Spring Cloud Feign设计原理
什么是Feign?
Feign 的英文表意为“假装,伪装,变形”, 是一个http请求调用的轻量级框架,可以以Java接口注解的方式调用Http请求,而不用像Java中通过封装HTTP请求报文的方式直接调用。Feign通过处理注解,将请求模板化,当实际调用的时候,传入参数,根据参数再应用到请求上,进而转化成真正的请求,这种请求相对而言比较直观。
Feign被广泛应用在Spring Cloud 的解决方案中,是学习基于Spring Cloud 微服务架构不可或缺的重要组件。
Feign解决了什么问题?
封装了Http调用流程,更适合面向接口化的变成习惯
在服务调用的场景中,我们经常调用基于Http协议的服务,而我们经常使用到的框架可能有HttpURLConnection、Apache HttpComponnets、OkHttp3 、Netty等等,这些框架在基于自身的专注点提供了自身特性。而从角色划分上来看,他们的职能是一致的提供Http调用服务。具体流程如下:
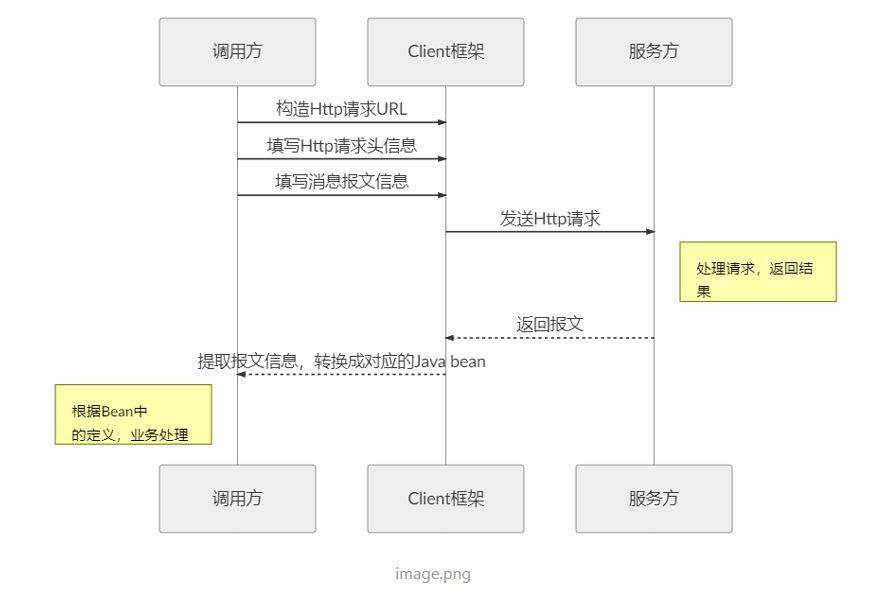
Feign是如何设计的?

PHASE 1. 基于面向接口的动态代理方式生成实现类
在使用feign 时,会定义对应的接口类,在接口类上使用Http相关的注解,标识HTTP请求参数信息,如下所示:
interface GitHub {
@RequestLine("GET /repos/{owner}/{repo}/contributors")
List<Contributor> contributors(@Param("owner") String owner, @Param("repo") String repo);
}
public static class Contributor {
String login;
int contributions;
}
public class MyApp {
public static void main(String... args) {
GitHub github = Feign.builder()
.decoder(new GsonDecoder())
.target(GitHub.class, "https://api.github.com");
// Fetch and print a list of the contributors to this library.
List<Contributor> contributors = github.contributors("OpenFeign", "feign");
for (Contributor contributor : contributors) {
System.out.println(contributor.login + " (" + contributor.contributions + ")");
}
}
}
在Feign 底层,通过基于面向接口的动态代理方式生成实现类,将请求调用委托到动态代理实现类,基本原理如下所示:
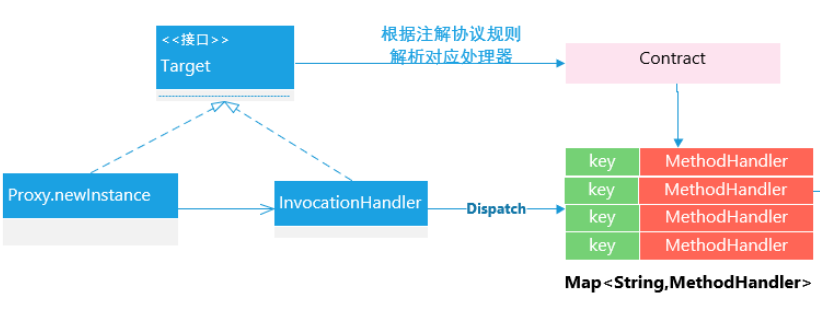
public class ReflectiveFeign extends Feign{
///省略部分代码
@Override
public <T> T newInstance(Target<T> target) {
//根据接口类和Contract协议解析方式,解析接口类上的方法和注解,转换成内部的MethodHandler处理方式
Map<String, MethodHandler> nameToHandler = targetToHandlersByName.apply(target);
Map<Method, MethodHandler> methodToHandler = new LinkedHashMap<Method, MethodHandler>();
List<DefaultMethodHandler> defaultMethodHandlers = new LinkedList<DefaultMethodHandler>();
for (Method method : target.type().getMethods()) {
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
continue;
} else if(Util.isDefault(method)) {
DefaultMethodHandler handler = new DefaultMethodHandler(method);
defaultMethodHandlers.add(handler);
methodToHandler.put(method, handler);
} else {
methodToHandler.put(method, nameToHandler.get(Feign.configKey(target.type(), method)));
}
}
InvocationHandler handler = factory.create(target, methodToHandler);
// 基于Proxy.newProxyInstance 为接口类创建动态实现,将所有的请求转换给InvocationHandler 处理。
T proxy = (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.type().getClassLoader(), new Class<?>[]{target.type()}, handler);
for(DefaultMethodHandler defaultMethodHandler : defaultMethodHandlers) {
defaultMethodHandler.bindTo(proxy);
}
return proxy;
}
//省略部分代码
PHASE 2. 根据Contract协议规则,解析接口类的注解信息,解析成内部表现:
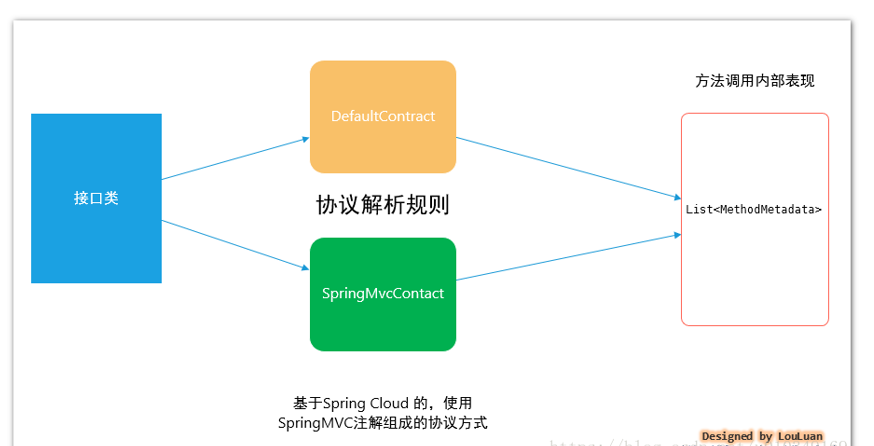
Feign 定义了转换协议,定义如下:
/**
* Defines what annotations and values are valid on interfaces.
*/
public interface Contract { /**
* Called to parse the methods in the class that are linked to HTTP requests.
* 传入接口定义,解析成相应的方法内部元数据表示
* @param targetType {@link feign.Target#type() type} of the Feign interface.
*/
// TODO: break this and correct spelling at some point
List<MethodMetadata> parseAndValidatateMetadata(Class<?> targetType);
}
默认Contract 实现
Feign 默认有一套自己的协议规范,规定了一些注解,可以映射成对应的Http请求,如官方的一个例子:
public interface GitHub {
@RequestLine("GET /repos/{owner}/{repo}/contributors")
List<Contributor> getContributors(@Param("owner") String owner, @Param("repo") String repository);
class Contributor {
String login;
int contributions;
}
}
上述的例子中,尝试调用GitHub.getContributors("foo","myrepo")的的时候,会转换成如下的HTTP请求:
GET /repos/foo/myrepo/contributors
HOST XXXX.XXX.XXX
Feign 默认的协议规范

基于Spring MVC的协议规范SpringMvcContract:
当前Spring Cloud 微服务解决方案中,为了降低学习成本,采用了Spring MVC的部分注解来完成 请求协议解析,也就是说 ,写客户端请求接口和像写服务端代码一样:客户端和服务端可以通过SDK的方式进行约定,客户端只需要引入服务端发布的SDK API,就可以使用面向接口的编码方式对接服务:

我们团队内部就是按照这种思路,结合Spring Boot Starter 的特性,定义了服务端starter,
服务消费者在使用的时候,只需要引入Starter,就可以调用服务。这个比较适合平台无关性,接口抽象出来的好处就是可以根据服务调用实现方式自有切换:
- 可以基于简单的Http服务调用;
- 可以基于Spring Cloud 微服务架构调用;
- 可以基于Dubbo SOA服务治理
这种模式比较适合在SaSS混合软件服务的模式下自有切换,根据客户的硬件能力选择合适的方式部署,也可以基于自身的服务集群部署微服务
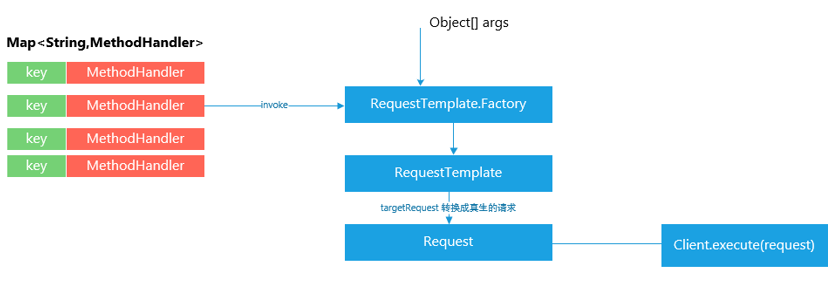
PHASE 3. 基于 RequestBean,动态生成Request
根据传入的Bean对象和注解信息,从中提取出相应的值,来构造Http Request 对象:
PHASE 4. 使用Encoder 将Bean转换成 Http报文正文(消息解析和转码逻辑)
Feign 最终会将请求转换成Http 消息发送出去,传入的请求对象最终会解析成消息体,如下所示:
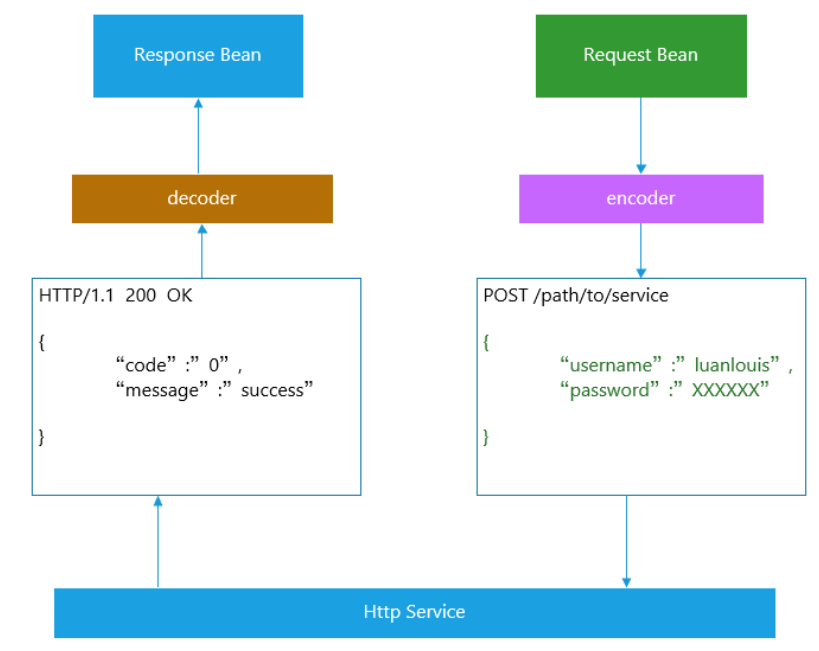
在接口定义上Feign做的比较简单,抽象出了Encoder 和decoder 接口:
public interface Encoder {
/** Type literal for {@code Map<String, ?>}, indicating the object to encode is a form. */
Type MAP_STRING_WILDCARD = Util.MAP_STRING_WILDCARD;
/**
* Converts objects to an appropriate representation in the template.
* 将实体对象转换成Http请求的消息正文中
* @param object what to encode as the request body.
* @param bodyType the type the object should be encoded as. {@link #MAP_STRING_WILDCARD}
* indicates form encoding.
* @param template the request template to populate.
* @throws EncodeException when encoding failed due to a checked exception.
*/
void encode(Object object, Type bodyType, RequestTemplate template) throws EncodeException;
/**
* Default implementation of {@code Encoder}.
*/
class Default implements Encoder {
@Override
public void encode(Object object, Type bodyType, RequestTemplate template) {
if (bodyType == String.class) {
template.body(object.toString());
} else if (bodyType == byte[].class) {
template.body((byte[]) object, null);
} else if (object != null) {
throw new EncodeException(
format("%s is not a type supported by this encoder.", object.getClass()));
}
}
}
}
public interface Decoder {
/**
* Decodes an http response into an object corresponding to its {@link
* java.lang.reflect.Method#getGenericReturnType() generic return type}. If you need to wrap
* exceptions, please do so via {@link DecodeException}.
* 从Response 中提取Http消息正文,通过接口类声明的返回类型,消息自动装配
* @param response the response to decode
* @param type {@link java.lang.reflect.Method#getGenericReturnType() generic return type} of
* the method corresponding to this {@code response}.
* @return instance of {@code type}
* @throws IOException will be propagated safely to the caller.
* @throws DecodeException when decoding failed due to a checked exception besides IOException.
* @throws FeignException when decoding succeeds, but conveys the operation failed.
*/
Object decode(Response response, Type type) throws IOException, DecodeException, FeignException;
/** Default implementation of {@code Decoder}. */
public class Default extends StringDecoder {
@Override
public Object decode(Response response, Type type) throws IOException {
if (response.status() == 404) return Util.emptyValueOf(type);
if (response.body() == null) return null;
if (byte[].class.equals(type)) {
return Util.toByteArray(response.body().asInputStream());
}
return super.decode(response, type);
}
}
}
目前Feign 有以下实现
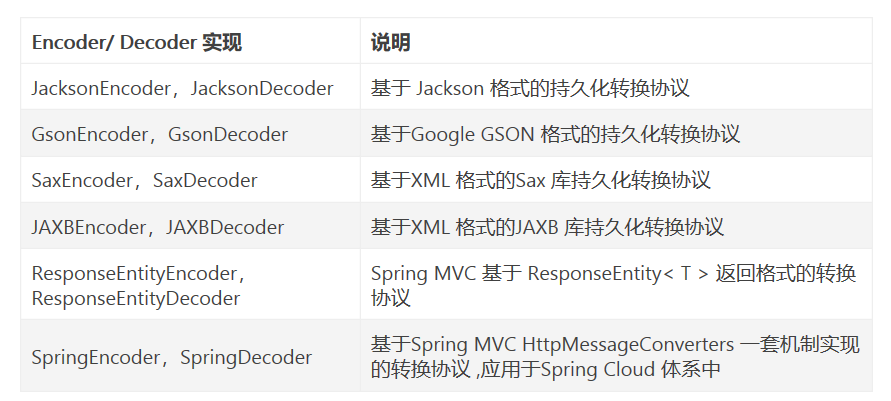
PHASE 5. 拦截器负责对请求和返回进行装饰处理
在请求转换的过程中,Feign 抽象出来了拦截器接口,用于用户自定义对请求的操作:
public interface RequestInterceptor {
/**
* 可以在构造RequestTemplate 请求时,增加或者修改Header, Method, Body 等信息
* Called for every request. Add data using methods on the supplied {@link RequestTemplate}.
*/
void apply(RequestTemplate template);
}
比如,如果希望Http消息传递过程中被压缩,可以定义一个请求拦截器:
public class FeignAcceptGzipEncodingInterceptor extends BaseRequestInterceptor {
/**
* Creates new instance of {@link FeignAcceptGzipEncodingInterceptor}.
*
* @param properties the encoding properties
*/
protected FeignAcceptGzipEncodingInterceptor(FeignClientEncodingProperties properties) {
super(properties);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void apply(RequestTemplate template) {
// 在Header 头部添加相应的数据信息
addHeader(template, HttpEncoding.ACCEPT_ENCODING_HEADER, HttpEncoding.GZIP_ENCODING,
HttpEncoding.DEFLATE_ENCODING);
}
}
PHASE 6. 日志记录
在发送和接收请求的时候,Feign定义了统一的日志门面来输出日志信息 , 并且将日志的输出定义了四个等级:

public abstract class Logger {
protected static String methodTag(String configKey) {
return new StringBuilder().append('[').append(configKey.substring(0, configKey.indexOf('(')))
.append("] ").toString();
}
/**
* Override to log requests and responses using your own implementation. Messages will be http
* request and response text.
*
* @param configKey value of {@link Feign#configKey(Class, java.lang.reflect.Method)}
* @param format {@link java.util.Formatter format string}
* @param args arguments applied to {@code format}
*/
protected abstract void log(String configKey, String format, Object... args);
protected void logRequest(String configKey, Level logLevel, Request request) {
log(configKey, "---> %s %s HTTP/1.1", request.method(), request.url());
if (logLevel.ordinal() >= Level.HEADERS.ordinal()) {
for (String field : request.headers().keySet()) {
for (String value : valuesOrEmpty(request.headers(), field)) {
log(configKey, "%s: %s", field, value);
}
}
int bodyLength = 0;
if (request.body() != null) {
bodyLength = request.body().length;
if (logLevel.ordinal() >= Level.FULL.ordinal()) {
String
bodyText =
request.charset() != null ? new String(request.body(), request.charset()) : null;
log(configKey, ""); // CRLF
log(configKey, "%s", bodyText != null ? bodyText : "Binary data");
}
}
log(configKey, "---> END HTTP (%s-byte body)", bodyLength);
}
}
protected void logRetry(String configKey, Level logLevel) {
log(configKey, "---> RETRYING");
}
protected Response logAndRebufferResponse(String configKey, Level logLevel, Response response,
long elapsedTime) throws IOException {
String reason = response.reason() != null && logLevel.compareTo(Level.NONE) > 0 ?
" " + response.reason() : "";
int status = response.status();
log(configKey, "<--- HTTP/1.1 %s%s (%sms)", status, reason, elapsedTime);
if (logLevel.ordinal() >= Level.HEADERS.ordinal()) {
for (String field : response.headers().keySet()) {
for (String value : valuesOrEmpty(response.headers(), field)) {
log(configKey, "%s: %s", field, value);
}
}
int bodyLength = 0;
if (response.body() != null && !(status == 204 || status == 205)) {
// HTTP 204 No Content "...response MUST NOT include a message-body"
// HTTP 205 Reset Content "...response MUST NOT include an entity"
if (logLevel.ordinal() >= Level.FULL.ordinal()) {
log(configKey, ""); // CRLF
}
byte[] bodyData = Util.toByteArray(response.body().asInputStream());
bodyLength = bodyData.length;
if (logLevel.ordinal() >= Level.FULL.ordinal() && bodyLength > 0) {
log(configKey, "%s", decodeOrDefault(bodyData, UTF_8, "Binary data"));
}
log(configKey, "<--- END HTTP (%s-byte body)", bodyLength);
return response.toBuilder().body(bodyData).build();
} else {
log(configKey, "<--- END HTTP (%s-byte body)", bodyLength);
}
}
return response;
}
protected IOException logIOException(String configKey, Level logLevel, IOException ioe, long elapsedTime) {
log(configKey, "<--- ERROR %s: %s (%sms)", ioe.getClass().getSimpleName(), ioe.getMessage(),
elapsedTime);
if (logLevel.ordinal() >= Level.FULL.ordinal()) {
StringWriter sw = new StringWriter();
ioe.printStackTrace(new PrintWriter(sw));
log(configKey, sw.toString());
log(configKey, "<--- END ERROR");
}
return ioe;
}
PHASE 7 . 基于重试器发送HTTP请求
Feign 内置了一个重试器,当HTTP请求出现IO异常时,Feign会有一个最大尝试次数发送请求,以下是Feign核心
代码逻辑:
final class SynchronousMethodHandler implements MethodHandler {
// 省略部分代码
@Override
public Object invoke(Object[] argv) throws Throwable {
//根据输入参数,构造Http 请求。
RequestTemplate template = buildTemplateFromArgs.create(argv);
// 克隆出一份重试器
Retryer retryer = this.retryer.clone();
// 尝试最大次数,如果中间有结果,直接返回
while (true) {
try {
return executeAndDecode(template);
} catch (RetryableException e) {
retryer.continueOrPropagate(e);
if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) {
logger.logRetry(metadata.configKey(), logLevel);
}
continue;
}
}
}
重试器有如下几个控制参数:

PHASE 8. 发送Http请求
Feign 真正发送HTTP请求是委托给 feign.Client 来做的:
public interface Client {
/**
* Executes a request against its {@link Request#url() url} and returns a response.
* 执行Http请求,并返回Response
* @param request safe to replay.
* @param options options to apply to this request.
* @return connected response, {@link Response.Body} is absent or unread.
* @throws IOException on a network error connecting to {@link Request#url()}.
*/
Response execute(Request request, Options options) throws IOException;
}
Feign 默认底层通过JDK 的 java.net.HttpURLConnection 实现了feign.Client接口类,在每次发送请求的时候,都会创建新的HttpURLConnection 链接,这也就是为什么默认情况下Feign的性能很差的原因。可以通过拓展该接口,使用Apache HttpClient 或者OkHttp3等基于连接池的高性能Http客户端,我们项目内部使用的就是OkHttp3作为Http 客户端。
如下是Feign 的默认实现,供参考:
public static class Default implements Client {
private final SSLSocketFactory sslContextFactory;
private final HostnameVerifier hostnameVerifier;
/**
* Null parameters imply platform defaults.
*/
public Default(SSLSocketFactory sslContextFactory, HostnameVerifier hostnameVerifier) {
this.sslContextFactory = sslContextFactory;
this.hostnameVerifier = hostnameVerifier;
}
@Override
public Response execute(Request request, Options options) throws IOException {
HttpURLConnection connection = convertAndSend(request, options);
return convertResponse(connection).toBuilder().request(request).build();
}
HttpURLConnection convertAndSend(Request request, Options options) throws IOException {
final HttpURLConnection
connection =
(HttpURLConnection) new URL(request.url()).openConnection();
if (connection instanceof HttpsURLConnection) {
HttpsURLConnection sslCon = (HttpsURLConnection) connection;
if (sslContextFactory != null) {
sslCon.setSSLSocketFactory(sslContextFactory);
}
if (hostnameVerifier != null) {
sslCon.setHostnameVerifier(hostnameVerifier);
}
}
connection.setConnectTimeout(options.connectTimeoutMillis());
connection.setReadTimeout(options.readTimeoutMillis());
connection.setAllowUserInteraction(false);
connection.setInstanceFollowRedirects(true);
connection.setRequestMethod(request.method());
Collection<String> contentEncodingValues = request.headers().get(CONTENT_ENCODING);
boolean
gzipEncodedRequest =
contentEncodingValues != null && contentEncodingValues.contains(ENCODING_GZIP);
boolean
deflateEncodedRequest =
contentEncodingValues != null && contentEncodingValues.contains(ENCODING_DEFLATE);
boolean hasAcceptHeader = false;
Integer contentLength = null;
for (String field : request.headers().keySet()) {
if (field.equalsIgnoreCase("Accept")) {
hasAcceptHeader = true;
}
for (String value : request.headers().get(field)) {
if (field.equals(CONTENT_LENGTH)) {
if (!gzipEncodedRequest && !deflateEncodedRequest) {
contentLength = Integer.valueOf(value);
connection.addRequestProperty(field, value);
}
} else {
connection.addRequestProperty(field, value);
}
}
}
// Some servers choke on the default accept string.
if (!hasAcceptHeader) {
connection.addRequestProperty("Accept", "*/*");
}
if (request.body() != null) {
if (contentLength != null) {
connection.setFixedLengthStreamingMode(contentLength);
} else {
connection.setChunkedStreamingMode(8196);
}
connection.setDoOutput(true);
OutputStream out = connection.getOutputStream();
if (gzipEncodedRequest) {
out = new GZIPOutputStream(out);
} else if (deflateEncodedRequest) {
out = new DeflaterOutputStream(out);
}
try {
out.write(request.body());
} finally {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException suppressed) { // NOPMD
}
}
}
return connection;
}
Response convertResponse(HttpURLConnection connection) throws IOException {
int status = connection.getResponseCode();
String reason = connection.getResponseMessage();
if (status < 0) {
throw new IOException(format("Invalid status(%s) executing %s %s", status,
connection.getRequestMethod(), connection.getURL()));
}
Map<String, Collection<String>> headers = new LinkedHashMap<String, Collection<String>>();
for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> field : connection.getHeaderFields().entrySet()) {
// response message
if (field.getKey() != null) {
headers.put(field.getKey(), field.getValue());
}
}
Integer length = connection.getContentLength();
if (length == -1) {
length = null;
}
InputStream stream;
if (status >= 400) {
stream = connection.getErrorStream();
} else {
stream = connection.getInputStream();
}
return Response.builder()
.status(status)
.reason(reason)
.headers(headers)
.body(stream, length)
.build();
}
}
Feign 的性能怎么样?
Feign 整体框架非常小巧,在处理请求转换和消息解析的过程中,基本上没什么时间消耗。真正影响性能的,是处理Http请求的环节。
扫描下方二维码获取更多知识和学习资料

Spring Cloud Feign设计原理的更多相关文章
- Spring Cloud OkHttp设计原理
Spring Cloud 框架最底层核心的组件就是服务调用方式,一般Spring Cloud框架采用的是HTTP的调用框架,本文将在 Spring Cloud应用场景下,介绍组件OkHttp3的设计原 ...
- Spring Could Feign 设计原理
什么是Feign? Feign 的英文表意为"假装,伪装,变形", 是一个http请求调用的轻量级框架,可以以Java接口注解的方式调用Http请求,而不用像Java中通过封装HT ...
- Spring cloud Feign 深度学习与应用
简介 Spring Cloud Feign是一个声明式的Web Service客户端,它的目的就是让Web Service调用更加简单.Feign提供了HTTP请求的模板,通过编写简单的接口和插入注解 ...
- Spring Cloud Feign原理详解
目录 1.什么是Feign? 2.Open Feign vs Spring Cloud Feign 2.1.OpenFeign 2.2.Spring Cloud Open Feign 3.Spring ...
