用C++调用tensorflow在python下训练好的模型(centos7)
本文主要参考博客https://blog.csdn.net/luoyexuge/article/details/80399265 [1]
bazel安装参考:https://blog.csdn.net/luoyi131420/article/details/78585989 [2]
首先介绍下自己的环境是centos7,tensorflow版本是1.7,python是3.6(anaconda3)。
要调用tensorflow c++接口,首先要编译tensorflow,要装bazel,要装protobuf,要装Eigen;然后是用python训练模型并保存,最后才是调用训练好的模型,整体过程还是比较麻烦,下面按步骤一步步说明。
1.安装bazel
以下是引用的[2]
首先安装bazel依赖的环境:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java
sudo apt-get install openjdk-8-jdk openjdk-8-source
sudo apt-get install pkg-config zip g++ zlib1g-dev unzip
注意:如果你没有安装add-apt-repository命令,需要执行sudo apt-get install software-properties-common命令。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
实际上我自己只缺jdk工具,加上我没有sudo权限,我自己是在网上直接下的jdk-8,链接是
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/java-archive-javase8-2177648.html
然后解压,最后将其路径添加到环境变量中:
export JAVA_HOME=/home/guozitao001/tools/jdk1.8.0_171
export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH
然后去git上下载bazel的安装文件https://github.com/bazelbuild/bazel/releases,具体是文件bazel-0.15.0-installer-linux-x86_64.sh。
(1) 终端切换到.sh文件存放的路径,文件添加可执行权限:
$ chmod +x bazel-0.5.3-installer-linux-x86_64.sh
(2)然后执行该文件:
$ ./bazel-0.5.3-installer-linux-x86_64.sh –user
注意:–user选项表示bazel安装到HOME/bin目录下,并设置.bazelrc的路径为HOME/.bazelrc。
安装完成后执行bazel看是否安装成功,这里我并没有添加环境变量就可以直接运行,大家根据自己需要添加。
2.安装protobuf
下载地址:https://github.com/google/protobuf/releases ,我下载的是3.5.1版本,如果你是下载新版的tensorflow,请确保protobuf版本也是最新的,安装步骤:
cd /protobuf
./configure
make
sudo make install
安装之后查看protobuf版本:
protoc --version- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
根据[1]的作者采坑经历所说,protoc一定要注意版本要和tensorflow匹配,总之这里3.5.1的protoc和tensorflow1.7是能够匹配的。
3.安装Eigen
wget http://bitbucket.org/eigen/eigen/get/3.3.4.tar.bz2
下载之后解压放在重新命名为eigen3,我存放的路径是,/Users/zhoumeixu/Downloads/eigen3- 1
- 2
这个没什么好多说的,如果wget失败就直接用浏览器或者迅雷下载就是了。
4.tensorflow下载以及编译:
1下载TensorFlow ,使用 git clone - –recursive https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow
2.下载bazel工具(mac下载installer-darwin、linux用installer-linux)
3. 进入tensorflow的根目录
3.1 执行./configure 根据提示配置一下环境变量,这个不大重要。
要GPU的话要下载nvidia驱动的 尽量装最新版的驱动吧 还有cudnn version为5以上的 这些在官网都有提及的
3.2 有显卡的执行 ” bazel build –config=opt –config=cuda //tensorflow:libtensorflow_cc.so ”
没显卡的 ” –config=cuda ” 就不要加了
bazel build –config=opt //tensorflow:libtensorflow_cc.so。
编译成功后会有bazel成功的提示。
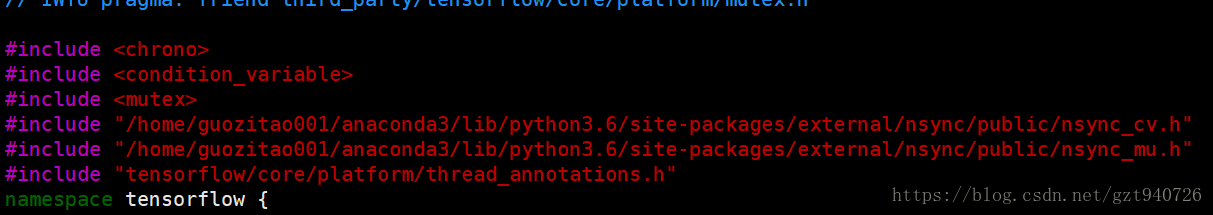
3.3这里编译完过后,最后调用tensorflow模型的时候的时候提示文件tensorflow/tensorflow/core/platform/default/mutex.h缺2个头文件:nsync_cv.h,nsync_mu.h,仔细查找后,发现这两个头文件在python的site-papackages里面,它只是没找到而已,所以我们在mutex.h中将这两个头文件的路径补充完整:
这样之后调用就不会提示缺少头文件了。
4.python训练tensorflow模型:
下面训练tensorflow模型的pb模型,[1]作者做了个简单的线性回归模型及生成pb格式模型代码:
# coding:utf-8
# python 3.6
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import os
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer('training_iteration', 1000,
'number of training iterations.')
