数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — —第10章:树
- 树的概览
- 树是层级式的集合
- 树中最顶端的节点叫做根
- 个或多个后继(子节点)。
- 没有子节点的节点叫做叶子节点
- 拥有子节点的节点叫做内部节点
- ,其子节点位于层级1,依次类推。一个空树的层级为 -1
- 树的术语
- 术语概览

- 示列
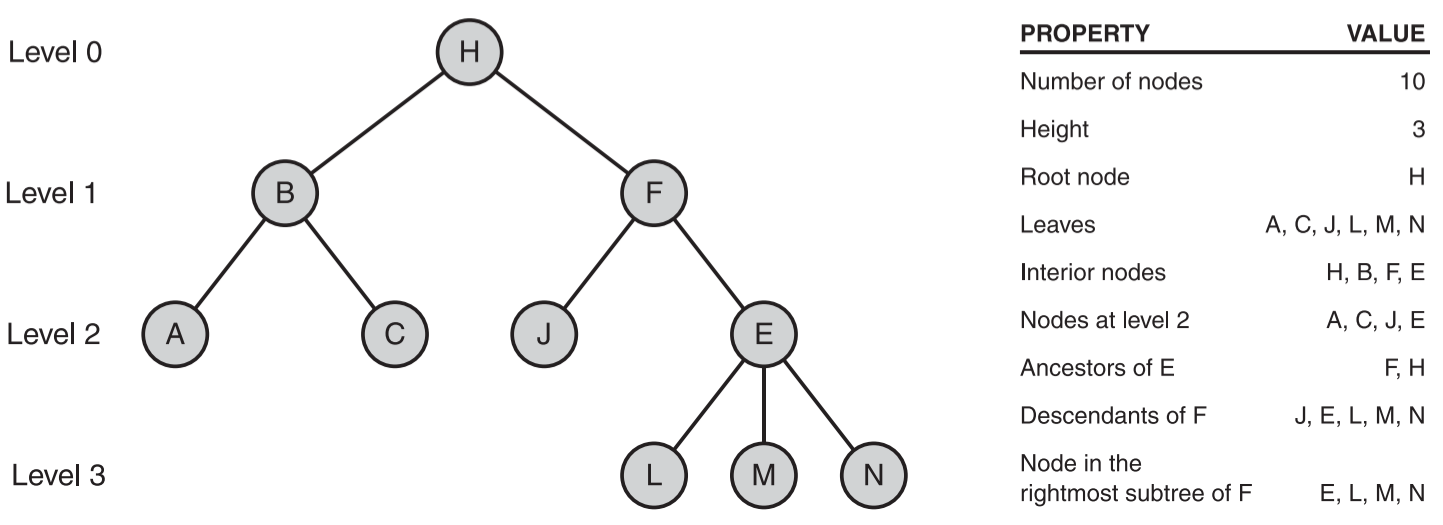
- 普通的树和二叉树
- 二叉树中,每个节点最多只有两个子节点,分别称为左子节点和右子节点
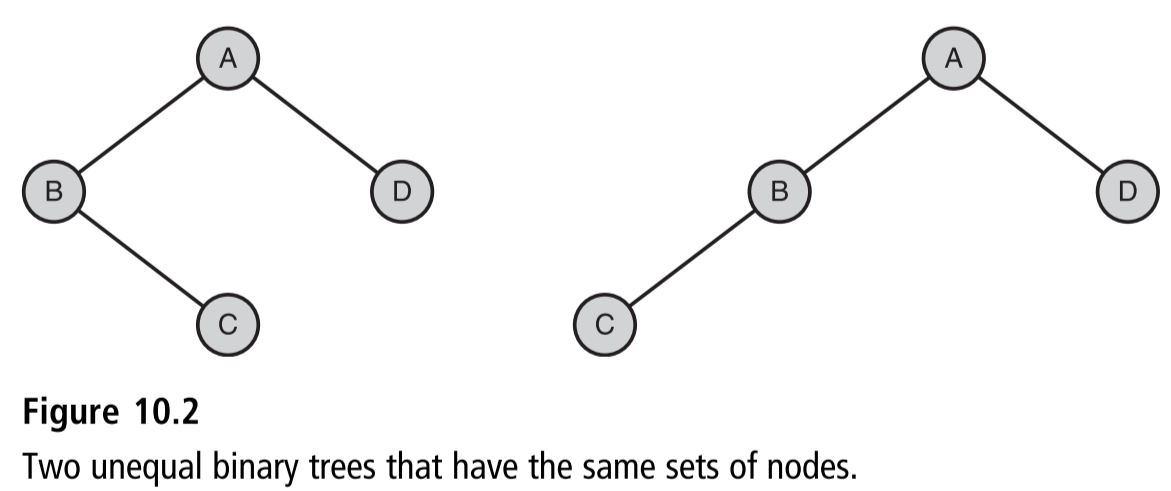
- 树的递归定义
- 普通的树
- 要么为空,要么包含一个有限的节点的集合 T。有一个和所有其他节点不同的节点r,称为根。此外,集合 T - {r}可以被划分为不相边的子集。每个子集都是一个普通的树。
- 二叉树
- 要么为空,要么包含一个根节点,外加一个左子树和一个右子树,每个子树都是一个二叉树
- 为什么要使用树
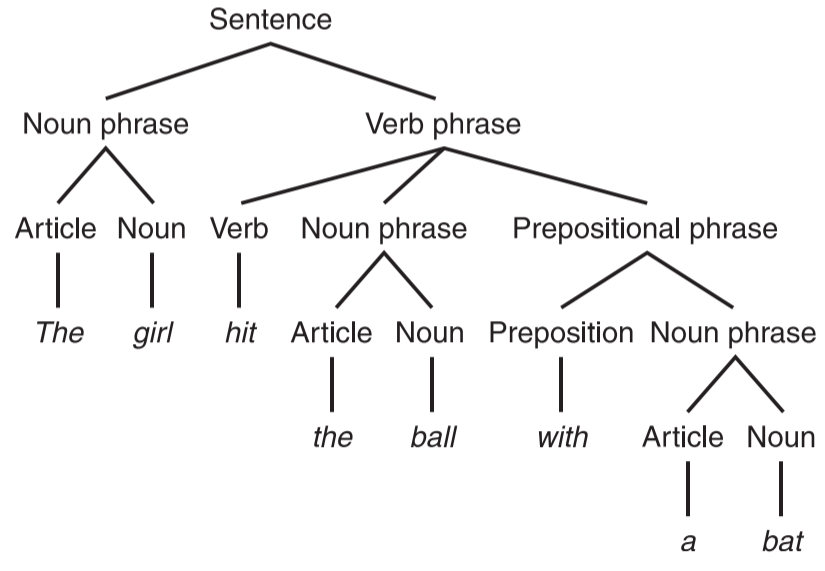
- 示例
- 一个句子的解析树
- 文件的系统结构
- 表示为二叉搜索树的一个有序集合
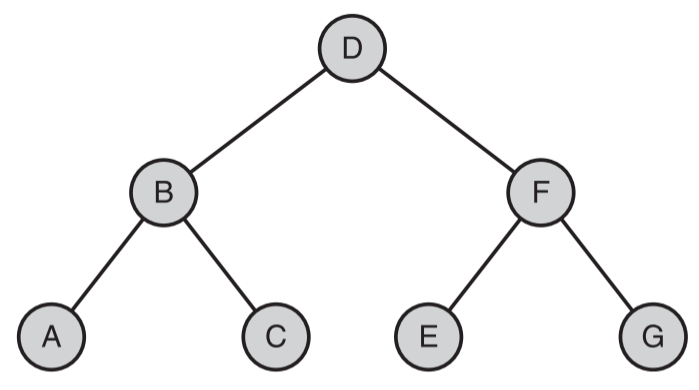
- 这些示例展示了树的一个最重要和有用的功能并不是定位其项,而是父节点和子节点之间的关系。
- 这些关系是结构化的数据的含义所必备的
- 它可能表示字母的顺序、短语的结构、子目录的包含关系,或者给定问题域中的一对多的关系
- 树中的数据的处理,是基于数据之间的父节点/子节点的关系的。
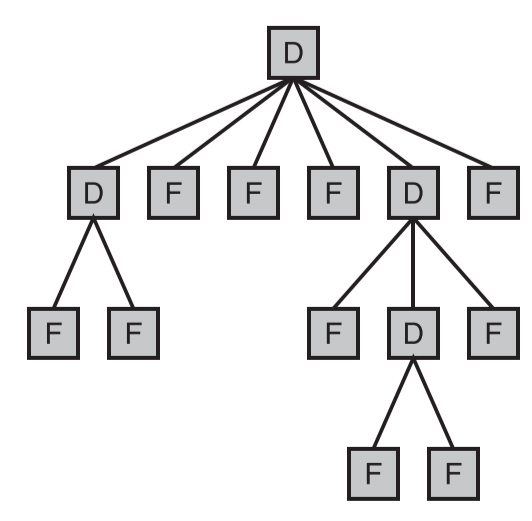
- 二叉树的形状
- 满二叉树
