Codeforces Round #311 (Div. 2)题解
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Soon a school Olympiad in Informatics will be held in Berland, n schoolchildren will participate there.
At a meeting of the jury of the Olympiad it was decided that each of the n participants,
depending on the results, will get a diploma of the first, second or third degree. Thus, each student will receive exactly one diploma.
They also decided that there must be given at least min1 and
at most max1 diplomas
of the first degree, at least min2 and
at most max2diplomas
of the second degree, and at least min3 and
at most max3 diplomas
of the third degree.
After some discussion it was decided to choose from all the options of distributing diplomas satisfying these limitations the one that maximizes the number of participants who receive diplomas of the first degree. Of all these options they select the one which
maximizes the number of the participants who receive diplomas of the second degree. If there are multiple of these options, they select the option that maximizes the number of diplomas of the third degree.
Choosing the best option of distributing certificates was entrusted to Ilya, one of the best programmers of Berland. However, he found more important things to do, so it is your task now to choose the best option of distributing of diplomas, based on the described
limitations.
It is guaranteed that the described limitations are such that there is a way to choose such an option of distributing diplomas that all nparticipants
of the Olympiad will receive a diploma of some degree.
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (3 ≤ n ≤ 3·106) — the
number of schoolchildren who will participate in the Olympiad.
The next line of the input contains two integers min1 and max1 (1 ≤ min1 ≤ max1 ≤ 106) — the
minimum and maximum limits on the number of diplomas of the first degree that can be distributed.
The third line of the input contains two integers min2 and max2 (1 ≤ min2 ≤ max2 ≤ 106) — the
minimum and maximum limits on the number of diplomas of the second degree that can be distributed.
The next line of the input contains two integers min3 and max3 (1 ≤ min3 ≤ max3 ≤ 106) — the
minimum and maximum limits on the number of diplomas of the third degree that can be distributed.
It is guaranteed that min1 + min2 + min3 ≤ n ≤ max1 + max2 + max3.
In the first line of the output print three numbers, showing how many diplomas of the first, second and third degree will be given to students in the optimal variant of distributing diplomas.
The optimal variant of distributing diplomas is the one that maximizes the number of students who receive diplomas of the first degree. Of all the suitable options, the best one is the one which maximizes the number of participants who receive diplomas of the
second degree. If there are several of these options, the best one is the one that maximizes the number of diplomas of the third degree.
6
1 5
2 6
3 7
1 2 3
10
1 2
1 3
1 5
2 3 5
6
1 3
2 2
2 2
2 2 2
水题:代码例如以下
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define foreach(it,v) for(__typeof(v.begin()) it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); ++it) using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e5;
int a[maxn];
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n,w[3][2];
while(cin>>n) {
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) cin>>w[i][0]>>w[i][1];
int a[3];
int limt = w[1][0] + w[2][0];
a[0] = min(w[0][1],n - limt);
n -= a[0];
limt = w[2][0];
a[1] = min(w[1][1],n - limt);
n -= a[1];
a[2] = min(n,w[2][1]);
printf("%d %d %d\n", a[0],a[1],a[2]);
}
return 0;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Pasha decided to invite his friends to a tea party. For that occasion, he has a large teapot with the capacity of w milliliters and 2n tea
cups, each cup is for one of Pasha's friends. The i-th cup can hold at most ai milliliters
of water.
It turned out that among Pasha's friends there are exactly n boys and exactly n girls
and all of them are going to come to the tea party. To please everyone, Pasha decided to pour the water for the tea as follows:
- Pasha can boil the teapot exactly once by pouring there at most w milliliters of water;
- Pasha pours the same amount of water to each girl;
- Pasha pours the same amount of water to each boy;
- if each girl gets x milliliters of water, then each boy gets 2x milliliters
of water.
In the other words, each boy should get two times more water than each girl does.
Pasha is very kind and polite, so he wants to maximize the total amount of the water that he pours to his friends. Your task is to help him and determine the optimum distribution of cups between Pasha's friends.
The first line of the input contains two integers, n and w (1 ≤ n ≤ 105, 1 ≤ w ≤ 109) —
the number of Pasha's friends that are boys (equal to the number of Pasha's friends that are girls) and the capacity of Pasha's teapot in milliliters.
