第十八节,TensorFlow中使用批量归一化(BN)
在深度学习章节里,已经介绍了批量归一化的概念,详情请点击这里:第九节,改善深层神经网络:超参数调试、正则化以优化(下)
神经网络在进行训练时,主要是用来学习数据的分布规律,如果数据的训练部分和测试部分分布不一样,那么网络的泛化能力会变得非常差.而且对于训练的数据,每批分布也是不一样的,那么网络在迭代的过程中也要学习和适应不同的分布.这会大大降低网络的训练速度.此外,数据的分布对于激活函数来说也非常重要,有时数据分布范围太大不利于利用激活函数的非线性特性,比如激活函使用Sigmoid函数时,会导致训练时出现饱和的问题。而批量归一化就是为了缓解这个问题提出的。在实际应用中,批量归一化的收敛非常快,并且具有很强的泛化能力,某种情况下完全可以替代正则化和弃权。
一 批量归一化函数
归一化算法可以描述为:

其中xi是batch_size样本中的第i个样本,μB是求得的每个特征均值,σB2是求得每个特征的方差。
1.TensorFlow中自带BN函数的定义:
def batch_normalization(x,
mean,
variance,
offset,
scale,
variance_epsilon,
name=None):
各个参数的说明如下:
- x:代表任意维度的输入张量。
- mean:代表样本的均值。
- variance:代表样本的方差。
- offset:代表偏移,即相加一个转化值,也是公式中的beta。
- scale:代表缩放,即乘以一个转化值,也是公式中的gamma。
- variance_epsilon:是为了避免分母为0的情况下,给分母加上的一个极小值,默认即可。
- name:名称。
要想使用这个整数,必须由另一个函数配合使用,tf.nn.moments,由它来计算均值和方差,然后就可以使用BN了。
2.tf.nn.moment()函数的定义如下:
def moments(x, axes, shift=None, name=None, keep_dims=False):
- x:输入张量。
- axes:指定沿哪个轴计算平均值和方差。
- shift:A `Tensor` containing the value by which to shift the data for numerical stability, or `None` in which case the true mean of the data is used as shift. A shift close to the true mean provides the most numerically stable results.
- name:名称。
- keep_dims:是否保留维度,即形状是否和输入一样。
有了以上两个函数还不够,因为如果使用tf.nn.moment()函数计算均值和方差,我们需要保存每批次训练的均值和方差,然后求平均。为了有更好的效果,我们通常使用指数加权平均的方法来优化每次的均值和方差,于是就用到了tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage()类,它的作用是让上一次的值对本次的值有个衰减后的影响,从而使每次的值连起来后会相对平滑一下:详细内容可以点击这里:第八节,改善深层神经网络:超参数调试、正则化以优化(中)
我们可以用一个表达式来表示这个函数的功能:
shadow_variable = decay * shadow_variable + (1 - decay) *variable
各参数说明如下:
- decay:代表衰减指数,是在ExponentialMovingAverage()中指定的,一般为0.9.
- variable:代表本批次样本中的值。
- 等式右边的shadow_variable:代表上次总样本的值。
- 等式左边的shadow_variable:代表本次次总样本的值。
对于shadow_variable的理解,你可以将其人为该数值表示的是1/(1-β)次的平均值,本次样本所占的权重为(1-decay),上次样本所占权重为(1-decay)decay,上上次样本所占权重为(1-decay)decay^2,以此类推....
3.tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage类的定义如下:
def __init__(self, decay, num_updates=None, zero_debias=False,
name="ExponentialMovingAverage"):
def apply(self, var_list=None):
参数说明如下:
- decay: Float. The decay to use.
- num_updates: Optional count of number of updates applied to variables. actual decay rate used is: `min(decay, (1 + num_updates) / (10 + num_updates))
- zero_debias: If `True`, zero debias moving-averages that are initialized with tensors.
