Spring5源码解析1-从启动容器开始
从启动容器开始
最简单的启动spring的代码如下:
@Configuration
@ComponentScan
public class AppConfig {
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
context.close();
}
}
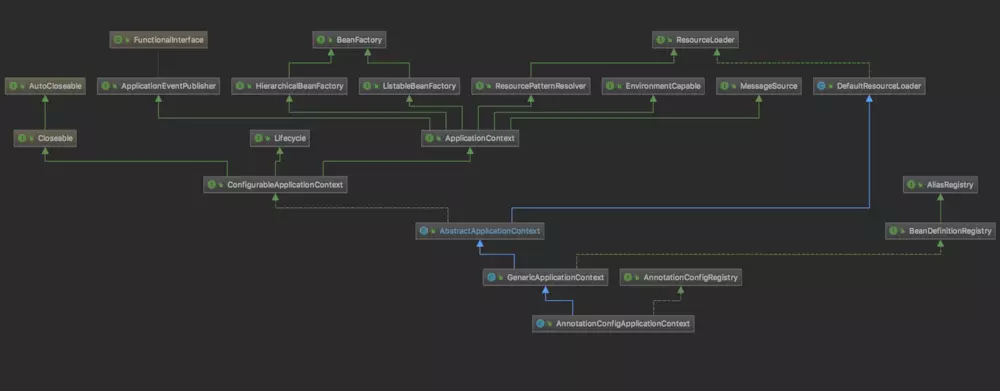
先来看一下AnnotationConfigApplicationContext类的UML图,留个印象。
点开AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);方法查看源码:
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
//调用默认无参构造器,里面有一大堆初始化逻辑
this();
//把传入的Class进行注册,Class既可以有@Configuration注解,也可以没有@Configuration注解
//怎么注册? 委托给了 org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader.register 方法进行注册
// 传入Class 生成 BeanDefinition , 然后通过 注册到 BeanDefinitionRegistry
register(annotatedClasses);
//刷新容器上下文
refresh();
}
该构造器允许我们传入一个或者多个class对象。class对象可以是被@Configuration标注的,也可以是一个普通的Java 类。
有参构造器调用了无参构造器,点开源码:
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
//隐式调用父类构造器,初始化beanFactory,具体实现类为DefaultListableBeanFactory
super(); // 这个代码是笔者添加的,方便定位到super方法
//创建 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader,
//创建时会向传入的 BeanDefinitionRegistry 中 注册 注解配置相关的 processors 的 BeanDefinition
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
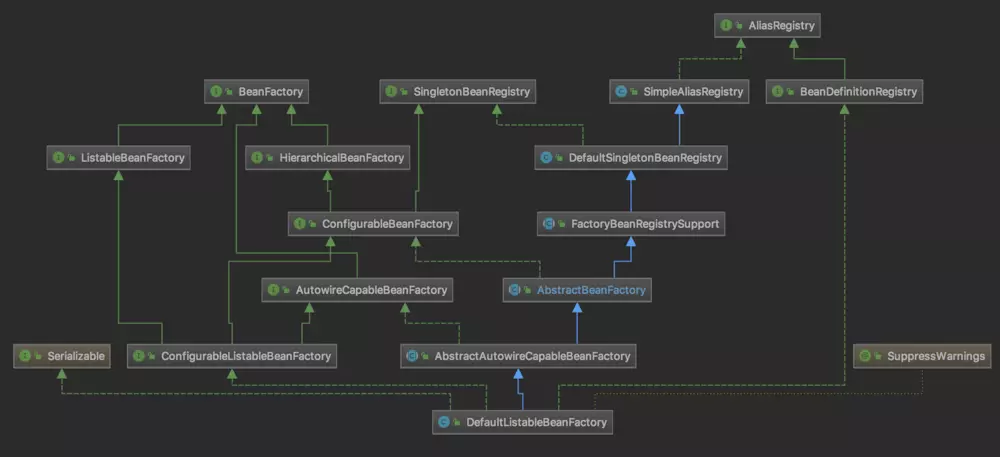
初始化子类时会先初始化父类,会默认调用父类无参构造器。AnnotationConfigApplicationContext继承了GenericApplicationContext,在GenericApplicationContext的无参构造器中,创建了BeanFactory的具体实现类DefaultListableBeanFactory。spring中的BeanFactory就是在这里被实例化的,并且使用DefaultListableBeanFactory做的BeanFactory的默认实现。
public GenericApplicationContext() {
this.beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
}
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的构造器中还创建了两个对象:AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 和 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner。
先说scanner的作用,通过查看源码可以发现,这个scanner只有在手动调用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的一些方法的时候才会被使用(通过后面的源码探究也可以发现,spring并不是使用这个scanner来扫描包获取Bean的)。
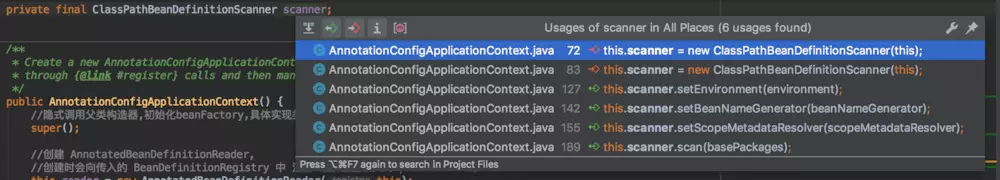
创建AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader对象。spring在创建reader的时候把this当做了参数传给了构造器。也就是说,reader对象里面包含了一个this对象,也就是AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象。AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口。点开this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);源码:
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
