基于MATLAB的语音信号处理
一、图形界面设计
1.新建GUI界面
2.新建空白页
3.命名为"yydsp",打开界面
4.拖放控件
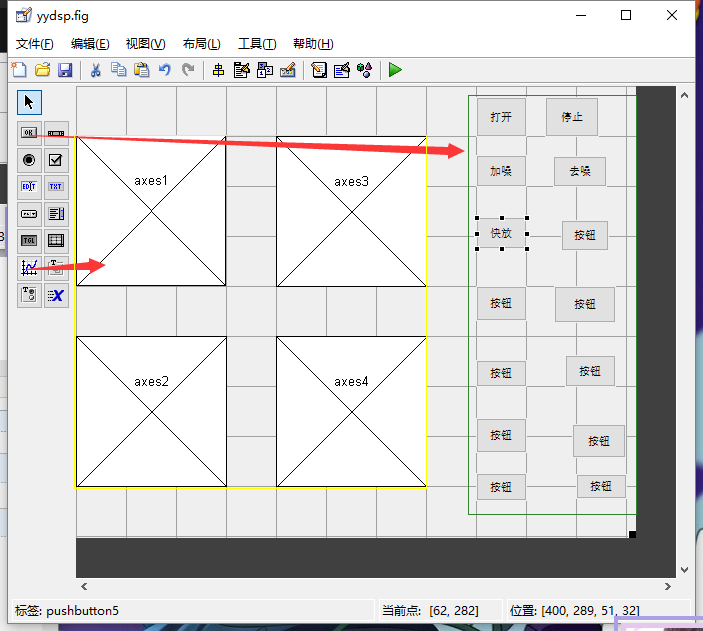
5.按预定功能修改界面
6.填写Callback函数
未填写前的代码:
- function varargout = yydsp(varargin)
- % YYDSP MATLAB code for yydsp.fig
- % YYDSP, by itself, creates a new YYDSP or raises the existing
- % singleton*.
- %
- % H = YYDSP returns the handle to a new YYDSP or the handle to
- % the existing singleton*.
- %
- % YYDSP('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
- % function named CALLBACK in YYDSP.M with the given input arguments.
- %
- % YYDSP('Property','Value',...) creates a new YYDSP or raises the
- % existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
- % applied to the GUI before yydsp_OpeningFcn gets called. An
- % unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
- % stop. All inputs are passed to yydsp_OpeningFcn via varargin.
- %
- % *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
- % instance to run (singleton)".
- %
- % See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
- % Edit the above text to modify the response to help yydsp
- % Last Modified by GUIDE v2. -Oct- ::
- % Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
- gui_Singleton = ;
- gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
- 'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
- 'gui_OpeningFcn', @yydsp_OpeningFcn, ...
- 'gui_OutputFcn', @yydsp_OutputFcn, ...
- 'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
- 'gui_Callback', []);
- })
- gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{});
- end
- if nargout
- [varargout{:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
- else
- gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
- end
- % End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
- % --- Executes just before yydsp is made visible.
- function yydsp_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
- % This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
- % hObject handle to figure
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % varargin command line arguments to yydsp (see VARARGIN)
- % Choose default command line output for yydsp
- handles.output = hObject;
- % Update handles structure
- guidata(hObject, handles);
- % UIWAIT makes yydsp wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
- % uiwait(handles.figure1);
- % --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
- function varargout = yydsp_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
- % hObject handle to figure
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % Get default command line output from handles structure
- varargout{} = handles.output;
- % --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
- function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % --- Executes on button press in pushbutton2.
- function pushbutton2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to pushbutton2 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % --- Executes on button press in pushbutton3.
- function pushbutton3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to pushbutton3 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % --- Executes on button press in pushbutton4.
- function pushbutton4_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to pushbutton4 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % --- Executes on button press in pushbutton5.
- function pushbutton5_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to pushbutton5 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % --- Executes on button press in pushbutton6.
- function pushbutton6_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to pushbutton6 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % --- Executes on button press in pushbutton7.
- function pushbutton7_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to pushbutton7 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % --- Executes on button press in pushbutton8.
- function pushbutton8_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to pushbutton8 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % --- Executes on button press in pushbutton9.
- function pushbutton9_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to pushbutton9 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % --- Executes on button press in pushbutton10.
- function pushbutton10_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to pushbutton10 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % --- Executes on button press in pushbutton11.
- function pushbutton11_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to pushbutton11 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % --- Executes on button press in pushbutton12.