- name: String. Optional prefix name to use for the name of ops added in.
var_list: A list of Variable or Tensor objects. The variables and Tensors must be of types float16, float32, or float64.apply
通过调用apply()函数可以更新指数加权平均值。
二 批量归一化的简单用法
上面的函数虽然参数不多,但是需要几个函数联合起来使用,于是TensorFlow中的layers模块里又实现了一次BN函数,相当于把几个函数合并到了一起,使用起来更加简单。下面来介绍一下,使用时需要引入:
from tensorflow.contrib.layers.python.layers import batch_norm
或者直接调用tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm(),该函数的定义如下:
def batch_norm(inputs,
decay=0.999,
center=True,
scale=False,
epsilon=0.001,
activation_fn=None,
param_initializers=None,
param_regularizers=None,
updates_collections=ops.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS,
is_training=True,
reuse=None,
variables_collections=None,
outputs_collections=None,
trainable=True,
batch_weights=None,
fused=False,
data_format=DATA_FORMAT_NHWC,
zero_debias_moving_mean=False,
scope=None,
renorm=False,
renorm_clipping=None,
renorm_decay=0.99):
参数说明如下:
- inputs: A tensor with 2 or more dimensions, where the first dimension has `batch_size`. The normalization is over all but the last dimension if `data_format` is `NHWC` and the second dimension if `data_format` is `NCHW`.代表输入,第一个维度为batch_size
- dacay:Decay for the moving average. Reasonable values for `decay` are close to 1.0, typically in the multiple-nines range: 0.999, 0.99, 0.9, etc. Lower `decay` value (recommend trying `decay`=0.9) if model experiences reasonably good training performance but poor validation and/or test performance. Try zero_debias_moving_mean=True for improved stability.代表加权指数平均值的衰减速度,是使用了一种叫做加权指数衰减的方法更新均值和方差。一般会设置为0.9,值太小会导致均值和方差更新太快,而值太大又会导致几乎没有衰减,容易出现过拟合,这种情况一般需要把值调小点。
- center: If True, add offset of `beta` to normalized tensor. If False, `beta` is ignored. 指定是否使用偏移beta。
- scale: If True, multiply by `gamma`. If False, `gamma` is not used. When the next layer is linear (also e.g. `nn.relu`), this can be disabled since the scaling can be done by the next layer.是否进行变换(通过乘以一个gamma进行缩放),我们习惯在BN后面接一个线性变化,如Relu,所以scale一般都设置为Flase,因为后面有对数据的转换处理,所以这里就不用再处理了。
- epsilon: Small float added to variance to avoid dividing by zero.是为了避免分母为0的情况下,给分母加上的一个极小值,默认即可。
- activation_fn: Activation function, default set to None to skip it and maintain a linear activation.激活函数,默认为None,即使用线性激活函数。
- param_initializers: Optional initializers for beta, gamma, moving mean and moving variance.可选的初始化参数。
- param_regularizers: Optional regularizer for beta and gamma.可选的正则化项。
- updates_collections: Collections to collect the update ops for computation. The updates_ops need to be executed with the train_op. If None, a control dependency would be added to make sure the updates are computed in place.其变量默认是tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS,在训练时提供了一种内置的均值和方差更新机制,即通过图中的tf.Graphs.UPDATE_OPS变量来更新,但它是在每次当前批次训练完成后才更新均值和方差,这样就导致当前数据总是使用前一次的均值和方差,没有得到最新的更新。所以一般都会将其设置为None,让均值和方差即时更新。这样虽然相比默认值在性能上稍慢点,但是对模型的训练还是有很大帮助的。
- is_training: Whether or not the layer is in training mode. In training mode it would accumulate the statistics of the moments into `moving_mean` and `moving_variance` using an exponential moving average with the given `decay`. When it is not in training mode then it would use the values of the `moving_mean` and the `moving_variance`.当它为True,代表是训练过程,这时会不断更新样本集的均值与方差。当测试时,要设置成False,这样就会使用训练样本集的均值和方差。
- reuse: Whether or not the layer and its variables should be reused. To be able to reuse the layer scope must be given.支持共享变量,与下面的scope参数联合使用。
- variables_collections: Optional collections for the variables.
- outputs_collections: Collections to add the outputs.
- trainable: If `True` also add variables to the graph collection `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see `tf.Variable`).
- batch_weights: An optional tensor of shape `[batch_size]`, containing a frequency weight for each batch item. If present, then the batch normalization uses weighted mean and variance. (This can be used to correct for bias in training example selection.)
