How-to: Do Statistical Analysis with Impala and R
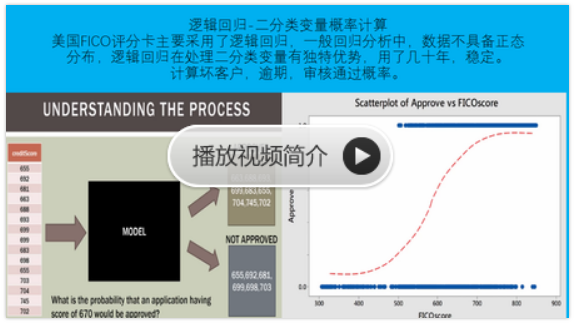
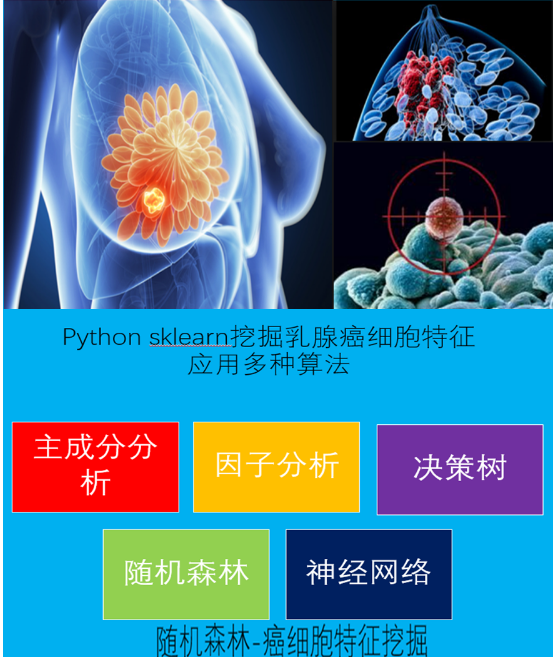
sklearn实战-乳腺癌细胞数据挖掘(博客主亲自录制视频教程)
https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005269003&utm_campaign=commission&utm_source=cp-400000000398149&utm_medium=share
http://blog.cloudera.com/blog/2013/12/how-to-do-statistical-analysis-with-impala-and-r/
The new RImpala package brings the speed and interactivity of Impala to queries from R.
Our thanks to Austin Chungath, Sachin Sudarshana, and Vikas Raguttahalli of Mu Sigma, a Decision Sciences and Big Data analytics company, for the guest post below.
As is well known, Apache Hadoop traditionally relies on the MapReduce paradigm for parallel processing, which is an excellent programming model for batch-oriented workloads. But when ad hoc, interactive querying is required, the batch model fails to meet performance expectations due to its inherent latency.
To overcome this drawback, Cloudera introduced Cloudera Impala, the open source distributed SQL query engine for Hadoop data. Impala brings the necessary speed to queries that were otherwise not interactive when executed by the batch Apache Hive engine; Hive queries that used to take minutes can be executed in a matter of seconds using Impala.
Impala is quite exciting for us at Mu Sigma because existing Hive queries can run interactively with few or no changes. Furthermore, because we do a lot of our statistical computing on R, the popular open source statistical computing language, we considered it worthwhile to bring the speed of Impala to R.
To meet that goal, we have created a new R package, RImpala, which connects Impala to R. RImpala enables querying the data residing in HDFS and Apache HBase from R, which can be further processed as an R object using R functions. RImpala is now available for download from the Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN) under GNU General Public License (GPL3).
The RImpala architecture is simple: we used the existing Impala JDBC drivers and wrote a Java program to connect and query Impala, which we then called from R using the rJava package. We put them all together in an R package that you can use to easily query Impala from R.

Steps for Installing RImpala
Assuming that you have R and Impala already installed, installing the RImpala package is straightforward and is done in a manner similar to any other R package. There are two steps to installing RImpala and getting it working:
Step 1: Install the package from CRAN
You can install RImpala directly using the install.packages() command in R.
|
1
|
> install.packages("RImpala")
|
Alternatively, if you need to do offline installation of the package, you can download it from here and install using the R CMD INSTALL command:
|
1
|
R CMD install RImpala_0.1.1.tar.gz
|
Step 2: Install the Impala JDBC drivers
You need to install Cloudera’s JDBC drivers before you can use the RImpala package that we installed earlier. Cloudera provides JBDC jars on its website that you can download directly. As of this writing, this is the link to zip file containing the JDBC jars.
There are two ways to do this:
- If you have Impala installed on the machine running R, then you will have the necessary JDBC jars already (probably in /usr/lib/impala/lib) and you can use them to initiate the connection to Impala.