- 特点
- 包含了给定高度 H 下的最大数目的节点
- 在每个层级都包含了完整的节点内容
- 所有的内部节点都有两个子节点
- 所有的叶子节点都在最低的一层
- 示例
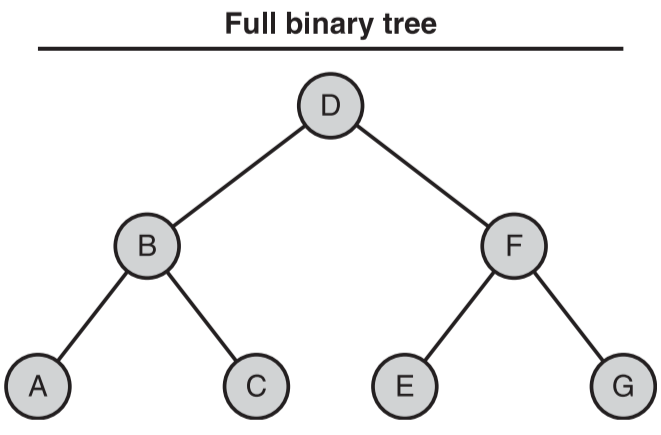
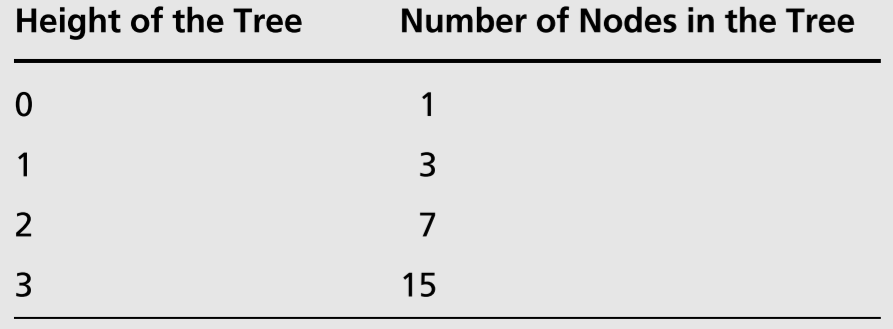
- 满二叉树高度 H 和节点数目 N 的对应关系
- 对应表
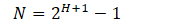
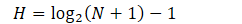
- 访问给定节点所需的最大工作是为

- 完美平衡二叉树
- 特征
- 在最后一个层级以外的每一个层上,都包含了完整的节点
- 其茂盛程序足以支持对叶子节点的访问在最坏的情况下也是对数级的
- 示例
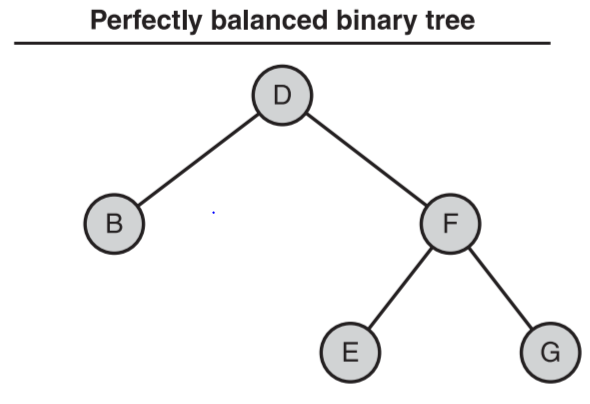
- 完全二叉树
- 特征
- 在最后一个层级以外的每一个层上,都包含了完整的节点
- 最后一层上的所有节点都是从左到右填充的
- 是完美平衡二叉树的一种特殊情况
- 示例
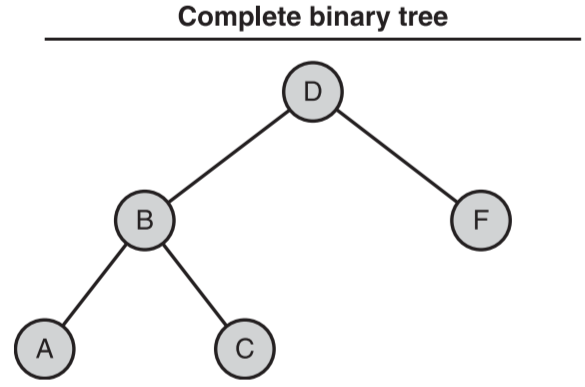
- 不平衡二叉树
- 示例
- 二叉树三种常见应用
- 堆
- 堆属性
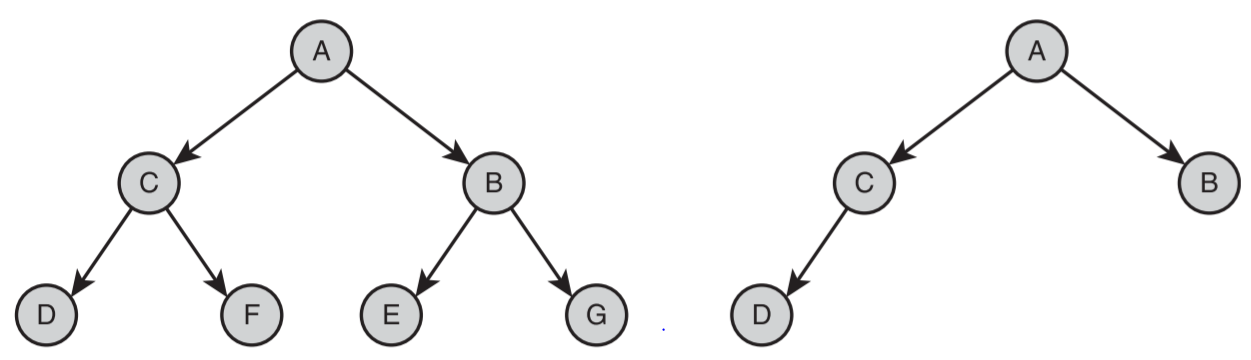
- 最小堆
- 特点
- 每一个节点都小于或等于其两个子节点的一个二叉树
- 最小的项位于根节点,最大的项位于叶子节点
- 示例
- 最大堆
- 特点
- 将最大的节点放置到最靠近根节点的位置
- 应用
- 排序
- 堆排序算法通过数据集来构建堆,然后重复的删除根节点的项,并且将其添加到一个列表的末尾。
- 实现优先队列