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer('model_version', 1, 'version number of the model.')
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string('work_dir', 'model/', 'Working directory.')
FLAGS = tf.app.flags.FLAGS
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
x = tf.placeholder('float', shape=[None, 5],name="inputs")
y_ = tf.placeholder('float', shape=[None, 1])
w = tf.get_variable('w', shape=[5, 1], initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer)
b = tf.get_variable('b', shape=[1], initializer=tf.zeros_initializer)
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
y = tf.add(tf.matmul(x, w) , b,name="outputs")
ms_loss = tf.reduce_mean((y - y_) ** 2)
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.005).minimize(ms_loss)
train_x = np.random.randn(1000, 5)
# let the model learn the equation of y = x1 * 1 + x2 * 2 + x3 * 3
train_y = np.sum(train_x * np.array([1, 2, 3,4,5]) + np.random.randn(1000, 5) / 100, axis=1).reshape(-1, 1)
for i in range(FLAGS.training_iteration):
loss, _ = sess.run([ms_loss, train_step], feed_dict={x: train_x, y_: train_y})
if i%100==0:
print("loss is:",loss)
graph = tf.graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants(sess, sess.graph_def,
["inputs", "outputs"])
tf.train.write_graph(graph, ".", FLAGS.work_dir + "liner.pb",
as_text=False)
print('Done exporting!')
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
注意这里一定要把需要输入和输出的变量要以string形式的name在tf.graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants中进行保存,比如说这里的inputs和outputs。得到一个后缀为pb的文件
然后加载该模型,验证是否成功保存模型:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
logdir = '/Users/zhoumeixu/Documents/python/credit-nlp-ner/model/'
output_graph_path = logdir+'liner.pb'
with tf.Graph().as_default():
output_graph_def = tf.GraphDef()
with open(output_graph_path, "rb") as f:
output_graph_def.ParseFromString(f.read())
_ = tf.import_graph_def(output_graph_def,name="")
with tf.Session() as sess:
input = sess.graph.get_tensor_by_name("inputs:0")
output = sess.graph.get_tensor_by_name("outputs:0")
result = sess.run(output, feed_dict={input: np.reshape([1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0],[-1,5])})
print(result)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
运行结果:[[14.998546]], 该结果完全符合预期。
5.C++项目代码,一共有4个文件
model_loader_base.h:
#ifndef CPPTENSORFLOW_MODEL_LOADER_BASE_H
#define CPPTENSORFLOW_MODEL_LOADER_BASE_H
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include "tensorflow/core/public/session.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/platform/env.h"
using namespace tensorflow;
namespace tf_model {
/**
* Base Class for feature adapter, common interface convert input format to tensors
* */
class FeatureAdapterBase{
public:
FeatureAdapterBase() {};
virtual ~FeatureAdapterBase() {};
virtual void assign(std::string, std::vector<double>*) = 0; // tensor_name, tensor_double_vector
std::vector<std::pair<std::string, tensorflow::Tensor> > input;
};
class ModelLoaderBase {
public:
ModelLoaderBase() {};
virtual ~ModelLoaderBase() {};
virtual int load(tensorflow::Session*, const std::string) = 0; //pure virutal function load method
virtual int predict(tensorflow::Session*, const FeatureAdapterBase&, const std::string, double*) = 0;
tensorflow::GraphDef graphdef; //Graph Definition for current model
};
}
#endif //CPPTENSORFLOW_MODEL_LOADER_BASE_H
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
ann_model_loader.h:
#ifndef CPPTENSORFLOW_ANN_MODEL_LOADER_H
#define CPPTENSORFLOW_ANN_MODEL_LOADER_H
#include "model_loader_base.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/public/session.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/platform/env.h"
using namespace tensorflow;
namespace tf_model {
/**
* @brief: Model Loader for Feed Forward Neural Network
* */
class ANNFeatureAdapter: public FeatureAdapterBase {
public:
ANNFeatureAdapter();
