Spring中argNames的含义
最近学习Spring,一直不太明白Srping的切面编程中的的argNames的含义,经过学习研究后,终于明白,分享一下
先看一个例子:
需要监控的类:
package bean;
public class HelloApi {
public void aspectTest(String a,String b){
System.out.println("in aspectTest:" + "a:" + a + ",b:" + b);
}
}
类HelloApi的aspectTest方法是需监控的方法,目标是调用前获取获得入参a和b的值,并打印出来。
切面类:
package aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.lang.String; @Component
@Aspect
public class HelloApiAspect2 { @Pointcut(value="execution(* bean.HelloApi.aspectTest(..)) && args(a1,b2)",argNames="a1,b2")
public void pointcut1(String a1,String b2){} @Before(value="pointcut1(a,b)",argNames="a,b")
public void beforecase1(String a,String b){
System.out.println("1 a:" + a +" b:" + b);
}
//注意和beforecase1的区别是argNames的顺序交换了
@Before(value="pointcut1(a,b)",argNames="b,a")
public void beforecase2(String a,String b){
System.out.println("2 a:" + a +" b:" + b);
} }
测试类:
package UnitTest; import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import bean.HelloApi; public class Test1 { @Test
public void aspectjTest1(){
BeanFactory beanFactory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("chapter2/aspectTest1.xml");
HelloApi helloapi1 = beanFactory.getBean("helloapi1",HelloApi.class);
helloapi1.aspectTest("a", "b");
}
}
Spring的配置文件aspectTest.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="aspect"></context:component-scan> <bean id="helloapi1" class="bean.HelloApi"></bean>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
</beans>
输出:
2 a:b b:a
1 a:a b:b
in aspectTest:a:a,b:b
说明:
HelloApiAspect2定义了一个切面pointcut,切面表达式是execution(* bean.HelloApi.aspectTest(..)) && args(a1,b2),表示配对bean.HelloApi.aspectTest()方法,并且传入参数是2个。
args(a1,b2)另外一个作用,就是定义了aspectTest(String a,String b)方法对应表达式args(a1,b2)。定义了args(a1,b2),才能把目标方法aspectTest的参数传入到切面方法beforecase1的参数中,a参数对应a1,b参数对应b2。使用的方法是按顺序一一对应,aspectTest第一个参数对args第一个参数,aspectTest第2个参数对args第2个参数.
argNames是可选的,如果没有argNames这个参数,而编译器设置了【在class文件生成变量调试信息】,则spring可以通过反射知道方法参数的名字,通过名字配对,Spring知道args(a1,b2)表达式里面的a1和b2,对应了pointcut1(String a1,String b2)方法里面的a1和b2。
目标方法和切入方法的参数的关系是这样确立的:aspectTest(String a,String b) 与 args(a1,b2)关系是a对a1,b对b2(),args(a1,b2)与pointcut1(String a1,String b2)关系是args的a1对pointcut1的a1,args的a2对pointcut1的a2。解决了目标方法参数传入到切入方法参数的问题。
但是,如果设置了argNames,Spring不再使用方法参数的名字来配对,使用argNames定义的顺序来定义pointcut1(String a1,String b2)的顺序,例如:argNames="a1,b2",a1在b2前面,表示pointcut1方法第一个参数是a1,第二个参数是b2。
既然不设置argNames,Spring可以根据参数名字进行配对,为什么还需要配置argNames?因为Spring要知道方法的参数名,编译器必须设置了【在class文件生成变量调试信息】,如果没有设置,Spring就不知道pointcut1方法的参数名了,这个时候,Spring只知道参数的类型,Spring会使用参数的类型进行配对,如果出现2个参数都是同一个类型的情况,就会报AmbiguousBindingException异常。
beforecase1和beforecase2的argNames设置的顺序交换了,调用beforecase1的顺序是beforecase1("a","b"),调用beforecase2的顺序是beforecase2("b","a"),所以最后的输出是
2 a:b b:a
1 a:a b:b
PS:
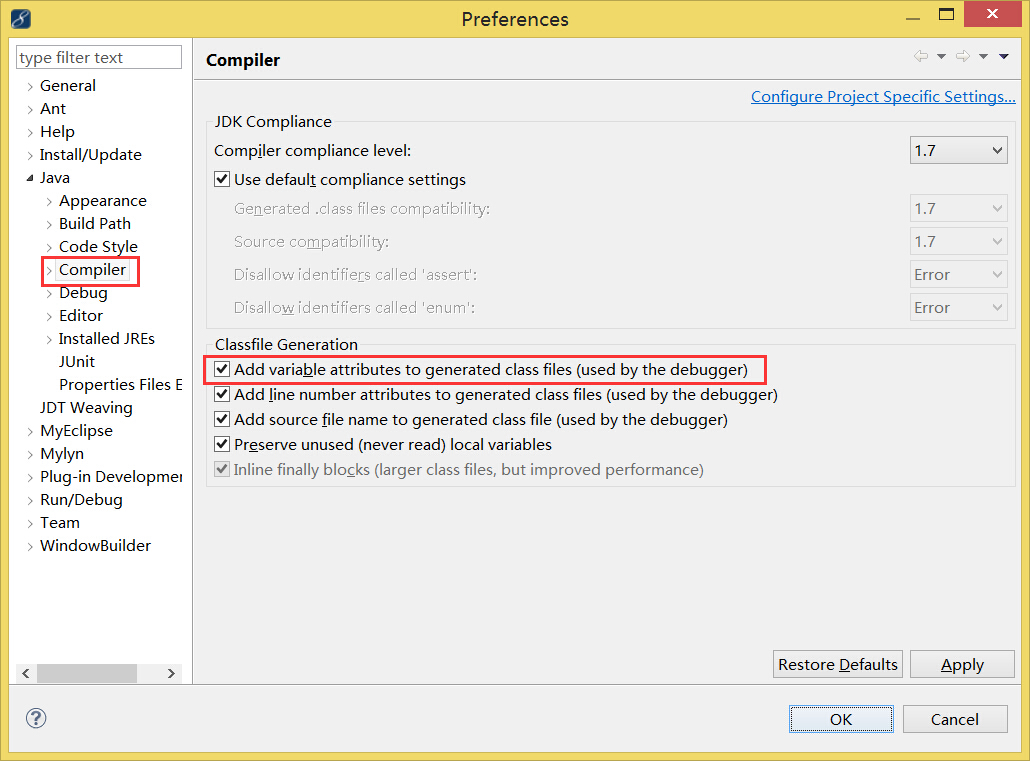
【class文件中生成变量调试信息】在myeclipse中打开windows-》preferences,设置如下:
Spring中argNames的含义的更多相关文章
- 深入理解spring中的各种注解
Spring中的注解大概可以分为两大类: 1)spring的bean容器相关的注解,或者说bean工厂相关的注解: 2)springmvc相关的注解. spring的bean容器相关的注解,先后有:@ ...
