起来和线性回归梯度下降中推导出来的公式是一样的,但是要注意 已经是sigmod函数而不是线性公式了,所以他们是两码事。
已经是sigmod函数而不是线性公式了,所以他们是两码事。
6 多分类 Multi-class classification: one-vs-all
我们可以降逻辑回归用于多分类问题,假设有K类,我们可以训练出K个分类器,每个分类器,将其中一种类别作为正类,其余的都是负类来训练,然后再预测时,类别属于概率最大的那个类。
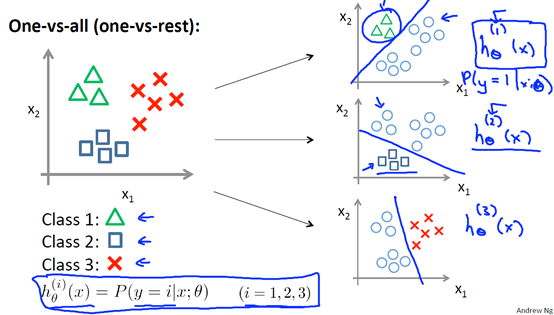
7 正则化regularization
7.1 过拟合 overfitting
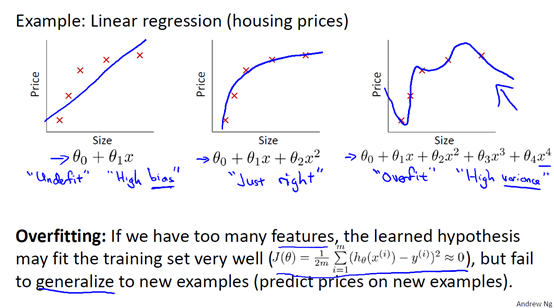

7.2 代价函数cost function
在代价函数中加入正则项,注意,这里对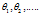 计算,而不是从开始。其中
计算,而不是从开始。其中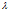 是正则项参数,如果
是正则项参数,如果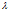 太大,那么
太大,那么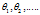 会趋向于0,使得
会趋向于0,使得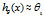 ,导致欠拟合。
,导致欠拟合。

7.3 正则化线性回归 Regularized linear regression
代价函数:
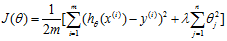
Gradeint descent
Repeat{
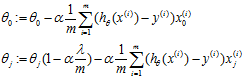
}
这里 是一个比1小一点点的数。
是一个比1小一点点的数。
在线性回归中,我们除了梯度下降,还有正规方程的方法,正规方法加入正则项后:
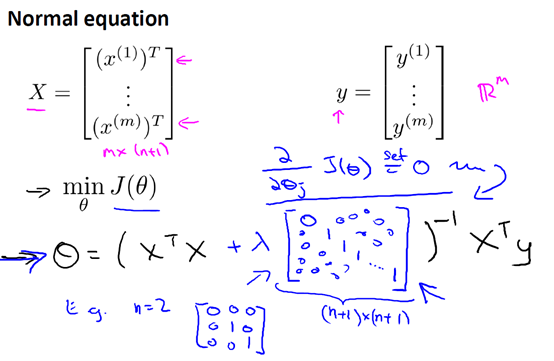
7.4 正则化逻辑回归Regularized logistic regression
代价函数:
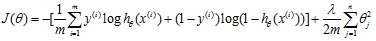
Gradient descent
Repeat{
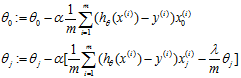
}
实验代码
正则化逻辑回归
function [J, grad] = costFunctionReg(theta, X, y, lambda)
%COSTFUNCTIONREG Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression with regularization
% J = COSTFUNCTIONREG(theta, X, y, lambda) computes the cost of using
% theta as the parameter for regularized logistic regression and the
% gradient of the cost w.r.t. to the parameters. % Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples % You need to return the following variables correctly
J = ;
grad = zeros(size(theta)); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
hx=sigmoid(X*theta);
Jnorm=(-/m)*(y'*log(hx)+(1-y)'*log(-hx));
theta0=theta(); %注意theta0不用正则化
theta1=theta(:end);
Jreg=(lambda/(*m))*sum(theta1.^);
J=Jnorm+Jreg; grad0=(hx-y)'*X(:,1)./m;
grad1=((hx-y)'*X(:,2:end)./m)'+(lambda/m).*theta1;
grad=[grad0;grad1];
% ============================================================= end
sigmoid函数
function g = sigmoid(z)
%SIGMOID Compute sigmoid functoon
% J = SIGMOID(z) computes the sigmoid of z. % You need to return the following variables correctly
g = zeros(size(z)); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the sigmoid of each value of z (z can be a matrix,
% vector or scalar).
g=./(+exp((-).*z));
% =============================================================
end
特征
function out = mapFeature(X1, X2)
% MAPFEATURE Feature mapping function to polynomial features
%
% MAPFEATURE(X1, X2) maps the two input features
% to quadratic features used in the regularization exercise.