- If the machine running R is a different server than the Impala server, then you need to download the JDBC jars from the above link and extract it to a location that can be accessed by the R user.
After you have installed the JDBC drivers you can start using the RImpala package:
- Load the library.
1library(RImpala)
- Initialize the JDBC jars.
1rimpala.init("/path/to/impala/jars")
- Connect to Impala.
1rimpala.connect("IP or Hostname of Impala server", "port")
The following is an Rscript showing how to connect to Impala:
123library(RImpala)rimpala.init(libs="/tmp/impala/jars/")rimpala.connect("192.168.10.1","21050")Location of JDBC jars = /tmp/impala/jars
IP of the server running impalad service = 192.168.10.1
Port where the impalad service is listening = 21050
The default parameter for the rimpala.init() function is “/usr/lib/impala/lib” and the default parameters for rimpala.connect() function are “localhost” and “21050” respectively.
To run a query on the impalad instance that the client has connected, you can use the rimpala.query() function. Example:
|
1
|
result
|
All the contents of the sample_table will be stored in the result object as a data frame. This data frame can now be used for further analytical processing in R.
You can also install the RImpala package on a client machine running Microsoft Windows. Since the JDBC jars are platform independent, you can extract them into a folder on a Windows machine (such as “C:\Program Files\impala”) and then this location can be passed as a parameter to the rimpala.init() function.
The following a simple example that shows you how to use RImpala:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
> library(RImpala)
Loading required package: rJava
> rimpala.init(libs="/tmp/impala/jars/") # Adds the impala JDBC jars present in the "/tmp/impala/jars/" folder to the classpath
[1] "Classpath added successfully"
> rimpala.connect(IP="192.168.10.1",port="21050") # Establishes a connection to impalad instance running on the machine 172.25.1.151 on the port 21050
[1] TRUE
> rimpala.invalidate() # Invalidates the metadata of all the tables present in the Hive metastore
[1] TRUE
> rimpala.showdatabases()# Displays all the databases available
# Output #
name
1 airlines
2 bank
3 default
> rimpala.usedatabase("bank") # Changes the current database to "bank"
Database changed to bank
[1] TRUE
> rimpala.showtables() # Displays all the tables present in the current database
# Output #
name
1 bank_web_clicks
2 ticker_100m
3 stock_1gb
4 weblog_10gb
> rimpala.describe("bank_web_clicks") # Describes the table "bank_web_clicks"
# Output #
Name type comment
1 customer_id int Customer ID
2 session_id int Session ID
3 page string Web page name
4 datestamp timestamp Date
> result result
# Output #
customer_id session_id cnt
1 32 21 5200
2 34 12 5100
3 35 49 4105
4 32 34 3600
5 36 32 3218
6 37 67 3190
7 31 45 2990
8 35 75 2300
9 34 69 2113
> rimpala.close() # Closes the connection to the impalad instance
[1] TRUE
|
Conclusion
Impala is an exciting new technology that is gaining popularity and will probably grow to be an enterprise asset in the Hadoop world. We hope that RImpala will be a fruitful package for all Big Data analysts to leverage the power of Impala from R.
Impala is an ongoing and thriving effort at Cloudera and will continue to evolve with richer functionality and improved performance – and so will RImpala. We will continue to improve the package over time and incorporate new features into RImpala as and when they are made available in Impala.
Austin Chungath is a Senior Research Analyst with Mu Sigma’s Innovation & Development Team and maintainer of the RImpala project. He does research on various tools in the Hadoop ecosystem and the possibilities that they bring for analytics. He spends his free time contributing to Open Source projects like Apache Tez or building small robots.
Sachin Sudarshana is a Research Analyst with Mu Sigma’s Innovation & Development Team. His responsibilities include researching emerging tools in the Hadoop ecosystem and how they can be leveraged in an analytics context.
Vikas Raguttahalli is a Research Lead with Mu Sigma’s Innovation & Development Team. He is responsible for working with client delivery teams and helping clients institutionalize Big Data within their organizations, as well as researching new and upcoming Big Data tools. His expertise includes R, MapReduce, Hive, Pig, Mahout and the wider Hadoop ecosystem.
python风控评分卡建模和风控常识(博客主亲自录制视频教程)
How-to: Do Statistical Analysis with Impala and R的更多相关文章
- [Python] Statistical analysis of time series
Global Statistics: Common seen methods as such 1. Mean 2. Median 3. Standard deviation: the larger ...