this(registry, getOrCreateEnvironment(registry));
}
从传入的BeanDefinitionRegistry对象,也就是AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象中获取Environment(共用同一个Environment),然后又接着调用另一个构造器。点开源码:
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Environment environment) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
this.conditionEvaluator = new ConditionEvaluator(registry, environment, null);
//在 BeanDefinitionRegistry 中注册 注解配置相关的 processors
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
在这个构造器中,执行了一个非常重要的方法AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);,顾名思义,spring通过这个方法注册了解析注解配置相关的处理器。点开源码:
public static void registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(registry, null);
}
//再点开源码
public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry);
if (beanFactory != null) {
if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) {
beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
}
if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) {
beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver());
}
}
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<>(8);
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
//org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor - ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class
//这个类非常的重要,它是一个 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition();
try {
def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME,
AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader()));
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex);
}
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME));
}
return beanDefs;
}
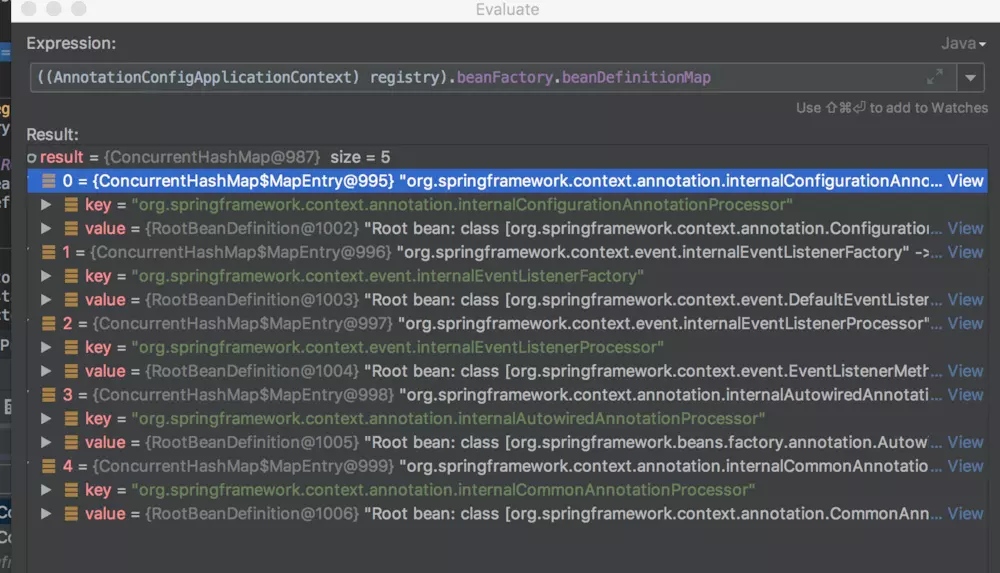
- 该方法从传入的
BeanDefinitionRegistry对象,也就是AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象中获取到DefaultListableBeanFactory对象。 - 为获取的
DefaultListableBeanFactory对象设置属性 - 往
DefaultListableBeanFactory对象中注册BeanDefinition,注册的是一些spring内置的PostProcessor的BeanDefinition(关于BeanDefinition的介绍下期在讲)。注意,此时只是注册BeanDefinition,并没有实例化bean。默认情况下,执行完该方法后,spring容器中所注册的BeanDefinition为:
源码学习笔记:https://github.com/shenjianeng/spring-code-study
Spring5源码解析1-从启动容器开始的更多相关文章
- Spring5源码解析系列一——IoC容器核心类图
基本概念梳理 IoC(Inversion of Control,控制反转)就是把原来代码里需要实现的对象创建.依赖,反转给容器来帮忙实现.我们需要创建一个容器,同时需要一种描述来让容器知道要创建的对象 ...
