Android源码学习之模板方法模式应用
一、模板方法模式定义
| 模板方法模式定义: |
| defines the skeleton of an algorithm in a method, deferring some steps to subclasses. Template Method lets subclasses redefine certain steps of an algorithm without changing the algorithm's structure. |
| 定义一个方法操作算法的框架(骨架结构),而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。模板方法使子类可以在不改变一个算法的结构的情况下,就可以重定义该算法的某些特定步骤。 |
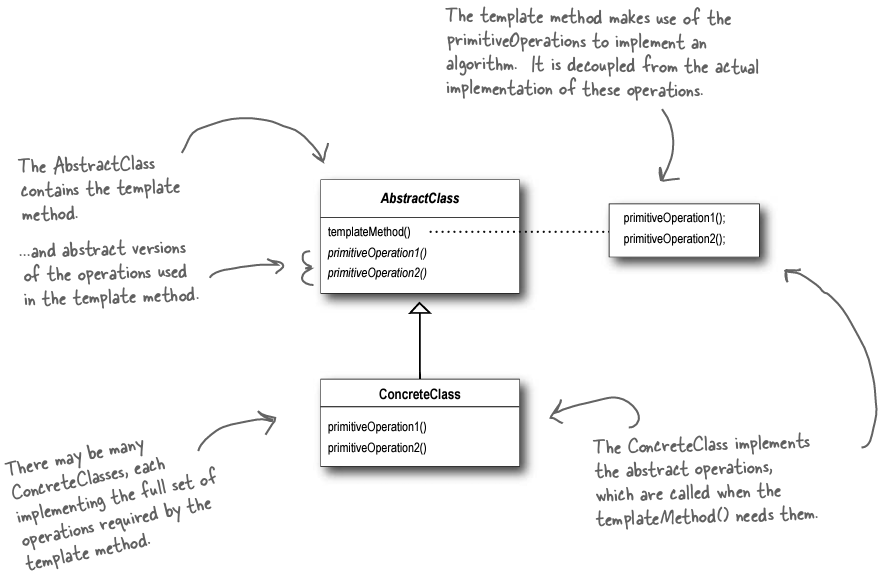
如上图所示(截取自《Head First Design Patterns》一书),具体各个部分有什么作用见上图,这里就不啰嗦了。
二、模板方法模式优势
|
封装不变部分,扩展可变部分。把不变部分的算法封装到父类实现,而可变部分的根据子类的具体需要,则可以通过继承来扩展。 |
| 提取公共部分,构成一个“模板”,模板的作用在于对算法或者流程的一个结构化、规范化,子类不能修改“模板方法”的整个算法骨架或者流程的顺序等,只能根据自身的不同,对模板方法中算法的某一步进行扩展。 |
|
行为由父类控制,子类实现。子类可以通过扩展的方法增加相应的功能,符合开闭原则。 |
三、模板方法模式在Android源码中的应用
在Android源码中,View中的Draw()方法就是一个“模板方法”。它定义了一系列“Draw”过程,主要包括这几个步骤(截取自源代码):
/*
* Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed
* in the appropriate order:
*
* 1. Draw the background
* 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading
* 3. Draw view's content
* 4. Draw children
* 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers
* 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance)
*/
具体函数代码如下所示:
其中第三步( Step 3)Draw view's content函数:

/**
* Implement this to do your drawing.
*
* @param canvas the canvas on which the background will be drawn
*/
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
}

第四步( Step 4) draw children

/**
* Called by draw to draw the child views. This may be overridden
* by derived classes to gain control just before its children are drawn
* (but after its own view has been drawn).
* @param canvas the canvas on which to draw the view
*/
protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) {
}