- 简单解析依赖注入(控制反转)在Spring中的应用
IoC——Inversion of Control 控制反转DI——Dependency Injection 依赖注入 大家都知道,依赖注入是Spring中非常重要的一种设计模式.可能很多初学者 ...
- Spring中的事务管理
事务简介: 事务管理是企业级应用程序开发中必不可少的技术,用来确保数据的完整性和一致性 事务就是一系列的动作,它们被当作一个单独的工作单元.这些动作要么全部完成,要么全部不起作用 事务的四个关键属性( ...
- Spring中的事务管理详解
在这里主要介绍Spring对事务管理的一些理论知识,实战方面参考上一篇博文: http://www.cnblogs.com/longshiyVip/p/5061547.html 1. 事务简介: 事务 ...
- 深入理解spring中的各种注解(转)
Spring中的注解大概可以分为两大类: 1)spring的bean容器相关的注解,或者说bean工厂相关的注解: 2)springmvc相关的注解. spring的bean容器相关的注解,先后有:@ ...
- Spring 中使用Quartz实现任务调度
前言:Spring中使用Quartz 有两种方式,一种是继承特定的基类:org.springframework.scheduling.quartz.QuartzJobBean,另一种则不需要,(推荐使 ...
- 剑指Offer——企业级项目中分层的含义与依据及多态的优势
剑指Offer--企业级项目中分层的含义与依据及多态的优势 关于以上两点,由于项目经验较少,自己不是很明白,特整理如下. 常见分层架构模式 三层架构 3-tier architecture 微 ...
- Spring中的AOP 专题
Caused by: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: ProceedingJoinPoint is only supported for around advi ...
- 框架源码系列十:Spring AOP(AOP的核心概念回顾、Spring中AOP的用法、Spring AOP 源码学习)
一.AOP的核心概念回顾 https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/5.1.3.RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/core.html#a ...
随机推荐
- gcc的使用
为了防止无良网站的爬虫抓取文章,特此标识,转载请注明文章出处.LaplaceDemon/ShiJiaqi. http://www.cnblogs.com/shijiaqi1066/p/6065410. ...
- Java 线程的状态
Java Thread的运行周期中, 有几种状态, 在 java.lang.Thread.State 中有详细定义和说明: NEW 状态是指线程刚创建, 尚未启动 RUNNABLE 状态是线程正在正常 ...
- Guzzle Unable to parse JSON data: JSON_ERROR_SYNTAX - Syntax error, malformed JSON
项目更新到正式平台时,出现Guzzle(5.3) client get请求出现:Unable to parse JSON data: JSON_ERROR_SYNTAX - Syntax error, ...
- 介绍map.entry接口
Map是java中的接口,Map.Entry是Map的一个内部接口.java.util.Map.Entry接口主要就是在遍历map的时候用到. Map提供了一些常用方法,如keySet().entry ...
- Spring的servlet context和application context
Spring lets you define multiple contexts in a parent-child hierarchy. The applicationContext.xml def ...
- java反射温习一下
public class LoveReflect { public static class Demo implements Serializable{ } public static void ma ...
- Fragment的数据传递
开发之中用到的Fragment的次数越来越多,很多小的项目都已经直接在使用Fragment作为Activity的载体来切换页面.而在开发之中页面的切换我们最关心的问题就是数据的传递了.今天我们主要来研 ...
- 树莓派配置AP模式
所需硬件:树莓派.无线网卡 1.查看无线网卡是否被识别 pi@raspberrypi ~ $ sudo lsusb Bus Device : ID : Standard Microsystems Co ...
- WCF编程系列(一)初识WCF
WCF编程系列(一)初识WCF Windows Communication Foundation(WCF)是微软为构建面向服务的应用程序所提供的统一编程模型.WCF的基本概念: 地址:定义服务的 ...
- C# ACM poj1004
水题.. public static void acm1004(float[] a) { ; foreach (var item in a) { sum += item; } Console.Writ ...