The second line of the input contains the sequence of integers ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109, 1 ≤ i ≤ 2n) — the
capacities of Pasha's tea cups in milliliters.
Print a single real number — the maximum total amount of water in milliliters that Pasha can pour to his friends without violating the given conditions. Your answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error doesn't exceed 10 - 6.
2 4
1 1 1 1
3
3 18
4 4 4 2 2 2
18
1 5
2 3
4.5
Pasha also has candies that he is going to give to girls but that is another task...
排序
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define foreach(it,v) for(__typeof(v.begin()) it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); ++it) using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e5;
int a[maxn];
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n,w;
while(cin>>n>>w) {
for(int i = 1; i <= n+n; i++) {
cin>>a[i];
}
sort(a+1,a+1+n+n);
double M = a[n + 1] / 2.0;
M = min(M,a[1]*1.0);
double ans = M * n + 2*M*n;
if(ans > w) ans = w;
printf("%.10f\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Arthur has bought a beautiful big table into his new flat. When he came home, Arthur noticed that the new table is unstable.
In total the table Arthur bought has n legs, the length of the i-th
leg is li.
Arthur decided to make the table stable and remove some legs. For each of them Arthur determined number di — the
amount of energy that he spends to remove the i-th leg.
A table with k legs is assumed to be stable if there are more than half legs of the maximum length. For example, to make a table with 5legs
stable, you need to make sure it has at least three (out of these five) legs of the maximum length. Also, a table with one leg is always stable and a table with two legs is stable if and only if they have the same lengths.
Your task is to help Arthur and count the minimum number of energy units Arthur should spend on making the table stable.
The first line of the input contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) — the
initial number of legs in the table Arthur bought.
The second line of the input contains a sequence of n integers li (1 ≤ li ≤ 105),
where li is
equal to the length of the i-th leg of the table.
The third line of the input contains a sequence of n integers di (1 ≤ di ≤ 200),
where di is
the number of energy units that Arthur spends on removing the i-th leg off the table.
Print a single integer — the minimum number of energy units that Arthur needs to spend in order to make the table stable.
2
1 5
3 2
2
3
2 4 4
1 1 1
0
6
2 2 1 1 3 3
4 3 5 5 2 1
8
枚举最高的那个脚的高度H。大于H的直接删掉(后缀和记录代价即可),设高度为H的有x根,小于H的有y根。那么我们必须删掉k = max(y-(x-1),0)根,本题d值较小开个cnt数组记录下即可,假设比較大的话能够用平衡树维护前k小的代价和。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define foreach(it,v) for(__typeof(v.begin()) it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); ++it) using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e5;
int l[maxn],d[maxn];
vector<int> g[maxn];
int s[maxn];
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n;
while(cin>>n) {
for(int i = 0; i <= 100001; i++) {
s[i] = 0;
g[i].clear();
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin>>l[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int x;cin>>x;
g[l[i]].push_back(x);
s[l[i]] +=x;
}
vector<int> t;
for(int i = 100000; i >= 0; i--) s[i] += s[i+1];
for(int i = 0; i <= 100000; i++)if(g[i].size()){
t.push_back(i);
}
int cost = 1e8,sum = 0;
int cnt[205];
memset(cnt,0,sizeof cnt);
foreach(id,t) {
int & x = *id;
int w = s[x+1] - s[100001];
int sz = g[x].size();
int d = sz - 1;
d = max(sum-d,0);
int i;
for(i = 0; i <= 200; i++) {
d -= cnt[i];
w += i*cnt[i];
if(d <= 0) break;
}
w += d*i;
cost = min(cost,w);
sum += g[x].size();
foreach(it,g[x]) {
++cnt[*it];
}
}
printf("%d\n", cost);
}
return 0;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
After Vitaly was expelled from the university, he became interested in the graph theory.
Vitaly especially liked the cycles of an odd length in which each vertex occurs at most once.
Vitaly was wondering how to solve the following problem. You are given an undirected graph consisting of n vertices and m edges,
not necessarily connected, without parallel edges and loops. You need to find t — the minimum number of edges that must be added to
the given graph in order to form a simple cycle of an odd length, consisting of more than one vertex. Moreover, he must find w — the
number of ways to add t edges in order to form a cycle of an odd length (consisting of more than one vertex). It is prohibited to
add loops or parallel edges.
