Spring MVC工作原理及源码解析(二)DispatcherServlet实现原理及源码解析
1、DispatcherServlet 处理流程
从上一篇文章中Spring MVC原理图中我们可以看出:DispatcherServlet 在 Spring MVC框架 中处于核心位置,它负责协调和组织不同组件完成请求处理并返回响应的工作。在分析 DispatcherServlet 源码之前,我们先来看一下请求处理的大致流程:
- Tomcat 上的项目(采用了Spring MVC框架)启动,对 DispatcherServlet 进行实例化,然后调用它的 init() 方法进行初始化,在这个初始化过程中完成了:对 web.xml 中初始化参数的加载;建立 WebApplicationContext (SpringMVC的IOC容器);进行组件的初始化;
- 用户在浏览器发出请求,由 Tomcat 接收到这个请求,如果匹配到 DispatcherServlet 在 web.xml 中配置的映射路径,Tomcat 就将请求转交给 DispatcherServlet 处理;
- DispatcherServlet 从容器中取出所有 HandlerMapping 实例(每个实例对应一个 HandlerMapping 接口的实现类)并遍历,每个 HandlerMapping 会根据请求信息,通过自己实现类中的方式去找到处理该请求的 Handler (执行程序,如Controller中的方法),并且将这个 Handler 与一堆 HandlerInterceptor (拦截器) 封装成一个 HandlerExecutionChain 对象,一旦有一个 HandlerMapping 可以找到 Handler 则退出循环;
- DispatcherServlet 取出 HandlerAdapter 组件,根据已经找到的 Handler,再从所有 HandlerAdapter 中找到可以处理该 Handler 的 HandlerAdapter 对象;
- 执行 HandlerExecutionChain 中所有拦截器的 preHandler() 方法,然后再利用 HandlerAdapter 执行 Handler ,执行完成得到 ModelAndView,再依次调用拦截器的 postHandler() 方法;
- 利用 ViewResolver 将 ModelAndView 或是 Exception(可解析成 ModelAndView)解析成 View,然后 View 会调用 render() 方法,再根据 ModelAndView 中的数据渲染出页面;
- 最后再依次调用拦截器的 afterCompletion() 方法,这一次请求就结束了。
2、DispatcherServlet 源码分析
DispatcherServlet 继承自 HttpServlet,它遵循 Servlet 里的“init-service-destroy”三个阶段,首先我们先来看一下它的 init() 阶段。
1、初始化
1.1、HttpServletBean 的 init() 方法
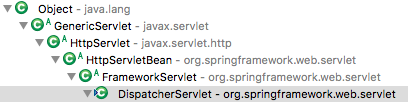
首先我们来看一下DispatcherServlet的继承关系,它继承自FrameworkServlet,而FrameworkServlet又继承自HttpServletBean。

DispatcherServlet 的 init() 方法在其父类 HttpServletBean 中实现的,它覆盖了 GenericServlet 的 init() 方法,主要作用是加载 web.xml 中 DispatcherServlet 的 <init-param> 配置,并调用子类的初始化。下面是 init() 方法的具体代码:
/**
* Map config parameters onto bean properties of this servlet, and
* invoke subclass initialization.
* @throws ServletException if bean properties are invalid (or required
* properties are missing), or if subclass initialization fails.
*/
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException { // Set bean properties from init parameters.(ServletConfigPropertyValues 是静态内部类,它使用 ServletConfig 获取 web.xml 中配置的参数)
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
// 使用 BeanWrapper 来构造 DispatcherServlet
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
} // Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.(让子类实现的方法,这种在父类定义在子类实现的方式叫做模版方法模式)
initServletBean();
}
如上所述,web.xml 中配置的参数是 ServletConfigPropertyValues 使用 ServletConfig 获取到的,ServletConfigPropertyValues 的代码如下所示:
/**
* PropertyValues implementation created from ServletConfig init parameters.
*/
private static class ServletConfigPropertyValues extends MutablePropertyValues { /**
* Create new ServletConfigPropertyValues.
* @param config the ServletConfig we'll use to take PropertyValues from
* @param requiredProperties set of property names we need, where
* we can't accept default values
* @throws ServletException if any required properties are missing
*/
public ServletConfigPropertyValues(ServletConfig config, Set<String> requiredProperties)
throws ServletException { Set<String> missingProps = (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(requiredProperties) ?
new HashSet<>(requiredProperties) : null); Enumeration<String> paramNames = config.getInitParameterNames();
while (paramNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String property = paramNames.nextElement();
Object value = config.getInitParameter(property);
addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue(property, value));
if (missingProps != null) {
missingProps.remove(property);
}
} // Fail if we are still missing properties.
