JavaScript 面向对象继承详解
题记
由于js不像java那样是完全面向对象的语言,js是基于对象的,它没有类的概念。所以,要想实现继承,一般都是基于原型链的方式;
一、继承初探
大多数JavaScript的实现用 __proto__ 属性来表示一个对象的原型链。
我们可以简单的把prototype看做是一个模版,新创建的自定义对象都是这个模版(prototype)的一个拷贝 (实际上不是拷贝而是链接,只不过这种链接是不可见,新实例化的对象内部有一个看不见的__proto__指针,指向原型对象)
当查找一个对象的属性时,JavaScript 会向上遍历原型链,直到找到给定名称的属性为止。查找方式可以这样表示:
- function getProperty(obj, prop) {
- if (obj.hasOwnProperty(prop)) {
- return obj[prop];
- }
- else if (obj.__proto__ !== null) {
- return getProperty(obj.__proto__, prop);
- }
- else {
- return undefined;
- }
- }
我们在js中使用面向对象很多时候是这样子的:
- function Person(name,age){
- this.name = name;
- this.age = age;
- }
- Person.prototype.printInfo = function(){
- console.log(this.name + ': ' + this.age);
- };
- var person = new Person('Jack',17);
- person.printInfo(); // Jack: 17
而变一下,可以发现,这种方式也是可以的
- var Person = {
- /* 声明所需的项 */
- name : 'name',
- age: 'age',
- printInfo: function(){
- console.log(this.name + ': ' + this.age);
- }
- };
- var person = {
- name: 'Jack',
- age: 17,
- __proto__: Person
- };
- person.printInfo(); // Jack: 17
其实这里就是通过将 __proto__ 指向了Person从而达到了原型继承的目的(这也许也是后续某种继承方式的来源)
以上两种方式是等价的,但我们看到的更多还是new方式来产生实例对象,其实new方式也是通过继承方式实现的,那一个new 究竟做了什么操作呢?
有两个版本,哪个比较中肯就用哪个吧
1)
1、创建一个空对象,并且 this 变量引用该对象,同时还继承了该函数的原型(即把__proto__属性设置为该对象的prototype。2、属性和方法被加入到 this 引用的对象中(使用apply传参调用)。
3、新创建的对象由 this 所引用,并且最后隐式的返回实例。
用代码实现应该就是这样的
- /* new Constructor() */
- function new (f) {
- var n = { '__proto__': f.prototype }; /* step 1 */
- return function () {
- f.apply(n, arguments); /* step 2 */
- return n; /* step 3 */
- };
- }
2)
- var obj = {};
- obj.__proto__ = Base.prototype;
- Base.call(obj);

不过我用代码实现的时候,两种情况都出现了无线调用堆栈溢出的情况,也许new的操作内部没那么简单



二、继承方式概览
说了那么多new 也乱了,不如直接切入正题,谈谈js流行的几种继承方式
1)对象冒充
对象冒充也分为几类 -- 添加临时属性、apply/call等方式
添加临时属性
缺点是只能继承显示指明的属性,原型上的属性没办法
- function Parent(name){
- this.name = name;
- this.words = 'words';
- this.say = function(){
- console.log(this.name + ': ' + this.words);
- };
- }
- Parent.prototype.say1 = function(){
- console.log(this.name + ': ' + this.words);
- };
- function Child(name){
- this.temp = Parent;
- this.temp(name);
- // 传参name后即可获取到相应name,words属性,即可销毁temp
- delete this.temp;
- }
- var child = new Child('child');
- child.say();
- child.say1();

call/apply
实际上是改变了Parent中this的指向,原理跟上个方法一样,但也不能拿到原型的属性
- function Parent(name){
- this.name = name;
- this.words = 'words';
- this.say = function(){
- console.log(this.name + ': ' + this.words);
- };
- }
- Parent.prototype.say1 = function(){
- console.log(this.name + ': ' + this.words);
- };
- function Child(name){
- //Parent.call(this,name);
- Parent.apply(this,[name]);
- }
- var child = new Child('child');
- child.say();
- child.say1();
对象冒充还有一个缺点就是易造成内存的浪费
因为每次冒充的过程都需要实例化一次父对象,而每次实例化的过程,this显示指明的属性将在每个实例中独立存在,不会共用。
比如say()这种方法,每次调用Child都会新产生并。而原型上的say1()方法就可以共用。
2)原型链继承
这种继承方式也许是最常见的了:将父类的新实例赋值给构造函数的原型
- function Parent(name){
- this.name = name;
- this.words = 'words';
- this.say = function(){
- console.log(this.name + ': ' + this.words);
- };
- }
- Parent.prototype.say1 = function(){
