Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) A B C 水
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
A soldier wants to buy w bananas in the shop. He has to pay k dollars for the first banana, 2k dollars for the second one and so on (in other words, he has to pay i·k dollars for the i-th banana).
He has n dollars. How many dollars does he have to borrow from his friend soldier to buy w bananas?
The first line contains three positive integers k, n, w (1 ≤ k, w ≤ 1000, 0 ≤ n ≤ 109), the cost of the first banana, initial number of dollars the soldier has and number of bananas he wants.
Output one integer — the amount of dollars that the soldier must borrow from his friend. If he doesn't have to borrow money, output 0.
3 17 4
13 题意:第i个香蕉i*k元 买w个香蕉 现在有n元 问需要借多少钱? 题解:k*(1+w)*w/2-n
//code by drizzle
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#define ll __int64
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
int k,n,w;
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d %d",&k,&n,&w);
if(k*(+w)*w/-n<)
cout<<""<<endl;
else
cout<<k*(+w)*w/-n<<endl;
return ;
}
3 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Colonel has n badges. He wants to give one badge to every of his n soldiers. Each badge has a coolness factor, which shows how much it's owner reached. Coolness factor can be increased by one for the cost of one coin.
For every pair of soldiers one of them should get a badge with strictly higher factor than the second one. Exact values of their factors aren't important, they just need to have distinct factors.
Colonel knows, which soldier is supposed to get which badge initially, but there is a problem. Some of badges may have the same factor of coolness. Help him and calculate how much money has to be paid for making all badges have different factors of coolness.
First line of input consists of one integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 3000).
Next line consists of n integers ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ n), which stand for coolness factor of each badge.
Output single integer — minimum amount of coins the colonel has to pay.
4
1 3 1 4
1
5
1 2 3 2 5
2
In first sample test we can increase factor of first badge by 1.
In second sample test we can increase factors of the second and the third badge by 1.
题意:n个数 现在要求这n个数完全不同 并且对于单个数只能增加x或不变
问min(Σ x)
题解:标记每个数的个数 从i=1开始遍历 因为要求每个数只能出现一次所以 对于其余的数
全部加1继承到下一个数 并且更新ans 一直遍历到i=2*3000; 考虑3000个3000的特殊数据;
//code by drizzle
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#define ll __int64
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
int n;
int a[];
int mp[];
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
memset(mp,,sizeof(mp));
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
mp[a[i]]++;
}
int ans=;
for(int i=;i<=;i++)
{
if(mp[i]>)
{
ans+=(mp[i]-);
mp[i+]+=(mp[i]-);
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Two bored soldiers are playing card war. Their card deck consists of exactly n cards, numbered from 1 to n, all values are different. They divide cards between them in some manner, it's possible that they have different number of cards. Then they play a "war"-like card game.
The rules are following. On each turn a fight happens. Each of them picks card from the top of his stack and puts on the table. The one whose card value is bigger wins this fight and takes both cards from the table to the bottom of his stack. More precisely, he first takes his opponent's card and puts to the bottom of his stack, and then he puts his card to the bottom of his stack. If after some turn one of the player's stack becomes empty, he loses and the other one wins.
You have to calculate how many fights will happen and who will win the game, or state that game won't end.
First line contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 10), the number of cards.
Second line contains integer k1 (1 ≤ k1 ≤ n - 1), the number of the first soldier's cards. Then follow k1 integers that are the values on the first soldier's cards, from top to bottom of his stack.
Third line contains integer k2 (k1 + k2 = n), the number of the second soldier's cards. Then follow k2 integers that are the values on the second soldier's cards, from top to bottom of his stack.
All card values are different.
If somebody wins in this game, print 2 integers where the first one stands for the number of fights before end of game and the second one is 1 or 2 showing which player has won.
If the game won't end and will continue forever output - 1.
4
2 1 3
2 4 2
6 2
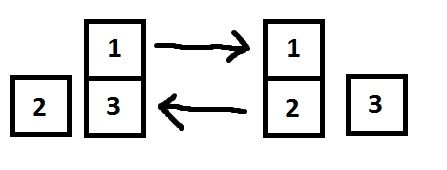
3
1 2
2 1 3
-1
First sample:
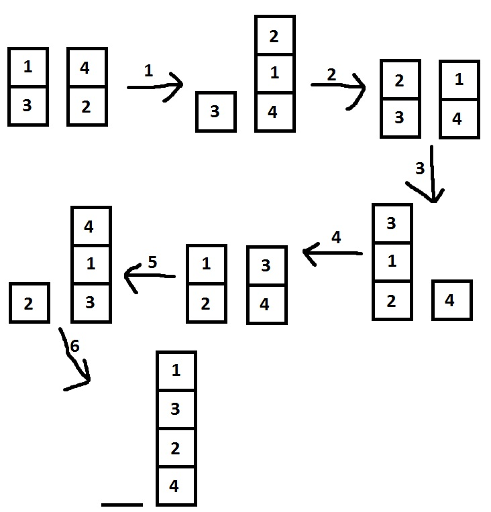
Second sample
题意: 给你初始两个队列 q1 q2 两个队头元素出队x y 比较大小 x>y y,x按照顺序入q1 反之亦然;
不存在x,y相等的情况
当某一个队列为空时 另一个队列获胜 输出游戏进行的回合数和获胜一方的编号1或2
若游戏一直进行无法结束输出-1;
题解:队列模拟整个过程 对于死循环的判断 设置一个回合进行的上限值 超过上限则break 输出-1;
//code by drizzle
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#define ll __int64
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
int n;
int k1,k2;
queue<int> q1;
queue<int> q2;
int exm;
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
scanf("%d",&k1);
while(!q1.empty())
q1.pop();
while(!q2.empty())
q2.pop();
for(int i=;i<=k1;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&exm);
q1.push(exm);
}
scanf("%d",&k2);
for(int i=;i<=k2;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&exm);
q2.push(exm);
}
int ans=;
int out=;
int flag=;
while(flag)
{
if(ans>)
{
cout<<"-1"<<endl;
return ;
}
if(q1.empty())
{
flag=;
out=;
}
if(q2.empty())
{
flag=;
out=;
}
if(flag==)
break;
ans++;
int x=q1.front(),y=q2.front();
q1.pop();
q2.pop();
if(x<y)
{
q2.push(x);
q2.push(y);
}
else
{
q1.push(y);
q1.push(x);
}
}
printf("%d %d\n",ans,out);
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) A B C 水的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) Break the Chocolate 水题
Break the Chocolate Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/546/ ...