- function pushbutton12_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to pushbutton12 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % --- Executes on button press in pushbutton13.
- function pushbutton13_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to pushbutton13 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % --- Executes on button press in pushbutton14.
- function pushbutton14_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to pushbutton14 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
填写后的代码
1)打开文件部分
- [filename,pathname]=uigetfile({'*.*','ALL FILES'},'选择声音');%显示模态对话框,
- %列出当前文件夹中的文件,如果文件有效,点击打开时会返回文件名,如果点击取消,返回0
- ,])
- return;
- end
- str=[pathname filename];%合成路径+文件名
- [temp,Fs]=audioread(str);%读取音频声音
- temp=temp(:,); %取一行提取矩阵
- temp1=resample(temp,,);%信号降采样处理
- handles.y=temp1;%降采样的句柄
- handles.y1=temp;%y1为原声
- handles.Fs=Fs;%采样频率
- guidata(hObject,handles);%存储或检索 UI 数据
程序中,resample为信号降采样处理,理解如下:
B=resample(x,90,250); %
采样从250Hz降到90Hz,如果250在前,就是插值从90到250,可以看B的长度,250Hz采样4000个数据等于90hz采样1440个数据,这就是降采样。
2)播放原声,画时频图
- fs=handles.Fs;
- Y=handles.y1;
- Y=Y(:,);%取单声道
- t1=:length(Y);
- t=t1/fs;
- sound(Y,fs); %播放原声
- F = fft(Y);%快速傅里叶变换
- freq = linspace(-fs/,fs/,length(Y)+);
- freq(end) = [];
- plot(handles.axes1,t,Y)
- xlabel(handles.axes1,'时间');
- ylabel(handles.axes1,'幅度');
- title(handles.axes1,'原声音的波形');
- y1=fft(Y);
- plot(handles.axes4,abs(y1));
- xlabel(handles.axes4,'圆频率');
- ylabel(handles.axes4,'幅度');
- title(handles.axes4,'未改变坐标轴的频率特性');
- plot(handles.axes2,freq,abs(fftshift(F)));
- title(handles.axes2,'原声音的真实频响');
- xlabel(handles.axes2,'圆频率');
- ylabel(handles.axes2,'幅度');
- title(handles.axes2,'频率特性');
3)男声变女声
- FL = ; % 帧移
- WL = ; % 窗长
- P = ; %预测系数个数
- s = handles.y;
- fs = handles.Fs;
- % 定义常数
- s = s/max(s); % 归一化
- L = length(s); % 读入语音长度
- FN = floor(L/FL)-; % 计算帧长,floor;向负无穷方向
- % 预测和重建滤波器
- exc = zeros(L,); % 激励信号,double类零矩阵L行1列
- zi_pre = zeros(P,); % 预测滤波器状态
- s_rec = zeros(L,); % 重建语音
- zi_rec = zeros(P,);
- % 变调滤波器
- exc_syn_t = zeros(L,); % 合成的激励信号,创建一个L行1列的0脉冲
- s_syn_t = zeros(L,); % 合成语音
- last_syn_t = ; % 存储上一个段的最后一个脉冲的下标
- zi_syn_t = zeros(P,); % 合成滤波器
- hw = hamming(WL); %汉明窗
- %滤波器
- % 依次处理每帧语音
- :FN %从第三个子数组开始
- % 计算预测系数
- s_w = s(n*FL-WL+:n*FL).*hw; %汉明窗加权
- [A,E]=lpc(s_w,P); %线性预测计算预测系数
- % A是预测系数,E会被用来计算合成激励的能量
- s_f=s((n-)*FL+:n*FL); % 本帧语音
- %利用filter函数重建语音
- [exc1,zi_pre] = filter(A,,s_f,zi_pre);
- exc((n-)*FL+:n*FL) = exc1; %计算激励
- %利用filter函数重建语音
- [s_rec1,zi_rec] = filter(,A,exc1,zi_rec);
- s_rec((n-)*FL+:n*FL) = s_rec1; %重建语音
- % 下面只有得到exc后才可以
- s_Pitch = exc(n*FL-:n*FL);
- PT(n) = findpitch(s_Pitch); %计算基音周期pt
- G = sqrt(E*PT(n)); %计算合成激励的能量G
- PT1 =floor(PT(n)/); %减小基音周期
- poles = roots(A);
- deltaOMG =**pi/fs;
- : %增加共振峰
- poles(p) = poles(p)*exp(1j*deltaOMG);
- elseif imag(poles(p))<
- poles(p) = poles(p)*exp(-1j*deltaOMG);
- end
- end
- A1=poly(poles);
- tempn_syn_t=(:n*FL-last_syn_t);