- console.log(this.name + ': ' + this.words);
- };
- function Child(name){
- this.name = name;
- }
- Child.prototype = new Parent();
// 如果不加上这句,Child的constructor就会被Parent的覆盖,变成 Parent- Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
- var child = new Child('child');
- child.say();
- child.say1();

可以看到,child不仅可以继承到parent的say()也能拿到say1() ,关键点在于 new Parent()这个new操作
根据最开始我们谈到的new操作,可以知道它具体干了什么
下面来一个变体,这种方式也行,虽然不必在Child中再次定义this.name ,但再次new Child()时,就不能更新我们需要的值。
所以这应该也算是原型链继承的一个不足吧
- function Parent(name){
- this.name = name;
- this.words = 'words';
- }
- Parent.prototype.say1 = function(){
- console.log(this.name + ': ' + this.words);
- };
- function Child(){}
- // 直接在参数中写child
- Child.prototype = new Parent('child');
- Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
- // 这样 newChild就无效了
- var child = new Child('newChild');
- child.say1();
- var p = new Parent();
- p.say1(); // child: words
3) 原型链+对象冒充(借用构造函数)
原型链方式和对象冒充方式都各有缺陷,两者的缺陷正是对方的优势。两者一结合,自然又是一个好方法,就叫它组合继承吧。
它背后的思路是 使用原型链实现对原型属性和方法的继承,而通过借用构造函数来实现对实例属性的继承。这样,既通过在原型上定义方法实现了函数复用,又保证每个实例都有它自己的属性。
- function Parent(name){
- this.name = name;
- this.words = 'words';
- }
- Parent.prototype.say1 = function(){
- console.log(this.name + ': ' + this.words);
- };
- function Child(name){
- // 对象冒充
- Parent.call(this,name);
- }
- // 原型链继承
- Child.prototype = new Parent();
- Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
- var child = new Child('child');
- child.say1(); // child: words
4)直接继承父类的 prototype
我们知道了原型链的继承是
- Child.prototype = new Parent();
那可不可以跳过实例化父类,直接拿Parent的原型呢?
- Child.prototype = Parent.prototype;
其实这也是可以的,来看个例子。
- function Parent(name){
- this.name = name;
- this.words = 'words';
- }
- Parent.prototype.age = 30;
- Parent.prototype.sayAge = function(){
- console.log(this.age);
- };
- Parent.prototype.say = function(){
- console.log(this.name + ': ' + this.words);
- };
- function Child(name){
- // Parent.call(this,name);
- }
- // 直接继承父类prototype
- Child.prototype = Parent.prototype;
- Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
- var child = new Child('child');
- child.say(); // undefined: undefined
- child.sayAge(); //30
可以看到,这种方式仅仅只能拿到父类的原型属性,实例上的name和words属性就拿不到了。
如果想拿,那就使用Parent.call(this.name)就可以啦。
由此看来,直接用prototype应该会更快,因为不需要像上一个方法那样实例化一个对象耗时。但也是有缺点的。
缺点是 Child.prototype和Parent.prototype现在指向了同一个对象,那么任何对Child.prototype的修改,都会反映到Parent.prototype。
- function Parent(name){
- this.name = name;
- this.words = 'words';
- }
- Parent.prototype.age = 30;
- Parent.prototype.sayAge = function(){
- console.log(this.age);
- };
- Parent.prototype.say = function(){
- console.log(this.name + ': ' + this.words);
- };
- function Child(name){
- Parent.call(this,name);
- }
- // 直接继承父类prototype
- Child.prototype = Parent.prototype;
- //Child.prototype = new Parent();
- Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
- var child = new Child('child');
- child.say();
- child.sayAge();
- Child.prototype.age = 40;
- console.log(Parent.prototype.age); //
可以看到父级的原型也被更改了,而原型链继承的方式则不会。
但聪明的人类想出了一个好办法:用一个空对象作为中介,再利用操作prototype,
既避免了实例化对象产生太多的耗时,又避免的父子prototype混用的情况。
