SpringCache的基本使用
SpringCache
SpringCache是一个框架,实现了基于注解的缓存功能。SpringCache提供了一层抽象,底层可以切换不同的cache实现。具体是通过CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术.
CacheManager是Spring提供的各种缓存技术抽象接口.
针对不同的缓存技术需要实现不同的CacheManager:
| CacheManmager | 描述 | |
|---|---|---|
| EhCacheCacheManager | 使用EhCache作为缓存技术 | |
| GuavaCacheManager | 使用Google的GuavaCache作为缓存技术 | |
| RedisCacheManager | 使用Redis作为缓存技术 | |
| ...... ...... | ||
| 使用Map也可以实现缓存 |
SpringCache常用注解
| 注解 | 说明 | |
|---|---|---|
| @EnableCaching | 开启缓存注解功能 | |
| @CachePut | 在方法执行前Spring先查看缓存中是否有数据,如果有数据,则直接返回缓存数据; 如果没有数据,调用方法并将方法返回值放到缓存中 | |
| @CacheEvict | 将一条或多条数据从缓存中删除 |
@SpringBoot项目中,使用缓存技术只需要在项目中导入相关缓存技术的依赖包,并在启动类上使用@EnableCaching开启缓存技术即可.
底层使用Map来实现缓存
首先导入相应的依赖
<!-- 导入这个就可以使用 SpringCache的基础功能了,因为相关依赖也被导入了,
这里暂时使用 Map来实现缓存,如果使用 Redis还需要导入Redis相关的依赖
spring-boot-starter-cache
很多基本的API都在 spring-context 上下文依赖中.
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
启动类上开启缓存注解
@Slf4j
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching // 开启缓存 基础的 API都在 spring-context jar包中 上下文 jar包.
public class CacheDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CacheDemoApplication.class,args);
log.info("项目启动成功...");
}
}
先看一下,此时提供的对CacheManager默认的实现
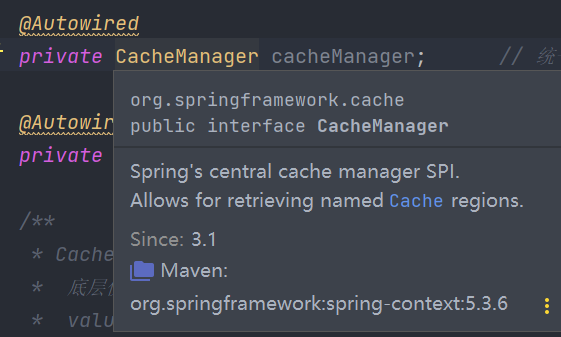
默认是提供了这五个实现
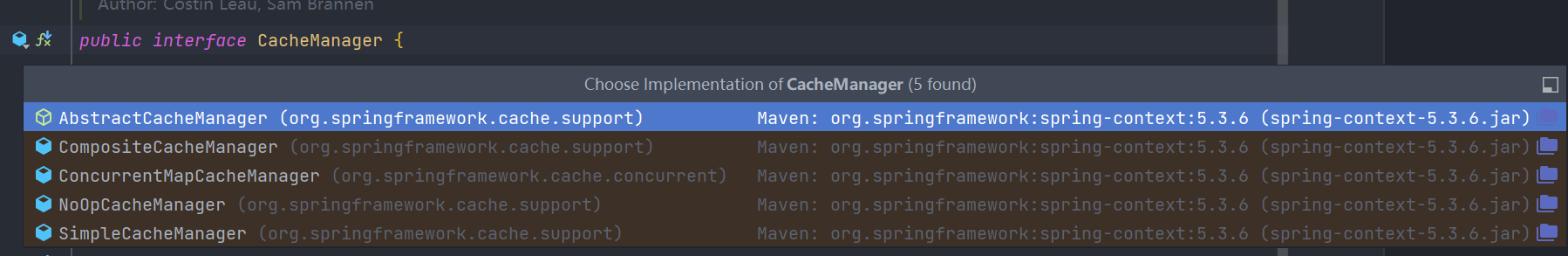
此案例使用的是 ConcurrentMapCacheManager
使用ConcurrentMap来实现缓存,也就是使用 Map 来实现缓存
controller层的练习案例
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
@Slf4j
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private CacheManager cacheManager; // 统一不同的缓存技术 默认用的是 ConcurrentMapManager,ConcurrentMap缓存数据
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
/**
* CachePut 将方法的返回值放入缓存中
* 底层使用什么缓存产品,就看当前配置的缓存。这个案例中使用的最基础的环境,使用的是 Map来实现的缓存.
