Python中内置的日志模块logging用法详解
logging模块简介
Python的logging模块提供了通用的日志系统,可以方便第三方模块或者是应用使用。这个模块提供不同的日志级别,并可以采用不同的方式记录日志,比如文件,HTTP GET/POST,SMTP,Socket等,甚至可以自己实现具体的日志记录方式。
logging模块与log4j的机制是一样的,只是具体的实现细节不同。模块提供logger,handler,filter,formatter。
- logger:提供日志接口,供应用代码使用。logger最长用的操作有两类:配置和发送日志消息。可以通过logging.getLogger(name)获取logger对象,如果不指定name则返回root对象,多次使用相同的name调用getLogger方法返回同一个logger对象。
- handler:将日志记录(log record)发送到合适的目的地(destination),比如文件,socket等。一个logger对象可以通过addHandler方法添加0到多个handler,每个handler又可以定义不同日志级别,以实现日志分级过滤显示。
- filter:提供一种优雅的方式决定一个日志记录是否发送到handler。
- formatter:指定日志记录输出的具体格式。formatter的构造方法需要两个参数:消息的格式字符串和日期字符串,这两个参数都是可选的。
与log4j类似,logger,handler和日志消息的调用可以有具体的日志级别(Level),只有在日志消息的级别大于logger和handler的级别。
logging用法解析
1. 初始化 logger = logging.getLogger("endlesscode"),getLogger()方法后面最好加上所要日志记录的模块名字,后面的日志格式中的%(name)s 对应的是这里的模块名字
2. 设置级别 logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG),Logging中有NOTSET < DEBUG < INFO < WARNING < ERROR < CRITICAL这几种级别,日志会记录设置级别以上的日志
3. Handler,常用的是StreamHandler和FileHandler,windows下你可以简单理解为一个是console和文件日志,一个打印在CMD窗口上,一个记录在一个文件上
4. formatter,定义了最终log信息的顺序,结构和内容,我喜欢用这样的格式 '[%(asctime)s] [%(levelname)s] %(message)s', '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',
%(name)s Logger的名字
%(levelname)s 文本形式的日志级别
%(message)s 用户输出的消息
%(asctime)s 字符串形式的当前时间。默认格式是 “2003-07-08 16:49:45,896”。逗号后面的是毫秒
%(levelno)s 数字形式的日志级别
%(pathname)s 调用日志输出函数的模块的完整路径名,可能没有
%(filename)s 调用日志输出函数的模块的文件名
%(module)s 调用日志输出函数的模块名
%(funcName)s 调用日志输出函数的函数名
%(lineno)d 调用日志输出函数的语句所在的代码行
%(created)f 当前时间,用UNIX标准的表示时间的浮 点数表示
%(relativeCreated)d 输出日志信息时的,自Logger创建以 来的毫秒数
%(thread)d 线程ID。可能没有
%(threadName)s 线程名。可能没有
%(process)d 进程ID。可能没有
5. 记录 使用object.debug(message)来记录日志
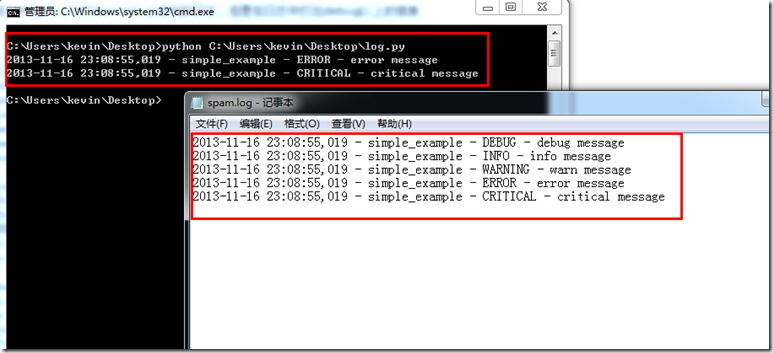
下面来写一个实例,在CMD窗口上只打出error以上级别的日志,但是在日志中打出debug以上的信息
import logging
logger = logging.getLogger("simple_example")
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
# 建立一个filehandler来把日志记录在文件里,级别为debug以上
fh = logging.FileHandler("spam.log")
fh.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
# 建立一个streamhandler来把日志打在CMD窗口上,级别为error以上
ch = logging.StreamHandler()
ch.setLevel(logging.ERROR)
# 设置日志格式
formatter = logging.Formatter("%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s")
ch.setFormatter(formatter)
fh.setFormatter(formatter)
#将相应的handler添加在logger对象中
logger.addHandler(ch)
logger.addHandler(fh)
# 开始打日志
logger.debug("debug message")
logger.info("info message")
logger.warn("warn message")
logger.error("error message")
logger.critical("critical message")
运行一下将会看到CMD窗口只记录两条,spam.log中记录了五条日志
当一个项目比较大的时候,不同的文件中都要用到Log,可以考虑将其封装为一个类来使用
#! /usr/bin/env python
#coding=gbk
import logging,os class Logger:
def __init__(self, path,clevel = logging.DEBUG,Flevel = logging.DEBUG):
self.logger = logging.getLogger(path)
self.logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
fmt = logging.Formatter('[%(asctime)s] [%(levelname)s] %(message)s', '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
#设置CMD日志
sh = logging.StreamHandler()