- exc_syn1_t = zeros(length(tempn_syn_t),);
- exc_syn1_t(mod(tempn_syn_t,PT1)==) = G;
- exc_syn1_t = exc_syn1_t((n-)*FL-last_syn_t+:n*FL-last_syn_t);
- [s_syn1_t,zi_syn_t] = filter(,A1,exc_syn1_t,zi_syn_t);
- exc_syn_t((n-)*FL+:n*FL) = exc_syn1_t; %合成激励
- s_syn_t((n-)*FL+:n*FL) = s_syn1_t; %合成语音
- last_syn_t = last_syn_t+PT1*floor((n*FL-last_syn_t)/PT1);
- end
- Y = s_syn_t;
- F = fft(Y);
- freq = linspace(-fs/,fs/,length(Y)+);
- freq(end) = [];
- plot(handles.axes4,freq,abs(fftshift(F)));
- xlabel(handles.axes4,'圆频率');
- ylabel(handles.axes4,'幅度');
- title(handles.axes4,'频率特性');
- handles.y=s_syn_t;
- guidata(hObject,handles);
- plot(handles.axes3,s_syn_t);
- t1=:length(s_syn_t);
- t=t1/;
- plot(handles.axes3,t,s_syn_t);
- title(handles.axes3,'时域图');
- xlabel(handles.axes3,'时间');
- ylabel(handles.axes3,'幅度');
- sound(handles.y,);
4)退出
- delete(handles.figure1);
5)快放
- fs=handles.Fs;
- Y=handles.y1;
- Y=Y(:,);
- F = fft(Y);
- freq = linspace(-fs/,fs/,length(Y)+);
- freq(end) = [];
- sound(Y,*fs);
- t1=:length(Y);
- t=t1/(*fs);
- plot(handles.axes3,t,Y)
- title(handles.axes3,'时域图');
- xlabel(handles.axes3,'时间');
- ylabel(handles.axes3,'幅度');
- plot(handles.axes4,freq,abs(fftshift(F)));
- xlabel(handles.axes4,'圆频率');
- ylabel(handles.axes4,'幅度');
- title(handles.axes4,'频率特性');
6)慢放
- fs=handles.Fs;
- Y=handles.y1;
- Y=Y(:,);
- sound(Y,0.5*fs);
- F = fft(Y);
- freq = linspace(-fs/,fs/,length(Y)+);
- freq(end) = [];%
- t1=:length(Y);
- t=t1/(0.5*fs);
- plot(handles.axes3,t,Y)
- title(handles.axes3,'时域图');
- xlabel(handles.axes3,'时间');
- ylabel(handles.axes3,'幅度');
- plot(handles.axes4,freq,abs(fftshift(F)));
- xlabel(handles.axes4,'圆频率');
- ylabel(handles.axes4,'幅度');
- title(handles.axes4,'频率特性');
7)制造回音
- fs=handles.Fs;
- N=length(handles.y1);
- x1=handles.y1(:N);
- x2=handles.y1(:N);
- x1=[x1,zeros(,)];
- x2=[zeros(,),,)];
- z=x1+x2;
- F = fft(z);
- freq = linspace(-fs/,fs/,length(z)+);
- freq(end) = [];
- t1=:length(z);
- t=t1/fs;
- plot(handles.axes3,t,z)
- title(handles.axes3,'含回音波形');
- xlabel(handles.axes3,'时间');
- ylabel(handles.axes3,'幅度');
- plot(handles.axes4,freq,abs(fftshift(F)));
- xlabel(handles.axes4,'圆频率');
- ylabel(handles.axes4,'幅度');
- title(handles.axes4,'频率特性');
- sound(z,fs);
8)回音还原
- fs=handles.Fs;
- N=length(handles.y1);
- x1=handles.y1(:N);
- x2=handles.y1(:N);
- x3=handles.y1(:N);
- x1=[x1,zeros(,)];
- x2=[zeros(,),,)];
- z=x1+x2;
- b=;
- a=zeros(,N);
- a()=;
- a()=0.4;
- z2=filter(b,a,z);
- F = fft(z2);
- freq = linspace(-fs/,fs/,length(z2)+);
- freq(end) = [];
- t1=:length(z2);
- t=t1/fs;
- plot(handles.axes3,t,z2)
- title(handles.axes3,'滤除回声的波形');
- xlabel(handles.axes3,'时间');
- ylabel(handles.axes3,'幅度');
- plot(handles.axes4,freq,abs(fftshift(F)));
- xlabel(handles.axes4,'圆频率');
- ylabel(handles.axes4,'幅度');
- title(handles.axes4,'频率特性');
- sound(z2,fs);
9)制造噪声
- fs=handles.Fs;
- x=handles.y1;
- y=x(:,); %取一行提取矩阵
- noise=*(:length(y))/fs)+*(:length(y))/fs)...
