ACM-ICPC 2018 沈阳赛区(网络赛)
D.Made In Heaven
One day in the jail, F·F invites Jolyne Kujo (JOJO in brief) to play tennis with her. However, Pucci the father somehow knows it and wants to stop her. There are NN spots in the jail and MM roads connecting some of the spots. JOJO finds that Pucci knows the route of the former (K-1)(K−1)-th shortest path. If Pucci spots JOJO in one of theseK−1 routes, Pucci will use his stand Whitesnake and put the disk into JOJO's body, which means JOJO won't be able to make it to the destination. So, JOJO needs to take the KK-th quickest path to get to the destination. What's more, JOJO only has TT units of time, so she needs to hurry.
JOJO starts from spot SS, and the destination is numbered E. It is possible that JOJO's path contains any spot more than one time. Please tell JOJO whether she can make arrive at the destination using no more than TT units of time.
Input
There are at most 50 test cases.
The first line contains two integers N and M(1≤N≤1000,0≤M≤10000). Stations are numbered from 1 to N.
The second line contains four numbers S, E, K and T (1≤K≤10000, 1≤T≤100000000 ).
Then M lines follows, each line containing three numbers U,V and W (1≤U,V≤N,1≤W≤1000) . It shows that there is a directed road from UU-th spot to V-th spot with time W.
It is guaranteed that for any two spots there will be only one directed road from spot A to spot B (1≤A,B≤N,A≠B), but it is possible that both directed road <A,B> and directed road <B,A>exist.
All the test cases are generated randomly.
Output
One line containing a sentence. If it is possible for JOJO to arrive at the destination in time, output "yareyaredawa" (without quote), else output "Whitesnake!" (without quote).
样例输入
2 2
1 2 2 14
1 2 5
2 1 4
样例输出
yareyaredawa
题目来源
题目思路:求个第k短路就好了
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;
const int INF = 0x7FFFFFFF;
const int MAXN = ;
const int MAXM = ; int S, E, K, T; struct Edge {
int u, v, c, next, next1;
Edge() {}
Edge(int u, int v,int c):u(u), v(v), c(c) {}
} edge[MAXM * ]; int first[MAXN], first1[MAXN], sign;
int n, m;
int dis[MAXN];
bool vis[MAXN]; struct Node {
int v, c;
Node() {}
Node(int v, int c):v(v), c(c) {}
bool operator < (const Node& a) const {
return c + dis[v] > a.c + dis[a.v];
}
}; void init() {
memset(first, -, sizeof(first));
memset(first1, -, sizeof(first1));
sign = ;
}
void addEdge(int u, int v, int c) {
edge[sign] = Edge(u, v, c);
edge[sign].next1 = first1[v];
first1[v] = sign;
edge[sign].next = first[u];
first[u] = sign++;
} priority_queue<Node>que; void dijkstra(int s) {
memset(vis, , sizeof(vis));
for(int i = ; i <= n; i++) {
dis[i] = INF;
}
while(!que.empty()) { que.pop(); }
dis[s] = ;
que.push(Node(s, ));
while(!que.empty()) {
Node cur = que.top();
que.pop();
if(!vis[cur.v]) {
vis[cur.v] = ;
dis[cur.v] = cur.c;
for(int i = first1[cur.v]; ~i; i = edge[i].next1) {
if(dis[edge[i].u] > dis[cur.v] + edge[i].c) {
que.push(Node(edge[i].u, edge[i].c + cur.c));
}
}
}
}
} int a_star(int src) {
// priority_queue<Node>que;
while(!que.empty()) { que.pop(); }
que.push(Node(src, ));
while(!que.empty()) {
Node cur = que.top();
que.pop();
if(cur.v == E) {
if(K > ) {
K--;
}
else {
return cur.c;
}
}
for(int i = first[cur.v]; ~i; i = edge[i].next) {
que.push(Node(edge[i].v, cur.c + edge[i].c));
}
}
return -;
} int main() {
int u, v, c;
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n, &m)) {
init();
scanf("%d %d %d %d", &S, &E, &K, &T);
while(m--) {
scanf("%d %d %d",&u, &v, &c);
addEdge(u, v, c);
}
dijkstra(E);
if(dis[S] == INF) {
puts("Whitesnake!");
continue;
}
if(S == E) {
K++;
}
int res = a_star(S);
if(res == -) {
puts("Whitesnake!");
continue;
}
if(res <= T) {
puts("yareyaredawa");
} else {
puts("Whitesnake!");
}
}
return ;
}
"Oh, There is a bipartite graph.""Make it Fantastic."