~ANNFeatureAdapter();
void assign(std::string tname, std::vector<double>*) override; // (tensor_name, tensor)
};
class ANNModelLoader: public ModelLoaderBase {
public:
ANNModelLoader();
~ANNModelLoader();
int load(tensorflow::Session*, const std::string) override; //Load graph file and new session
int predict(tensorflow::Session*, const FeatureAdapterBase&, const std::string, double*) override;
};
}
#endif //CPPTENSORFLOW_ANN_MODEL_LOADER_H
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
ann_model_loader.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include "ann_model_loader.h"
//#include <tensor_shape.h>
using namespace tensorflow;
namespace tf_model {
/**
* ANNFeatureAdapter Implementation
* */
ANNFeatureAdapter::ANNFeatureAdapter() {
}
ANNFeatureAdapter::~ANNFeatureAdapter() {
}
/*
* @brief: Feature Adapter: convert 1-D double vector to Tensor, shape [1, ndim]
* @param: std::string tname, tensor name;
* @parma: std::vector<double>*, input vector;
* */
void ANNFeatureAdapter::assign(std::string tname, std::vector<double>* vec) {
//Convert input 1-D double vector to Tensor
int ndim = vec->size();
if (ndim == 0) {
std::cout << "WARNING: Input Vec size is 0 ..." << std::endl;
return;
}
// Create New tensor and set value
Tensor x(tensorflow::DT_FLOAT, tensorflow::TensorShape({1, ndim})); // New Tensor shape [1, ndim]
auto x_map = x.tensor<float, 2>();
for (int j = 0; j < ndim; j++) {
x_map(0, j) = (*vec)[j];
}
// Append <tname, Tensor> to input
input.push_back(std::pair<std::string, tensorflow::Tensor>(tname, x));
}
/**
* ANN Model Loader Implementation
* */
ANNModelLoader::ANNModelLoader() {
}
ANNModelLoader::~ANNModelLoader() {
}
/**
* @brief: load the graph and add to Session
* @param: Session* session, add the graph to the session
* @param: model_path absolute path to exported protobuf file *.pb
* */
int ANNModelLoader::load(tensorflow::Session* session, const std::string model_path) {
//Read the pb file into the grapgdef member
tensorflow::Status status_load = ReadBinaryProto(Env::Default(), model_path, &graphdef);
if (!status_load.ok()) {
std::cout << "ERROR: Loading model failed..." << model_path << std::endl;
std::cout << status_load.ToString() << "\n";
return -1;
}
// Add the graph to the session
tensorflow::Status status_create = session->Create(graphdef);
if (!status_create.ok()) {
std::cout << "ERROR: Creating graph in session failed..." << status_create.ToString() << std::endl;
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
/**
* @brief: Making new prediction
* @param: Session* session
* @param: FeatureAdapterBase, common interface of input feature
* @param: std::string, output_node, tensorname of output node
* @param: double, prediction values
* */
int ANNModelLoader::predict(tensorflow::Session* session, const FeatureAdapterBase& input_feature,
const std::string output_node, double* prediction) {
// The session will initialize the outputs
std::vector<tensorflow::Tensor> outputs; //shape [batch_size]
// @input: vector<pair<string, tensor> >, feed_dict
// @output_node: std::string, name of the output node op, defined in the protobuf file
tensorflow::Status status = session->Run(input_feature.input, {output_node}, {}, &outputs);
if (!status.ok()) {
std::cout << "ERROR: prediction failed..." << status.ToString() << std::endl;
return -1;
}
//Fetch output value
std::cout << "Output tensor size:" << outputs.size() << std::endl;
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < outputs.size(); i++) {
std::cout << outputs[i].DebugString();
}
std::cout << std::endl;
Tensor t = outputs[0]; // Fetch the first tensor
int ndim = t.shape().dims(); // Get the dimension of the tensor
auto tmap = t.tensor<float, 2>(); // Tensor Shape: [batch_size, target_class_num]
int output_dim = t.shape().dim_size(1); // Get the target_class_num from 1st dimension
std::vector<double> tout;
// Argmax: Get Final Prediction Label and Probability