* value: 缓存的名称
* key: 缓存的 key 一般不写死,key的值应该是动态的. key支持 SpEL Spring表达式语言,可以动态地计算 key值. #表达式
* #result 代表方法的返回值
* #root 代表当前的方法 root.method root.methodName root.targetClass root.caches
* 获取方法参数 #user,user就是形参变量,注意名字要一样 #user.name #user.id
* 还可以这样获取参数,#root.args[index],下标从 0开始.
* 或者这样 #pindex p是固定写法,后面跟下标. #p1 #p0
* 每个缓存名称下面可以有多个 key
*
* 这个 Map是基于内存的,服务重启之后,缓存中的数据就没有了.
* @param user 用户对象
* @return 保存的用户对象数据
*/
@CachePut(value = "userCache", key = "#result.id") // 把插入的数据放到缓存中,需要指定 value,value 代表缓存的名称, key代表缓存的 key.
@PostMapping // value 是 一类缓存;具体这个分类下面可能会有多个缓存数据,多个缓存数据就需要根据 key来进行区分.
public User save(User user){
userService.save(user);
return user;
}
/**
* CacheEvict 清理指定缓存
* value
* key
* 具体哪个缓存,由 value 和 key 来指定. 唯一锁定缓存数据.
* @param id
*/
// @CacheEvict(value = "userCache", key = "#p0")
// @CacheEvict(value = "userCache", key = "#root.args[0]")
@CacheEvict(value = "userCache", key = "#id") // 注意,这个名字要和参数名保持一致,这样可以获取参数变量
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public void delete(@PathVariable Long id){
userService.removeById(id);
}
// @CacheEvict(value = "userCache", key = "#p0.id")
// @CacheEvict(value = "userCache", key = "#user.id")
// @CacheEvict(value = "userCache", key = "#root.args[0].id")
@CacheEvict(value = "userCache", key = "#result.id") // 从返回结果中获取.
@PutMapping
public User update(User user){
userService.updateById(user);
return user;
}
/**
* Cacheable 若缓存中有数据,直接在缓存中拿; 如果没有,先从数据库中查出,然后再放入缓存中
* value
* key
* condition: 条件,满足条件时才会缓存数据
* unless: 满足这个条件时,不会缓存数据, 和 condition 相反.
* @param id id
* @return 查询结果
*/
@Cacheable(value = "userCache", key = "#id", condition = "#result != null") // 如果有缓存,则直接从缓存中拿数据. 没有的话先从数据库中取,然后再放入缓存.
@GetMapping("/{id}") // 查不存在的数据,返回为空,也会给缓存上. id 为 key,value 为 null 缓存
public User getById(@PathVariable Long id){ // 如何配置,value 不为空时才会缓存呢? 使用 condition属性或者 unless属性
User user = userService.getById(id);
return user;
}
@Cacheable(value = "userCache", key = "#user.id + '_' + #user.name") // 不同的查询条件分别对应不同的缓存数据.
@GetMapping("/list")
public List<User> list(User user){
LambdaQueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(user.getId() != null,User::getId,user.getId());
queryWrapper.eq(user.getName() != null,User::getName,user.getName());
List<User> list = userService.list(queryWrapper);
return list;
}
}
底层使用Redis来实现缓存技术
引入依赖
<!-- SpringCache使用Redis实现缓存技术
spring-boot-starter-cache 扩展了一些对缓存技术的整合
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Redis的 cacheManager RedisCacheManager
在这个依赖中.