sh.setFormatter(fmt)
sh.setLevel(clevel)
#设置文件日志
fh = logging.FileHandler(path)
fh.setFormatter(fmt)
fh.setLevel(Flevel)
self.logger.addHandler(sh)
self.logger.addHandler(fh) def debug(self,message):
self.logger.debug(message) def info(self,message):
self.logger.info(message) def war(self,message):
self.logger.warn(message) def error(self,message):
self.logger.error(message) def cri(self,message):
self.logger.critical(message) if __name__ =='__main__':
logyyx = Logger('yyx.log',logging.ERROR,logging.DEBUG)
logyyx.debug('一个debug信息')
logyyx.info('一个info信息')
logyyx.war('一个warning信息')
logyyx.error('一个error信息')
logyyx.cri('一个致命critical信息')
这样每次使用的时候只要实例化一个对象就可以了
|
1
|
logobj = Logger(‘filename',clevel,Flevel) |
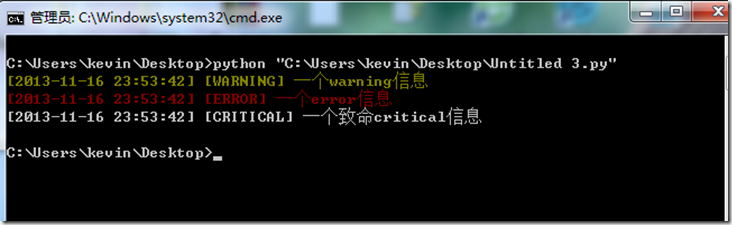
如果想在CMD窗口中对于error的日志标红,warning的日志标黄,那么可以使用ctypes模块
#! /usr/bin/env python
#coding=gbk
import logging,os
import ctypes FOREGROUND_WHITE = 0x0007
FOREGROUND_BLUE = 0x01 # text color contains blue.
FOREGROUND_GREEN= 0x02 # text color contains green.
FOREGROUND_RED = 0x04 # text color contains red.
FOREGROUND_YELLOW = FOREGROUND_RED | FOREGROUND_GREEN STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE= -11
std_out_handle = ctypes.windll.kernel32.GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE)
def set_color(color, handle=std_out_handle):
bool = ctypes.windll.kernel32.SetConsoleTextAttribute(handle, color)
return bool class Logger:
def __init__(self, path,clevel = logging.DEBUG,Flevel = logging.DEBUG):
self.logger = logging.getLogger(path)
self.logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
fmt = logging.Formatter('[%(asctime)s] [%(levelname)s] %(message)s', '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
#设置CMD日志
sh = logging.StreamHandler()
sh.setFormatter(fmt)
sh.setLevel(clevel)
#设置文件日志
fh = logging.FileHandler(path)
fh.setFormatter(fmt)
fh.setLevel(Flevel)
self.logger.addHandler(sh)
self.logger.addHandler(fh) def debug(self,message):
self.logger.debug(message) def info(self,message):
self.logger.info(message) def war(self,message,color=FOREGROUND_YELLOW):
set_color(color)
self.logger.warn(message)
set_color(FOREGROUND_WHITE) def error(self,message,color=FOREGROUND_RED):
set_color(color)
self.logger.error(message)
set_color(FOREGROUND_WHITE) def cri(self,message):
self.logger.critical(message) if __name__ =='__main__':
logyyx = Logger('yyx.log',logging.WARNING,logging.DEBUG)
logyyx.debug('一个debug信息')
logyyx.info('一个info信息')
logyyx.war('一个warning信息')
logyyx.error('一个error信息')
logyyx.cri('一个致命critical信息')
多模块使用logging
logging模块保证在同一个python解释器内,多次调用logging.getLogger('log_name')都会返回同一个logger实例,即使是在多个模块的情况下。所以典型的多模块场景下使用logging的方式是在main模块中配置logging,这个配置会作用于多个的子模块,然后在其他模块中直接通过getLogger获取Logger对象即可。
配置文件:
[loggers]
keys=root,main [handlers]
keys=consoleHandler,fileHandler [formatters]
keys=fmt [logger_root]
level=DEBUG
handlers=consoleHandler [logger_main]
level=DEBUG
qualname=main
handlers=fileHandler [handler_consoleHandler]
class=StreamHandler
level=DEBUG
formatter=fmt