- +*(:length(y))/fs);%噪声 10000rad/s++
- VNnoise=y+noise';%向量维度一致
- F = fft(VNnoise);
- freq = linspace(-fs/,fs/,length(VNnoise)+);
- freq(end) = [];
- t1=:length(VNnoise);
- t=t1/fs;
- plot(handles.axes3,t,VNnoise)
- xlabel(handles.axes3,'时间');
- ylabel(handles.axes3,'幅度');
- title(handles.axes3,'添加噪声的波形');
- plot(handles.axes4,freq,abs(fftshift(F)));
- xlabel(handles.axes4,'圆频率');
- ylabel(handles.axes4,'幅度');
- title(handles.axes4,'频率特性');
- sound(VNnoise,fs);
10)滤除噪声
- fs=handles.Fs;
- x=handles.y1;
- y=x(:,); %取一行提取矩阵
- noise=*(:length(y))/fs)+*(:length(y))/fs)...
- +*(:length(y))/fs);%噪声 10000rad/s++
- VNnoise=y+noise';%向量维度一致
- %[b,a] = butter(,*/fs,'LOW') ; %巴特沃斯滤波器
- %result=filter(b,a,VNnoise);
- Hd = ditong1;%Fdatool滤波
- result=filter(Hd,x);
- result=result(:,);
- sound(result,fs);
- F = fft(result);
- freq = linspace(-fs/,fs/,length(result)+);
- freq(end) = [];
- t1=:length(result);
- t=t1/fs;
- plot(handles.axes3,t,result)
- xlabel(handles.axes3,'时间');
- ylabel(handles.axes3,'幅度');
- title(handles.axes3,'添加噪声的波形');
- plot(handles.axes4,freq,abs(fftshift(F)));
- xlabel(handles.axes4,'圆频率');
- ylabel(handles.axes4,'幅度');
- title(handles.axes4,'频率特性');
11)左右声道合唱
- fs=handles.Fs;
- sound(original,fs);
- a1=;
- a2=-;
- b1=;
- b2=-;
- Soundleft=original(:,);%左声道
- Soundright=original(:,);%右声道
- newleft=Soundleft+Soundright; %新的左声道为原来的全部声道
- newright=b1*Soundleft+b2*Soundright; %新的右声道为原来的左声道-原来的右
- Sound(:,)=newleft;
- Sound(:,)=newright;
- bp=fir1(,[,]/(fs/));
- cutdown=filter(bp,,Sound);
- Sound_final=Sound-0.6*abs(cutdown);
- sound(Sound_final,fs)
- F = fft(Sound_final);
- freq = linspace(-fs/,fs/,length(Sound_final)+);
- freq(end) = [];
- t1=:length(Sound_final);
- t=t1/fs;
- plot(handles.axes3,t,Sound_final)
- xlabel(handles.axes3,'时间');
- ylabel(handles.axes3,'幅度');
- title(handles.axes3,'时域波形');
- plot(handles.axes4,freq,abs(fftshift(F)));
- xlabel(handles.axes4,'圆频率');
- ylabel(handles.axes4,'幅度');
- title(handles.axes4,'频率特性');
12)反放
- fs=handles.Fs;
- y=handles.y1;
- M=length(y):-:;
- rever=y(M);
- sound(rever,fs);%反播
- F = fft(rever);
- freq = linspace(-fs/,fs/,length(rever)+);
- freq(end) = [];
- t1=:length(rever);
- t=t1/fs;
- plot(handles.axes3,t,rever)
- xlabel(handles.axes3,'时间');
- ylabel(handles.axes3,'幅度');
- title(handles.axes3,'反播的波形');
- plot(handles.axes4,freq,abs(fftshift(F)));
- xlabel(handles.axes4,'圆频率');
- ylabel(handles.axes4,'幅度');
- title(handles.axes4,'频率特性');
基于MATLAB的语音信号处理的更多相关文章
- 基于Matlab的MMSE的语音增强算法的研究
本课题隶属于学校的创新性课题研究项目.2012年就已经做完了,今天一并拿来发表. 目录: --基于谱减法的语音信号增强算法..................................... ...
- python做语音信号处理
音频信号的读写.播放及录音 标准的python已经支持WAV格式的书写,而实时的声音输入输出需要安装pyAudio(http://people.csail.mit.edu/hubert/pyaudio ...
- 基于MATLAB的离散小波变换
申明,本文非笔者原创,原文转载自: 基于Matlab的离散小波变换 http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_725866260100ryh3.html 简介 在 ...
- 基于MATLAB的GUI(Graphical User Interface)音频实时显示设计
摘要:本文章的设计主要讲基于matlab的gui音频实时显示设计,此次设计的gui相当于一个简洁的音乐播放器,界面只有”录音“和”播放“两个控件,哈哈,够简洁吧.通过”录音“按钮可以实现声音从电脑的声 ...
- 语音信号处理之(三)矢量量化(Vector Quantization)
语音信号处理之(三)矢量量化(Vector Quantization) zouxy09@qq.com http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09 这学期有<语音信号处理>这门 ...
- 基于MATLAB的中值滤波均值滤波以及高斯滤波的实现
基于MATLAB的中值滤波均值滤波以及高斯滤波的实现 作者:lee神 1. 背景知识 中值滤波法是一种非线性平滑技术,它将每一像素点的灰度值设置为该点某邻域窗口内的所有像素点灰度值的中值. 中值滤 ...
- 语音信号处理之(一)动态时间规整(DTW)
语音信号处理之(一)动态时间规整(DTW) zouxy09@qq.com 原文:http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09 这学期有<语音信号处理>这门课,快考试了,所以也要 ...
- 语音信号处理之动态时间规整(DTW)(转)
这学期有<语音信号处理>这门课,快考试了,所以也要了解了解相关的知识点.呵呵,平时没怎么听课,现在只能抱佛脚了.顺便也总结总结,好让自己的知识架构清晰点,也和大家分享下.下面总结的是第一个 ...
- 【VS开发】【智能语音处理】语音信号处理之(一)动态时间规整(DTW)
语音信号处理之(一)动态时间规整(DTW) zouxy09@qq.com http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09 这学期有<语音信号处理>这门课,快考试了,所以也要了解了 ...
随机推荐
- Spring MVC-视图解析器(View Resolverr)-内部资源视图解析器(Internal Resource View Resolver)示例(转载实践)
以下内容翻译自:https://www.tutorialspoint.com/springmvc/springmvc_internalresourceviewresolver.htm 说明:示例基于S ...
- SDUT OJ -2892 A
A nid=24#time" title="C.C++.go.haskell.lua.pascal Time Limit60ms Memory Limit 65536K java. ...
- Latex 排版技巧 1——数学公式对齐
在我们排版数学推导式时,非常多时候我们希望可以让公式的等号对齐 这样更接近人的数学推导习惯 例如以下图效果图 使用 begin{aligned} end{aligned}将所需对齐的数学公式代码块包起 ...
- codeforces 437D The Child and Zoo
time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input output standa ...
- jmeter默认生成测试报告
我的jmeter安装在F:\study\apache-jmeter-3.1\apache-jmeter-3.1下,在bin目录下执行 其中E:\code\jmeterReport\Course-tes ...
- 学习笔记——node.js
node.js的作用在于,号称可以让服务器支持更多的连接.比如说,php + apche可以让服务器支持4000个并发连接,那么node.js + apche可以让服务器支持并发几万个. 为什么这么牛 ...
- yum install tomcat
安装tomcat6 yum install tomcat6 tomcat6-webapps tomcat6-admin-webapps 启动tomcat6 service tomcat6 start ...
- 【NOI 2015】 荷马史诗
[题目链接] https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=4198 [算法] 不难发现,题目中所说的编码方式就是哈夫曼编码 注意合并时优先合并深度 ...
- P1390--公约数的和
这个题比较狗,一开始没有啥思路,但是看完题解觉得还是比较好理解的.主要思路就是需要把每个数是几个数的最大公约数求出来,然后求和就行了.蓝书P124例九 设f(n) = gcd(1,n) + gcd(2 ...
- Django day02
一:Django 中 app 的概念 每个项目里面都会 有很多不同的模块,我们可以把它们写在一个项目里,我们把模块分成一个一个不同的app,这样写可以便于管理,写的一些项目也可能不单单是一个页面,还可 ...