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
引入 spring-boot-starter-cache 后,看一下底层对 CacheManager 的实现扩展了哪些
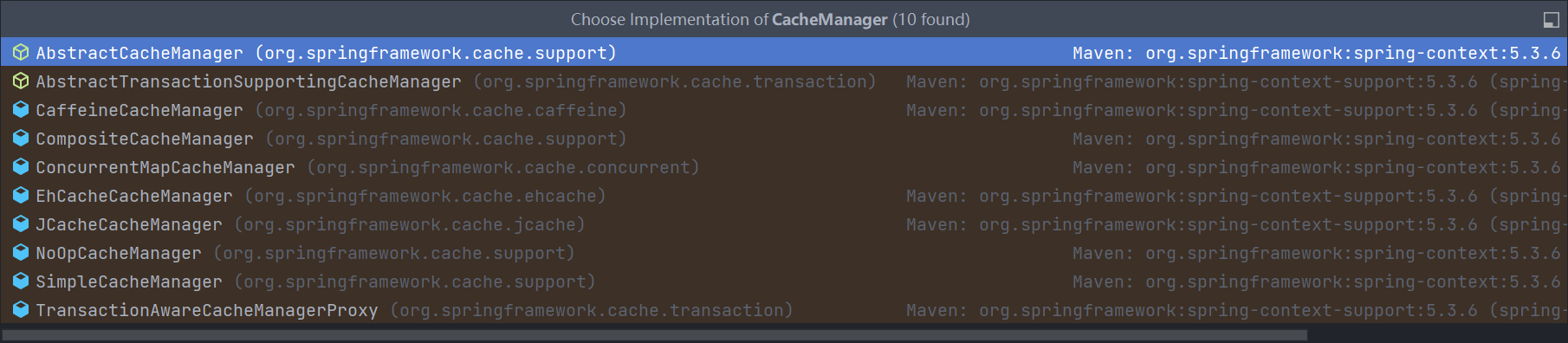
这里扩展了很多实现,但是没有 Redis 的 cacheManager,那么需要再引入 spring-boot-starter-data-redis 依赖才可以,引入后再观察
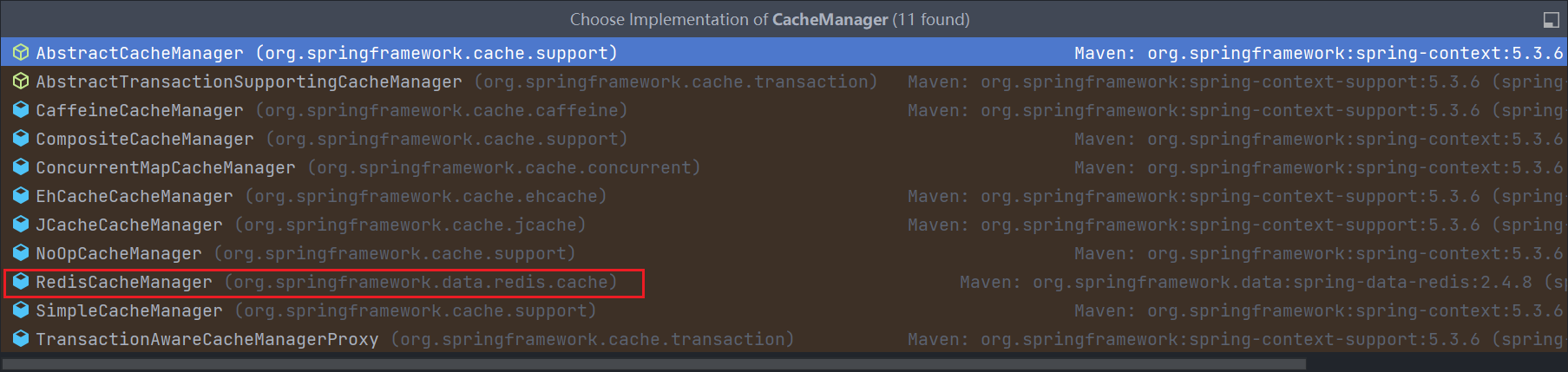
可以看到有了关于 RedisCacheManager 的实现.