Two ways to add edges to the graph are considered equal if they have the same sets of added edges.
Since Vitaly does not study at the university, he asked you to help him with this task.
The first line of the input contains two integers n and m ( — the
— the
number of vertices in the graph and the number of edges in the graph.
Next m lines contain the descriptions of the edges of the graph, one edge per line. Each edge is given by a pair of integers ai, bi(1 ≤ ai, bi ≤ n) — the
vertices that are connected by the i-th edge. All numbers in the lines are separated by a single space.
It is guaranteed that the given graph doesn't contain any loops and parallel edges. The graph isn't necessarily connected.
Print in the first line of the output two space-separated integers t and w — the
minimum number of edges that should be added to the graph to form a simple cycle of an odd length consisting of more than one vertex where each vertex occurs at most once, and the number of ways to do this.
4 4
1 2
1 3
4 2
4 3
1 2
3 3
1 2
2 3
3 1
0 1
3 0
3 1
The simple cycle is a cycle that doesn't contain any vertex twice.
加入最少的边构成奇环。并输出方案数。
首先假设有0条边那么任选3个点就能构成奇环。答案是3 c(n,3)
假设每一个节点最多仅仅有一条边与其关联且m > 0,那么对于每条边(u,v),任选节点k。仅仅须要加入两条边就能构成奇环。答案是2,m*(n-2)。
假设存在节点的度大于2,那么推断是否是否是二分图。假设不是意味着已经存在奇环,答案是 0,1
否则对每一个联通分量仅仅须要在同色节点里任选两个加边就能形成奇环,答案是1,,sum(c(ci[0],2)+c(ci[1],2));
盗用Quailty的代码QAQ......
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
vector<int>e[100005];
int vis[100005],cnt[2];
bool bfs(int st)
{
queue<int>q;
vis[st]=1;
q.push(st);
while(!q.empty())
{
int u=q.front();
q.pop();
cnt[vis[u]-1]++;
for(int i=0;i<e[u].size();i++)
{
if(!vis[e[u][i]])
{
vis[e[u][i]]=3-vis[u];
q.push(e[u][i]);
}
else
{
if(vis[e[u][i]]==vis[u])return 0;
}
}
}
return 1;
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
int a,b;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
e[a].push_back(b);
e[b].push_back(a);
}
int maxd=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
maxd=max(maxd,(int)e[i].size());
}
if(maxd==0)
{
printf("3 %I64d\n",1LL*n*(n-1)*(n-2)/6);
}
else if(maxd==1)
{
printf("2 %I64d\n",1LL*m*(n-2));
}
else
{
bool odd=0;
ll ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!vis[i])
{
cnt[0]=cnt[1]=0;
if(!bfs(i))
{
odd=1;
break;
}
ans+=1LL*cnt[0]*(cnt[0]-1)/2;
ans+=1LL*cnt[1]*(cnt[1]-1)/2;
}
}
if(odd)printf("0 1\n");
else printf("1 %I64d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
1.5 seconds
512 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Tomorrow Ann takes the hardest exam of programming where she should get an excellent mark.
On the last theoretical class the teacher introduced the notion of a half-palindrome.
String t is a half-palindrome, if for all the odd positions i (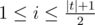 )
)
the following condition is held: ti = t|t| - i + 1,
where |t| is the length of string t if
positions are indexed from 1. For example, strings "abaa",
"a", "bb", "abbbaa"
are half-palindromes and strings "ab", "bba"
and "aaabaa" are not.
Ann knows that on the exam she will get string s, consisting only of letters a and b,
and number k. To get an excellent mark she has to find the k-th
in the lexicographical order string among all substrings of s that are half-palyndromes. Note that each substring in this order is
considered as many times as many times it occurs in s.
The teachers guarantees that the given number k doesn't exceed the number of substrings of the given string that are half-palindromes.
Can you cope with this problem?
The first line of the input contains string s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 5000),
consisting only of characters 'a' and 'b',
where |s| is the length of string s.