int output_class_id = -1;
double output_prob = 0.0;
for (int j = 0; j < output_dim; j++) {
std::cout << "Class " << j << " prob:" << tmap(0, j) << "," << std::endl;
if (tmap(0, j) >= output_prob) {
output_class_id = j;
output_prob = tmap(0, j);
}
}
// Log
std::cout << "Final class id: " << output_class_id << std::endl;
std::cout << "Final value is: " << output_prob << std::endl;
(*prediction) = output_prob; // Assign the probability to prediction
return 0;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
main.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include "tensorflow/core/public/session.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/platform/env.h"
#include "ann_model_loader.h"
using namespace tensorflow;
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
if (argc != 2) {
std::cout << "WARNING: Input Args missing" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
std::string model_path = argv[1]; // Model_path *.pb file
// TensorName pre-defined in python file, Need to extract values from tensors
std::string input_tensor_name = "inputs";
std::string output_tensor_name = "outputs";
// Create New Session
Session* session;
Status status = NewSession(SessionOptions(), &session);
if (!status.ok()) {
std::cout << status.ToString() << "\n";
return 0;
}
// Create prediction demo
tf_model::ANNModelLoader model; //Create demo for prediction
if (0 != model.load(session, model_path)) {
std::cout << "Error: Model Loading failed..." << std::endl;
return 0;
}
// Define Input tensor and Feature Adapter
// Demo example: [1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0] for Iris Example, including bias
int ndim = 5;
std::vector<double> input;
for (int i = 0; i < ndim; i++) {
input.push_back(1.0);
}
// New Feature Adapter to convert vector to tensors dictionary
tf_model::ANNFeatureAdapter input_feat;
input_feat.assign(input_tensor_name, &input); //Assign vec<double> to tensor
// Make New Prediction
double prediction = 0.0;
if (0 != model.predict(session, input_feat, output_tensor_name, &prediction)) {
std::cout << "WARNING: Prediction failed..." << std::endl;
}
std::cout << "Output Prediction Value:" << prediction << std::endl;
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
将这四个文件放在同一个路径下,然后还需要添加一个Cmake的txt文件:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(cpptensorflow)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -std=gnu++0x -g -fopenmp -fno-strict-aliasing")
link_directories(/home/xxx/tensorflow/bazel-bin/tensorflow)
include_directories(
/home/xxx/tensorflow
/home/xxx/tensorflow/bazel-genfiles
/home/xxx/tensorflow/bazel-bin/tensorflow
/home/xxx/tools/eigen3
)
add_executable(cpptensorflow main.cpp ann_model_loader.h model_loader_base.h ann_model_loader.cpp)
target_link_libraries(cpptensorflow tensorflow_cc tensorflow_framework)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
这里注意cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)要和自己系统的cmake最低版本相符合。
然后在当前目录下建立一个build的空文件夹:
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
生成cpptensorflow执行文件,后接保存的模型pb文件路径:
./cpptensorflow /Users/zhoumeixu/Documents/python/credit-nlp-ner/model/liner.pb
Final value is: 14.9985
Output Prediction Value:14.9985- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
到此基本就结束了,最后感谢下作者[1],我真是差点被搞疯了。。。
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/gzt940726/article/details/81053378
用C++调用tensorflow在python下训练好的模型(centos7)的更多相关文章
- 在 C/C++ 中使用 TensorFlow 预训练好的模型—— 直接调用 C++ 接口实现
现在的深度学习框架一般都是基于 Python 来实现,构建.训练.保存和调用模型都可以很容易地在 Python 下完成.但有时候,我们在实际应用这些模型的时候可能需要在其他编程语言下进行,本文将通过直 ...
- 在 C/C++ 中使用 TensorFlow 预训练好的模型—— 间接调用 Python 实现
现在的深度学习框架一般都是基于 Python 来实现,构建.训练.保存和调用模型都可以很容易地在 Python 下完成.但有时候,我们在实际应用这些模型的时候可能需要在其他编程语言下进行,本文将通过 ...
- TensorFlow 调用预训练好的模型—— Python 实现
1. 准备预训练好的模型 TensorFlow 预训练好的模型被保存为以下四个文件 data 文件是训练好的参数值,meta 文件是定义的神经网络图,checkpoint 文件是所有模型的保存路径,如 ...