%
% Returns a new feature array with more features, comprising of
% X1, X2, X1.^, X2.^, X1*X2, X1*X2.^, etc..
%
% Inputs X1, X2 must be the same size
% degree = ;%6次函数
out = ones(size(X1(:,)));
for i = :degree
for j = :i
out(:, end+) = (X1.^(i-j)).*(X2.^j);
end
end end
主函数
%% Machine Learning Online Class - Exercise : Logistic Regression
%
% Instructions
% ------------
%
% This file contains code that helps you get started on the second part
% of the exercise which covers regularization with logistic regression.
%
% You will need to complete the following functions in this exericse:
%
% sigmoid.m
% costFunction.m
% predict.m
% costFunctionReg.m
%
% For this exercise, you will not need to change any code in this file,
% or any other files other than those mentioned above.
% %% Initialization
clear ; close all; clc %% Load Data
% The first two columns contains the X values and the third column
% contains the label (y). data = load('ex2data2.txt');
X = data(:, [, ]); y = data(:, ); plotData(X, y); % Put some labels
hold on; % Labels and Legend
xlabel('Microchip Test 1')
ylabel('Microchip Test 2') % Specified in plot order
legend('y = 1', 'y = 0')
hold off; %% =========== Part : Regularized Logistic Regression ============
% In this part, you are given a dataset with data points that are not
% linearly separable. However, you would still like to use logistic
% regression to classify the data points.
%
% To do so, you introduce more features to use -- in particular, you add
% polynomial features to our data matrix (similar to polynomial
% regression).
% % Add Polynomial Features % Note that mapFeature also adds a column of ones for us, so the intercept
% term is handled
X = mapFeature(X(:,), X(:,)); % Initialize fitting parameters
initial_theta = zeros(size(X, ), ); % Set regularization parameter lambda to
lambda = ; % Compute and display initial cost and gradient for regularized logistic
% regression
[cost, grad] = costFunctionReg(initial_theta, X, y, lambda); fprintf('Cost at initial theta (zeros): %f\n', cost); fprintf('\nProgram paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause; %% ============= Part : Regularization and Accuracies =============
% Optional Exercise:
% In this part, you will get to try different values of lambda and
% see how regularization affects the decision coundart
%
% Try the following values of lambda (, , , ).
%
% How does the decision boundary change when you vary lambda? How does
% the training set accuracy vary?
% % Initialize fitting parameters
initial_theta = zeros(size(X, ), ); % Set regularization parameter lambda to (you should vary this)
lambda = ; % Set Options
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', ); % Optimize
[theta, J, exit_flag] = ...
fminunc(@(t)(costFunctionReg(t, X, y, lambda)), initial_theta, options); % Plot Boundary
plotDecisionBoundary(theta, X, y);
hold on;
title(sprintf('lambda = %g', lambda)) % Labels and Legend
xlabel('Microchip Test 1')
ylabel('Microchip Test 2') legend('y = 1', 'y = 0', 'Decision boundary')
hold off; % Compute accuracy on our training set
p = predict(theta, X); fprintf('Train Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(p == y)) * );
实验中参数lamda的大小也十分重要,不同的lamda可能会过拟合或者欠拟合。
ML 逻辑回归 Logistic Regression的更多相关文章
- Coursera公开课笔记: 斯坦福大学机器学习第六课“逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)” 清晰讲解logistic-good!!!!!!
原文:http://52opencourse.com/125/coursera%E5%85%AC%E5%BC%80%E8%AF%BE%E7%AC%94%E8%AE%B0-%E6%96%AF%E5%9D ...
- 机器学习总结之逻辑回归Logistic Regression
机器学习总结之逻辑回归Logistic Regression 逻辑回归logistic regression,虽然名字是回归,但是实际上它是处理分类问题的算法.简单的说回归问题和分类问题如下: 回归问 ...