- DP+埃氏筛法 Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) D. Soldier and Number Game
题目传送门 /* 题意:b+1,b+2,...,a 所有数的素数个数和 DP+埃氏筛法:dp[i] 记录i的素数个数和,若i是素数,则为1:否则它可以从一个数乘以素数递推过来 最后改为i之前所有素数个 ...
- queue+模拟 Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) C. Soldier and Cards
题目传送门 /* 题意:两堆牌,每次拿出上面的牌做比较,大的一方收走两张牌,直到一方没有牌 queue容器:模拟上述过程,当次数达到最大值时判断为-1 */ #include <cstdio&g ...
- 贪心 Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) B. Soldier and Badges
题目传送门 /* 题意:问最少增加多少值使变成递增序列 贪心:排序后,每一个值改为前一个值+1,有可能a[i-1] = a[i] + 1,所以要 >= */ #include <cstdi ...
- 水题 Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) A. Soldier and Bananas
题目传送门 /* 水题:ans = (1+2+3+...+n) * k - n,开long long */ #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm ...
- 数学+DP Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) D. Soldier and Number Game
题目传送门 /* 题意:这题就是求b+1到a的因子个数和. 数学+DP:a[i]保存i的最小因子,dp[i] = dp[i/a[i]] +1;再来一个前缀和 */ /***************** ...
- Codeforces Round #367 (Div. 2) A. Beru-taxi (水题)
Beru-taxi 题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/706/problem/A Description Vasiliy lives at point (a, b ...
- Codeforces Round #603 (Div. 2) A. Sweet Problem(水.......没做出来)+C题
Codeforces Round #603 (Div. 2) A. Sweet Problem A. Sweet Problem time limit per test 1 second memory ...
- Codeforces Round #334 (Div. 2) A. Uncowed Forces 水题
A. Uncowed Forces Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/604/pro ...
随机推荐
- tk.mybatis Example 多个or条件拼接
//需要的查询条件为 a and (b or c or d) 可以转换为 (a and b) or (a and c) or (a and d) private Example madeExample ...
- C#箴言之用属性来访问类的私有成员
在程序中,难免要访问某个对象的私有成员.那么以前实现这类功能的方法有两种,第一种方法最简单,就是把成员访问符从“private”改为“public”即可:而另一个就是提供公有的成员访问函数来进行访问. ...
- cookie 和 localStorage 、sessionStorage、 session不同
1. cookie:存储大小4k 有时间限制,会跟在ajax的请求头上 2. localStorage: 存储大小5M 没有时间限制 3. sessionStorage: 临时会话存储 当浏览器关闭的 ...
- 洛谷P2468 [SDOI2010]粟粟的书架(二分答案 前缀和 主席树)
题意 题目链接 给出一个矩形,每个点都有一些值,每次询问一个子矩阵最少需要拿几个数才能构成给出的值 Sol 这题是真坑啊.. 首先出题人强行把两个题拼到了一起, 对于前$50 \%$的数据,考虑二分答 ...
- innobackup 参数
innobackupex [--compress] [--compress-threads=NUMBER-OF-THREADS] [--compress-chunk-size=CHUNK-SIZE] ...
- PHP PDO 使用类
PDO类 <?php class MYPDO { protected static $_instance = null; protected $dbName = ''; protected $d ...
- ZendFramework-2.4 源代码 - 关于Module - 模块入口文件
<?php // /data/www/www.domain.com/www/module/Album/Module.php namespace Album; use Zend\ModuleMan ...
- ZendFramework-2.4 源代码 - 关于服务管理器
// ------ 决定“服务管理器”配置的位置 ------ // 1.在模块的入口类/data/www/www.domain.com/www/module/Module1/Module.php中实 ...
- 【PHP】判断变量是否为控
1. isset功能:判断变量是否被初始化 说明:它并不会判断变量是否为空,并且可以用来判断数组中元素是否被定义过注意:当使用isset来判断数组元素是否被初始化过时,它的效率比array_key_e ...
- 06.VUE学习之非常实用的计算属性computed实例
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta http ...