- function Parent(name){
- this.name = name;
- this.words = 'words';
- }
- Parent.prototype.age = 30;
- Parent.prototype.sayAge = function(){
- console.log(this.age);
- };
- Parent.prototype.say = function(){
- console.log(this.name + ': ' + this.words);
- };
- function Child(name){
- Parent.call(this,name);
- }
- // 封装成函数
- function extend(Child,Parent){
- // 中介对象
- function F(){}
- F.prototype = Parent.prototype;
- Child.prototype = new F();
- Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
- }
- // 继承
- extend(Child,Parent);
- var child = new Child('child');
- child.say();
- child.sayAge();
- Child.prototype.age = 40;
- console.log(Parent.prototype.age); //

5)原型式继承
这种继承借助原型并基于已有的对象创建新对象,同时还不用创建自定义类型的方式称为原型式继承。
可以封装成一个方法,这方法其实只做一件事,就是把子对象的prototype属性,指向父对象,从而使得子对象与父对象连在一起。
- var Parent = {
- name : 'parent',
- words: ['word1','word2'],
- say: function(){
- console.log(this.name + ': ' + this.words);
- }
- };
- // 封装成方法
- Object.create = function(Parent){
- function F(){}
// 这里不用F.prototype = Parent.prototype的原因是
// 通过对象字面量定义的Parent对象没有这个直接的prototype属性(属于Object的)
// 如果通过 function Parent()方式定义则可以- F.prototype = Parent;
- return new F();
- };
- var Child = Object.create(Parent);
- Child.say();
- Child.name = 'child';
- Child.words.push('word3');
- Child.say();
- Parent.say();
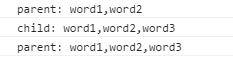
Child继承了父类的属性方法后就可以自行更新属性值或再定义了,不过这里存在一个属性共享问题。
如果是引用类型的数据,比如Object ,就比如Child往words里添加了一项,父类也会被更新,造成某种程度上的问题。
而解决引用类型数据共享问题的方法,一般就是不继承该属性,或者
6)把父对象的属性,全部拷贝给子对象
除了使用"prototype链"以外,还有另一种思路:把父对象的属性,全部拷贝给子对象,也能实现继承。
- var Parent = {
- name : 'parent',
- words: ['word1','word2'],
- say: function(){
- console.log(this.name + ': ' + this.words);
- }
- };
- // 对象拷贝函数
- function extendCopy(obj){
- var newObj = {};
- for(var item in obj){
- newObj[item] = obj[item];
- }
- return newObj;
- }
- var Child = extendCopy(Parent);
- Child.say(); // parent: word1,word2
- Child.name = 'child';
- Child.words.push('word3');
- Child.say(); // child: word1,word2,word3
- Parent.say();// parent: word1,word2,word3
这样的拷贝有一个问题。
那就是,如果父对象的属性等于数组或另一个对象,那么实际上,子对象获得的只是一个内存地址,而不是真正拷贝,因此存在父对象被篡改的可能。
所以上方Child修改之后也会反应到Parent上去。
所以需要进行深度拷贝,一直到拿到真正的值为止
- var Parent = {
- name : 'parent',
- words: ['word1','word2'],
- say: function(){
- console.log(this.name + ': ' + this.words);
- }
- };
- // 引用类型 深拷贝函数
- function deepCopy(obj,newObj){
- newObj = newObj || {};
- for(var item in obj){
- if(typeof obj[item] === 'object'){
- newObj[item] = (Object.prototype.toString.call(obj[item]) === '[object Array]') ? [] : {};
- deepCopy(obj[item],newObj[item]);
- }else{
- newObj[item] = obj[item]
- }
- }
- return newObj;
- }
- var Child = deepCopy(Parent);
- Child.say(); // parent: word1,word2
- Child.name = 'child';
- Child.words.push('word3');
- Child.say(); // child: word1,word2,word3
- Parent.say();// parent: word1,word2
最后附图两张:

JavaScript 面向对象继承详解的更多相关文章
- webpack环境搭建开发环境,JavaScript面向对象的详解,UML类图的使用
PS:因为所有的设计模式都是基于面向对象来完成的,所以在讲解设计模式之前先来过一下面向对象都有哪些知识点 搭建开发环境 初始化npm环境 下载安装nodejs安装即可,nodejs自带npm管理包,然 ...
