Flask —— 信号(5)
Flask框架中的信号基于blinker,其主要就是让开发者可是在flask请求过程中定制一些用户行为。
pip3 install blinker
1. 内置信号
request_started = _signals.signal('request-started') # 请求到来前执行
request_finished = _signals.signal('request-finished') # 请求结束后执行
before_render_template = _signals.signal('before-render-template') # 模板渲染前执行
template_rendered = _signals.signal('template-rendered') # 模板渲染后执行
got_request_exception = _signals.signal('got-request-exception') # 请求执行出现异常时执行
request_tearing_down = _signals.signal('request-tearing-down') # 请求执行完毕后自动执行(无论成功与否)
appcontext_tearing_down = _signals.signal('appcontext-tearing-down')# 请求上下文执行完毕后自动执行(无论成功与否)
appcontext_pushed = _signals.signal('appcontext-pushed') # 请求上下文push时执行
appcontext_popped = _signals.signal('appcontext-popped') # 请求上下文pop时执行
message_flashed = _signals.signal('message-flashed') # 调用flask在其中添加数据时,自动触发
源码示例
class Flask(_PackageBoundObject):
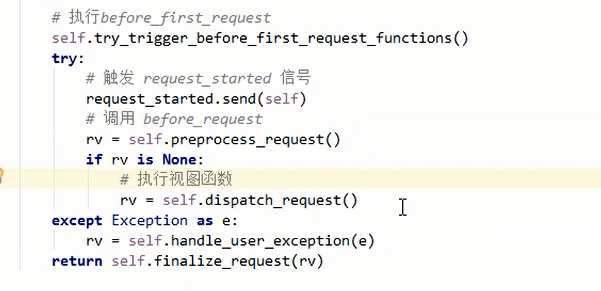
def full_dispatch_request(self):
self.try_trigger_before_first_request_functions()
try:
# ############### 触发request_started 信号 ###############
request_started.send(self)
rv = self.preprocess_request()
if rv is None:
rv = self.dispatch_request()
except Exception as e:
rv = self.handle_user_exception(e)
response = self.make_response(rv)
response = self.process_response(response)
# ############### request_finished 信号 ###############
request_finished.send(self, response=response)
return response
def wsgi_app(self, environ, start_response):
ctx = self.request_context(environ)
ctx.push()
error = None
try:
try:
response = self.full_dispatch_request()
except Exception as e:
error = e
response = self.make_response(self.handle_exception(e))
return response(environ, start_response)
finally:
if self.should_ignore_error(error):
error = None
ctx.auto_pop(error)
request_started
request_started
同上
request_finished
def render_template(template_name_or_list, **context):
"""Renders a template from the template folder with the given
context. :param template_name_or_list: the name of the template to be
rendered, or an iterable with template names
the first one existing will be rendered
:param context: the variables that should be available in the
context of the template.
"""
ctx = _app_ctx_stack.top
ctx.app.update_template_context(context)
return _render(ctx.app.jinja_env.get_or_select_template(template_name_or_list),
context, ctx.app) def _render(template, context, app):
"""Renders the template and fires the signal""" # ############### before_render_template 信号 ###############
before_render_template.send(app, template=template, context=context)
rv = template.render(context) # ############### template_rendered 信号 ###############
template_rendered.send(app, template=template, context=context)
return rv
before_render_template
同上
template_rendered
class Flask(_PackageBoundObject):
def handle_exception(self, e):
exc_type, exc_value, tb = sys.exc_info()
# ############### got_request_exception 信号 ###############
got_request_exception.send(self, exception=e)
handler = self._find_error_handler(InternalServerError())
if self.propagate_exceptions:
# if we want to repropagate the exception, we can attempt to
# raise it with the whole traceback in case we can do that
# (the function was actually called from the except part)
# otherwise, we just raise the error again
if exc_value is e:
reraise(exc_type, exc_value, tb)
else:
raise e
self.log_exception((exc_type, exc_value, tb))
if handler is None:
return InternalServerError()
return handler(e)
def wsgi_app(self, environ, start_response):
ctx = self.request_context(environ)
ctx.push()
error = None
try:
try:
response = self.full_dispatch_request()
except Exception as e:
error = e
# 这里这里这里这里这里这里这里这里这里这里这里这里 #
response = self.make_response(self.handle_exception(e))
return response(environ, start_response)
finally:
if self.should_ignore_error(error):
error = None
ctx.auto_pop(error)
got_request_exception
class AppContext(object):
def push(self):
"""Binds the app context to the current context."""