X wants to check whether a bipartite graph is a fantastic graph. He has two fantastic numbers, and he wants to let all the degrees to between the two boundaries. You can pick up several edges from the current graph and try to make the degrees of every point to between the two boundaries. If you pick one edge, the degrees of two end points will both increase by one. Can you help X to check whether it is possible to fix the graph?
Input
There are at most 30 test cases.
For each test case,The first line contains three integers NN the number of left part graph vertices, MM the number of right part graph vertices, and KK the number of edges (1≤N≤2000,0≤M≤2000,0≤K≤6000 ). Vertices are numbered from 11 to NN.
The second line contains two numbers L, R (0≤L≤R≤300). The two fantastic numbers.
Then KK lines follows, each line containing two numbers U, V(1≤U≤N,1≤V≤M). It shows that there is a directed edge from U-th spot to V-th spot.
Note. There may be multiple edges between two vertices.
Output
One line containing a sentence. Begin with the case number. If it is possible to pick some edges to make the graph fantastic, output "Yes" (without quote), else output "No" (without quote).
样例输入
3 3 7
2 3
1 2
2 3
1 3
3 2
3 3
2 1
2 1
3 3 7
3 4
1 2
2 3
1 3
3 2
3 3
2 1
2 1
样例输出
Case 1: Yes
Case 2: No
题目来源
题目大意:给出一个二分图,再给出一些边,再给出L,R,从这些边中选取一些使得每一个点的度都在[L,R]之间。
题目思路:建立超级源点S,连接二分图左边的所有点,流量下界L,上界为R,同理将右半边所有点连接到超级汇点T。
将给出的边连接,流量下界0,上界为1。然后套个有上下界的网络流板子判断是否有解就行了。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int LEN = 1e5 + ;
const int oo = (1LL << ) - ;
namespace DINIC {
int tot, src, tar, qh, qt, cnt, s, t, S, T;
int ans, flow;
struct edge {
int vet, next, len;
} E[LEN * ];
int dis[LEN], head[LEN], cur[LEN], q[LEN], IN[LEN];
void add(int u, int v, int c) {
E[++tot] = (edge) {
v, head[u], c
};
head[u] = tot;
}
void join(int u, int v, int c) {
add(u, v, c);
add(v, u, );
}
void init() {
tot = -;
for (int i = ; i <= cnt + ; i++)
head[i] = -;
}
bool bfs() {
memset(dis, , sizeof(dis));
qh = qt = ;
q[++qt] = src;
dis[src] = ;
while (qh < qt) {
int u = q[++qh];
for (int e = head[u]; e != -; e = E[e].next) {
int v = E[e].vet;
if (E[e].len && !dis[v]) {
dis[v] = dis[u] + ;
if (v == tar)
return ;
q[++qt] = v;
}
}
}
return dis[tar];
}
int dfs(int u, int aug) {
if (u == tar || !aug)
return aug;
int tmp = ;
for (int &e = cur[u]; e != -; e = E[e].next) {
int v = E[e].vet;
if (dis[v] == dis[u] + ) {
if (tmp = dfs(v, min(aug, E[e].len))) {
E[e].len -= tmp;
E[e ^ ].len += tmp;
return tmp;
}
}
}
return ;
}
int maxflow(int s, int t) {
src = s, tar = t;
int res = , flow = ;
while (bfs()) {
for (int i = ; i <= cnt + ; i++)
cur[i] = head[i];
while (flow = dfs(src, oo))
res += flow;
}
return res;
}
}
using namespace DINIC; int N, M, K, L, R; int main() {
int cas = ;
while(~scanf("%d %d %d", &N, &M, &K)) {
scanf("%d %d", &L, &R);
memset(IN, , sizeof(IN));
ans = flow = ;
cnt = N + M + ;
s = N + M + ;
t = N + M + ;
S = ++cnt, T = ++cnt;
init();
for(int i = ; i <= K; i++ ) {
int u, v, l = , r = ;
scanf("%d %d", &u, &v);
join(u, v + N, r - l);