- 关于javascript面向对象的详解!
认识面向对象 1.面向对象中的概念 一切事物皆对象 对象具有封装和继承特性 信息隐藏 2.基本面向对象 3.函数构造器构造对象 深入了解面向对象 第一种书写格式 第二种书写格式
- JavaScript—面向对象开发详解和垃圾回收
面向对象的概述 ECMAScript 有两种开发模式:1.函数式(过程化),2.面向对象(OOP). 面向对象的语言有一个标志,那就是类的概念,而通过类可以创建任意多个具有相同属性和方法的对象.但是, ...
- javascript对象继承详解
问题 比如我们有一个"动物"对象的构造函数. function animal() { this.type = '动物'; } 还有一个"猫"对象的构造函数. f ...
- <JavaScript> 寄生继承详解
// 将原型继承和非原型继承组合为一体的继承方式叫做组合继承,但是这种方法的继承是有一点小缺陷的,下级函数继承了无用的属性,所以我们有了寄生继承来解决污染问题; //创建上级构造函数-食物 funct ...
- [原创]JavaScript继承详解
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/sanshi/archive/2009/07/08/1519036.html 面向对象与基于对象 几乎每个开发人员都有面向对象语言(比如C++. ...
- 从mixin到new和prototype:Javascript原型机制详解
从mixin到new和prototype:Javascript原型机制详解 这是一篇markdown格式的文章,更好的阅读体验请访问我的github,移动端请访问我的博客 继承是为了实现方法的复用 ...
- JavaScript数组方法详解
JavaScript数组方法详解 JavaScript中数组的方法种类众多,在ES3-ES7不同版本时期都有新方法:并且数组的方法还有原型方法和从object继承的方法,这里我们只介绍数组在每个版本中 ...
- 「万字图文」史上最姨母级Java继承详解
摘要:继承是面向对象软件技术中的一个概念.它使得复用以前的代码非常容易,能够大大缩短开发周期,降低开发费用. 本文分享自华为云社区<「万字图文」史上最姨母级Java继承详解丨[奔跑吧!JAVA] ...
随机推荐
- string的+操作与StringBuilder对象
习惯在C#代码中写str+="xxx";这样代码的请注意啦,如果这种操作是针对单个变量作很多次叠加操作的,很有可能导致性能降低. 大家都知道string与StringBuilder ...
- python 相关安装和配置
永久链接: http://michaelzqm.iteye.com/blog/1841966 预览文章: python环境搭建 2013-04-04 博客分类: 综合 一. window环境安 ...
- emoji和utf8mb4字符集
mysql 的 utf8 不支持 emoji,需要修改设置为utf8mb4 <?php 'mysql' => [ 'charset' => 'utf8mb4', 'collation ...
- LINQ TO ENTITY 根据Birthday获取Age
from emp in EmployeeInfo let years = EntityFunctions.DiffYears(emp.Birthday.Value,DateTime.Now) let ...
- iOS常用宏 定义
总结了iOS开发过程中的一些常用宏,以后会陆陆续续添加进来. 字符串是否为空 1 #define kStringIsEmpty(str) ([str isKindOfClass:[NSNull c ...
- 第 3 章 MySQL 存储引擎简介
第 3 章 MySQL 存储引擎简介 前言 3.1 MySQL 存储引擎概述 MyISAM 存储引擎是 MySQL 默认的存储引擎,也是目前 MySQL 使用最为广泛的存储引擎之一.他的前身就是我们在 ...
- java ConcurrentModificationException探究
当集合结构被修改,会抛出Concurrent Modification Exception. fail-fast会在以下两种情况下抛出ConcurrentModificationException ( ...
- 基本的文件 I/O
基本的文件 I/O MSDN 抽象基类 Stream 支持读取和写入字节.Stream 集成了异步支持.其默认实现根据其相应的异步方法来定义同步读取和写入,反之亦然. 所有表示流的类都是从 Strea ...
- Android JNI框架图
- sublime返回上一编辑位置
用了sublime好长时间了,最近发现一个python插件可以在编辑的时候返回上一编辑位置,这个功能在eclipse很常用,现在终于能在sublime上使用了.好爽. 贴个地址:https://for ...
