AnswerOpenCV一周佳作欣赏(0615-0622)
一、How to make auto-adjustments(brightness and contrast) for image Android Opencv Image Correction
i'm using OpenCV for Android.
I would like to know,how to make image correction(auto adjustments of brightness/contrast) for image(bitmap) in android via OpenCV or that can be done by native ColorMatrixFilter from Android!??
I tried to google,but didn't found good tutorials/examples.
So how can i achieve my goal? Any ideas?
Thanks!
算法问题,需要寻找到自动调整亮度和对比度的算法。
回答:
Brightness and contrast is linear operator with parameter alpha and beta
O(x,y) = alpha * I(x,y) + beta
In OpenCV you can do this with convertTo.
The question here is how to calculate alpha and beta automatically ?
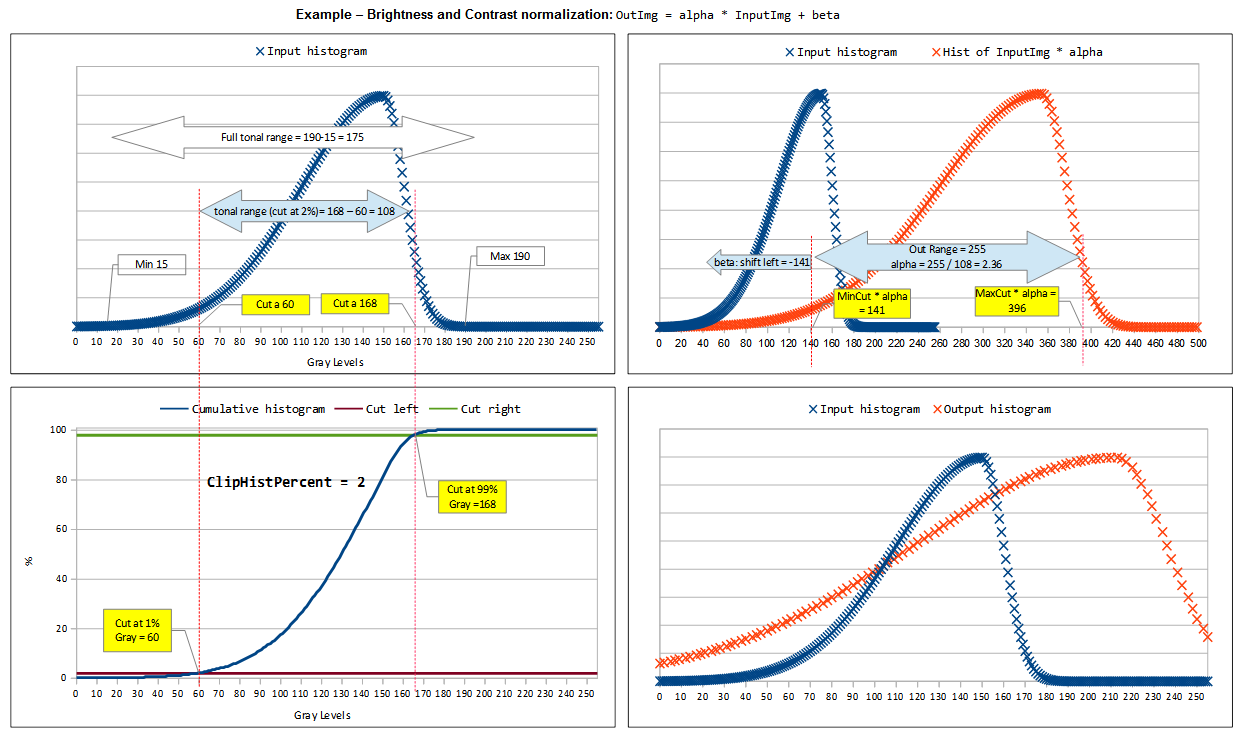
Looking at histogram, alpha operates as color range amplifier, beta operates as range shift.