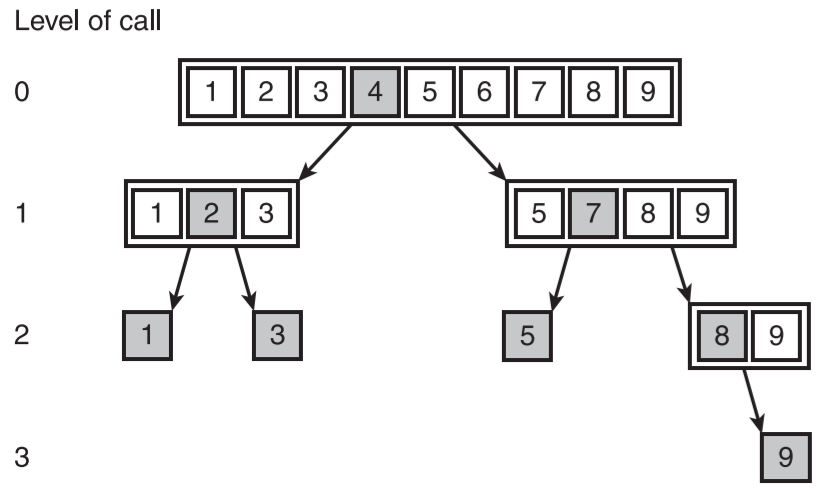
- 二叉搜索树 BST ( binary search tree )
- 特征
- 在一个 BST 中,给定节点的左子树中的节点要小于它,其右子树中的节点要大于给定的节点
- 当 BST 的形状接近于完美平衡二叉树的时候,在最坏的情况下,搜索和插入都是 O( log n )的
- 在最坏的情况下,BST会变为线性的,并且支持线性的搜索
- 示例

- 表达式树
- 转换一种语言中句子的过程,叫做解析。解析可以通过构建解析树来完成,解析树即为表达式树
- 示意图
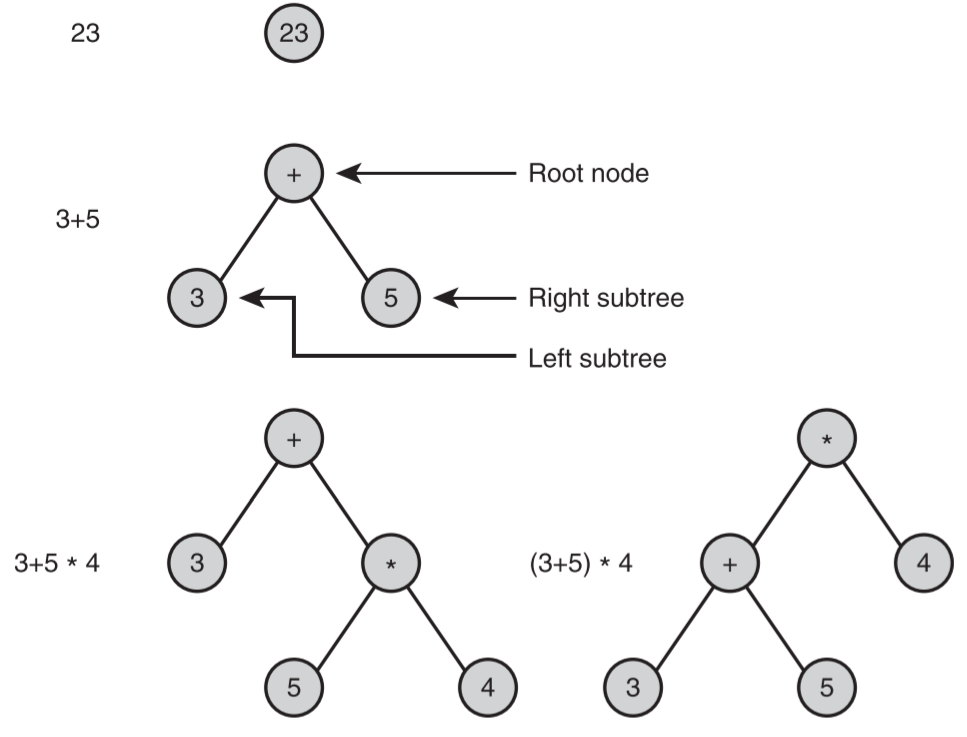
- 表达式树的特点
- 表达式树绝不能为空
- 每个内部节点表示一个复合表达式,包括一个运算符及其运算数。因此,每一个内部节点都一定有 2 个子节点,这两个子节点表示其运算数
- 每一个叶子节点表示一个原子性的、数值性的运算数
- 具有较高优先级的运算数通常出现在靠近树的底部的地方,除非它们在源表达式中被圆括号覆盖了
- 一个表示中缀表达式结构的表达式树,可以执行下述操作
- 求表达式的值
- 求表达式的后缀形式
- 求表达式的前缀形式
- 求表达式的中缀形式
- 二叉树的遍历
- 前序遍历
- 先访问树的根节点,然后以类似的方式分别遍历左子树和右子树
- 示意图
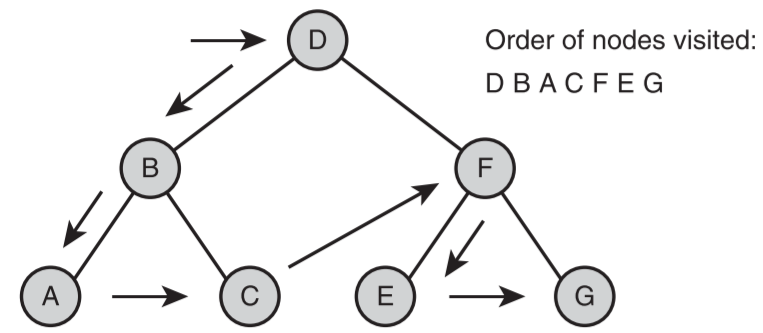
- 中序遍历
- 先遍历左子树,然后访问根节点,最后遍历右子树
- 先尽量移动到树的最左边,然后开始访问节点
- 示意图
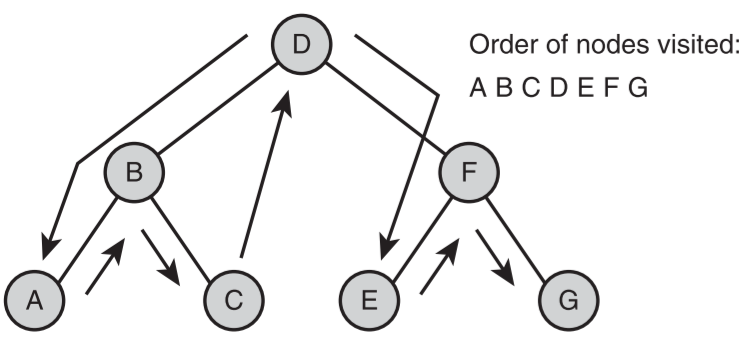
- 后序遍历
- 先遍历左子树,然后是右子树,最后访问根节点
- 示意图
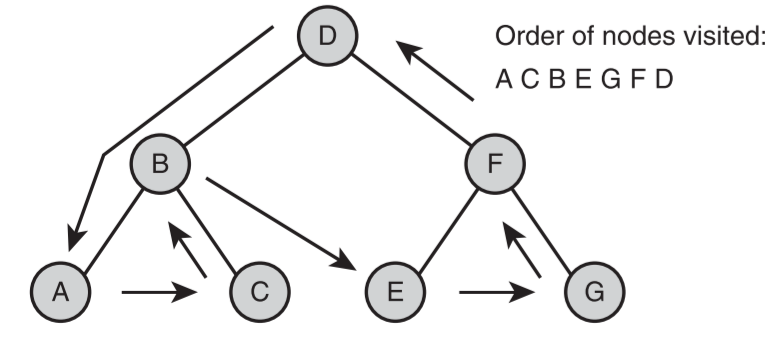
- 层序遍历
- 在每一个层级按照从左到右的顺序访问节点
- 示意图
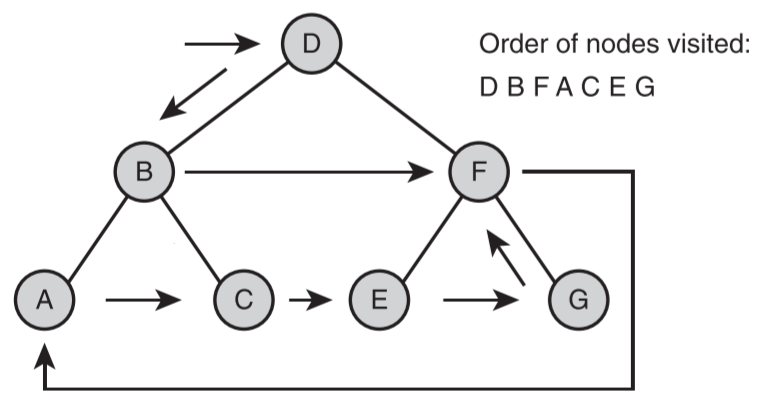
- 总结
- 前、中、后序遍历根据访问根节点的顺序来进行区分
- 中序遍历适合按照排序的顺序来访问二叉树中的项
- 对表达式树进行前序遍历、中序遍历和后序遍历,分别可以得到表达式的前缀、中缀和后缀表达式形式
- 开发二叉搜索树
- 二叉搜索树接口

- 链表实现数据结构
- 初始化
from abstractcollection import AbstractCollection
from bstnode import BSTNode
from arraylist import ArrayList
from linkedqueue import LinkedQueue
from arraystack import ArrayStack
class LinkedBST(AbstractCollection):
"""A link-based binary search tree implementation."""
def __init__(self, sourceCollection=None):
""""Sets the initial state of self, which includes the
contents of sourceCollection, if it's present."""
self._root = None
AbstractCollection.__init__(self, sourceCollection)
- 搜索二叉搜索树
- 借助一个嵌套的递归辅助方法
- 代码
def find(self, item):
"""Return data if item is found or None otherwise."""
# Helper function to search the binary tree
def recurse(node):
if node is None:
return None
elif item == node.data:
return node.data
elif item < node.data:
return recurse(node.left)
else:
return recurse(node.right)
# Top-level call on the root node
return recurse(self._root)
- 遍历二叉搜索树
- 中序遍历和后序遍历可以借助列表和递归的辅助函数来实现,但是需要线性的运行时间和线性的线性的内存使用量
- 中序遍历
def inorder(self):
"""Supports an inorder traversal on a view of self."""
lyst = ArrayList()
def recurse(node):
if node is not None:
recurse(node.left)
lyst.add(node.data)
recurse(node.right)
recurse(self._root)
return iter(lyst)
- 后序遍历
def postorder(self):
"""Supports an postorder traversal on a view of self."""
lyst = ArrayList()
def recurse(node):
if node is not None:
recurse(node.left)
recurse(node.right)
lyst.add(node.data)
recurse(self._root)
return iter(lyst)
- 层序遍历可以借助队列来实现
- 代码
def levelorder(self):
"""Supports an leveloredr traversal on a view of self."""
queue = LinkedQueue()
if self._root is not None:
queue.add(self._root)
while not queue.isEmpty():
node = queue.pop()
yield node.data
if node.left is not None:
queue.add(node.left)
if node.right is not None:
queue.add(node.right)
- 前序遍历可以借助列表和递归的辅助函数来实现,但是需要线性的运行时间和线性的线性的内存使用量后才能访问项。可以使用栈来实现与其它集合相同的遍历方式。
def __iter__(self):
"""Supports an preorder traversal on a view of self."""
stack = ArrayStack()
if self._root is not None:
stack.push(self._root)
while not stack.isEmpty():
node = stack.pop()
yield node.data
if node.right is not None:
stack.push(node.right)
if node.left is not None:
stack.push(node.left)
def preorder(self):
"""Supports a preorder traversal on a view of self."""
return iter(self)
- 二叉搜索树的字符串表示
- 度后输出
- 代码
def __str__(self):
"""Returns a string representation with the tree rotated 90 degrees counterclockwise."""
def recurse(node, level):
s = ""
if node is not None:
)
s += "| " * level
s += str(node.data) + "\n"
)
return s
)
- 输出示例

- 插入项
- 在所有的情况下,项都会添加到叶子节点中
- 代码
def add(self, item):
"""Add item to the tree."""
# Helper function to find the position of the tree
def recurse(node):
if item < node.data:
if node.left is None:
node.left = BSTNode(item)
else:
recurse(node.left)
else:
if node.right is None:
node.right = BSTNode(item)
else:
recurse(node.right)
# If the tree is empty, add the item to its root
if self._root is None:
self._root = BSTNode(item)
else:
recurse(self._root)
- 删除项
- 过程
- 创建一个空的根节点 E,并将原树作为此节点的左子树。如此可以应对原根节点被删除的特殊情况
- 示意图
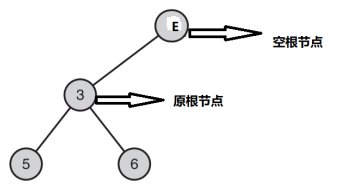
- 找到要删除的节点 A,其父子节点B,以及它们父节点对该节点的引用关系LorR
- 如果该节点有一个左子节点和右子节点,用该节点左子树中的最大值来代替该节点的值,并且从左子树中删除该节点
- 左子树的最大值,即为该子树最右边的值,设其为C,设其父节点为 D
- 使用C的值替代A的值
- 如果 C 为 A 的左子节点(即C没有右子树),即 D 为 A
- 将 A 的左子节点设置为 C 的左子节点
- 否则,C一定为D的一个右子节点,且其没有右子树
- 将 D 的右子节点设置为 C 的左子节点
- 否则,将 B 对 A 的引用,设置为B对 A 的子节点(左子节点或右子节点或为None)的引用
- 将根节点设置为 E 的左子节点
- ,并且返回删除的项
- 代码
def remove(self, item):
"""Precondition: item is in self.
Raise: raise KeyError if item is not in self
PostCondition: item is removed from self."""
# Helper function to lift max item in the left subtree to the top.
def liftMaxInLeftSubtreeToTop(top):
# Replace the top datum with the maximum datum in the left subtree
# Precondition: top has a left child
# Post: The maximum node of the left subtree is removed and top.data = Maximum datum in
# top's left subtree
parent = top
currentNode = top.left
while currentNode.right is not None:
parent = currentNode
currentNode = currentNode.right
top.data = currentNode.data
if parent == top:
top.left = top.left.left
else:
parent.right = currentNode.left
preRoot = BSTNode(None)
preRoot.left = self._root
parent = preRoot
currentNode = preRoot.left
direction = 'L'
removedItem = None
# Try to find the position of the target item, and it's parent node and direction.
while currentNode is not None:
if currentNode.data == item:
removedItem = item
break
parent = currentNode
if item < currentNode.data:
currentNode = currentNode.left
direction = 'L'
else:
currentNode = currentNode.right
direction = 'R'
# If item not in self, raise KeyError
if removedItem is None:
raise KeyError("Item is not in the list.")
# The item is in self, so remove it
# Case 1: the target node has left and right child
# Replace the node'value with the maximum value in left subtree
# Delete the maximum node in the left subtree
if currentNode.left is not None and currentNode.right is not None:
liftMaxInLeftSubtreeToTop(currentNode)
else:
# Case 2: the target node has no left child
if currentNode.left is None:
newChild = currentNode.right
# Case 3: the node has no right child
else:
newChild = currentNode.left
# Case 2 & 3: tie the newChild to the parent
if direction == 'L':
parent.left = newChild
else:
parent.right = newChild
# All cases: Decrement the collection's size counter
# Reset the root
# Returun the removed data
if self.isEmpty():
self._root = None
else:
self._root = preRoot.left
return removedItem
- 二叉搜索树的复杂度分析
- 完美平衡的二叉树,支持对数时间的搜索
- BST和文本之间的互相转换
- 使用中序遍历转换为文本,文本是排好序后,再还原为 BST,即为线性形状的树
- 使用前序遍历转换为文本,再还原为 BST,会你保留树的形状
- 递归的后代解析和编程语言
- 巴科斯范式 ( Extended Backus-Naur Form,EBNF )语法
- 算术表达式语法示例
expression = term { addingOperator term }
term = factor { multiplyOperator factor }
factor = number | "(" expression ")"
number = digit { digit }
digit = "0" | "1" | "2" | "3" | "4" | "5" | "6" | "7" | "8" | "9"
addingOperator = "+" | "-"
multiplyOperator = "*" | "/"
- 终结符号
- 位于语言的词汇表中,并且直接出现在语言的程序之中,例如示例中的"+" 和"*"
- 非终结符号
- 这些符号在语言中命名短语,例如示例中的expression或 factor。短语通常包含一个或多个终结符号或其他短语的名称
- 元符号
- 用来组织语法中的规则
符号
用法
""
包括字面值项
=
表示定义为
[ ]
包含可选的项(零个或一个)
{ }
包含零个或多个项
( )
将必须的选项组织在一起(和圆括号相同)
|
表示是可选的
- 开始标记
- 在示例中,开始标记为expression
- 语法中包含有递归的特性
- 示例中 expression 中包含term,term中包含 factor,factor中可能包含放在圆括号中的 expression,即一个 expression 中可能包含另外一个 expression
- 在语言中识别、解析和解释句子
- 识别器(recognizer)
- 分析字符串,以确定这是否是给定语言中的一个句子
- 解析器(parser)
- 拥有识别器所有的功能,并且返回了一个包含有关语法的信息以及该句子的语意结构的解析树
- 识别器和解析器一般统称为解析器
- 解释器(interpreter)
- 执行由句子所指定的动作
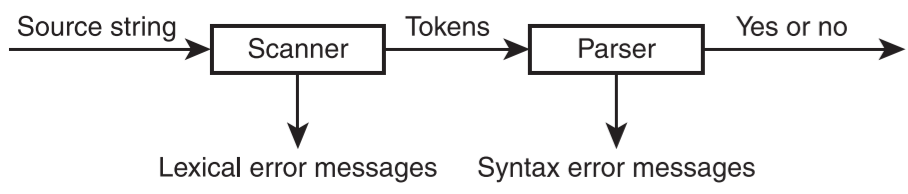
- 词法分析和扫描器
- 扫描器(scanner)
- 执行词法分析,该分析从一个字符流中挑选出单个的单词,输出的是单词(标记)流
- 会输出词法错误信息
- 一个数字中不正确的字符
- 无法识别的符号
- 解析器
- 语法分析器,确定单词组合起来是否形成了正确的句子
- 示意图
- 解析策略
- 递归下降分析
- 为语法中的每一个规则都定义了一个函数,每个函数处理输入句子中符合其规则的短语或部分
- 示例
# Synatx rule:
# expression = term [ addingOperator term ]
# Parsing function
def expression():
term()
token = scanner.get()
while token.getType() in (Token.PLUS, Token.MINUS):
scanner.next()
term()
token = scanner.get()
- 注意事项
- 语法中的每一个非终结符号,在解析中都变成了一个函数的名称
- 函数体处理规则的右端的短语
- 要处理非终结符号,直接调用一个函数
- 要处理可选的项,使用 if 语句
- 通过在解析器对象上调用get方法,来观察当前的标记
- 通过在解析器对象上调用next方法,来扫描下一个标记
- 解析器沿着语法规则下降。从顶端函数开始,并且一路处理到较低端的函数,较低端的函数随后递归调用较高端的函数
- 案例学习:解析和表达式树
- 要求
- 编写一个程序,其使用表达式树来计算表达式,并且将其转换为可替代的形式
- 分析
- 由于表达式树一定不为空,因此它自身会支持一种非常优雅的调用过程
- 解析系统的类及其之间的关系
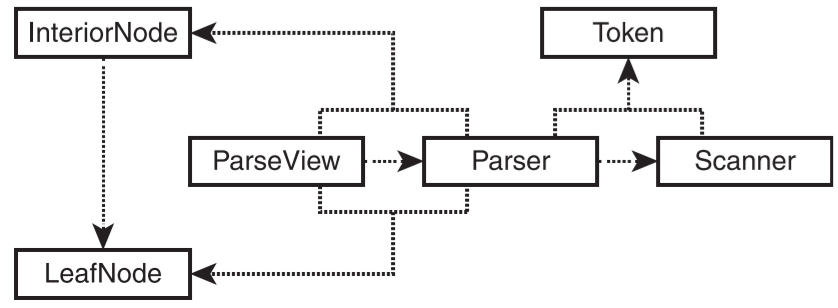
- 节点类的设计和实现
- 表达式树的构建
- 叶子节点,其中只包含一个数字
- 内部节点,其值是一个运算符,并且其左子树和右子树都是表示运算数表达式的节点
- 代码
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author:Lijunjie
"""
File: expressiontree.py
"""
class LeafNode(object):
"""Represent an integer"""
def __init__(self, data):
self._data = data
def value(self):
return self._data
def __str__(self):
return str(self._data)
def prefix(self):
return str(self)
def infix(self):
return str(self)
def postfix(self):
return str(self)
class InteriorNode(object):
"""Represent an operator and its two operands"""
def __init__(self, op, leftOper, rightOper):
self._operator = op
self._leftOperand = leftOper
self._rightOperand = rightOper
def value(self):
if self._operator == "-":
return self._leftOperand.value() - self._rightOperand.value()
elif self._operator == "+":
return self._leftOperand.value() + self._rightOperand.value()
elif self._operator == "/":
return self._leftOperand.value() // self._rightOperand.value()
elif self._operator == "*":
return self._leftOperand.value() * self._rightOperand.value()
def prefix(self):
return self._operator + " " + \
self._leftOperand.prefix() + " " + \
self._rightOperand.prefix()
def infix(self):
return "(" + self._leftOperand.infix() + " " + \
self._operator + " " + \
self._rightOperand.infix() + ")"
def postfix(self):
return self._leftOperand.postfix() + " " + \
self._rightOperand.postfix() + " " + \
self._operator
def main():
"""A simple test program."""
)
))
c = InteriorNode("*", a, b)
c = InteriorNode("-", c, b)
print("Expect ((4 * (2 + 3)) - (2 + 3)) :", c.infix())
print("Expect - * 4 + 2 3 + 2 3 :", c.prefix())
print("Expect 4 2 3 + * 2 3 + - :", c.postfix())
print("Expect 15 :", c.value())
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
- 解析器类的设计和实现
- 采用递归下降策略的解析器
- 代码
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author:Lijunjie
"""
File: parsers.py
"""
from scanner import Scanner
from tokens import Token
from expressiontree import LeafNode, InteriorNode
class Parser(object):
"""Defines parser."""
def parser(self, sourceStr):
self._completionMessage = "No errors"
self._parseSuccessful = True
self._scanner = Scanner(sourceStr)
tree = self._expression()
self._accept(self._scanner.get(), Token.EOE, "symbol after end of expression.")
return tree
def parseStatus(self):
return self._completionMessage
def _accept(self, token, expected, errorMessage):
if token.getType() != expected:
self._fatalError(token, errorMessage)
def _fatalError(self, token, errorMessage):
self._parseSuccessful = False
self._completionMessage = "Parsing error -- " + \
errorMessage + \
"\n Expression so far = " + \
self._scanner.stringToCurrentToken()
raise Exception(self._completionMessage)
def _expression(self):
"""Synatx rule: expression = term { addingOperator term }"""
tree = self._term()
token = self._scanner.get()
while token.getType() in (Token.PLUS, token.MINUS):
op = str(token)
self._scanner.next()
tree = InteriorNode(op, tree, self._term())
token = self._scanner.get()
return tree
def _term(self):
"""Synatx rule: term = factor { multiplyOperator factor }"""
tree = self._factor()
token = self._scanner.get()
while token.getType() in (Token.MUL, Token.DIV):
op = str(token)
self._scanner.next()
tree = InteriorNode(op, tree, self._factor())
token = self._scanner.get()
return tree
def _factor(self):
"""Synatx rule: factor = number | "(" expression ")" """
token = self._scanner.get()
if token.getType() == Token.INT:
tree = LeafNode(token.getValue())
self._scanner.next()
elif token.getType() == Token.L_PAR:
self._scanner.next()
tree = self._expression()
self._accept(self._scanner.get(), Token.R_PAR, "')' expected")
self._scanner.next()
else:
tree = None
self._fatalError(token, "bad factor")
return tree
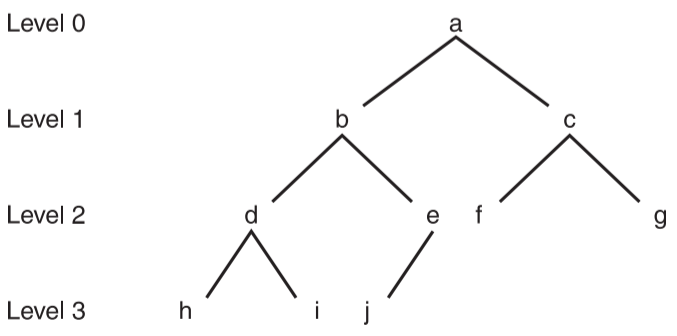
- 二叉树的数组实现
- 一个完全二叉树可以很方便的通过数组来实现
- 将完全二叉树按照层序遍历的方式存储进数组中
- 示例
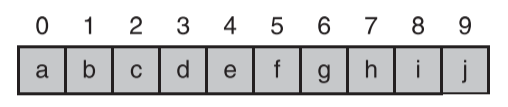
- 完全二叉树数组表示中项的位置

- 实现堆
- 堆是一种二叉树,其中较小的项接近于根节点。可以用堆来实现 的堆排序算法和优先队列

- 堆接口中的方法

- 堆可以基于数组的列表来实现
- add方法
- 策略
- 将项A添加到堆的底部,即列表的尾部
- 然后进入循环,只要A小于其父节点的值,就让A往上走,直到到达顶部
- 代码
def add(self, item):
"""Add an item to the heap"""
self._heap.add(item)
:
parentItem = self._heap[parent]
if item >= parentItem:
break
else:
self._heap[curPos] = parentItem
self._heap[parent] = item
curPos = parent
- pop方法
- 策略
- 保留堆的根节点的值A,弹出堆的底部节点值B(即列表的最后一个值),并将B放置在堆的根节点
- 从堆的顶部往下走,如果下一层的最小值C大于等于 B,则停止。否则,交换B和 C 的值,然后让B继续向下走
- 代码
def pop(self):
"""Pop and return the root item of the heap
Precondition: self is not empty
Raise: Exception Error if self is empty"""
if self.isEmpty():
raise Exception("Heap is empty.")
]
)
:
return bottomItem
] = bottomItem
while True:
if leftChild > lastIndex:
break
elif rightChild > lastIndex:
minChild = leftChild
else:
leftItem = self._heap[leftChild]
rightItem = self._heap[rightChild]
if leftItem < rightItem:
minChild = leftChild
else:
minChild = rightChild
minItem = self._heap[minChild]
if bottomItem <= minItem:
break
else:
self._heap[curPos] = minItem
self._heap[minChild] = bottomItem
curPos = minChild
return topItem
- __iter__方法
- pop方法每次弹出的均是最小值,因此可以借助pop方法来实现从小到大的遍历
- 代码
def __iter__(self):
"""Supports ascending order traversal on a view of self."""
tempList = ArrayList(self._heap)
resultList = ArrayList()
while not self.isEmpty():
resultList.add(self.pop())
self._heap = tempList
self._size = len(self._heap)
return iter(resultList)
- 总代码
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author:Lijunjie
"""
File: arrayheap.py
"""
from abstractcollection import AbstractCollection
from arraylist import ArrayList
class ArrayHeap(AbstractCollection):
"""An array-based heap implementation"""
def __init__(self, sourceCollecton=None):
"""Sets the initial state of self, which includes the contents
of sourceCollection, if it's present."""
self._heap = ArrayList()
AbstractCollection.__init__(self, sourceCollecton)
# Accessor method
def __str__(self):
"""Returns a string representation with the tree rotated 90 degrees counterclockwise."""
def strHelper(index, level):
s = ""
if index < len(self):
)
s += "| " * level + str(self._heap[index]) + "\n"
)
return s
)
def __iter__(self):
"""Supports ascending order traversal on a view of self."""
tempList = ArrayList(self._heap)
resultList = ArrayList()
while not self.isEmpty():
resultList.add(self.pop())
self._heap = tempList
self._size = len(self._heap)
return iter(resultList)
# Mutator method
def add(self, item):
"""Add an item to the heap"""
# Add the item to the end of the array, and move it forward to its right position
self._heap.add(item)
:
parentItem = self._heap[parent]
if item >= parentItem:
break
else:
self._heap[curPos] = parentItem
self._heap[parent] = item
curPos = parent
def pop(self):
"""Pop and return the root item of the heap
Precondition: self is not empty
Raise: Exception Error if self is empty"""
if self.isEmpty():
raise Exception("Heap is empty.")
# Exchange the top and bottom item, then pop the bottom item, and move the top item
# to its right position.
]
)
:
return bottomItem
] = bottomItem
while True:
if leftChild > lastIndex:
break
elif rightChild > lastIndex:
minChild = leftChild
else:
leftItem = self._heap[leftChild]
rightItem = self._heap[rightChild]
if rightItem >= leftItem:
minChild = leftChild
else:
minChild = rightChild
minItem = self._heap[minChild]
if minItem >= bottomItem:
break
else:
self._heap[curPos] = minItem
self._heap[minChild] = bottomItem
curPos = minChild
return topItem
def peek(self):
"""Return the root item of the heap
Precondition: self is not empty
Raise: Exception Error if self is empty"""
if self.isEmpty():
raise Exception("Heap is empty.")
]
def main():
"""A simple test program"""
heap = ArrayHeap()
print("Adding D B A C F E G")
heap.add("D")
heap.add("B")
heap.add("A")
heap.add("C")
heap.add("F")
heap.add("E")
heap.add("G")
print("\nPeek:", heap.peek())
print("\nString:\n" + str(heap))
print("\nfor loop: ")
for item in heap:
print(item, end=" ")
print("\n\nRemovals: ")
while not heap.isEmpty(): print(heap.pop(), end=" ")
))
print("\n\nHeap with 1..7:")
print(heap)
print("\nfor loop: ")
for item in heap:
print(item, end=" ")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — —第10章:树的更多相关文章
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — —第9章:列表
概念 列表是一个线性的集合,允许用户在任意位置插入.删除.访问和替换元素 使用列表 基于索引的操作 基本操作 数组与列表的区别 数组是一种具体的数据结构,拥有基于单个的物理内存块的一种特定的,不变的实 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第7章:栈
栈概览 栈是线性集合,遵从后进先出原则( Last - in first - out , LIFO )原则 栈常用的操作包括压入( push ) 和弹出( pop ) 栈的应用 将中缀表达式转换为后缀 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第5章:接口、实现和多态
接口 接口是软件资源用户可用的一组操作 接口中的内容是函数头和方法头,以及它们的文档 设计良好的软件系统会将接口与其实现分隔开来 多态 多态是在两个或多个类的实现中使用相同的运算符号.函数名或方法.多 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第3章:搜索、排序和复杂度分析
评估算法的性能 评价标准 正确性 可读性和易维护性 运行时间性能 空间性能(内存) 度量算法的运行时间 示例 """ Print the running times fo ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第4章:数据和链表结构
数据结构是表示一个集合中包含的数据的一个对象 数组数据结构 数组是一个数据结构 支持按照位置对某一项的随机访问,且这种访问的时间是常数 在创建数组时,给定了用于存储数据的位置的一个数目,并且数组的长度 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — —第11章:集和字典
使用集 集是没有特定顺序的项的一个集合,集中的项中唯一的 集上可以执行的操作 返回集中项的数目 测试集是否为空 向集中添加一项 从集中删除一项 测试给定的项是否在集中 获取两个集的并集 获取两个集的交 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第1章:Python编程基础
变量和赋值语句 在同一条赋值语句中可以引入多个变量 交换变量a 和b 的值 a,b = b,a Python换行可以使用转义字符\,下一行的缩进量相同 )\ 帮助文档 help() 控制语句 条件式语 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第2章:集合概览
集合类型 定义 个或多个其他对象的对象.集合拥有访问对象.插入对象.删除对象.确定集合大小以及遍历或访问集合的对象的操作 分类 根据组织方式进行 线性集合 线性集合按照位置排列其项,除了第一项,每一项 ...
- 数据结构( Pyhon 语言描述 ) — — 第8章:队列
队列概览 队列是线性的集合 队列的插入限制在队尾,删除限制在队头.支持先进先出协议( FIFIO, first-in first-out ) 两个基本操作 add:在队尾添加一项 pop:从队头弹出一 ...
随机推荐
- Tinghua Data Mining 5
ID3 ID3算法倾向于分的很细的变量 C4.5加入分母为惩罚量
- laravel之null替换空字符串中间件
在laravel写接口的时候免不了数据库中保存null,可用诸如设置ORM的访问器或以下方法处理 $goods->name?$goods->name:''; 其实可以利用路由中间件,在需要 ...
- robot framework 在pycharm中语法无法高亮显示的,显示绿色解决办法(Robot Framework with PyCharm)
Robot Framework with PyCharm up vote1down votefavorite 1 I am totally new to automation and trying t ...
- @Results( 中 params 怎么用
http://blog.csdn.net/z69183787/article/details/16342553 struts2的@Result annotation 如何添加params,并且在页面取 ...
- 现在的Unix时间戳(Unix timestamp)
如何在不同编程语言中获取现在的Unix时间戳(Unix timestamp)? Java time JavaScript Math.round(new Date().getTime()/1000)ge ...
- 前端之css(宽高)设置小技巧
一.css宽高自适应: 1.宽度自适应: 元素宽度设为100%(块状元素的默认宽度为100%) 注:应用在通栏效果中 2.高度自适应: height:auto;或者不设置高度 3.最小,最大高度,最小 ...
- vue2.0:(二)、mock数据
什么是mock数据呢?很多情况下,后台的搭建比起前端来说要麻烦的多,所以,常常是前端写好了页面以后后台接口却没有写好,但是在一个项目中,接口调试确实是最浪费时间的,所以,往往前端需要自己模拟数据. 第 ...
- vue-cli脚手架(框架)
一.创建vue项目 npm install vue-cli -g #-g全局 (sudo)npm install vue-cli -g #mac笔记本 vue-init webpack myvue # ...
- vue样式操作与事件绑定
Vue笔记 1 Vue实例 (VM) var vm = new Vue({ el:'#app', //挂载元素 //数据 data: { title:'值', ...
- linux各文件夹的作用(转)
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/amboyna/archive/2008/02/16/1070474.html linux下的文件结构,看看每个文件夹都是干吗用的/bin 二进制可 ...