- TensorFlow Object Detection API(Windows下训练)
本文为作者原创,转载请注明出处(http://www.cnblogs.com/mar-q/)by 负赑屃 最近事情比较多,前面坑挖的有点久,今天终于有时间总结一下,顺便把Windows下训练跑通.Li ...
- TensorFlow 同时调用多个预训练好的模型
在某些任务中,我们需要针对不同的情况训练多个不同的神经网络模型,这时候,在测试阶段,我们就需要调用多个预训练好的模型分别来进行预测. 调用单个预训练好的模型请点击此处 弄明白了如何调用单个模型,其实调 ...
- TensorFlow利用A3C算法训练智能体玩CartPole游戏
本教程讲解如何使用深度强化学习训练一个可以在 CartPole 游戏中获胜的模型.研究人员使用 tf.keras.OpenAI 训练了一个使用「异步优势动作评价」(Asynchronous Advan ...
- DRL 教程 | 如何保持运动小车上的旗杆屹立不倒?TensorFlow利用A3C算法训练智能体玩CartPole游戏
本教程讲解如何使用深度强化学习训练一个可以在 CartPole 游戏中获胜的模型.研究人员使用 tf.keras.OpenAI 训练了一个使用「异步优势动作评价」(Asynchronous Advan ...
- tensorflow和python操作中的笔记
前一段时间做了一些项目,把一些笔记放在了txt中,现分享出来,自己也能够时长预习. 1) 读取文件时,将固定的文件地址,采用数组或者字符串的形式,提前表示出来,后期使用时候采用拼接操作 2) # 得到 ...
- 人脸检测及识别python实现系列(5)——利用keras库训练人脸识别模型
人脸检测及识别python实现系列(5)——利用keras库训练人脸识别模型 经过前面稍显罗嗦的准备工作,现在,我们终于可以尝试训练我们自己的卷积神经网络模型了.CNN擅长图像处理,keras库的te ...
随机推荐
- iOS 开发笔记-NSURLConnection的使用
通过NSURLConnection发送一个HTTP GET请求 //send a GET request to server with some params -(void)httpGetWithPa ...
- cocos2dx 3.x(纯代码实现弹出对话框/提示框/警告框)
头文件: // // PopAlertDialog.h // macstudycocos2dx // // Created by WangWei on 15/6/8. // // #ifndef ...
- 设置sqlplus不显示除查询结果外的信息
背景:客户提出一个需求,写SQL脚本的时候,内容是拼接的,如何将这个拼接SQL执行的结果取出来调用执行呢? 我想到的方案是先把结果取出来,存为一个中间文件,再调用该文件即可. 知识点:如何将sqlpl ...
- 例子:动能并不是特别强(2-3)后,下M5的同时,也是恢复期到期的前一天
动能并不是特别强(2-3)后,下M5的同时,但是恢复期到期 EG.002195 2017/06/23-->2017/06/29
- HTTP参数污染【转】
HTTP参数污染注入源于网站对于提交的相同的参数的不同处理方式导致. 例如: www.XX.com/a?key=ab&key=3 如果服务端返回输入key的值,可能会有 一: ab 二:3 三 ...
- MYSQL5.6.X 非在线安装版(解压版)安装过程
一.卸载以前旧版本(本人5.5版本) 1.关闭MySQL服务 以管理员身份运行cmd,执行以下命令: net stop mysql 或者右键我的电脑,在管理——服务——停止MySQL 2.卸载MySQ ...
- Oracle中找出用户的上次登录时间
可以使用如下sql语句: select t1.username,t1.logon_time last_logon_time,t2.account_status,created 账号创建时间 from ...
- QT5中QByteArray转QString中文乱码
1.添加头文件 #include <QTextCodec> 2.用QTextCodec 设置格式转换 QByteArray barr; barr.insert(0,(char*)(pMsg ...
- 超简单系列:ubuntu 13.04 安装 apache2.2+mod_wsgi+Django
1,Ubuntu更新系统 sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade 2,安装apache,mod_wsgi,Django sudo apt-get instal ...
- sitecore系列教程之Sitecore个性化-配置文件,模式和角色
这是利用Sitecore规则引擎实现数字化转换的三部分系列的第二部分.阅读上一篇文章,通过为您的个性化体验定义内容策略来设置基础. Sitecore有一个非常强大的规则引擎,可以帮助推动个性化的用 ...