Automatic brightness and contrast optimization calculates alpha and beta so that the output range is 0..255.
input range = max(I) - min(I)
wanted output range = 255;
alpha = output range / input range = 255 / ( max(I) - min(I) )
min(O) = alpha * min(I) + beta
beta = -min(I) * alpha
Histogram Wings Cut (clipping)
To maximize the result of it's useful to cut out some color with few pixels.
This is done cutting left right and wings of histogram where color frequency is less than a value (typically 1%). Calculating cumulative distribution from the histogram you can easly find where to cut.
may be sample chart helps to understand:
By the way BrightnessAndContrastAuto could be named normalizeHist because it works on BGR and gray images stretching the histogram to the full range without touching bins balance. If input image has range 0..255 BrightnessAndContrastAuto will do nothing.
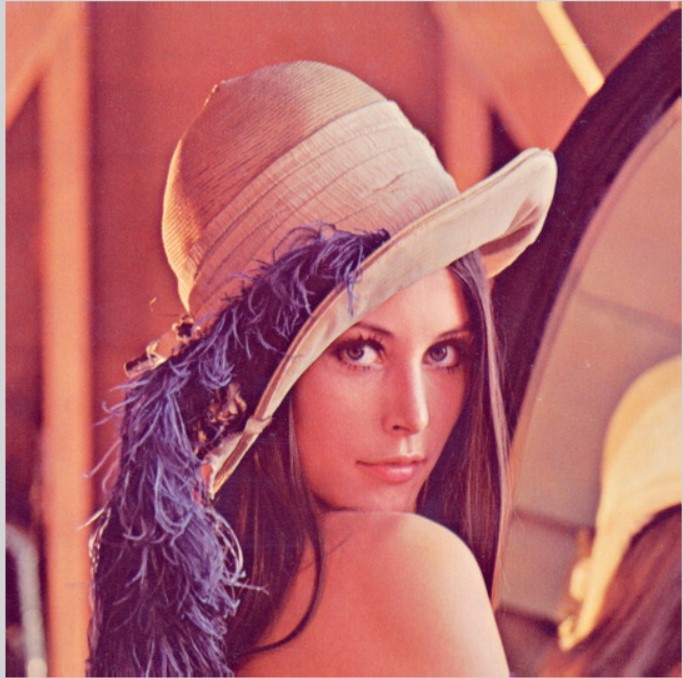
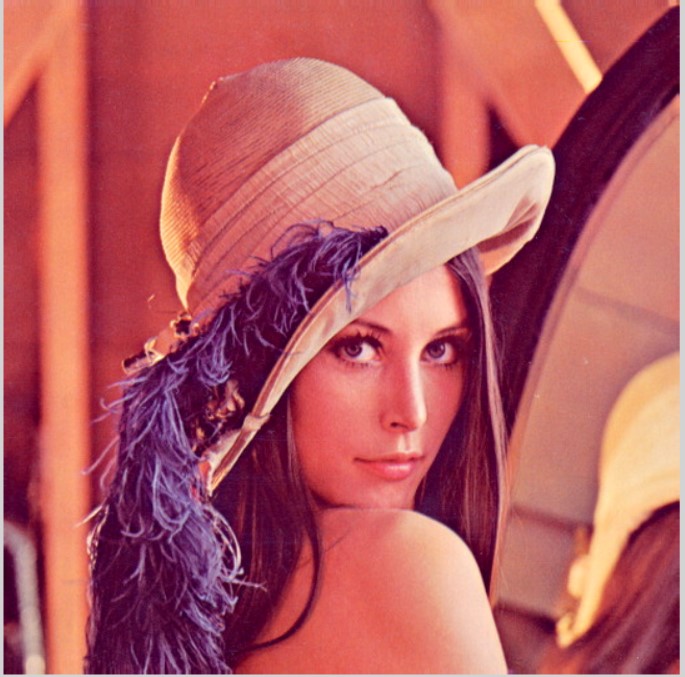
Histogram equalization and CLAE works only on gray images and they change grays level balancing. look at the images below:
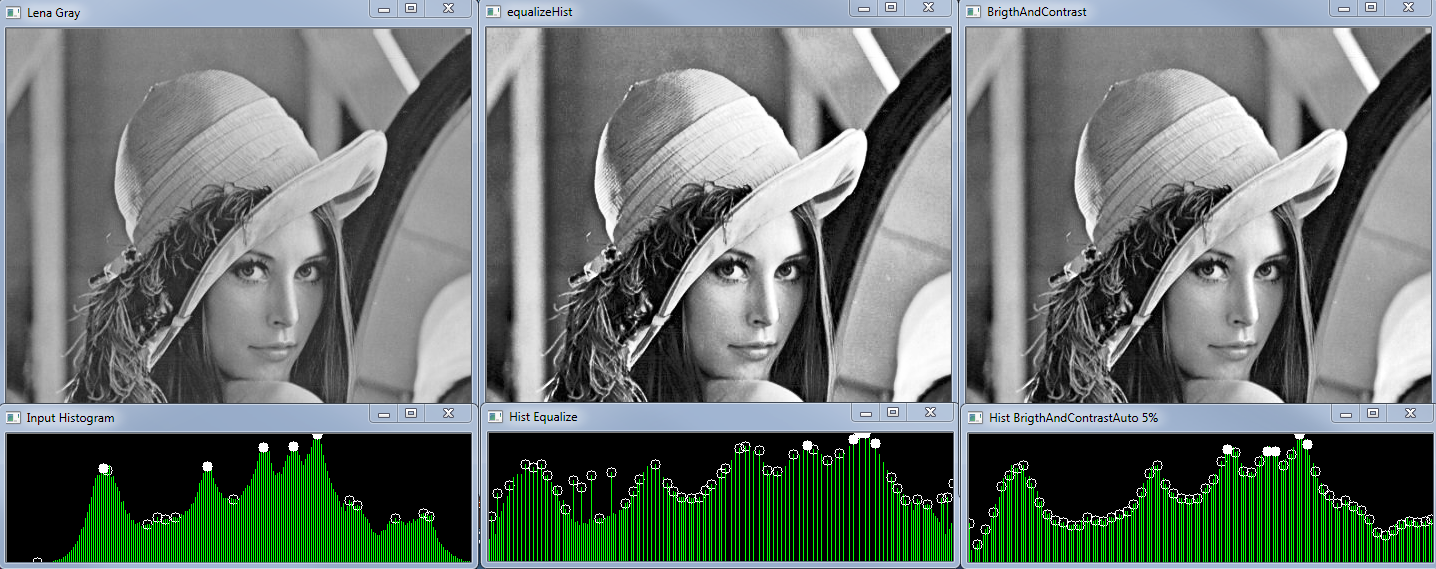
{
CV_Assert(clipHistPercent >= 0);
CV_Assert((src.type() == CV_8UC1) || (src.type() == CV_8UC3) || (src.type() == CV_8UC4));
int histSize = 256;
float alpha, beta;
double minGray = 0, maxGray = 0;
//to calculate grayscale histogram
cv::Mat gray;
if (src.type() == CV_8UC1) gray = src;
else if (src.type() == CV_8UC3) cvtColor(src, gray, CV_BGR2GRAY);
else if (src.type() == CV_8UC4) cvtColor(src, gray, CV_BGRA2GRAY);
if (clipHistPercent == 0)
{
// keep full available range
cv::minMaxLoc(gray, &minGray, &maxGray);
}
else
{