self._refcnt += 1
if hasattr(sys, 'exc_clear'):
sys.exc_clear()
_app_ctx_stack.push(self)
# ############## 触发 appcontext_pushed 信号 ##############
appcontext_pushed.send(self.app) def pop(self, exc=_sentinel):
"""Pops the app context."""
try:
self._refcnt -= 1
if self._refcnt <= 0:
if exc is _sentinel:
exc = sys.exc_info()[1]
# ############## 触发 appcontext_tearing_down 信号 ##############
self.app.do_teardown_appcontext(exc)
finally:
rv = _app_ctx_stack.pop()
assert rv is self, 'Popped wrong app context. (%r instead of %r)' \
% (rv, self) # ############## 触发 appcontext_popped 信号 ##############
appcontext_popped.send(self.app) class RequestContext(object):
def push(self):
top = _request_ctx_stack.top
if top is not None and top.preserved:
top.pop(top._preserved_exc) app_ctx = _app_ctx_stack.top
if app_ctx is None or app_ctx.app != self.app: # ####################################################
app_ctx = self.app.app_context()
app_ctx.push()
self._implicit_app_ctx_stack.append(app_ctx)
else:
self._implicit_app_ctx_stack.append(None) if hasattr(sys, 'exc_clear'):
sys.exc_clear() _request_ctx_stack.push(self) # Open the session at the moment that the request context is
# available. This allows a custom open_session method to use the
# request context (e.g. code that access database information
# stored on `g` instead of the appcontext).
self.session = self.app.open_session(self.request)
if self.session is None:
self.session = self.app.make_null_session() class Flask(_PackageBoundObject): def wsgi_app(self, environ, start_response): ctx = self.request_context(environ)
ctx.push()
error = None
try:
try:
response = self.full_dispatch_request()
except Exception as e:
error = e
response = self.make_response(self.handle_exception(e))
return response(environ, start_response)
finally:
if self.should_ignore_error(error):
error = None
ctx.auto_pop(error) def pop(self, exc=_sentinel):
app_ctx = self._implicit_app_ctx_stack.pop() try:
clear_request = False
if not self._implicit_app_ctx_stack:
self.preserved = False
self._preserved_exc = None
if exc is _sentinel:
exc = sys.exc_info()[1] # ################## 触发 request_tearing_down 信号 ##################
self.app.do_teardown_request(exc) # If this interpreter supports clearing the exception information
# we do that now. This will only go into effect on Python 2.x,
# on 3.x it disappears automatically at the end of the exception
# stack.
if hasattr(sys, 'exc_clear'):
sys.exc_clear() request_close = getattr(self.request, 'close', None)
if request_close is not None:
request_close()
clear_request = True
finally:
rv = _request_ctx_stack.pop() # get rid of circular dependencies at the end of the request
# so that we don't require the GC to be active.
if clear_request:
rv.request.environ['werkzeug.request'] = None # Get rid of the app as well if necessary.
if app_ctx is not None:
# ####################################################
app_ctx.pop(exc) assert rv is self, 'Popped wrong request context. ' \
'(%r instead of %r)' % (rv, self) def auto_pop(self, exc):
if self.request.environ.get('flask._preserve_context') or \
(exc is not None and self.app.preserve_context_on_exception):
self.preserved = True
self._preserved_exc = exc
else:
self.pop(exc)
request_tearing_down
同上
appcontext_tearing_down
同上
appcontext_pushed
同上
appcontext_popped
def flash(message, category='message'):
"""Flashes a message to the next request. In order to remove the
flashed message from the session and to display it to the user,
the template has to call :func:`get_flashed_messages`. .. versionchanged:: 0.3
`category` parameter added. :param message: the message to be flashed.