- 机器学习(四)--------逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)
逻辑回归(Logistic Regression) 线性回归用来预测,逻辑回归用来分类. 线性回归是拟合函数,逻辑回归是预测函数 逻辑回归就是分类. 分类问题用线性方程是不行的 线性方程拟合的是连 ...
- 机器学习入门11 - 逻辑回归 (Logistic Regression)
原文链接:https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/crash-course/logistic-regression/ 逻辑回归会生成一个介于 0 ...
- 机器学习方法(五):逻辑回归Logistic Regression,Softmax Regression
欢迎转载,转载请注明:本文出自Bin的专栏blog.csdn.net/xbinworld. 技术交流QQ群:433250724,欢迎对算法.技术.应用感兴趣的同学加入. 前面介绍过线性回归的基本知识, ...
- 机器学习 (三) 逻辑回归 Logistic Regression
文章内容均来自斯坦福大学的Andrew Ng教授讲解的Machine Learning课程,本文是针对该课程的个人学习笔记,如有疏漏,请以原课程所讲述内容为准.感谢博主Rachel Zhang 的个人 ...
- 逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)详解,公式推导及代码实现
逻辑回归(Logistic Regression) 什么是逻辑回归: 逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)是一种基于概率的模式识别算法,虽然名字中带"回归",但实际上 ...
- 逻辑回归 Logistic Regression
逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)是广义线性回归的一种.逻辑回归是用来做分类任务的常用算法.分类任务的目标是找一个函数,把观测值匹配到相关的类和标签上.比如一个人有没有病,又因为噪声的 ...
- 【机器学习】Octave 实现逻辑回归 Logistic Regression
ex2data1.txt ex2data2.txt 本次算法的背景是,假如你是一个大学的管理者,你需要根据学生之前的成绩(两门科目)来预测该学生是否能进入该大学. 根据题意,我们不难分辨出这是一种二分 ...
随机推荐
- 【BZOJ2794】[Poi2012]Cloakroom 离线+背包
[BZOJ2794][Poi2012]Cloakroom Description 有n件物品,每件物品有三个属性a[i], b[i], c[i] (a[i]<b[i]).再给出q个询问,每个询问 ...
- 《从零开始学Swift》学习笔记(Day 35)——会使用下标吗?
原创文章,欢迎转载.转载请注明:关东升的博客 看下面的示例代码是不是使用过: var studentList: String[] = ["张三","李四",&q ...
- hihoCoder 1549 或运算和
#1549 : 或运算和 时间限制:10000ms 单点时限:1000ms 内存限制:256MB 描述 给定N个数A1...AN (0 <= Ai < 220) 和一个正整数K,我们用An ...
- width: 50%; display:inline-flex;
<style lang="less"> @import "../style/weui.wxss"; @wx-width: 750rpx; @wx ...
- 解决windows server 2003不识别移动硬盘
解决windows server2003不显示移动硬盘的问题: 1.进入命令提示符环境(也就是DOS) 2.进入DISKPART程序 3.输入AUTOMOUNT ENABLE指令 4.输入OK 下次U ...
- CF145E Lucky Queries
CF145E Lucky Queries 英文题面不放了,直接上翻译: 题目描述 给你n个数,每个数是4或者7,给你m个任务完成 switch l r 把[l,r]位置的4换成7,7换成4 count ...
- 0x09 Python连接MySQL数据库
本文介绍Python3连接MySQL的第三方库--PyMySQL的基本使用. PyMySQL介绍 PyMySQL 是在 Python3.x 版本中用于连接 MySQL 服务器的一个库,Python2中 ...
- Python 中星号作用:解包&打散
python中’*’和’**’的使用分两个方面,一个是计算,另一个是参数传递过程中元素的打包和解包. 计算方面 ‘*’和’**’在python中最常见的作用分别是‘相乘’和‘乘幂’,如下: > ...
- OC、C#与JAVA语法特点一些异同(差集&交集)
C#对JAVA: 1.扩展方法 2.部分类 3.动态对象 4.匿名返回类型 5.表达式树 6.Linq 7.没有函数指针,委托,事件的直接提供方式 8.JAVA接口不规定以I开头,这个很烂的思想! J ...
- PHP获取域名、IP地址的方法
本文介绍下,在php中,获取域名以及域名对应的IP地址的方法,有需要的朋友参考下. 在php中可以使用内置函数gethostbyname获取域名对应的IP地址,比如: 1 <?php 2 ech ...