cv::Mat hist; //the grayscale histogram
float range[] = { 0, 256 };
const float* histRange = { range };
bool uniform = true;
bool accumulate = false;
calcHist(&gray, 1, 0, cv::Mat (), hist, 1, &histSize, &histRange, uniform, accumulate);
// calculate cumulative distribution from the histogram
std::vector<float> accumulator(histSize);
accumulator[0] = hist.at<float>(0);
for (int i = 1; i < histSize; i++)
{
accumulator[i] = accumulator[i - 1] + hist.at<float>(i);
}
// locate points that cuts at required value
float max = accumulator.back();
clipHistPercent *= (max / 100.0); //make percent as absolute
clipHistPercent /= 2.0; // left and right wings
// locate left cut
minGray = 0;
while (accumulator[minGray] < clipHistPercent)
minGray++;
// locate right cut
maxGray = histSize - 1;
while (accumulator[maxGray] >= (max - clipHistPercent))
maxGray--;
}
// current range
float inputRange = maxGray - minGray;
alpha = (histSize - 1) / inputRange; // alpha expands current range to histsize range
beta = -minGray * alpha; // beta shifts current range so that minGray will go to 0
// Apply brightness and contrast normalization
// convertTo operates with saurate_cast
src.convertTo(dst, -1, alpha, beta);
// restore alpha channel from source
if (dst.type() == CV_8UC4)
{
int from_to[] = { 3, 3};
cv::mixChannels(&src, 4, &dst,1, from_to, 1);
}
return;
}


效果比较不错。
I am evaluating template matching algorithm to differentiate similar and dissimilar objects. What I found is confusing, I had an impression of template matching is a method which compares raw pixel intensity values. Hence when the pixel value varies I expected Template Matching to give a less match percentage.