IN[v] += l, IN[u] -= l;
}
for(int i = ; i <= N; i++ ) {
int u, v, l = L, r = R;
u = s, v = i;
join(u, v, r - l);
IN[v] += l, IN[u] -= l;
}
for(int i = ; i <= M; i++ ) {
int u, v, l = L, r = R;
u = i + N, v = t;
join(u, v, r - l);
IN[v] += l, IN[u] -= l;
} for (int i = ; i <= N + M + ; i++) {
if (IN[i] < ) {
join(i, T, -IN[i]);
} else if (IN[i] > ) {
flow += IN[i];
join(S, i, IN[i]);
}
}
join(t, s, oo);
ans = maxflow(S, T);
printf("Case %d: ", cas++);
if (ans != flow)
puts("No");
else {
// ans = maxflow(s, t);
// printf("%lld\n", ans);
puts("Yes");
}
}
return ;
}
G.Spare Tire
A sequence of integer \lbrace a_n \rbrace{an} can be expressed as:
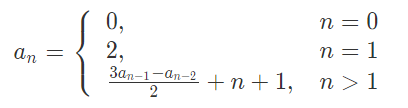
Now there are two integers nn and mm. I'm a pretty girl. I want to find all b1,b2,b3⋯bp that 1≤bi≤n and bi is relatively-prime with the integer m. And then calculate:

But I have no time to solve this problem because I am going to date my boyfriend soon. So can you help me?
Input
Input contains multiple test cases ( about 15000 ). Each case contains two integers nn and mm.1≤n,m≤10^8.
Output
For each test case, print the answer of my question(after mod 1,000,000,007).
Hint
In the all integers from 1 to 4, 1 and 3 is relatively-prime with the integer 4. So the answer is a1+a3=14.
样例输入
4 4
样例输出
14
题目来源
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int mod=1e9+;
int vis[],pri[],top;
int a[],h;
ll n,m,ans,sum;
ll p1,p2;
void init()
{
top=;
for(int i=; i<; i++)
{
if(!vis[i])
{
pri[++top]=i;
for(int j=i+i; j<; j+=i)
vis[j]=;
}
}
}
ll qpow(ll a,ll b)
{
ll ans=;
while(b)
{
if(b&)
ans=ans*a%mod;
a=a*a%mod;
b>>=;
}
return ans;
}
ll getsum(int x)
{
if(!x||x==)
return ;
int i,j,k;
ll ans;
k=n/x;
ans=1LL*k*(k+)%mod*p1%mod*x%mod;
ans+=(1LL*k*(k+)%mod*(*k+)%mod*p2%mod*x%mod*x%mod);
ans=ans%mod;
return ans;
}
void dfs(int i,int num,int x)
{
if(x>n)
return ;
if(i==h)
{
if(num%)
{
sum+=getsum(x);
sum=sum%mod;
}
else
sum-=getsum(x);
return ;
}
dfs(i+,num+,x*a[i]);
dfs(i+,num,x); }
int main()
{
int i,j,k,t,cas;
ll w;
init();
p1=qpow(,mod-);
p2=qpow(,mod-);
while(scanf("%lld%lld",&n,&m)!=EOF)
{
ans=1LL*n*(n+)%mod*p1%mod;
ans+=(1LL*n*(n+)%mod*(*n+)%mod*p2%mod);
ans=ans%mod;
h=;
w=m;
for(i=; i<=top; i++)
{
if(w%pri[i]==)
{
a[h++]=pri[i];
while(w%pri[i]==)
w=w/pri[i];
}
}
if(w!=)
a[h++]=w;
sum=;
dfs(,,);
ans=(ans+mod-sum)%mod;
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return ;
}
I.Lattice's basics in digital electronics
LATTICE is learning Digital Electronic Technology. He is talented, so he understood all those pieces of knowledge in 10^{-9}10−9 second. In the next 10^{-9}10−9 second, he built a data decoding device that decodes data encoded with his special binary coding rule to meaningful words.
His coding rule is called "prefix code", a type of code system (typically a variable-length code) distinguished by its possession of the "prefix property", which requires that there is no whole code word in the system that is a prefix (initial segment) of any other code word in the system. Note that his code is composed of only 0 and 1.