从上面的Draw()“模板方法”可以看出,当继承View子类中,如果要重写或者扩展这个方法时,整个方法流程和基本内容不能够修改,子类只能通过扩展onDraw(Canvas canvas)和dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas)两个函数,使子类自己的View显示效果和别的具体子类的不同。现在来看看继承自View类的具体子类如何扩展Draw()模板方法显示自己的与众不同:
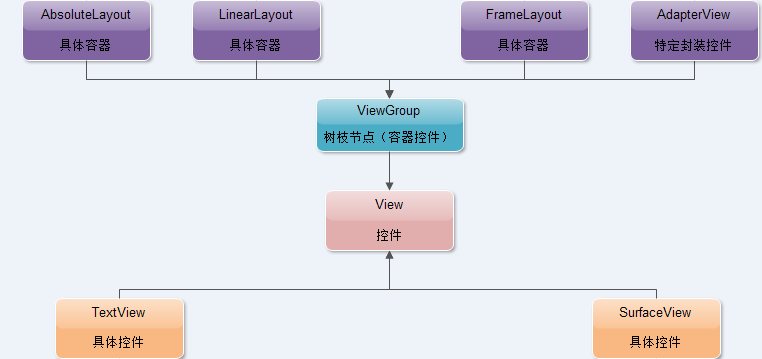
1、TextView类中重写了OnDraw函数

@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
if (mPreDrawState == PREDRAW_DONE) {
final ViewTreeObserver observer = getViewTreeObserver();
observer.removeOnPreDrawListener(this);
mPreDrawState = PREDRAW_NOT_REGISTERED;
} if (mCurrentAlpha <= ViewConfiguration.ALPHA_THRESHOLD_INT) return; restartMarqueeIfNeeded(); // Draw the background for this view
super.onDraw(canvas); final int compoundPaddingLeft = getCompoundPaddingLeft();
final int compoundPaddingTop = getCompoundPaddingTop();
final int compoundPaddingRight = getCompoundPaddingRight();
final int compoundPaddingBottom = getCompoundPaddingBottom();
final int scrollX = mScrollX;
final int scrollY = mScrollY;
final int right = mRight;
final int left = mLeft;
final int bottom = mBottom;
final int top = mTop; final Drawables dr = mDrawables;
if (dr != null) {
/*
* Compound, not extended, because the icon is not clipped
* if the text height is smaller.
。。。
}

2、SurfaceView重写了dispatchDraw()函数:

@Override
protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) {
if (mWindowType != WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_APPLICATION_PANEL) {
// if SKIP_DRAW is cleared, draw() has already punched a hole
if ((mPrivateFlags & SKIP_DRAW) == SKIP_DRAW) {
// punch a whole in the view-hierarchy below us
canvas.drawColor(0, PorterDuff.Mode.CLEAR);
}
}
super.dispatchDraw(canvas);
}

3、ViewGroup类重写了dispatchDraw()函数:

@Override
protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) {
final int count = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
int flags = mGroupFlags; if ((flags & FLAG_RUN_ANIMATION) != 0 && canAnimate()) {
final boolean cache = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_ANIMATION_CACHE) == FLAG_ANIMATION_CACHE; final boolean buildCache = !isHardwareAccelerated();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = children[i];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE) {
final LayoutParams params = child.getLayoutParams();
attachLayoutAnimationParameters(child, params, i, count);
bindLayoutAnimation(child);
if (cache) {
child.setDrawingCacheEnabled(true);
if (buildCache) {
child.buildDrawingCache(true);
}
}
}
} final LayoutAnimationController controller = mLayoutAnimationController;
if (controller.willOverlap()) {
mGroupFlags |= FLAG_OPTIMIZE_INVALIDATE;
} controller.start(); mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_RUN_ANIMATION;
mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_ANIMATION_DONE; if (cache) {
mGroupFlags |= FLAG_CHILDREN_DRAWN_WITH_CACHE;
} if (mAnimationListener != null) {
mAnimationListener.onAnimationStart(controller.getAnimation());
}
} int saveCount = 0;
final boolean clipToPadding = (flags & CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK) == CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK;
if (clipToPadding) {
saveCount = canvas.save();
canvas.clipRect(mScrollX + mPaddingLeft, mScrollY + mPaddingTop,
mScrollX + mRight - mLeft - mPaddingRight,
mScrollY + mBottom - mTop - mPaddingBottom); } // We will draw our child's animation, let's reset the flag
mPrivateFlags &= ~DRAW_ANIMATION;
mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_INVALIDATE_REQUIRED; boolean more = false;
final long drawingTime = getDrawingTime(); if ((flags & FLAG_USE_CHILD_DRAWING_ORDER) == 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = children[i];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE || child.getAnimation() != null) {
more |= drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime);
}
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = children[getChildDrawingOrder(count, i)];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE || child.getAnimation() != null) {
more |= drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime);}}}// Draw any disappearing views that have animationsif(mDisappearingChildren !=null){finalArrayList<View> disappearingChildren = mDisappearingChildren;finalint disappearingCount = disappearingChildren.size()-1;// Go backwards -- we may delete as animations finishfor(int i = disappearingCount; i >=0; i--){finalView child = disappearingChildren.get(i);
more |= drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime);}}if(clipToPadding){
canvas.restoreToCount(saveCount);}// mGroupFlags might have been updated by drawChild()
flags = mGroupFlags;if((flags & FLAG_INVALIDATE_REQUIRED)== FLAG_INVALIDATE_REQUIRED){
invalidate(true);}if((flags & FLAG_ANIMATION_DONE)==0&&(flags & FLAG_NOTIFY_ANIMATION_LISTENER)==0&&
mLayoutAnimationController.isDone()&&!more){// We want to erase the drawing cache and notify the listener after the// next frame is drawn because one extra invalidate() is caused by// drawChild() after the animation is over
mGroupFlags |= FLAG_NOTIFY_ANIMATION_LISTENER;finalRunnableend=newRunnable(){publicvoid run(){
notifyAnimationListener();}};
post(end);}}

总之,首先在View.Draw()“模板方法”函数将设计界面分成6个步骤,合并不变部分,然后将可变部分提取、独立出来,让子类TextView等扩展修改成自己“独特”的界面效果。在我们自己的实际开发中,如果要设计自己的界面效果大部分的时候,我们都是覆盖重写onDraw(Canvas canvas)函数。
此外:根据模版方法中的方法,可以分为两大类:模版方法(Template Method)和基本方法(Primitive Method)。其中我们这里的例子Draw()函数就是一个“模板方法”。
而基本方法又可以分为三种:抽象方法(Abstract Method)、具体方法(Concrete Method)和钩子方法(Hook Method):
抽象方法:一个抽象方法由抽象类声明,由具体子类实现。
具体方法:一个具体方法由抽象类声明并实现,而子类并不实现或置换。
钩子方法:一个钩子方法由抽象类声明并实现,而子类会加以扩展。我们这里的onDraw()函数就是一个钩子方法。
最后记住:

本人能力和时间有限(缺少“模式使用”内容,以后会添加),写的很粗糙,恭候大家的批评指正,谢谢~~~
Android源码学习之模板方法模式应用的更多相关文章
- 《Android源码设计模式》--模板方法模式
No1: 模板方法模式包括:抽象类(其中定义了一系列顺序方法).具体实现类A.具体实现类B 如果子类有实现不一样的细节,重写父类的某个方法即可 No2: AsyncTask对象调用execute方法后 ...
- Android源码学习之装饰模式应用
首先得了解最基础的装饰器模式 参考 设计模式之八 --- 装饰模式(Decorator) 参考链接:http://blog.csdn.net/cjjky/article/details/7478788 ...
- Android源码-学习随笔
在线代码网站1:http://grepcode.com/project/repository.grepcode.com/java/ext/com.google.android/android/ 书籍: ...
- 《Android源码设计模式》--Builder模式
No1: 将一个复杂对象的构建与它的表示分离,使得同样的构建过程可以创建不同的表示 No2: 在Android源码中,最常用到的Builder模式就是AlertDialog.Builder No3: ...
- Android源码学习(一) 数据集观察者
查看Android源码发现这个,决定记下下来. 1.在android.database这个包下面,存在这样一个抽象类DataSetObserver,里面包括onChanged()和onInvalida ...
- Android 源码学习
工具篇:如何使用 Visual Studio Code 阅读 Android 源码:https://jekton.github.io/2018/05/11/how-to-read-android-so ...
- 结合JDK源码看设计模式——模板方法模式
前言: 相信很多人都听过一个问题:把大象关进冰箱门,需要几步? 第一,把冰箱门打开:第二,把大象放进去:第三,把冰箱门关上.我们可以看见,这个问题的答案回答的很有步骤.接下来我们介绍一种设计模式--模 ...
- 【转】Android源码学习(2)使用Git和Repo进行版本管理
原文网址:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-26074270-id-2458828.html Android项目采用Git和Repo进行版本管理.在大多数情况下,Git都可以 ...
- 《Android源码设计模式》--状态模式--责任链模式--解释器模式--命令模式--观察者模式--备忘录模式--迭代器模式
[状态模式] No1: Wifi设置界面是一个叫做WifiSetting的Fragment实现的 No2: 在不同的状态下对于扫描Wifi这个请求的处理是完全不一样的.在初始状态下扫描请求被直接忽略, ...
随机推荐
- ffmpeg-20160813-bin.7z
ESC 退出 0 进度条开关 1 屏幕原始大小 2 屏幕1/2大小 3 屏幕1/3大小 4 屏幕1/4大小 S 下一帧 [ -2秒 ] +2秒 ; -1秒 ' +1秒 下一个帧 -> -5秒 f ...
- ffmpeg-20160718-git-bin.7z
官方 2016-07-18 发布的bin,彻底不支持 xp. ESC 退出 0 进度条开关 1 屏幕原始大小 2 屏幕1/2大小 3 屏幕1/3大小 4 屏幕1/4大小 S 下一帧 [ -2秒 ] + ...
- Java for LeetCode 204 Count Primes
Description: Count the number of prime numbers less than a non-negative number, n. 解题思路: 空间换时间,开一个空间 ...
- nyoj130 相同的雪花
相同的雪花 时间限制:1000 ms | 内存限制:65535 KB 难度:4 描述 You may have heard that no two snowflakes are alike. ...
- MST:Agri-Net(POJ 1258)
Agri-Net 题目大意:农夫有一片农场,现在他要把这些田地用管子连起来,田地之间有一定距离,铺设每一段管子的长度与这些田地与田地距离是一样的,问你最小的铺设方案. 这一题很裸,Kruskal算法 ...
- codeforces 581C. Developing Skills 解题报告
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/581/C 题目意思:给出 n 个数:a1, a2, ..., an (0 ≤ ai ≤ 100).给出值 ...
- codeforces 495A. Digital Counter 解题报告
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/495/A 这个题目意思好绕好绕~~好绕~~~~~,昨天早上做得 virtual 看不懂,晚上继续看还是,差 ...
- 火狐----此地址使用了一个通常用于网络浏览以外的端口。出于安全原因,Firefox 取消了该请求。
FirFox打开80以外的端口,会弹出以下提示: “此地址使用了一个通常用于网络浏览以外的端口.出于安全原因,Firefox 取消了该请求.”.经网上搜索,解决方法如下: 在Firefox地址栏输入a ...
- Eclipse的各种快捷键
参考他人总结好的 Eclipse快捷键大全(转载) Ctrl+1 快速修复(最经典的快捷键,就不用多说了) ---->例如:add unimplement methodCtrl+D: ...
- mysql扩展库-1
启用mysql扩展库 在php.ini文件中去配置mysql扩展库 extension=php_mysql.dll 可以通过 phpinfo() 查看当前php支持什么扩展库. 在sql扩展库中创建一 ...