I have a template and search image having same shape and size differing only in color(Images attached). When I did template matching surprisingly I am getting match percentage greater than 90%.
img = cv2.imread('./images/searchtest.png', cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)template = cv2.imread('./images/template.png', cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
res = cv2.matchTemplate(img, template, cv2.TM_CCORR_NORMED)
min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(res)print(max_val)
Template Image :

Search Image :
Can someone give me an insight why it is happening so? I have even tried this in HSV color space, Full BGR image, Full HSV image, Individual channels of B,G,R and Individual channels of H,S,V. In all the cases I am getting a good percentage.
Any help could be really appreciated.
这个问题的核心就是彩色模板匹配。很有趣的问题。回答直接给出了source code,
关于这个问题,我认为,彩色模板匹配的意义不是很大,毕竟用于定位的时候,黑白效果更好。
三、likely position of Feature Matching.
I am using Brute Force Matcher with L2 norm. Referring this link https://docs.opencv.org/2.4/doc/tutor...
After the process, I get below image as output

What is the likely position of the object suggested by the feature matching?
I don't understand how to choose the likely position using this image :(
这是一个只知其一不知其二的问题,他能够找到旋转的地方,但是对于下一步如何做没有思路。其实,解决此类问题,最好的方法就是参考教程做一遍。
当然,管理员的回答非常明确:
to retrieve the position of your matched object, you need some further steps :
- filter the matches for outliers
- extract the 2d point locations from the keypoints
- apply findHomography() on the matched 2d points to get a transformation matrix between your query and the scene image
- apply perspectiveTransform on the boundingbox of the query object, to see, where it is located in the scene image.
我也给出具体回答:

//used surf
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat img_1 ;
Mat img_2 ;
Mat img_raw_1 = imread("c1.bmp");
Mat img_raw_2 = imread("c3.bmp");
cvtColor(img_raw_1,img_1,CV_BGR2GRAY);
cvtColor(img_raw_2,img_2,CV_BGR2GRAY);
//-- Step 1: 使用SURF识别出特征点
int minHessian = 400;
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
detector.detect( img_1, keypoints_1 );
detector.detect( img_2, keypoints_2 );
//-- Step 2: 描述SURF特征
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
extractor.compute( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
extractor.compute( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- Step 3: 匹配
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;//BFMatcher为强制匹配
std::vector< DMatch > matches;
matcher.match( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches );
//取最大最小距离
double max_dist = 0; double min_dist = 100;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
std::vector< DMatch > good_matches;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
if( matches[i].distance <= 3*min_dist )//这里的阈值选择了3倍的min_dist
{
good_matches.push_back( matches[i]);
}
}
//-- Localize the object from img_1 in img_2
std::vector<Point2f> obj;
std::vector<Point2f> scene;
for( int i = 0; i < (int)good_matches.size(); i++ )
{
//这里采用“帧向拼接图像中添加的方法”,因此左边的是scene,右边的是obj
scene.push_back( keypoints_1[ good_matches[i].queryIdx ].pt );
obj.push_back( keypoints_2[ good_matches[i].trainIdx ].pt );
}
//直接调用ransac,计算单应矩阵
Mat H = findHomography( obj, scene, CV_RANSAC );
//图像对准
Mat result;
warpPerspective(img_raw_2,result,H,Size(2*img_2.cols,img_2.rows));
Mat half(result,cv::Rect(0,0,img_2.cols,img_2.rows));
img_raw_1.copyTo(half);
imshow("result",result);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
四、Run OpenCV to MFC
I have reproduced this sample, in a MFC app.