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(missingProps)) {
throw new ServletException(
"Initialization from ServletConfig for servlet '" + config.getServletName() +
"' failed; the following required properties were missing: " +
StringUtils.collectionToDelimitedString(missingProps, ", "));
}
}
}
1.2、FrameworkServlet 的 initServletBean() 方法
在 HttpServletBean 的 init() 方法中调用了 initServletBean() 这个方法,它是在 FrameworkServlet 类中实现的,主要作用是建立 WebApplicationContext 容器(有时也称上下文),并加载 SpringMVC 配置文件中定义的 Bean 到改容器中,最后将该容器添加到 ServletContext 中。下面是 initServletBean() 方法的具体代码:
/**
* Overridden method of {@link HttpServletBean}, invoked after any bean properties
* have been set. Creates this servlet's WebApplicationContext.
*/
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try {
// 初始化 WebApplicationContext (即SpringMVC的IOC容器)
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
} if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ?
"shown which may lead to unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data" :
"masked to prevent unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data";
logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails='" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails +
"': request parameters and headers will be " + value);
} if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Completed initialization in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms");
}
}
WebApplicationContext 继承于 ApplicationContext 接口,从容器中可以获取当前应用程序环境信息,它也是 SpringMVC 的 IOC 容器。下面是 initWebApplicationContext() 方法的具体代码:
/**
* Initialize and publish the WebApplicationContext for this servlet.
* <p>Delegates to {@link #createWebApplicationContext} for actual creation
* of the context. Can be overridden in subclasses.
* @return the WebApplicationContext instance
* @see #FrameworkServlet(WebApplicationContext)
* @see #setContextClass
* @see #setContextConfigLocation
*/
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
// 获取 ContextLoaderListener 初始化并注册在 ServletContext 中的根容器,即 Spring 的容器
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null; if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it(因为 WebApplicationContext 不为空,说明该类在构造时已经将其注入,可以直接使用它)
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent(将 Spring 的容器设为 SpringMVC 容器的父容器)
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id(如果 WebApplicationContext 为空,则进行查找,能找到说明上下文已经在别处初始化。)
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one(如果 WebApplicationContext 仍为空,则以 Spring 的容器为父上下文建立一个新的。)
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
} if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
// 模版方法,由 DispatcherServlet 实现
onRefresh(wac);
}
} if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.(发布这个 WebApplicationContext 容器到 ServletContext 中)
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
} return wac;
}
下面是查找 WebApplicationContext 的 findWebApplicationContext() 方法代码:
/**
* Retrieve a {@code WebApplicationContext} from the {@code ServletContext}
* attribute with the {@link #setContextAttribute configured name}. The
* {@code WebApplicationContext} must have already been loaded and stored in the
* {@code ServletContext} before this servlet gets initialized (or invoked).
* <p>Subclasses may override this method to provide a different
* {@code WebApplicationContext} retrieval strategy.
* @return the WebApplicationContext for this servlet, or {@code null} if not found
* @see #getContextAttribute()
*/
@Nullable
protected WebApplicationContext findWebApplicationContext() {
String attrName = getContextAttribute();
if (attrName == null) {
return null;
}
// 从 ServletContext 中查找已经发布的 WebApplicationContext 容器
WebApplicationContext wac =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext(), attrName);
if (wac == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No WebApplicationContext found: initializer not registered?");
}
return wac;
}
1.3、DispatcherServlet 的 onRefresh() 方法
建立好 WebApplicationContext(上下文) 后,通过 onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) 方法回调,进入 DispatcherServlet 类中。onRefresh() 方法,提供 SpringMVC 的初始化,具体代码如下:
/**
* This implementation calls {@link #initStrategies}.
*/
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
} /**
* Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses.
* <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects.
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
在 initStrategies() 方法中进行了各个组件的初始化,先来看一下这些组件的初始化方法,稍后再来详细分析这些组件。
1.3.1、initHandlerMappings 方法
initHandlerMappings() 方法从 SpringMVC 的容器及 Spring 的容器中查找所有的 HandlerMapping 实例,并把它们放入到 handlerMappings 这个 list 中。这个方法并不是对 HandlerMapping 实例的创建,HandlerMapping 实例是在上面 WebApplicationContext 容器初始化,即 SpringMVC 容器初始化的时候创建的。
/**
* Initialize the HandlerMappings used by this class.
* <p>If no HandlerMapping beans are defined in the BeanFactory for this namespace,
* we default to BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping.
*/
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null; if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.(从 SpringMVC 的 IOC 容器及 Spring 的 IOC 容器中查找 HandlerMapping 实例)
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.(按一定顺序放置 HandlerMapping 对象)
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
} // Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering
// a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found.(如果没有找到 HandlerMapping,则加载默认的)
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No HandlerMappings declared for servlet '" + getServletName() +
"': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties");
}
}
}
1.3.2、initHandlerAdapters 方法
/**
* Initialize the HandlerAdapters used by this class.
* <p>If no HandlerAdapter beans are defined in the BeanFactory for this namespace,
* we default to SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter.
*/
private void initHandlerAdapters(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerAdapters = null; if (this.detectAllHandlerAdapters) {
// Find all HandlerAdapters in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.(从 SpringMVC 的 IOC 容器及 Spring 的 IOC 容器中查找 HandlerAdapters 实例)
Map<String, HandlerAdapter> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerAdapter.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerAdapters = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerAdapters in sorted order.(按一定顺序放置 HandlerAdapters 对象)
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerAdapters);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerAdapter ha = context.getBean(HANDLER_ADAPTER_BEAN_NAME, HandlerAdapter.class);
this.handlerAdapters = Collections.singletonList(ha);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerAdapter later.