The second line contains a positive integer k — the lexicographical number of the requested string among all the half-palindrome substrings
of the given string s. The strings are numbered starting from one.
It is guaranteed that number k doesn't exceed the number of substrings of the given string that are half-palindromes.
Print a substring of the given string that is the k-th in the lexicographical order of all substrings of the given string that are
half-palindromes.
abbabaab
7
abaa
aaaaa
10
aaa
bbaabb
13
bbaabb
By definition, string a = a1a2... an is
lexicographically less than string b = b1b2... bm,
if either a is a prefix of b and
doesn't coincide with b, or there exists such i,
that a1 = b1, a2 = b2, ... ai - 1 = bi - 1, ai < bi.
In the first sample half-palindrome substrings are the following strings — a, a, a, a, aa, aba, abaa, abba, abbabaa, b, b, b, b, baab,bab, bb, bbab, bbabaab (the
list is given in the lexicographical order).
半回文串指的是对于每一个奇数位置i(1=<i<=(L+1)/2),满足s[i] = s[L-i+1],下标从1開始,给出一个字符串,求字典序第k小的半回文子串。
Trie的应用,挺奇妙的,把每一个回文子串插到Trie中去。cnt[u]记录u这个子树有多少个串。然后在树上查找即可,
不能暴力插子串。能够用一个数组ok[i][j]表示子串s[i...j]是否是半回文串,然后对每一个后缀suffix(x)插入。假设ok[x][i]为true就更新cnt数组,插入完之后须要dfs一遍求子树的siz。查找算法例如以下,假设当前到了节点root,子树1和2的大小分别为w1和w2,那么显然以u为结束节点的子串有w = cnt[root]-w1-w2个,假设w>=k那么算法终止。否则更新k =
k - w。假设w1 >= k,那么进入子树1,否则更新k = k-w1,进入子树2。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define foreach(it,v) for(__typeof(v.begin()) it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); ++it)
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 5e3 + 10;
typedef long long ll;
char s[maxn];
bool ok[maxn][maxn];
int ch[maxn*maxn][2],cnt[maxn*maxn];
struct Trie
{
int tot;
Trie() {
cnt[tot = 0] = 0;
ch[0][0] = ch[0][1] = -1;
}
void Insert(const char *s,int st) {
int u = 0;
for(int i = st; s[i]; i++) {
int c = s[i] - 'a';
if(ch[u][c]==-1) {
ch[u][c] = ++tot;
cnt[tot] = 0;
ch[tot][0] = ch[tot][1] = -1;
}
u = ch[u][c];
if(ok[st][i])++cnt[u];
}
}
int Init(int u) {
if(u==-1) return 0;
cnt[u] += Init(ch[u][0]);
cnt[u] += Init(ch[u][1]);
return cnt[u];
}
};
int pre(char * s)
{
s[0] = ' ';
int n = strlen(s);
--n;
for(int w = 1; w <= n; w++) {
for(int x = 1; x + w -1 <= n; x++) {
ok[x][x+w-1] = (s[x]==s[x+w-1]);
if(w >= 5) ok[x][x+w-1] &= ok[x+2][x+w-3];
}
}
return n;
}
void solve(int root,int k)
{
if(k < 1||root==-1) return;
int v1 = ch[root][0],v2 = ch[root][1];
int w1= (v1 == -1 ? 0 : cnt[v1]),w2 = (v2 == -1? 0: cnt[v2]);
int w = cnt[root] - w1 - w2;
if(w >= k) return;
k -= w;
if(w1 >= k) {
putchar('a');
solve(v1,k);
}else {
k -= w1;
putchar('b');
solve(v2,k);
}
}
int main()
{
// ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
// cin.tie(0);
int k;
while(scanf("%s%d",s+1,&k)==2) {
int n = pre(s);
Trie A;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) A.Insert(s,i);
A.Init(0);
solve(0,k);
putchar('\n');
}
return 0;
}
Codeforces Round #311 (Div. 2)题解的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #182 (Div. 1)题解【ABCD】
Codeforces Round #182 (Div. 1)题解 A题:Yaroslav and Sequence1 题意: 给你\(2*n+1\)个元素,你每次可以进行无数种操作,每次操作必须选择其 ...