The cv::Mat is a CDOcument variable member:
// Attributes
public:
std::vector<CBlob> m_blobs;
cv::Mat m_Mat;
and I draw rectangles over image, with an method (called at some time intervals, according FPS rate):
DrawBlobInfoOnImage(m_blobs, m_Mat);
Here is the code of this method:
void CMyDoc::DrawBlobInfoOnImage(std::vector<CBlob>& blobs, cv::Mat& Mat)
{
for (unsigned int i = 0;i < blobs.size();++i)
{
if (blobs[i].m_bStillBeingTracked)
{
cv::rectangle(Mat, blobs[i].m_rectCurrentBounding, SCALAR_RED, 2);
double dFontScale = blobs[i].m_dCurrentDiagonalSize / 60.0;
int nFontThickness = (int)roundf(dFontScale * 1.0);
cv::putText(Mat, (LPCTSTR)IntToString(i), blobs[i].m_vecPointCenterPositions.back(), CV_FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, dFontScale, SCALAR_GREEN, nFontThickness);
}
}
}
but the result of this method is something like that:
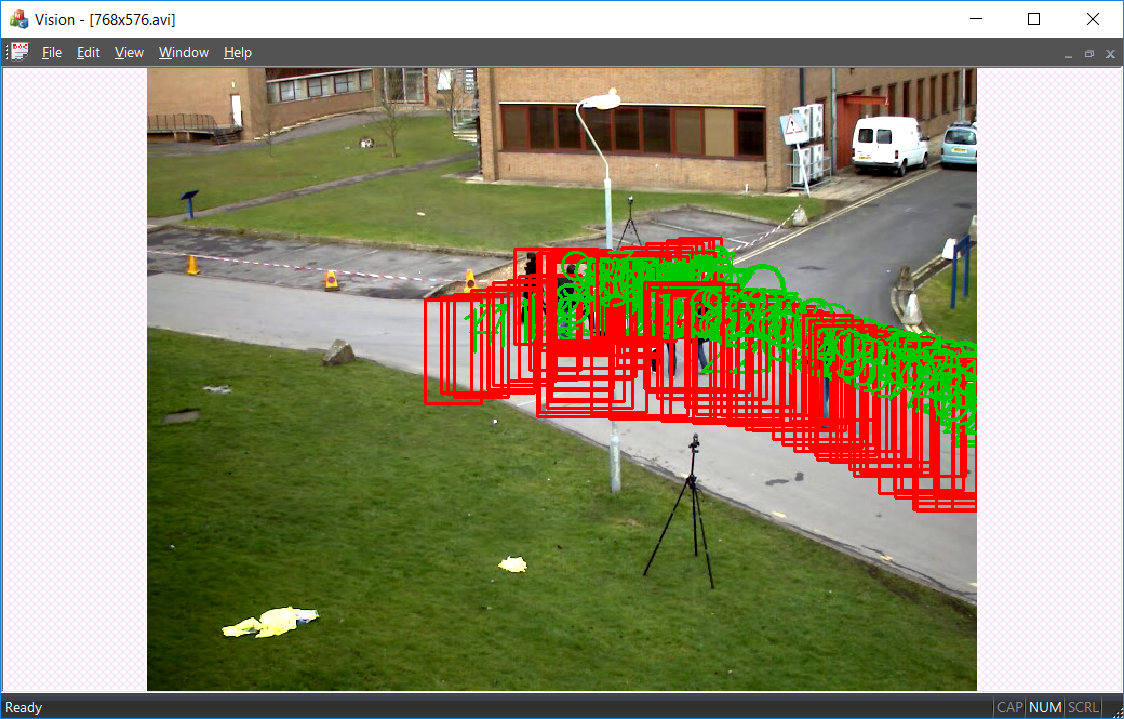
My question is: how can I draw only the last blobs result over my image ?
