HDU 1619 Unidirectional TSP(单向TSP + 路径打印)
Unidirectional TSP
This problem deals with finding a minimal path through a grid of points while traveling only from left to right.
Given an m*n matrix of integers, you are to write a program that computes a path of minimal weight. A path starts anywhere in column 1 (the first column) and consists of a sequence of steps terminating in column n (the last column). A step consists of traveling from column i to column i+1 in an adjacent (horizontal or diagonal) row. The first and last rows (rows 1 and m) of a matrix are considered adjacent, i.e., the matrix ``wraps'' so that it represents a horizontal cylinder. Legal steps are illustrated below.
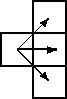
The weight of a path is the sum of the integers in each of the n cells of the matrix that are visited.
For example, two slightly different 5*6 matrices are shown below (the only difference is the numbers in the bottom row).
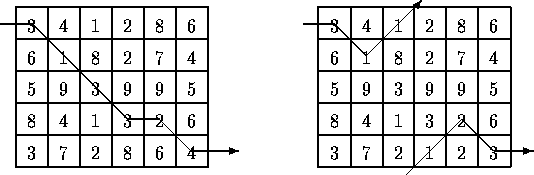
The minimal path is illustrated for each matrix. Note that the path for the matrix on the right takes advantage of the adjacency property of the first and last rows.
For each specification the number of rows will be between 1 and 10 inclusive; the number of columns will be between 1 and 100 inclusive. No path's weight will exceed integer values representable using 30 bits
# include<stdio.h>
# include<string.h>
# include<iostream>
using namespace std;
# define inf 0xffffff
int map[][];
int p[][];
int s[];
int main()
{
int m,n,i,j;
while(scanf("%d%d",&m,&n)!=EOF)
{
memset(p,-,sizeof(p));
for(i=; i<=m; i++)
for(j=; j<=n; j++)
scanf("%d",&map[i][j]);
for(j=n-; j>=; j--) //从后往前计算,因为要打印路径
for(i=; i<=m; i++)
{
int b=i,a,c,d,e=-; //a,b,c分别为向左上,向左,向左下的坐标
if(i>=) a=i-;
else a=m;
if(i<m) c=i+;
else c=;
d = min(min(map[a][j+],map[b][j+]),map[c][j+]); //取最小值
map[i][j] += d;
if(d==map[a][j+]) e=a;
if(d==map[b][j+]&&(e==-||(e!=-&&b<e))) e=b; //e的作用当两行的数字相同时去小的一个
if(d==map[c][j+]&&(e==-||(e!=-&&c<e))) e=c;
p[i][j] = e; //记录路径
}
int flag = ;
int sum =inf;
for(i=; i<=m; i++)
if(map[i][] < sum)
{
sum = map[i][];
flag=i;
}
printf("%d",flag);
flag = p[flag][];
for(i=; i<=n && flag != -; i++)
{
printf(" %d",flag);
flag = p[flag][i];
}
printf("\n%d\n",sum);
}
return ;
}
HDU 1619 Unidirectional TSP(单向TSP + 路径打印)的更多相关文章
- UVA116 Unidirectional TSP 单向TSP
分阶段的DAG,注意字典序的处理和路径的保存. 定义状态d[i][j]为从i,j 出发到最后一列的最小花费,转移的时候只有三种,向上,向下,或平移. #include<bits/stdc++.h ...
- UVa116 (单向TSP,多决策问题)
/*----UVa1347 单向TSP 用d(i,j)表示从格子(i,j)出发到最后一列的最小开销 则在(i,j)处有三种决策,d(i,j)转移到d(i-1,j+1),d(i,j+1),d(i+1,j ...
- ZOJ 1076 Gene Assembly(LIS+路径打印 贪心)
题目链接:http://acm.zju.edu.cn/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemId=76 题目大意:在一个DNA上,给定许多基因的起始位置和结束位置,求出这 ...
- L2-001 紧急救援 (25 分) (最短路+路径打印)
链接:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805046380707840/problems/994805073643683840 题目: 作为一个城市的应急救援队伍的负 ...
- HDU 6311 Cover (无向图最小路径覆盖)
HDU 6311 Cover (无向图最小路径覆盖) Time Limit: 6000/3000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/ ...
- Minimum Transport Cost HDU1385(路径打印)
最短路的路径打印问题 同时路径要是最小字典序 字典序用floyd方便很多 学会了两种打印路径的方法!!! #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h& ...
- POJ 3984 迷宫问题(简单bfs+路径打印)
传送门: http://poj.org/problem?id=3984 迷宫问题 Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions ...
- 代码实现:从键盘输入接收一个文件夹路径,打印出该文件夹下所有的.java文件名
package com.loaderman.test; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileReader; import java.util.Scanner ...
- uva 116 Unidirectional TSP【号码塔+打印路径】
主题: uva 116 Unidirectional TSP 意甲冠军:给定一个矩阵,当前格儿童值三个方向回格最小值和当前的和,就第一列的最小值并打印路径(同样则去字典序最小的). 分析:刚開始想错了 ...
随机推荐
- Linux经久不衰的应用程序
Linux里面的应用程序一贯以高安全性,高性价比(功能/所占空间),此次记录一下Linux里面比较常用的而且经久不衰的应用程序. Shell: bash(它结合了 csh ...
- https://hub.docker.com/
- 用java面向对象的思想实现的汉诺塔问题
package hanoi.com; public class Disc { private String name; private int level; public Disc(){ name = ...
- hdoj 5112 A Curious Matt
A Curious Matt Time Limit: 2000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 512000/512000 K (Java/Others) ...
- 升级web项目步骤
1.备份数据库(数据库服务器cmd执行,exp pra/pra@ORCL file=c:\name.dmp)2.删除原有表,导入新的备份文件(数据库服务器cmd执行,imp pra/pra@ORCL ...
- 非刚性图像配准 matlab简单示例 demons算法
2011-05-25 17:21 非刚性图像配准 matlab简单示例 demons算法, % Clean clc; clear all; close all; % Compile the mex f ...
- EasyUI实例源码
jQuery+EasyUI实例源码 http://www.51aspx.com/code/jQueryEasyUIExample ASP.NET MVC+EF+EasyUI权限 http://www. ...
- oncopy和onpaste
在Javascript中,有对应的事件能够监听复制和粘贴,那就是oncopy和onpaste. oncopy: demo: <body oncopy="alert('不能复制');re ...
- redis-BOOK
https://www.gitbook.com/book/gnuhpc/redis-all-about/details
- cocos2dx下最大纹理大小取决于平台
原文:http://www.cocos2d-x.org/wiki/Max_size_of_textures_in_cocos2d-x_depends_on_each_platform 在理论上,coc ...