- used: Use nn.fused_batch_norm if True, nn.batch_normalization otherwise.
- data_format: A string. `NHWC` (default) and `NCHW` are supported.
- zero_debias_moving_mean: Use zero_debias for moving_mean. It creates a new air of variables 'moving_mean/biased' and 'moving_mean/local_step'.
- scope: Optional scope for `variable_scope`.指定变量的作用域variable_scope。
- renorm: Whether to use Batch Renormalization https://arxiv.org/abs/1702.03275). This adds extra variables during raining. The inference is the same for either value of this parameter.
- renorm_clipping: A dictionary that may map keys 'rmax', 'rmin', 'dmax' to scalar `Tensors` used to clip the renorm correction. The correction `(r, d)` is used as `corrected_value = normalized_value * r + d`, with `r` clipped to [rmin, rmax], and `d` to [-dmax, dmax]. Missing rmax, rmin, dmax are set to inf, 0, inf, respectively.
- renorm_decay: Momentum used to update the moving means and standard deviations with renorm. Unlike `momentum`, this affects training and should be neither too small (which would add noise) nor too large (which would give stale estimates). Note that `decay` is still applied to get the means and variances for inference.
三 为CIFAR10分类添加BN
这里继续在第十三节cifar10分类的代码基础上修改:
1.添加BN函数
def avg_pool_6x6(x):
'''
全局平均池化层,使用一个与原有输入同样尺寸的filter进行池化,'SAME'填充方式 池化层后
out_height = in_hight / strides_height(向上取整)
out_width = in_width / strides_width(向上取整) args;
x:输入图像 形状为[batch,in_height,in_width,in_channels]
'''
return tf.nn.avg_pool(x,ksize=[1,6,6,1],strides=[1,6,6,1],padding='SAME') def batch_norm_layer(value,is_training=False,name='batch_norm'):
'''
批量归一化 返回批量归一化的结果 args:
value:代表输入,第一个维度为batch_size
is_training:当它为True,代表是训练过程,这时会不断更新样本集的均值与方差。当测试时,要设置成False,这样就会使用训练样本集的均值和方差。
默认测试模式
name:名称。
'''
if is_training is True:
#训练模式 使用指数加权函数不断更新均值和方差
return tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm(inputs=value,decay=0.9,updates_collections=None,is_training = True)
else:
#测试模式 不更新均值和方差,直接使用
return tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm(inputs=value,decay=0.9,updates_collections=None,is_training = False)
2.为BN函数添加占位符参数
由于BN函数里需要设置是否为训练状态,所以需要定义一个占位符来传入我们处于训练模式还是测试模式。
#定义占位符
input_x = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32,shape=[None,24,24,3]) #图像大小24x24x
input_y = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32,shape=[None,10]) #0-9类别
is_training = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.bool) #设置为True,表示训练 Flase表示测试
3。修改网络结构添加BN层
在第一层h_conv1和第二层h_conv2激活函数前添加BN层。
x_image = tf.reshape(input_x,[batch_size,24,24,3]) #1.卷积层 ->池化层 在激活函数之前追加BN层
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5,5,3,64])
b_conv1 = bias_variable([64]) h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm_layer(conv2d(x_image,W_conv1) + b_conv1,is_training=is_training)) #输出为[-1,24,24,64]
print_op_shape(h_conv1)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1) #输出为[-1,12,12,64]
print_op_shape(h_pool1) #2.卷积层 ->池化层 在激活函数之前追加BN层
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5,5,64,64])
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64]) h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm_layer(conv2d(h_pool1,W_conv2) + b_conv2,is_training=is_training)) #输出为[-1,12,12,64]
print_op_shape(h_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2) #输出为[-1,6,6,64]
print_op_shape(h_pool2) #3.卷积层 ->全局平均池化层
W_conv3 = weight_variable([5,5,64,10])
b_conv3 = bias_variable([10]) h_conv3 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool2,W_conv3) + b_conv3) #输出为[-1,6,6,10]
print_op_shape(h_conv3) nt_hpool3 = avg_pool_6x6(h_conv3) #输出为[-1,1,1,10]
print_op_shape(nt_hpool3)
nt_hpool3_flat = tf.reshape(nt_hpool3,[-1,10]) y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(nt_hpool3_flat)
4 加入退化学习率
将原来的学习率改为退化学习率,让其每1000步衰退0.9.