}
} // Ensure we have at least some HandlerAdapters, by registering
// default HandlerAdapters if no other adapters are found.(如果没有找到 HandlerAdapters,则加载默认的)
if (this.handlerAdapters == null) {
this.handlerAdapters = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerAdapter.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No HandlerAdapters declared for servlet '" + getServletName() +
"': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties");
}
}
}
2、处理请求
HttpServlet 提供了 doGet()、doPost() 等方法,DispatcherServlet 中这些方法是在其父类 FrameworkServlet 中实现的,代码如下:
/**
* Delegate GET requests to processRequest/doService.
* <p>Will also be invoked by HttpServlet's default implementation of {@code doHead},
* with a {@code NoBodyResponse} that just captures the content length.
* @see #doService
* @see #doHead
*/
@Override
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
} /**
* Delegate POST requests to {@link #processRequest}.
* @see #doService
*/
@Override
protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
这些方法又都调用了 processRequest() 方法,我们来看一下它的代码:
/**
* Process this request, publishing an event regardless of the outcome.
* <p>The actual event handling is performed by the abstract
* {@link #doService} template method.
*/
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null; // 返回与当前线程相关联的 LocaleContext
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
// 根据请求构建 LocaleContext,公开请求的语言环境为当前语言环境
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request); // 返回当前绑定到线程的 RequestAttributes
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
// 根据请求构建ServletRequestAttributes
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes); // 获取当前请求的 WebAsyncManager,如果没有找到则创建
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor()); // 使 LocaleContext 和 requestAttributes 关联
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes); try {
// 由 DispatcherServlet 实现
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
} finally {
// 重置 LocaleContext 和 requestAttributes,解除关联
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager);
// 发布 ServletRequestHandlerEvent 事件
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
DispatcherServlet 的 doService() 方法主要是设置一些 request 属性,并调用 doDispatch() 方法进行请求分发处理,doDispatch() 方法的主要过程是通过 HandlerMapping 获取 Handler,再找到用于执行它的 HandlerAdapter,执行 Handler 后得到 ModelAndView ,ModelAndView 是连接“业务逻辑层”与“视图展示层”的桥梁,接下来就要通过 ModelAndView 获得 View,再通过它的 Model 对 View 进行渲染。doDispatch() 方法如下:
/**
* Process the actual dispatching to the handler.
* <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order.
* The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters
* to find the first that supports the handler class.
* <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers
* themselves to decide which methods are acceptable.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure
*/
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; // 获取当前请求的WebAsyncManager,如果没找到则创建并与请求关联
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null; try {
// 检查是否有 Multipart,有则将请求转换为 Multipart 请求
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // Determine handler for the current request.(遍历所有的 HandlerMapping 找到与请求对应的 Handler,并将其与一堆拦截器封装到 HandlerExecution 对象中。)
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
} // Determine handler adapter for the current request.(遍历所有的 HandlerAdapter,找到可以处理该 Handler 的 HandlerAdapter)
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.(处理 last-modified 请求头)
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
} // 遍历拦截器,执行它们的 preHandle() 方法
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
} // Actually invoke the handler.(执行实际的处理程序)
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
} applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// 遍历拦截器,执行它们的 postHandle() 方法
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
// 处理执行结果,是一个 ModelAndView 或 Exception,然后进行渲染
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
// 遍历拦截器,执行它们的 afterCompletion() 方法
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
Spring MVC工作原理及源码解析(二)DispatcherServlet实现原理及源码解析的更多相关文章
- Spring MVC工作原理及源码解析(三) HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter实现原理及源码解析
1.HandlerMapping实现原理及源码解析 在前面讲解Spring MVC工作流程的时候我们说过,前端控制器收到请求后会调⽤处理器映射器(HandlerMapping),处理器映射器根据请求U ...
- Spring MVC工作原理及源码解析(一) MVC原理介绍、与IOC容器整合原理
MVC原理介绍 Spring MVC原理图 上图是Spring MVC工作原理图(图片来自网上搜索),根据上图,我们可以得知Spring MVC的工作流程如下: 1.用户(客户端,即浏览器)发送请求至 ...
- Spring MVC工作原理(好用版)
Spring MVC工作原理 参考: SpringMVC工作原理 - 平凡希 - 博客园https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoxi/p/6164383.html SpringMVC的 ...
- 浅析Spring MVC工作机制
1.如何使用Spring MVC? 在web.xml中配置一个DispatcherServlet DispatchServlet初始化的时候会去寻找一个在应用程序的WEB-INF目录下的配置文件,命名 ...
- Spring MVC工作原理 及注解说明
SpringMVC框架介绍 1) spring MVC属于SpringFrameWork的后续产品,已经融合在Spring Web Flow里面. