SpringBoot2启动流程分析
首先上一张图,图片来自 SpringBoot启动流程解析
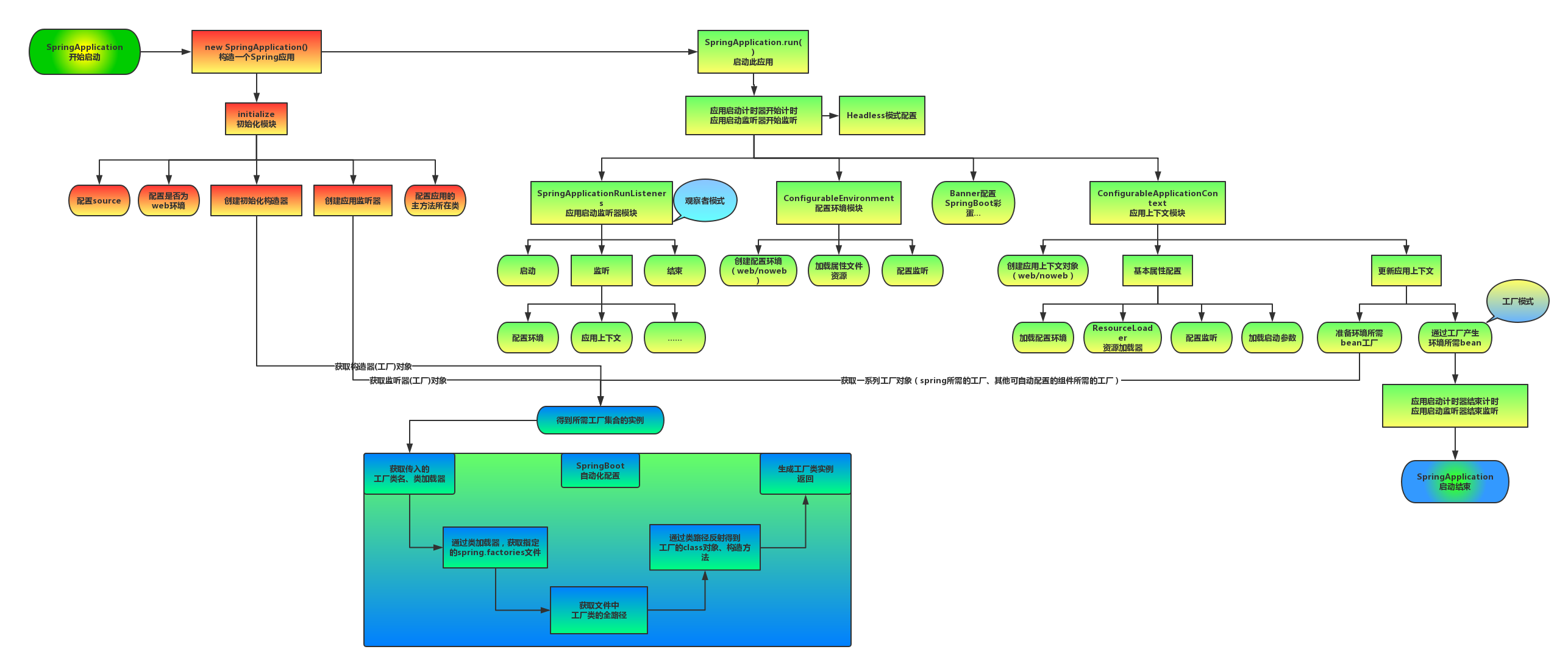
本文基于spring-boot-2.0.4.RELEASE.jar包分析。
程序启动入口
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot2Application.class, args);
}
run是一个静态方法,最后会调用创建SpringApplication实例并run
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class[]{primarySource}, args);
}
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return (new SpringApplication(primarySources)).run(args);
}
我们先看new SpringApplication(xx)构建的实例。
public SpringApplication(Class... primarySources) {
this((ResourceLoader)null, primarySources);
}
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class... primarySources) {
this.sources = new LinkedHashSet();
this.bannerMode = Mode.CONSOLE;
this.logStartupInfo = true;
this.addCommandLineProperties = true;
this.headless = true;
this.registerShutdownHook = true;
this.additionalProfiles = new HashSet();
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
//配置source
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
//判断是否web应用
this.webApplicationType = this.deduceWebApplicationType();
//创建初始化构造器
this.setInitializers(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
//创建应用监听器
this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
//推断出main方法类
this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
SpringApplication的构造函数主要设置了一些基本参数并配置source、判断了是否web应用、创建初始化构造器、创建应用监听器、找出main方法所在的类。
getSpringFactoriesInstances为获取spring工厂中的实例,具体代码块为
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
return this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class[0]);
}
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
//获取类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
//通过类加载器、获取指定的spring.factories文件,并获取文件中工厂类的全路径名
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
//通过类路径反射得到工厂class对象、构造方法
List<T> instances = this.createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
new SpringApplication(xx)构建完实例后,会进行run方法。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
//应用启动计时器开始计时
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
//Headless模式配置
configureHeadlessProperty();
//获取启动监听器
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
//应用启动监听器开始计时
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
//配置环境模块(祥见下面prepareEnvironment方法)
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
//配置需要忽略的bean
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
//Banner配置
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//创建应用上下文对象
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
//上下文基本属性配置(祥见下面prepareContext方法)
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
//更新应用上下文(祥见下面refresh方法)
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// 创建配置环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
//加载属性文件
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
//监听器监听配置
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (this.webApplicationType == WebApplicationType.NONE) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader())
.convertToStandardEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment);
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
//加载配置环境
context.setEnvironment(environment);
//ResourceLoader资源加载器
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
//初始化环境
applyInitializers(context);
//配置监听
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments",
applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
//加载启动参数
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
//监听加载应用上下文
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
Object var1 = this.startupShutdownMonitor;
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
//准备更新上下文时的预备工作:1.初始化PropertySource; 2.验证Enrivonment中必要的属性
this.prepareRefresh();
//获取上下文中的BeanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory();
//对BeanFactory做些预备工作
this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
//对BeanFactory进行预处理
this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//执行容器中的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//注册BeanPostProcessor
this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//初始化MessageSource(国际化相关)
this.initMessageSource();
//初始化容器事件广播器(用来发布事件)
this.initApplicationEventMulticaster();
//初始化一些特殊的Bean,主要做了: 1.初始化ThemeSource(跟国际化相关的接口) 2.创建WebServer
this.onRefresh();
//将所有监听器注册到前两步创建的事件广播器中
this.registerListeners();
//结束BeanFactory的初始化工作(这一步主要用来将所有的单例BeanDefinition实例化)
this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
//上下文刷新完毕
this.finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException var9) {
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var9);
}
this.destroyBeans();
this.cancelRefresh(var9);
throw var9;
} finally {
this.resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
SpringBoot2启动流程分析的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(五):SpringBoot自动装配原理实现
SpringBoot系列文章简介 SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇: Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现 SpringBoot启动流程源码分析: SpringBoot启动流程分析(一) ...
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(六):IoC容器依赖注入
SpringBoot系列文章简介 SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇: Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现 SpringBoot启动流程源码分析: SpringBoot启动流程分析(一) ...
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(一):SpringApplication类初始化过程
SpringBoot系列文章简介 SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇: Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现 SpringBoot启动流程源码分析: SpringBoot启动流程分析(一) ...
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(二):SpringApplication的run方法
SpringBoot系列文章简介 SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇: Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现 SpringBoot启动流程源码分析: SpringBoot启动流程分析(一) ...
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(三):SpringApplication的run方法之prepareContext()方法
SpringBoot系列文章简介 SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇: Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现 SpringBoot启动流程源码分析: SpringBoot启动流程分析(一) ...
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(四):IoC容器的初始化过程
SpringBoot系列文章简介 SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇: Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现 SpringBoot启动流程源码分析: SpringBoot启动流程分析(一) ...
- u-boot启动流程分析(2)_板级(board)部分
转自:http://www.wowotech.net/u-boot/boot_flow_2.html 目录: 1. 前言 2. Generic Board 3. _main 4. global dat ...
- u-boot启动流程分析(1)_平台相关部分
转自:http://www.wowotech.net/u-boot/boot_flow_1.html 1. 前言 本文将结合u-boot的“board—>machine—>arch—> ...
- Cocos2d-x3.3RC0的Android编译Activity启动流程分析
本文将从引擎源代码Jni分析Cocos2d-x3.3RC0的Android Activity的启动流程,以下是具体分析. 1.引擎源代码Jni.部分Java层和C++层代码分析 watermark/2 ...
随机推荐
- 小爬爬5:scrapy介绍3持久化存储
一.两种持久化存储的方式 1.基于终端指令的吃持久化存储: 特点:终端指令的持久化存储,只可以将parse方法的返回值存储到磁盘文件 因此我们需要将上一篇文章中的author和content作为返回值 ...
- linux驱动开发满三年,回首一下基本看不到其它选择
刚刚搞完一个处理器BSP项目,准备搞下一个自研处理器.说不上来什么喜悦,仅仅有些许茫然.没有刚毕业时对这个行业的痴迷,慢慢认同这仅仅是个谋生工具的想法. 回忆当初编写第一个驱动,就像上了战场.被长官踢 ...
- 2019-8-31-dotnet-控制台-Hangfire-后台定时任务
title author date CreateTime categories dotnet 控制台 Hangfire 后台定时任务 lindexi 2019-08-31 16:55:58 +0800 ...
- Android 高仿微信语音聊天页面高斯模糊效果
目前的应用市场上,使用毛玻璃效果的APP随处可见,比如用过微信语音聊天的人可以发现,语音聊天页面就使用了高斯模糊效果. 先看下效果图: 仔细观察上图,我们可以发现,背景图以用户头像为模板,对其进行了高 ...
- init()方法必须使用super.init(config)的原因--Servlet
原 因: 一个servlet在它的init()方法中传递它的ServletConfig实例,在其他的方法中却不可以.当一个servlet在 init()方法外需要调用config对象时就会产生问题.使 ...
- MapReduce数据流-Partiton&Shuffle
- oracle 尽量多使用COMMIT
只要有可能,在程序中尽量多使用COMMIT, 这样程序的性能得到提高,需求也会因为COMMIT所释放的资源而减少: COMMIT所释放的资源: a. 回滚段上用于恢复数据的信息. b. ...
- H3C 星型以太网拓扑扩展
- H3C 网络层
- RegExp类型
一.创建正则表达式的方法 1.字面量形式 var expressiion=/pattern/flags; flags:g全局模式,即将被应用于所有字符串,而非在发现第一个匹配项时立即停止: i不区分大 ...