LATTICE's device only receives data that perfectly matches LATTICE's rules, in other words, people who send message to LATTICE will always obey his coding rule. However, in the process of receiving data, there are errors that cannot avoid, so LATTICE uses parity check to detect error bytes, after every 88-bit data there is 11 bit called parity bit, which should be '0' if there are odd number of '1's in the previous 88bits and should be '1' if there are even number of '1's. If the parity bit does not meet the fact, then the whole 99 bits (including the parity bit) should be considered as invalid data and ignored. Data without parity bit is also considered as invalid data. Parity bits will be deleted after the parity check.
For example, consider the given data "101010101010101010101010", it should be divided into 33parts:"101010101","010101010" and "101010". For the first part, there are 44 '1's in the first 88 bits, and parity bit is '1', so this part passed the check. For the second part, there are 44 '1's and parity bit is '0', so this part failed the check. For the third part, it has less than 99 bits so it contains no parity bit, so this part also failed the check. The data after parity check is "10101010", which is the first 88 bits of first part.
Data passed the parity check will go into a process that decodes LATTICE's code. The process is described in the following example: consider a situation that, "010" represents 'A' and "1011" represents 'B', if the data after parity check is "01010110101011010010", it can be divided into "010"+"1011"+"010"+"1011"+"010"+"010", which means "ABABAA" . LATTICE's device is so exquisite that it can decode all visible characters in the ASCII table .
LATTICE is famous for his Talk show, some reporters have sneaked into his mansion, they stole the data LATTICE to decode in hexadecimal, the coding rule consists of N pairs of corresponding relations from a bit string Si to an ASCII code Ci, and the message length MM, they want to peek his privacy so they come to you to write a program that decodes messages that LATTICE receives.
Input
The first line an integer T (T<35) represents the number of test cases.
Every test case starts with one line containing two integers, M (0<M≤100000), the number of original characters, and N (1≤N≤256), then N lines, every line contains an integer Ci, and a string Si(0<∣Si∣≤10), means that Si represents Ci, the ASCII code to a visible character and Si only contains '0'or '1' and there are no two numbers ii and jj that S_iSi is prefix of S_jSj.
Then one line contains data that is going to be received in hexadecimal. (0<∣data∣<200000).
Output
For each test case, output the decoded message in a new line, the length of the decoded message should be the same with the length of original characters, which means you can stop decoding having outputted M characters. Input guarantees that it will have no less than M valid characters and all given ASCII codes represent visible characters.
样例输入
2
15 9
32 0100
33 11
100 1011
101 0110
104 1010
108 00
111 100
114 0111
119 0101
A6Fd021171c562Fde1
8 3
49 0001
50 01001
51 011
14DB24722698
样例输出
hello world!!!!
12332132
题目来源
题目大意:
给出 二进制和ASCLL码的对映规则,再给出一个16进制的字符串。将16进制的字符串转二进制,然后每九位校验一下(前八位中1的个数是奇数且第九位为1 或 前八位中1的个数是偶数且第九位为0 则正确)
将正确的留下,再用题目给的规则转换成字符,只要前m个。暴力模拟下即可。
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std; struct Trie
{
int num;
int next[];
} tree[];
int cnt = ;
char ttr[];
char ltr[];
bool a[];
int top = ; void getBit()
{
int len = strlen(ttr);
top = ;
for(int i=; i<len; i++)
{
switch (ttr[i])
{
case '':
ltr[top]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',top+=;
break;
case '':
ltr[top]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',top+=;
break;
case '':
ltr[top]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',top+=;
break;
case '':
ltr[top]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',top+=;
break;
case '':
ltr[top]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',top+=;
break;
case '':
ltr[top]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',top+=;