:param category: the category for the message. The following values
are recommended: ``'message'`` for any kind of message,
``'error'`` for errors, ``'info'`` for information
messages and ``'warning'`` for warnings. However any
kind of string can be used as category.
"""
# Original implementation:
#
# session.setdefault('_flashes', []).append((category, message))
#
# This assumed that changes made to mutable structures in the session are
# are always in sync with the session object, which is not true for session
# implementations that use external storage for keeping their keys/values.
flashes = session.get('_flashes', [])
flashes.append((category, message))
session['_flashes'] = flashes # ############### 触发 message_flashed 信号 ###############
message_flashed.send(current_app._get_current_object(),
message=message, category=category) message_flashed
message_flashed
执行的流程
a. before_first_request
b. 触发 request_started 信号
c. before_request
d. 模板渲染
渲染前的信号 before_render_template.send(app, template=template, context=context)
rv = template.render(context) # 模板渲染
渲染后的信号 template_rendered.send(app, template=template, context=context)
e. after_request
f. session.save_session()
g. 触发 request_finished信号 如果上述过程出错:
触发错误处理信号 got_request_exception.send(self, exception=e) h. 触发信号 request_tearing_down 由信号引发的源码流程:找扩展点
在请求到来的时候执行信号
from flask import Flask,signals,render_template app = Flask(__name__) # 往信号中注册函数
def func(*args,**kwargs):
print('触发型号',args,kwargs) signals.request_started.connect(func) # 触发信号: signals.request_started.send() @app.before_first_request
def before_first1(*args,**kwargs):
pass
@app.before_first_request
def before_first2(*args,**kwargs):
pass @app.before_request
def before_first3(*args,**kwargs):
pass @app.route('/',methods=['GET',"POST"])
def index():
print('视图')
return render_template('index.html') if __name__ == '__main__':
app.wsgi_app
app.run()
2. 自定义信号
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from flask import Flask, current_app, flash, render_template
from flask.signals import _signals app = Flask(import_name=__name__) # 自定义信号
xxxxx = _signals.signal('xxxxx') def func(sender, *args, **kwargs):
print(sender) # 自定义信号中注册函数
xxxxx.connect(func) @app.route("/x")
def index():
# 触发信号
xxxxx.send('123123', k1='v1')
return 'Index' if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
Flask —— 信号(5)的更多相关文章
- flask信号使用
flask信号: 安装: flask中的信号使用的是一个第三方插件,叫做blinker.通过pip list看一下,如果没有安装,通过以下命令即可安装blinker: pip install blin ...
- 信号(Django信号、Flask信号、Scrapy信号)
简介 Django.Flask.scrapy都包含了一个“信号分配器”,使得当一些动作在框架的其他地方发生的时候,解耦的应用可以得到提醒. 通俗来讲,就是一些动作发生的时候,信号允许特定的发送者去提醒 ...
- 了解Flask 信号机制
Flask框架中的信号基于blinker,其主要就是让开发者可是在flask请求过程中定制一些用户行为. pip3 install blinker 1. 内置信号 request_started = ...
- flask—信号(blinker)
Flask框架中的信号基于blinker,主要是让开发者在flask请求过程中定制一些用户行为. 安装blinker pip3 install blinker 1.内置信号 request_start ...
- 22、Flask实战第22天:Flask信号
Flask中的信号使用的是一个第三方插件blinker.通过pip list看一下是否安装,如果没有,则使用如下命令安装 pip install blinker 自定义信号 自定义信号分为3步: ①定 ...