#softmax交叉熵代价函数
cost = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(input_y * tf.log(y_conv),axis=1)) #加入退化学习率 初始值为learning_rate,让其每1000步,衰减0.9 学习率 = learning_rate*0.9^(global_step/1000)
global_step = tf.Variable(0,trainable=False)
decaylearning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(learning_rate,global_step,1000,0.9) #求解器 执行一次train global_step变量会自加1
train = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost,global_step = global_step) #返回一个准确度的数据
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.arg_max(y_conv,1),tf.arg_max(input_y,1))
#准确率
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,dtype=tf.float32))
5 开始训练
这这里我们需要给BN函数传入一个is_training参数,表明当前是在训练模式还是处于测试模式。
'''
四 开始训练
'''
sess = tf.Session();
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# 启动计算图中所有的队列线程 调用tf.train.start_queue_runners来将文件名填充到队列,否则read操作会被阻塞到文件名队列中有值为止。
tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess) for step in range(training_step):
#获取batch_size大小数据集
image_batch,label_batch = sess.run([images_train,labels_train]) #one hot编码
label_b = np.eye(10,dtype=np.float32)[label_batch] #开始训练 执行一次train global_step变量会自加1,这样decaylearning_rate值就会改变
rate,_ = sess.run([decaylearning_rate,train],feed_dict={input_x:image_batch,input_y:label_b,is_training:True}) if step % display_step == 0:
train_accuracy = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={input_x:image_batch,input_y:label_b,is_training:False})
print('Step {0} tranining accuracy {1}'.format(step,train_accuracy)) image_batch, label_batch = sess.run([images_test, labels_test])
label_b = np.eye(10,dtype=np.float32)[label_batch]
test_accuracy = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={input_x:image_batch,input_y:label_b,is_training:False})
print('finished! test accuracy {0}'.format(test_accuracy))

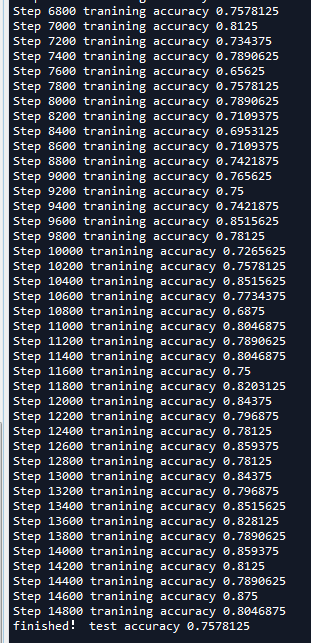
可以看到准确率有了很大的提升,比第十三节的70%提升了很多,训练时的准确率已经达到了80%左右,然而测试时模型的准确率下降了不少。除此之外,我们可以使用cifar10_input中的distorted_inputs()函数来增大数据集,或者采用一些过拟合的方法继续优化。
第十八节,TensorFlow中使用批量归一化(BN)的更多相关文章
- Tensorflow 中(批量)读取数据的案列分析及TFRecord文件的打包与读取
内容概要: 单一数据读取方式: 第一种:slice_input_producer() # 返回值可以直接通过 Session.run([images, labels])查看,且第一个参数必须放在列表中 ...
- 第十八节 JS中的正则表达式
复习字符串操作: search 查找 substring 获取子字符串 charAt 获取某个字符 split 分割字符串,获取数组 var str = 'abcdefghijk'; alert(st ...
- TensorFlow——批量归一化操作
批量归一化 在对神经网络的优化方法中,有一种使用十分广泛的方法——批量归一化,使得神经网络的识别准确度得到了极大的提升. 在网络的前向计算过程中,当输出的数据不再同一分布时,可能会使得loss的值非常 ...
- 第十四节,TensorFlow中的反卷积,反池化操作以及gradients的使用
反卷积是指,通过测量输出和已知输入重构未知输入的过程.在神经网络中,反卷积过程并不具备学习的能力,仅仅是用于可视化一个已经训练好的卷积神经网络,没有学习训练的过程.反卷积有着许多特别的应用,一般可以用 ...