- survival analysis 生存分析与R 语言示例 入门篇
原创博客,未经允许,不得转载. 生存分析,survival analysis,顾名思义是用来研究个体的存活概率与时间的关系.例如研究病人感染了病毒后,多长时间会死亡:工作的机器多长时间会发生崩溃等. ...
- Why many EEG researchers choose only midline electrodes for data analysis EEG分析为何多用中轴线电极
Source: Research gate Stafford Michahial EEG is a very low frequency.. and literature will give us t ...
- Methods for follow-up research of exome analysis:外显子后续分析研究思路总结
外显子后续分析研究思路一般有以下几种(Methods for follow-up research of exome analysis): 1.对突变频率.突变类型.突变方式进行统计分析 Mutati ...
- MAST 397B: Introduction to Statistical Computing
MAST 397B: Introduction to Statistical ComputingABSTRACTNotes: (i) This project can be done in group ...
- PayPal高级工程总监:读完这100篇论文 就能成大数据高手(附论文下载)
100 open source Big Data architecture papers for data professionals. 读完这100篇论文 就能成大数据高手 作者 白宁超 2016年 ...
- 100 open source Big Data architecture papers for data professionals
zhuan :https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/100-open-source-big-data-architecture-papers-anil-madan Big Da ...
- 一些我推荐的和想上的网络课程(Coursera, edX, Udacity)
从面向找工作的角度出发,我觉得以下课程有很大帮助: 首推Robert Sedgewick,也是我觉得对我帮助最大的老师,讲课特点是能把复杂的算法讲解清楚(典型例子:红黑树,KMP算法) 他在Cours ...
- 斯坦福CS课程列表
http://exploredegrees.stanford.edu/coursedescriptions/cs/ CS 101. Introduction to Computing Principl ...
随机推荐
- 训练赛-Eyad and Math
题意:给你四个数,求出a^b是否小于c^d,是的话输出<,否则输出>; 思路:因为数据很大,所以我们需要降低数据的规模,比如用一个log10()函数,这就能解决了,注意,要用scanf输入 ...
- Go中的Init函数
init函数会在main函数执行之前进行执行.init用在设置包.初始化变量或者其他要在程序运行前优先完成的引导工作. 举例:在进行数据库注册驱动的时候. 这里有init函数 package post ...
- BZOJ2342[Shoi2011]双倍回文——回文自动机
题目描述 输入 输入分为两行,第一行为一个整数,表示字符串的长度,第二行有个连续的小写的英文字符,表示字符串的内容. 输出 输出文件只有一行,即:输入数据中字符串的最长双倍回文子串的长度,如果双倍回文 ...
- 洛谷P1916 小书童——蚂蚁大战
题目背景 小A在你的帮助下,开始“刷题”,他在小书童里发现了一款叫“蚂蚁大战”(又称蛋糕保卫战)的游戏.(你懂得) 题目描述 游戏中会出现n只蚂蚁,分别有a1,a2……an的血量,它们要吃你的蛋糕.当 ...
- spring05-Spring事务管理
事务的第一个方面是传播行为(propagation behavior).当事务方法被另一个事务方法调用时,必须指定事务应该如何传播.例如:方法可能继续在现有事务中运行,也可能开启一个新事务,并在自己的 ...
- 【GZOI2015】石子游戏 博弈论 SG函数
题目大意 有\(n\)堆石子,两个人可以轮流取石子.每次可以选择一堆石子,做出下列的其中一点操作: 1.移去整堆石子 2.设石子堆中有\(x\)个石子,取出\(y\)堆石子,其中\(1\leq y&l ...
- codevs 2606 约数和问题 (数学+分块)
题目描述 Description Smart最近沉迷于对约数的研究中. 对于一个数X,函数f(X)表示X所有约数的和.例如:f(6)=1+2+3+6=12.对于一个X,Smart可以很快的算出f(X) ...
- 【最短路算法】Dijkstra+heap和SPFA的区别
单源最短路问题(SSSP)常用的算法有Dijkstra,Bellman-Ford,这两个算法进行优化,就有了Dijkstra+heap.SPFA(Shortest Path Faster Algori ...
- 洛谷SP22343 NORMA2 - Norma(分治,前缀和)
洛谷题目传送门 这题推式子恶心..... 考虑分治,每次统计跨过\(mid\)的所有区间的答案和.\(i\)从\(mid-1\)到\(l\)枚举,统计以\(i\)为左端点的所有区间. 我们先维护好\( ...
- 24 Zabbix系统配置日志监控告警--关键字触发
点击返回:自学Zabbix之路 点击返回:自学Zabbix4.0之路 点击返回:自学zabbix集锦 24 Zabbix系统配置日志监控告警--关键字触发 trapper是被监控主机主动发送数据给za ...