I have tried to clean up m_Mat, and to enable to draw only blobs.size() - 1 blob over image, none of this worked ...
非常有意思的问题,主要就是说他能够用mfc调用oepncv了,但是不知道如何将视频中的框子正确显示(也就是不要有拖尾)
这个也是对问题思考不是很深造成的问题。其实,解决的方法无外乎两个
一是直接修改视频流,也就是在原来的“读取-显示”循环里面添加一些东西(也就是框子),如果是这种方法,你使用或者不使用mfc基本没有什么影响;
比如<PariticalFilter在MFC上的运行,源代码公开>
https://www.cnblogs.com/jsxyhelu/p/6336429.html
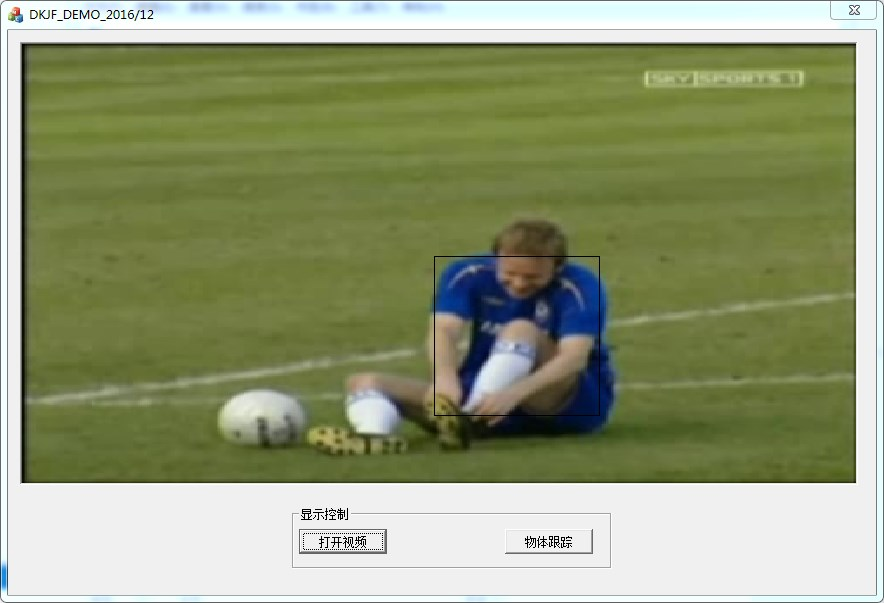
二是采用mfc的机制。mfc不是都是对话框吗?那就创建一个窗体,专门用来显示这个矩形就好啦。
比如<GreenOpenPaint的实现(五)矩形框>https://www.cnblogs.com/jsxyhelu/p/6354341.html
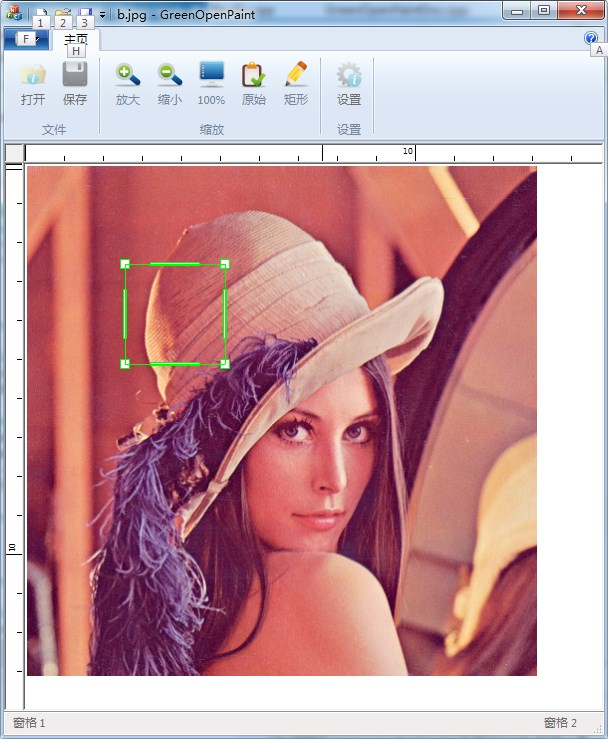
五、How to find the thickness of the red color sealent in the image ????