- Spring5源码解析-Spring框架中的单例和原型bean
Spring5源码解析-Spring框架中的单例和原型bean 最近一直有问我单例和原型bean的一些原理性问题,这里就开一篇来说说的 通过Spring中的依赖注入极大方便了我们的开发.在xml通过& ...
- Spring5源码解析-论Spring DispatcherServlet的生命周期
Spring Web框架架构的主要部分是DispatcherServlet.也就是本文中重点介绍的对象. 在本文的第一部分中,我们将看到基于Spring的DispatcherServlet的主要概念: ...
- Netty源码解析---服务端启动
Netty源码解析---服务端启动 一个简单的服务端代码: public class SimpleServer { public static void main(String[] args) { N ...
- Spring5源码解析_IOC之容器的基本实现
前言: 在分析源码之前,我们简单回顾一下SPring核心功能的简单使用: 容器的基本用法 Bean是Spring最核心的东西,Spring就像是一个大水桶,而Bean就是水桶中的水,水桶脱离了水就没有 ...
- Spring源码解析二:IOC容器初始化过程详解
IOC容器初始化分为三个步骤,分别是: 1.Resource定位,即BeanDefinition的资源定位. 2.BeanDefinition的载入 3.向IOC容器注册BeanDefinition ...
- Spring5源码解析5-ConfigurationClassPostProcessor (上)
接上回,我们讲到了refresh()方法中的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)方法主要在执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor和其子 ...
- Spring源码解析一:IOC容器设计
一.IOC接口设计 IOC容器设计的源码主要在spring-beans.jar.spring-context.jar这两个包中.IOC容器主要接口设计如下: 这里的接口设计有两条主线:BeanFact ...
- Spring源码解析三:IOC容器的依赖注入
一般情况下,依赖注入的过程是发生在用户第一次向容器索要Bean是触发的,而触发依赖注入的地方就是BeanFactory的getBean方法. 这里以DefaultListableBeanFactory ...
随机推荐
- Linux下动态切换EHCI控制器下端口的速率(即切换为12M)
在sys目录下找到对应的控制器 例如:/sys/devices/platform/soc/ehci,直接操作该目录下的companion echo 1 > companion 将port1设 ...
- Gradle如何在任务失败后继续构建
如果我们运行Gradle构建并且其中一项任务失败,则整个构建将立即停止.因此,我们可以快速反馈构建状态.如果我们不想这样做,并且希望Gradle执行所有任务,即使某些任务可能失败了,我们也可以使用命令 ...
- mysql的repeat()函数
用来复制字符串,如下'ab'表示要复制的字符串,2表示复制的份数 mysql> select repeat('ab',2); +----------------+ | repeat('ab',2 ...
- js鼠标滚轮事件上滚下滚判断
onmousewheel <script> var scrollFunc = function (e){ //其实我一开始也不知道用啥 //console.log(e)我们可以打印一下 / ...
- SpringBoot+MyBatisPlus整合时提示:Invalid bound statement(not found):**.dao.UserDao.queryById
场景 在使用SpringBoot+MyBatisPlus搭建后台启动项目时,使用EasyCode自动生成代码. 在访问后台接口时提示: Invilid bound statement (not fou ...
- sed 面试题
#oldboy my qq num is 49000448.$ not 4900000448. my god ,i am not oldbey,but clsn!$ #oldboy my name i ...
- ES6变量的解构赋值(一)数组的解构赋值
let[a,...arr]=[1,2,3,4];//a==>1 arr==>[2,3,4] let [x, y, ...z] = ['a'];//a==>'a' y==>und ...
- [转]UiPath实践经验总结(二)
本文转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/ybyebo/p/10086473.html 1. UI操作容易受到各种意外的干扰,因此应该缩短UI操作阶段的总体时间.而为了缩短 ...
- CamlQuery对SharePointOnline List 发起查询请求
最近的项目中遇到了一个需求,需要向SharePointList 查询Item是否存在,找到了CamlQuery这样一个方法,但是没有找到使用这个接口的频率限制说明文档,于是就有了这篇随笔. 新接触这个 ...
- 003 C/C++ 数据类型_数组
#include "stdio.h" #include "stdlib.h" //数据类型的本质: 固定大小内存块的别名. void main() { int ...