- flask信号
骚师博客:信号 信号你就可以这么理解,请求比喻成赛车,请求走的流程就是赛车道,而信号坐落在赛车道上的加油站和维修站,信号注册的函数好比维修站的人,每经过维修站并且维修站里有人就进行维修 信号这里理解: ...
- Flask信号流程
首先先我们来看看Flask里面的信号是什么样的,我们可以找到一个叫signals.py的文件 这里面是所有定义了的后面请求流程中会用到的信号 二.哪些地方用到了信号 1.请求app上下文时执行的,在执 ...
- 七十四:flask信号之flask的内置信号
flask所有的内置信号 1.template_rendered:模板渲染完成后的信号2.before_render_template:模板渲染之前的信号3.request_started:模板开始渲 ...
- 七十三:flask信号之信号机制和使用场景
若安装flask是未默认安装blinker,则pip install blinker 使用信号分为3步,第一是定义一个信号,第二是监听一个信号,第三是发送一个信号 1.定义信号:定义信号需要使用到bl ...
随机推荐
- Smobiler 4.0 正式发布
l Smobiler4.0提供了三大技术亮点:第三方插件.JS.自定义控件等: 强大的插件移动应用引擎 Smobiler支持分插件打包功能和插件扩展机制,让应用开发更加灵活. 分插件打包是指Smo ...
- .Net语言 APP开发平台——Smobiler学习日志:如何快速实现Timer计时功能
最前面的话:Smobiler是一个在VS环境中使用.Net语言来开发APP的开发平台,也许比Xamarin更方便 一.目标样式 我们要实现上图中的效果,需要如下的操作: 1.从工具栏上的”Smobil ...
- [转]在node.js中,使用基于ORM架构的Sequelize,操作mysql数据库之增删改查
本文转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/kongxianghai/p/5582661.html Sequelize是一个基于promise的关系型数据库ORM框架,这个库完全采用Ja ...
- 拼多多、饿了么、蚂蚁金服Java面试题大集合
自己当初找工作时参加过众多一线互联网公司的Java研发面试,这段时间处于寒冬,然而前几天跳槽找工作,两天面了3家,已经拿了两个offer,觉得可以和大家分享下: 下面为拼多多.饿了么.蚂蚁金服.哈啰出 ...
- 深入了解浏览器存储:对比Cookie、LocalStorage、sessionStorage与IndexedDB
摘要: 对比Cookie.LocalStorage.sessionStorage与IndexedDB 作者:浪里行舟 Fundebug经授权转载,版权归原作者所有. 前言 随着移动网络的发展与演化,我 ...
- CSS---伪类与伪元素的区别
在CSS中对于伪类和伪元素并没有做出很明显的区别定义,两者的语法是一样的,都是以 : 开头,这样导致我们将一些伪元素误认为伪类,如 :before :after 而在CSS3中给出了明显的定义. ☞ ...
- pthread_exit在main线程中的用处
在main线程中调用pthread_exit会起到只让main线程退出,但是保留进程资源,供其他由main创建的线程使用,直至所有线程都结束,但在其他线程中不会有这种效果 https://stacko ...
- 从零学习Fluter(五):Flutter中手势滑动拖动已经网络请求
从六号开始搞Flutter,到今天写这篇blog已经过了4天时间,文档初步浏览了一遍,写下了这个demo.demo源码分享在github上,现在对flutter有种说不出的喜欢了.大家一起搞吧! 废话 ...
- 章节九、1-Selenium环境配置
一.Selenium环境安装配置,这里使用Selenium WebDriver 3.6.0 1.下载Selenium WebDriver (点击后网站响应比较慢,需要多等等) 2.打开该网址后点击“d ...
- mysql 查询数据中文乱码
解决方式: 数据库连接字符串中添加编码方式:CharSet=utf8