Hi,
I want to find the thickness of the red colored sealent in the image.
First I'm extracting the sealent portion by using findcontours by having minimum and maximum conotur area.And then check the Area,length and thickness of the sealent,i can find the area as well as length but i m not able to find the thickness of the sealent portion.
Please help me guys........below is the example image.
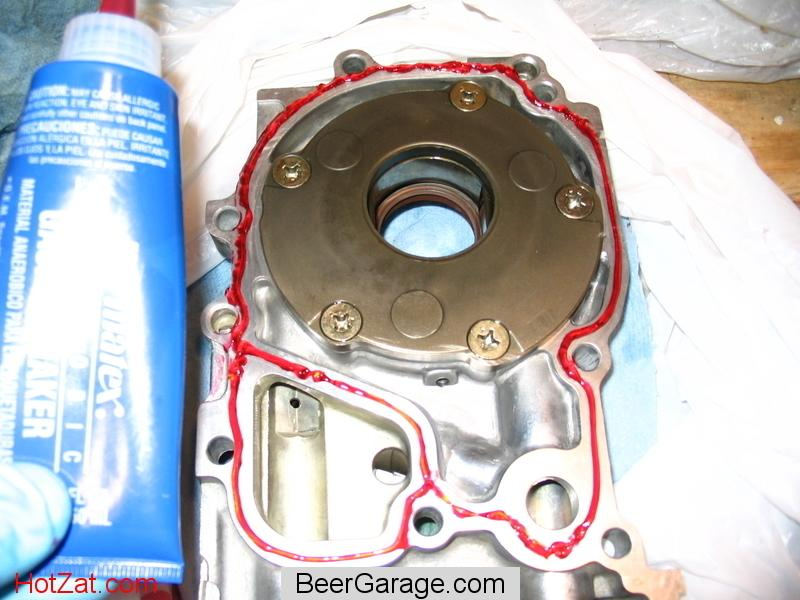

提示一下:
do a distance transform and a skeleton on the binary image.
这是一个算法问题,具体解决,下周给出实现。大家可以先研究一下。
AnswerOpenCV一周佳作欣赏(0615-0622)的更多相关文章
- AnswerOpenCV(1001-1007)一周佳作欣赏
外国不过十一,所以利用十一假期,看看他们都在干什么. 一.小白问题 http://answers.opencv.org/question/199987/contour-single-blob-with ...
- AnswerOpenCV(0826-0901)一周佳作欣赏
1.OpenCV to detect how missing tooth in equipment Hello everyone. I am just starting with OpenCV and ...
- (原创)古典主义——平凡之美 佳作欣赏(摄影,欣赏)
文中图片摘自腾讯文化网:www.cal.qq.com 1.Abstract 生活本就是平淡的,如同真理一般寂静.平时生活中不经意的瞬间,也有它本来的美丽.下面一组图是上上个世纪到上个世纪末一个 ...
- Python爬虫之抓取豆瓣影评数据
脚本功能: 1.访问豆瓣最受欢迎影评页面(http://movie.douban.com/review/best/?start=0),抓取所有影评数据中的标题.作者.影片以及影评信息 2.将抓取的信息 ...