args=(sys.stdout,) [handler_fileHandler]
class=logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler
level=DEBUG
formatter=fmt
args=('tst.log','a',20000,5,) [formatter_fmt]
format=%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s
datefmt=
主模块main.py:
import logging
import logging.config logging.config.fileConfig('logging.conf')
root_logger = logging.getLogger('root')
root_logger.debug('test root logger...') logger = logging.getLogger('main')
logger.info('test main logger')
logger.info('start import module \'mod\'...')
import mod logger.debug('let\'s test mod.testLogger()')
mod.testLogger() root_logger.info('finish test...')
子模块mod.py:
import logging
import submod logger = logging.getLogger('main.mod')
logger.info('logger of mod say something...') def testLogger():
logger.debug('this is mod.testLogger...')
submod.tst()
子子模块submod.py:
import logging
logger = logging.getLogger('main.mod.submod')
logger.info('logger of submod say something...')
def tst():
logger.info('this is submod.tst()...')
然后运行python main.py,控制台输出
2012-03-09 18:22:22,793 - root - DEBUG - test root logger...
2012-03-09 18:22:22,793 - main - INFO - test main logger
2012-03-09 18:22:22,809 - main - INFO - start import module 'mod'...
2012-03-09 18:22:22,809 - main.mod.submod - INFO - logger of submod say something...
2012-03-09 18:22:22,809 - main.mod - INFO - logger say something...
2012-03-09 18:22:22,809 - main - DEBUG - let's test mod.testLogger()
2012-03-09 18:22:22,825 - main.mod - DEBUG - this is mod.testLogger...
2012-03-09 18:22:22,825 - main.mod.submod - INFO - this is submod.tst()...
2012-03-09 18:22:22,841 - root - INFO - finish test...
可以看出,和预想的一样,然后在看一下tst.log,logger配置中的输出的目的地:
tst.log中没有root logger输出的信息,因为logging.conf中配置了只有main logger及其子logger使用RotatingFileHandler,而root logger是输出到标准输出。
#! /usr/bin/env python#coding=gbkimport logging,osclass Logger: def __init__(self, path,clevel = logging.DEBUG,Flevel = logging.DEBUG): self.logger = logging.getLogger(path) self.logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG) fmt = logging.Formatter('[%(asctime)s] [%(levelname)s] %(message)s', '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') #设置CMD日志 sh = logging.StreamHandler() sh.setFormatter(fmt) sh.setLevel(clevel) #设置文件日志 fh = logging.FileHandler(path) fh.setFormatter(fmt) fh.setLevel(Flevel) self.logger.addHandler(sh) self.logger.addHandler(fh) def debug(self,message): self.logger.debug(message) def info(self,message): self.logger.info(message) def war(self,message): self.logger.warn(message) def error(self,message): self.logger.error(message) def cri(self,message): self.logger.critical(message)if __name__ =='__main__': logyyx = Logger('yyx.log',logging.ERROR,logging.DEBUG) logyyx.debug('一个debug信息') logyyx.info('一个info信息') logyyx.war('一个warning信息') logyyx.error('一个error信息') logyyx.cri('一个致命critical信息')Python中内置的日志模块logging用法详解的更多相关文章
- Python中第三方库Requests库的高级用法详解
Python中第三方库Requests库的高级用法详解 虽然Python的标准库中urllib2模块已经包含了平常我们使用的大多数功能,但是它的API使用起来让人实在感觉不好.它已经不适合现在的时代, ...