break;
case '':
ltr[top]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',top+=;
break;
case '':
ltr[top]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',top+=;
break;
case '':
ltr[top]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',top+=;
break;
case '':
ltr[top]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',top+=;
break;
case 'a':
case 'A':
ltr[top]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',top+=;
break;
case 'b':
case 'B':
ltr[top]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',top+=;
break;
case 'c':
case 'C':
ltr[top]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',top+=;
break;
case 'd':
case 'D':
ltr[top]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',top+=;
break;
case 'e':
case 'E':
ltr[top]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',top+=;
break;
case 'f':
case 'F':
ltr[top]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',ltr[top+]='',top+=;
break;
}
}
ltr[top]='\0';
} void insert_tree(char str[],int num)
{
int p = ;
int len = strlen(str);
for(int i=; i<len; i++)
{
if(tree[p].next[str[i]-''])
{
p = tree[p].next[str[i]-''];
}
else
{
tree[p].next[str[i]-''] = ++cnt;
p = tree[p].next[str[i]-''];
}
}
tree[p].num = num;
} void solve()
{
cnt = ;
int tot = ;
memset(tree,,sizeof(tree));
memset(a,,sizeof(a));
memset(ttr,,sizeof(ttr));
memset(ltr,,sizeof(ltr));
int m,n,num;
char str[];
scanf("%d%d",&m,&n);
while(n--)
{
scanf("%d%s",&num,str);
insert_tree(str,num);
}
scanf("%s",ttr);
getBit(); for(int i=; i<top; i+=)
{
int cc=;
if(i+>top)continue;
for(int j=i; j<i+; j++)
{
if(ltr[j]=='')
cc++;
}
if((cc%==&<r[i+]=='')||(cc%==&<r[i+]==''))
{
for(int j=i; j<i+; j++)
{
a[tot++] = ltr[j]-'';
}
}
}
int root = ;
for(int i=;i<tot;i++)
{
root = tree[root].next[a[i]];
if(tree[root].num)
{
printf("%c",tree[root].num);
m--;
root = ;
}
if(!m)break;
}
puts("");
} int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
solve();
}
return ;
}
K.Supreme Number
A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that cannot be formed by multiplying two smaller natural numbers.
Now lets define a number NN as the supreme number if and only if each number made up of an non-empty subsequence of all the numeric digits of NN must be either a prime number or 1.
For example, 17 is a supreme number because 1, 7, 17 are all prime numbers or 1, and 19 is not, because 9 is not a prime number.
Now you are given an integer N (2≤N≤10^100), could you find the maximal supreme number that does not exceed NN?
Input
In the first line, there is an integer T≤100000 indicating the numbers of test cases.
In the following TT lines, there is an integer N (2≤N≤10^100).
Output
For each test case print "Case #x: y", in which xx is the order number of the test case and yy is the answer.
样例输入
2
6
100
样例输出
Case #1: 5
Case #2: 73
题目来源
题意:找一个小于n的超级质数(其子序列也是质数),搜索。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int a[],top=;
int b[]= {,,,,},c[],d[];
int vis[];
int l,f;
void init()
{
for(int i=; i<; i++)
if(!vis[i])
for(int j=i+i; j<; j+=i)
vis[j]=;
}
void dfs1(int len,int x)
{
if(len==l)
{
if(vis[x])
f=;
return ;
}
dfs1(len+,x*+c[len]);
dfs1(len+,x); }
int check(int x)
{
f=;
l=;
while(x)
{
d[l++]=x%;
x=x/;
}
for(int i=; i<l; i++)
c[i]=d[l-i-];
dfs1(,);
return f;
}
void dfs(int len,int x)
{
if(check(x)&&x)
a[++top]=x;
if(len==)
{
return ;
}
for(int i=; i<; i++)
dfs(len+,x*+b[i]);
}
int main()
{
int i,j,t,cas=,len,mmax,ans;
char s[];
init();
dfs(,);
sort(a+,a+top+);
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
++cas;
scanf("%s",&s);
len=strlen(s);
if(len>)
mmax=;
else
{
mmax=;
for(i=; i<len; i++)
mmax=mmax*+(s[i]-'');
}
//printf("%d\n",mmax);
for(i=; i<=top; i++)
if(a[i]<=mmax)
ans=a[i];
printf("Case #%d: %d\n",cas,ans); }
return ;
}
ACM-ICPC 2018 沈阳赛区(网络赛)的更多相关文章
- HDU 4046 Panda (ACM ICPC 2011北京赛区网络赛)
HDU 4046 Panda (ACM ICPC 2011北京赛区网络赛) Panda Time Limit: 10000/4000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: ...
- ICPC 2018 徐州赛区网络赛
ACM-ICPC 2018 徐州赛区网络赛 去年博客记录过这场比赛经历:该死的水题 一年过去了,不被水题卡了,但难题也没多做几道.水平微微有点长进. D. Easy Math 题意: ...