相关配置文件中的配置
spring:
# redis 配置
redis:
host: your ip
port: your port
password: your password
database: 0
# 设置缓存有效期
cache:
redis:
time-to-live: 1800000 #单位毫秒,30min
那么此时底层就换成了redis来实现缓存技术了,用法都是一样的
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.LambdaQueryWrapper;
import com.itheima.entity.User;
import com.itheima.service.UserService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
@Slf4j
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private CacheManager cacheManager; // 统一不同的缓存技术 默认用的是 ConcurrentMapManager,ConcurrentMap缓存数据
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
/**
* CachePut 将方法的返回值放入缓存中
* 底层使用什么缓存产品,就看当前配置的缓存。这个案例中使用的最基础的环境,使用的是 Map来实现的缓存.
* value: 缓存的名称
* key: 缓存的 key 一般不写死,key的值应该是动态的. key支持 SpEL Spring表达式语言,可以动态地计算 key值. #表达式
* #result 代表方法的返回值
* #root 代表当前的方法 root.method root.methodName root.targetClass root.caches
* 获取方法参数 #user,user就是形参变量,注意名字要一样 #user.name #user.id
* 还可以这样获取参数,#root.args[index],下标从 0开始.
* 或者这样 #pindex p是固定写法,后面跟下标. #p1 #p0
* 每个缓存名称下面可以有多个 key
*
* 这个 Map是基于内存的,服务重启之后,缓存中的数据就没有了.
* @param user 用户对象
* @return 保存的用户对象数据
*/
@CachePut(value = "userCache", key = "#result.id") // 把插入的数据放到缓存中,需要指定 value,value 代表缓存的名称, key代表缓存的 key.
@PostMapping // value 是 一类缓存;具体这个分类下面可能会有多个缓存数据,多个缓存数据就需要根据 key来进行区分.
public User save(User user){
userService.save(user);
return user;
}
/**
* CacheEvict 清理指定缓存
* value
* key
* 具体哪个缓存,由 value 和 key 来指定. 唯一锁定缓存数据.
* @param id
*/
// @CacheEvict(value = "userCache", key = "#p0")
// @CacheEvict(value = "userCache", key = "#root.args[0]")
@CacheEvict(value = "userCache", key = "#id") // 注意,这个名字要和参数名保持一致,这样可以获取参数变量
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public void delete(@PathVariable Long id){
userService.removeById(id);
}
// @CacheEvict(value = "userCache", key = "#p0.id")
// @CacheEvict(value = "userCache", key = "#user.id")
// @CacheEvict(value = "userCache", key = "#root.args[0].id")
@CacheEvict(value = "userCache", key = "#result.id") // 从返回结果中获取.
@PutMapping
public User update(User user){
userService.updateById(user);
return user;
}
/**
* Cacheable 若缓存中有数据,直接在缓存中拿; 如果没有,先从数据库中查出,然后再放入缓存中
* value
* key
* condition: 条件,满足条件时才会缓存数据
* unless: 满足这个条件时,不会缓存数据, 和 condition 相反.
* @param id id
* @return 查询结果
*/
// @Cacheable(value = "userCache", key = "#id", condition = "#result != null") // 如果有缓存,则直接从缓存中拿数据. 没有的话先从数据库中取,然后再放入缓存.
@Cacheable(value = "userCache", key = "#id", unless = "#result == null") // 换成了 redis,redis的 condition中是不能使用 result返回结果的.
@GetMapping("/{id}") // 查不存在的数据,返回为空,也会给缓存上. id 为 key,value 为 null 缓存
public User getById(@PathVariable Long id){ // 如何配置,value 不为空时才会缓存呢? 使用 condition属性或者 unless属性
User user = userService.getById(id);
return user;
}
@Cacheable(value = "userCache", key = "#user.id + '_' + #user.name") // 不同的查询条件分别对应不同的缓存数据.