- 详解Python中内置的NotImplemented类型的用法
它是什么? ? 1 2 >>> type(NotImplemented) <type 'NotImplementedType'> NotImplemented 是Pyth ...
- thinkPHP内置字符串截取msubstr函数用法详解
作者:陈达辉 字体:[增加 减小] 类型:转载 时间:2016-11-15 我要评论 这篇文章主要介绍了thinkPHP内置字符串截取函数用法,结合实例形式分析了thinkPHP内置的字符串截取函数功 ...
- Beautifulsoup模块基础用法详解
目录 Beautifulsoup模块 官方中文文档 介绍 基本使用 遍历文档树 搜索文档树 五种过滤器 **find_all( name , attrs , recursive , text , ** ...
- Python函数(函数定义、函数调用)用法详解
Python 中,函数的应用非常广泛,前面章节中我们已经接触过多个函数,比如 input() .print().range().len() 函数等等,这些都是 Python 的内置函数,可以直接使用. ...
- JavaScript中return的用法和this的用法详解
JavaScript中return的用法详解 最近,跟身边学前端的朋友了解,有很多人对this和函数中的return的用法和意思理解的比较模糊,这里写一篇博客跟大家一起探讨一下return和this的 ...
- Python(2.7.6) 标准日志模块 - Logging Handler
Python 标准日志模块使用 Handler 控制日志消息写到不同的目的地,如文件.流.邮件.socket 等.除了StreamHandler. FileHandler 和 NullHandler ...
- Python日志模块logging用法
1.日志级别 日志一共分成5个等级,从低到高分别是:DEBUG INFO WARNING ERROR CRITICAL. DEBUG:详细的信息,通常只出现在诊断问题上 INFO:确认一切按预期运行 ...
- Python中内置函数的介绍
内置函数的功能介绍 常用内置函数如下: 1.abs() 绝对值 格式:abs(x) 例如:print(abs(-18)) >>> 18 返回值:number #该函数主要用于数值类的 ...
随机推荐
- 几种不同的json格式解析
转连接: http://blog.csdn.net/whx405831799/article/details/42171191 内容很好 给服务端发送请求后,服务端会返回一连串的数据,这些数据在大部分 ...
- 关于javascript中的this 一段小实例深有体会啊
先声明鄙人正在努力的把脚抬进门来,说的都是比较粗浅的知识,但都是我实践中得出的体会,很深刻. 正在自学中挣扎的DOG. 先看段代码: function highlightRows() { if(!d ...
- 转:使用 Nginx Upload Module 实现上传文件功能
普通网站在实现文件上传功能的时候,一般是使用Python,Java等后端程序实现,比较麻烦.Nginx有一个Upload模块,可以非常简单的实现文件上传功能.此模块的原理是先把用户上传的文件保存到临时 ...
- 动态规划:划分DP
划分型动态规划之数的划分 先贴上2014年10月31日的那份代码,甚至怀念当时在机房YY这道题的场面 高中最快乐的时候.. #include<iostream> using namespa ...
- 【CodeForces】841C. Leha and Function(Codeforces Round #429 (Div. 2))
[题意]定义函数F(n,k)为1~n的集合中选择k个数字,其中最小数字的期望. 给定两个数字集A,B,A中任意数字>=B中任意数字,要求重组A使得对于i=1~n,sigma(F(Ai,Bi))最 ...
- 如何打开小米,oppo,华为等手机的系统应用的指定页面
如题,拿Oppo 手机做个示例,小米 华为也是如此. 在编写Android应用的时候,我们经常会有这样的需求,我们想直接打开系统应用的某个页面.比如在Oppo R9 手机上我们想打开某个应用的通知管理 ...
- HDU 1840 Equations (数学)
title: Equations 数学 杭电1840 tags: [数学] 题目链接 Problem Description All the problems in this contest tota ...
- C# 反射 名称不区分大小写
一 Type type = Type.GetType(className,false,true); //第一个是“类型的全名”,第二个参数:找不到时触发异常,第三个参数:寻找的时候是否忽略大小写 二 ...
- LBP简单实现
Local Binary Pattern 确实够简单...先写个代码在这儿,空了再弄 #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> #include <iostream ...
- [Leetcode Week8]Subsets II
Subsets II 题解 原创文章,拒绝转载 题目来源:https://leetcode.com/problems/subsets-ii/description/ Description Given ...