- Codeforces Round #608 (Div. 2) 题解
目录 Codeforces Round #608 (Div. 2) 题解 前言 A. Suits 题意 做法 程序 B. Blocks 题意 做法 程序 C. Shawarma Tent 题意 做法 ...
- Codeforces Round #525 (Div. 2)题解
Codeforces Round #525 (Div. 2)题解 题解 CF1088A [Ehab and another construction problem] 依据题意枚举即可 # inclu ...
- Codeforces Round #528 (Div. 2)题解
Codeforces Round #528 (Div. 2)题解 A. Right-Left Cipher 很明显这道题按题意逆序解码即可 Code: # include <bits/stdc+ ...
- Codeforces Round #466 (Div. 2) 题解940A 940B 940C 940D 940E 940F
Codeforces Round #466 (Div. 2) 题解 A.Points on the line 题目大意: 给你一个数列,定义数列的权值为最大值减去最小值,问最少删除几个数,使得数列的权 ...
- Codeforces Round #677 (Div. 3) 题解
Codeforces Round #677 (Div. 3) 题解 A. Boring Apartments 题目 题解 简单签到题,直接数,小于这个数的\(+10\). 代码 #include &l ...
- Codeforces Round #665 (Div. 2) 题解
Codeforces Round #665 (Div. 2) 题解 写得有点晚了,估计都官方题解看完切掉了,没人看我的了qaq. 目录 Codeforces Round #665 (Div. 2) 题 ...
- Codeforces Round #160 (Div. 1) 题解【ABCD】
Codeforces Round #160 (Div. 1) A - Maxim and Discounts 题意 给你n个折扣,m个物品,每个折扣都可以使用无限次,每次你使用第i个折扣的时候,你必须 ...
- Codeforces Round #383 (Div. 2) 题解【ABCDE】
Codeforces Round #383 (Div. 2) A. Arpa's hard exam and Mehrdad's naive cheat 题意 求1378^n mod 10 题解 直接 ...
随机推荐
- ym——物联网入口之中的一个Android蓝牙4.0
转载请注明本文出自Cym的博客(http://blog.csdn.net/cym492224103),谢谢支持! 假设还有同学不知道蓝牙4.0能够做什么请查看Android+蓝牙 4.0 将带来什么? ...
- Ubuntu(64位)编译Android源码常见错误解决办法
2013年07月10日 14:47:27 阅读数:1239 错误: /usr/include/gnu/stubs.h:7:27: error: gnu/stubs-32.h: No such file ...
- windows命令行方式下打印和设置PATH变量
点击开始菜单,运行=>cmd打印当前变量:echo %PATH%结果:C:\WINDOWS\system32;C:\WINDOWS;C:\WINDOWS\System32\Wbem;d:\PRO ...
- 关于content-type
content-type 包含了表单类型和边界字符串信息. 关于content-type get请求的headers中没有content-type这个字段 post 的 content-type 有两 ...
- Windows 10 游戏录制工具栏
- C++中static和const关键字的作用
static关键字至少有下列几个作用: 函数体内static变量的作用范围为该函数体,不同于auto变量,该变量的内存只被分配一次,因此其值在下次调用时仍维持上次的值: 在模块内的static全局变量 ...
- RunLoop主要处理以下6类事件
1.Observer事件,runloop中状态变化时进行通知.(微信卡顿监控就是利用这个事件通知来记录下最近一次main runloop活动时间,在另一个check线程中用定时器检测当前时间距离最后一 ...
- python简单的购物系统
#coding = utf-8 #2016-11-19#我的工资是存在文件中的,执行后会判断是否存过工资,如果存过无需输入,直接购物,没存过需要输入工资#wages.txt是存工资的文件 import ...
- Mysql ERROR 1067: Invalid default value for 字段
问题: //今天把一个数据库的sql文件导入到另一个数据库出现以下异常: Mysql ERROR 1067: Invalid default value for 字段 //原因是因为之前导出数据里面有 ...
- linux下安装Tomcat和java jdk
1:上传jdk的gz文件到linux’系统 2:解压缩这个文件 tar –zxvf 文件名.tar.gz –C 指定目录 比如我这里解压到 /root/apps/jdk tar –zxvf jd ...