- ACM-ICPC 2018 沈阳赛区网络预赛 K Supreme Number(规律)
https://nanti.jisuanke.com/t/31452 题意 给出一个n (2 ≤ N ≤ 10100 ),找到最接近且小于n的一个数,这个数需要满足每位上的数字构成的集合的每个非空子集 ...
- ACM-ICPC 2018 沈阳赛区网络预赛-K:Supreme Number
Supreme Number A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 11 that cannot be formed ...
- ACM-ICPC 2018 沈阳赛区网络预赛-D:Made In Heaven(K短路+A*模板)
Made In Heaven One day in the jail, F·F invites Jolyne Kujo (JOJO in brief) to play tennis with her. ...
- 图上两点之间的第k最短路径的长度 ACM-ICPC 2018 沈阳赛区网络预赛 D. Made In Heaven
131072K One day in the jail, F·F invites Jolyne Kujo (JOJO in brief) to play tennis with her. Howe ...
- ACM-ICPC 2018 沈阳赛区网络预赛 J树分块
J. Ka Chang Given a rooted tree ( the root is node 11 ) of NN nodes. Initially, each node has zero p ...
- ACM-ICPC 2018 沈阳赛区网络预赛 K. Supreme Number
A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 11 that cannot be formed by multiplying ...
- ACM-ICPC 2018 沈阳赛区网络预赛 F. Fantastic Graph
"Oh, There is a bipartite graph.""Make it Fantastic." X wants to check whether a ...
随机推荐
- jboss 未授权访问漏洞复现
jboss 未授权访问漏洞复现 一.漏洞描述 未授权访问管理控制台,通过该漏洞,可以后台管理服务,可以通过脚本命令执行系统命令,如反弹shell,wget写webshell文件. 二.漏洞环境搭建及复 ...
- bit、byte、kb、mb、g的区别
1Byte=8bit1KB=1024Byte(字节)=8*1024bit1MB=1024KB1GB=1024MB1TB=1024GB bit是计算机数据的最小单元.要么是0,要么是1. byte 关键 ...
- 再记一次经典Net程序的逆向过程
1.前言 上次发完,有网友问了一个问题:如果不绕过编译,而是直接编译怎么办? 记一次Net软件逆向的过程:https://www.cnblogs.com/dotnetcrazy/p/10142315. ...
- JDK的命令行工具系列 (二) javap、jinfo、jmap
javap: 反编译工具, 可用来查看java编译器生成的字节码 参数摘要: -help 帮助 -l 输出行和变量的表 -public 只输出public方法和域 -protected 只输出publ ...
- 【JDK】JDK源码分析-CountDownLatch
概述 CountDownLatch 是并发包中的一个工具类,它的典型应用场景为:一个线程等待几个线程执行,待这几个线程结束后,该线程再继续执行. 简单起见,可以把它理解为一个倒数的计数器:初始值为线程 ...
- CodeGlance右侧窗口缩略图消失不见
说明下问题,idea中的CodeGlance插件会在右侧显示缩略图,可以快速定位代码.今天遇到个问题升级了插件后右侧窗口消失.经过卸载插件,重启,reset一系列操作后还是没能恢复. 能去搜索引擎搜索 ...
- eclipse使用(一)
使用eclipse时,编写对象的返回值非常麻烦,而使用返回值快捷键可以简化这一过程. 第一种 Alt+shift+L 将光标放在有返回值的代码句的分号后面: Resources.getResource ...
- Liunx之nginx代理
一.代理 正向代理 正向代理,也就是传说中的代理,他的工作原理就像一个跳板(VPN),简单的说: 我是一个用户,我访问不了某网站,但是我能访问一个代理服务器,这个代理服务器呢,他能访问那个我不能访问的 ...
- 从输入URL到浏览器显示页面发生了哪些事情---个人理解
经典面试题:从输入URL到页面显示发生了哪些事情 以前一直都记不住,这次自己理解了一下 用自己的话总结了一次,不对的地方希望大佬给我指出来 1.主机通过DHCP协议获取客户端的IP地址.子网掩码和DN ...
- 树莓派dht11,土壤湿度传感器,继电器的使用。树莓派云灌溉(二)
关于传感器的一些说明 我的想法是这样的 我尽量用易于理解的语言去说我的想法 首先,土壤湿度传感器和dh11会获取数据,然后树莓派会处理这些数据,读出土壤温湿度和空气温湿度,并将这些数据上传到云服务器, ...