- SpringCloud微服务实战二:Spring Cloud Ribbon 负载均衡 + Spring Cloud Feign 声明式调用
1.Spring Cloud Ribbon的作用 Ribbon是Netflix开发的一个负载均衡组件,它在服务体系中起着重要作用,Pivotal将其整合成为Spring Cloud Ribbon,与其 ...
- spring cloud --- Feign --- 心得
spring boot 1.5.9.RELEASE spring cloud Dalston.SR1 1.前言 什么是Feign? 为了简化我们的开发,Spring Cloud Fei ...
- Spring Cloud Feign 如何使用对象参数
概述 Spring Cloud Feign 用于微服务的封装,通过接口代理的实现方式让微服务调用变得简单,让微服务的使用上如同本地服务.但是它在传参方面不是很完美.在使用 Feign 代理 GET 请 ...
- 撸一撸Spring Cloud Ribbon的原理-负载均衡器
在上一篇<撸一撸Spring Cloud Ribbon的原理>中整理发现,RestTemplate内部调用负载均衡拦截器,拦截器内最终是调用了负载均衡器来选择服务实例. 接下来撸一撸负载均 ...
- 笔记:Spring Cloud Feign Ribbon 配置
由于 Spring Cloud Feign 的客户端负载均衡是通过 Spring Cloud Ribbon 实现的,所以我们可以直接通过配置 Ribbon 的客户端的方式来自定义各个服务客户端调用的参 ...
随机推荐
- [7.19NOIP模拟测试6]失恋三连(雾 题解
题面(加密) 不得不说这次的题除了引起单身汪极度不适之外还是出的很有水平的…… A. 很好的dp题 模型非常简单,如果数据范围足够友好的话就是一道dp入门题 30%: 我们可以设$dp[i][j]$为 ...
- “今日头条杯”首届湖北省大学程序设计竞赛(网络同步赛 )--E. DoveCCL and Resistance
题目描述:链接点此 这套题的github地址(里面包含了数据,题解,现场排名):点此 链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/104/D来源:牛客网 题目描述 ...
- LIBRARY_PATH是编译时候用的,LD_LIBRARY_PATH是程序运行是使用的
LD_LIBRARY_PATH与LIBRARY_PATH的区别 看起来很像,但是完全是两码事. LIBRARY_PATH is used by gcc before compilation to se ...
- linux R环境安装以及注意事项
安装Ryum install Ryum install readline-develyum install libXt-devel 1.安装后在R命令行启动Rserve,在脚本中不要重复加载Rserv ...
- 教你一些IDE中比较骚的操作技巧!
本文转自微信公众号「程序员的成长之路」id:cxydczzl IDEA 有个很牛逼的功能,那就是后缀补全(不是自动补全),很多人竟然不知道这个操作,还在手动敲代码. 这个功能可以使用代码补全来模板式地 ...
- source insight和vim同时使用
https://blog.csdn.net/wangn222/article/details/72721993 1.Source Insight中,Options->Custom Command ...
- could not stop cortex-m device
检查一下STM32复位管脚是不是0V,如果是0V的话并且你有上拉电阻,那么就断电后检查一下STM32的VCC和GND是否短路,我的就是两个贴片电容击穿造成的短路从而使RST无法拉高.
- python数据结构之快速排序
def quick_sort(nums): if not nums: return [] else: # 这里取第0个数为基点 flag = nums[0] # 小于flag 的放到左边 left = ...
- 第十二篇 requests模拟登陆知乎
了解http常见状态码 可以通过输入错误的密码来找到登陆知乎的post:url 把Headers拉到底部,可以看到form data _xsrf是需要发送的,需要发送给服务端,否则会返回403错误,提 ...
- S1#Python之shebang
点1 - Python之shebang 一. shebang 在计算机科学中,Shebang是一个由井号和叹号构成的字符串行,其出现在文本文件的第一行的前两个字符. 在文件中存在Shebang的情况下 ...