@GetMapping("/list")
public List<User> list(User user){
LambdaQueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(user.getId() != null,User::getId,user.getId());
queryWrapper.eq(user.getName() != null,User::getName,user.getName());
List<User> list = userService.list(queryWrapper);
return list;
}
}
注意: Cacheable 的 condition属性,其 SpEL 是没有 result的
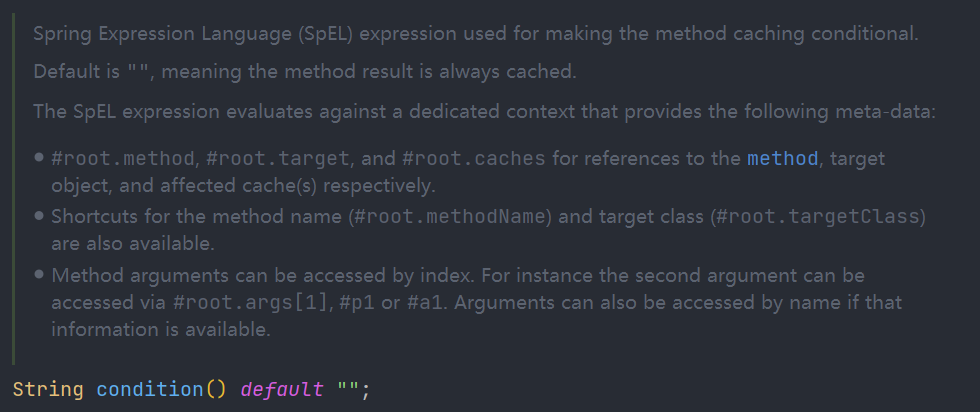
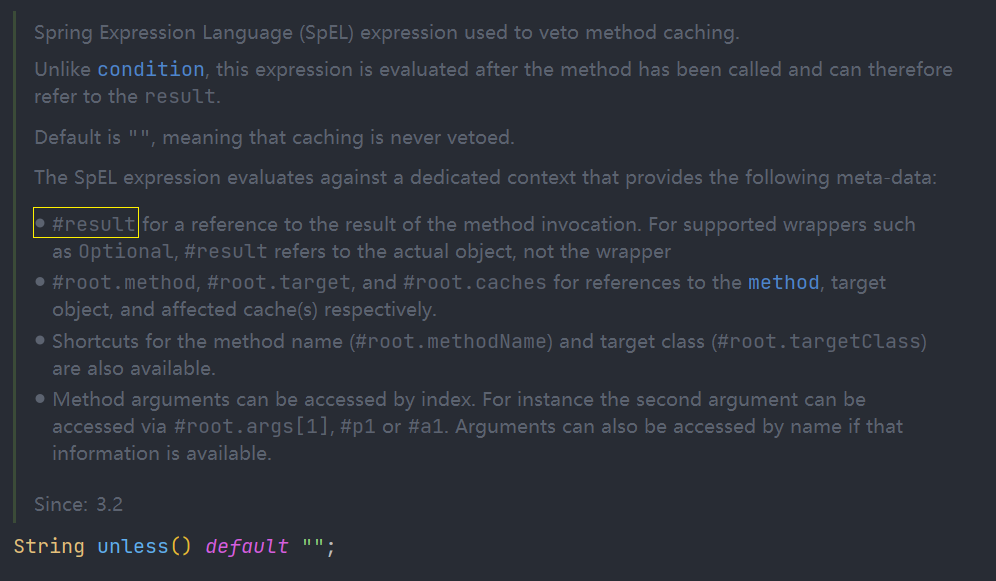
而 unless属性是可以使用 result 的
SpringCache的基本使用的更多相关文章
- SpringCache缓存初探
body,table tr { background-color: #fff } table tr td,table tr th { border: 1px solid #ccc; text-alig ...
- SpringCache与redis集成,优雅的缓存解决方案
缓存可以说是加速服务响应速度的一种非常有效并且简单的方式.在缓存领域,有很多知名的框架,如EhCache .Guava.HazelCast等.Redis作为key-value型数据库,由于他的这一特性 ...
- SpringCache @Cacheable 在同一个类中调用方法,导致缓存不生效的问题及解决办法
由于项目需要使用SpringCache来做一点缓存,但自己之前没有使用过(其实是没有听过)SpringCache,于是,必须先学习之. 在网上找到一篇文章,比较好,就先学习了,地址是: https:/ ...