- 第三百五十八节,Python分布式爬虫打造搜索引擎Scrapy精讲—将bloomfilter(布隆过滤器)集成到scrapy-redis中
第三百五十八节,Python分布式爬虫打造搜索引擎Scrapy精讲—将bloomfilter(布隆过滤器)集成到scrapy-redis中,判断URL是否重复 布隆过滤器(Bloom Filter)详 ...
- 从头学pytorch(十九):批量归一化batch normalization
批量归一化 论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03167 批量归一化基本上是现在模型的标配了. 说实在的,到今天我也没搞明白batch normalize能够使得模型训练 ...
- 第二十二节,TensorFlow中的图片分类模型库slim的使用、数据集处理
Google在TensorFlow1.0,之后推出了一个叫slim的库,TF-slim是TensorFlow的一个新的轻量级的高级API接口.这个模块是在16年新推出的,其主要目的是来做所谓的“代码瘦 ...
- 第二十二节,TensorFlow中RNN实现一些其它知识补充
一 初始化RNN 上一节中介绍了 通过cell类构建RNN的函数,其中有一个参数initial_state,即cell初始状态参数,TensorFlow中封装了对其初始化的方法. 1.初始化为0 对于 ...
- centos shell编程4【分发系统】 服务器标准化 mkpasswd 生成密码的工具 expect讲解 expect传递参数 expect自动同步文件 expect指定host和要同步的文件 expect文件分发系统 expect自动发送密钥脚本 Linux脚本执行方式 第三十八节课
centos shell编程4[分发系统] 服务器标准化 mkpasswd 生成密码的工具 expect讲解 expect传递参数 expect自动同步文件 expect指定host和要 ...
随机推荐
- Antd & ice
Antd & ice Angular https://github.com/NG-ZORRO/ng-zorro-antd https://ng.ant.design/docs/introduc ...
- pycharm 安装
pycharm 1.模板 file->setting->Editor->file and code template->python script->右上方 #!/usr ...
- PHP的特质Trait使用
参考: Trait的使用,网站地址https://www.jianshu.com/p/fc053b2d7fd1
- python数据结构与算法第七天【链表】
1.链表的定义 如图: 注意: (1)线性表包括顺序表和链表 (2)顺序表是将元素顺序地存放在一块连续的存储区里 (3)链表是将元素存放在通过链构造的存储快中 2. 单向链表的实现 #!/usr/bi ...
- Missing artifact com.oracle:ojdbc6:jar:11.2.0.3 Maven中不能引入ojdbc解决方法,错误
今天从服务器检出Maven项目的时候,遇到了一个问题,就是在pom.xml中引入ojdbc的jar包的时候出错了,提示是Missing artifact com.oracle:ojdbc6:jar:1 ...
- Lodop的JS模版代码、文档式模版 生成加载赋值博文索引
Lodop获取全部JS代码,传统JS模版的生成.LODOP设置打印设计返回JS代码是变量 LodopJS代码模版的加载和赋值 Lodop生成文档式模版 LodopJS文档式模版的加载和赋值 由于加载J ...
- 学习 Spring (六) 自动装配
Spring入门篇 学习笔记 No: (默认)不做任何操作 byName: 根据属性名自动装配.此选项将检查容器并根据名字查找与属性完全一致的 bean,并将其与属性自动装配 byType: 如果容器 ...
- Ubuntu16.04安装使用wps
Ubuntu16.04安装使用wps 1.wps官网下载并安装wps 此处以Debian安装包为例,官网下载路径 http://www.wps.cn/product/wpslinux/# 直接安装: ...
- HDU5769-Substring-多校#4-1006-后缀数组
给定一个字符x和一个字符串.要求输出包含此字符的所有不同字串. 后缀数组可以计算一个字符串的所有不同字串,理解了原理就能做这题了. 对于每一个后缀i,将产生len-sa[i]-hight[i]的前缀, ...
- The Unique MST POJ - 1679 次小生成树prim
求次小生成树思路: 先把最小生成树求出来 用一个Max[i][j] 数组把 i点到j 点的道路中 权值最大的那个记录下来 used数组记录该条边有没有被最小生成树使用过 把没有使用过的一条边加 ...