- 2017年4月16日 一周AnswerOpenCV佳作赏析
2017年4月16日 一周AnswerOpenCV佳作赏析 1.HelloHow to smooth edge of text in binary image, based on threshold. ...
- 一个java实习生两周八次的面试经历
以前从来没有因为求职出去面试过,一直觉得面试很可怕,没想到最近两周我也成为了面霸,两周面试八次,我的找工作之路就这样开始了!大概两个星期之前,我看着自己在招聘网站上写好的简历连投出去的勇气都没有,战战 ...
- html5开发制作,漂亮html5模板欣赏,H5网站建设
html5是什么? HTML5 是下一代的 HTML(超文本标记语言,网页的组成部分),HTML5是web开发世界的一次重大的改变,能适配pc.手机等各终端,跨平台性能极强,移动互联网是未来的趋势,h ...
- 『创意欣赏』30幅逼真的 3D 虚拟现实环境呈现
又到周末了,给大家分享30幅漂亮的 3D 虚拟现实环境呈现,放松一下.这些创造性的场景都是通过 3D 图形设计软件,结合三维现实环境渲染制作出来的.一起欣赏:) 您可能感兴趣的相关文章 20幅温馨浪漫 ...
- C语言--第0周作业
1.翻阅邹欣老师博客关于师生关系博客,并回答下列问题: 1)最理想的师生关系是健身教练和学员的关系,在这种师生关系中你期望获得来自老师的哪些帮助? 答: 若教练和学员的关系是最理想的师生关系,那就意味 ...
随机推荐
- iOS UI布局-定时器
定时器是比较常用的一个UI控件,在付款.抢购时,经常会使用到.提取成一个通用的方法 /** * 倒计时GCD通用方法 * 通常用的计时器都是用NSTimer,但是NSTimer在线程很吃紧的时候效果不 ...
- android怎么抓取双向认证https的包
这里仅提供思路. 第一种方法: dex层面,可以直接用插日志方法,找到app使用的https库,这里以某app为例,使用okhttp, okhttp收发包相关代码: Request request = ...
- Appium基础(三)对象抓取
一.启动Android模拟器 二.打开App应用,这里以计算器为例子 三.打开uiautomatorviewer.bat 这个文件在Android SDK-->Tool目录下 双击uiautom ...
- 实验验证sys和system用户全库导出的区别
我们在做逻辑数据泵全库导出的时候,有两种流行的写法,一种是sys用户导出,一种是使用system用户导出. 现在想知道二者之间有什么区别?实验验证之前不妨先思考一下: sys和system用户的权限区 ...
- !! zcl_TD 用法注释02 力攻(动能<4)
力攻(动能<4)创新高下M5可持有力攻(动能<4)不创新高下M5可减仓
- 问题:mysql服务正在启动 mysql服务无法启动 && mysql启动脚本 mysql关闭脚本
此篇目编写两个核心目的: 1.mysql服务启动脚本(start_mysql.bat),mysql服务停止脚本(stop_mysql.bat)的讲解. 2.解决问题:mysql服务无法启动. 操作流程 ...
- Abp项目构建、swagger及代码生成器
前段时间在学习abp,在配置swagger时踩了不少坑,特此整理一下,方便同行参考.幸运的是又发现了神奇的代码生成器,分享下亲身经验. 觉得此博客非常有用的朋友可以在右侧赞助打赏下,非常感谢大家支持. ...
- Day5 装饰器和文件操作
一.装饰器 1.什么是装饰器 装饰器即函数 装饰即修饰,意指为其他函数添加新功能 装饰器定义:本质就是函数,功能是为其他函数添加新功能 2. 装饰器需要遵循的原则 1.不修改被装饰函数的源代码(开放封 ...
- html5-颜色的表示
div{width: 100%;height: 100px;}body{background: url(../pic/2.png);}/*#div1{background: #ff0000;}#div ...
- JavaScript <script>标签的位置、延迟脚本(defer属性)与 异步脚本(async属性)
一.<script>标签的位置 传统的做法是将<script>元素放在<head>元素中,例如: <!DOCTYPE html><html > ...