- SpringCache学习之操作redis
一.redis快速入门 1.redis简介 在java领域,常见的四大缓存分别是ehcache,memcached,redis,guava-cache,其中redis与其他类型缓存相比,有着得天独厚的 ...
- SpringBoot基础系列-SpringCache使用
原创文章,转载请标注出处:<SpringBoot基础系列-SpringCache使用> 一.概述 SpringCache本身是一个缓存体系的抽象实现,并没有具体的缓存能力,要使用Sprin ...
- spring-boot的spring-cache中的扩展redis缓存的ttl和key名
原文地址:spring-boot的spring-cache中的扩展redis缓存的ttl和key名 前提 spring-cache大家都用过,其中使用redis-cache大家也用过,至于如何使用怎么 ...
- SpringCache实战遇坑
1. SpringCache实战遇坑 1.1. pom 主要是以下两个 <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</g ...
- SpringCache学习实践
1. SpringCache学习实践 1.1. 引用 <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> ...
- SpringBoot2.X + SpringCache + redis解决乱码问题
环境:SpringBoot2.X + SpringCache + Redis Spring boot默认使用的是SimpleCacheConfiguration,使用ConcurrentMapCach ...
- AOP方法增强自身内部方法调用无效 SpringCache 例子
开启注解@EnableCaChing,配置CacheManager,结合注解@Cacheable,@CacheEvit,@CachePut对数据进行缓存操作 缺点:内部调用,非Public方法上使用注 ...
随机推荐
- SQLite数据库损坏及其修复探究
数据库如何发生损坏 SQLite 数据库具有很强的抗损坏能力.在执行事务时如果发生应用程序崩溃.操作系统崩溃甚至电源故障,那么在下次访问数据库文件时,会自动回滚部分写入的事务.恢复过程是全自动的, ...
- BUUCTF-BJDCTF2020]just_a_rar
BJDCTF2020]just_a_rar 压缩包提示是四位数密码 爆破得知压缩包密码 16进制查看解压的图片后发现flag flag{Wadf_123}
- Vue回炉重造之router路由(更新中)
安装vue-router npm i vue-router -S 配置1.创建文件夹与文件 创建一个router文件夹,在文件夹中创建两个文件,分别是router.js和routes.js文件.2.编 ...
- SpringBoot之缓存
一.准备工作 首先整合使用Spring整合MyBatis. 可参阅:SpringBoot整合MyBatis SpringBoot整合MyBatis完后后,我们需要在pom.xml中添加缓存相关的依赖. ...
- UiPath手把手教程
UiPath下载安装与激活 链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1o5Ur-QNTxsnlhi97-losJQ 提取码: 9dmf 复制这段内容后打开百度网盘手机App,操作更方便 ...
- Python教程:执行cmd命令
我们通常可以使用os模块的命令进行执行cmd 方法一:os.system def system(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown "&qu ...
- 数组基础篇(对应C++ Primer plus 4.10)
概要:数组是由一组同类型的元素组成的集合,在内存上是一片连续的存储空间.C++提供了三种数组的表示方法:普通数组,模板类vector(C++98 新增的标准模板库STL提供该模板类)和模板类array ...
- 详解HashMap源码解析(下)
上文详解HashMap源码解析(上)介绍了HashMap整体介绍了一下数据结构,主要属性字段,获取数组的索引下标,以及几个构造方法.本文重点讲解元素的添加.查找.扩容等主要方法. 添加元素 put(K ...
- 递归概念&分类&注意事项和练习_使用递归计算1-n之间的和
递归:方法自己调用自己 递归的分类: 递归分为两种,直接递归和间接递归 直接递归称为方法自身调用自己 间接递归可以A方法调用B方法,B方法调用C方法,C方法调用A方法 注意事项: 递归一定要有条件限定 ...
- 【cartographer_ros】六: 发布和订阅路标landmark信息
上一节介绍了陀螺仪Imu传感数据的订阅和发布. 本节会介绍路标Landmark数据的发布和订阅.Landmark在cartographer中作为定位的修正补充,避免定位丢失. 这里着重解释一下Land ...
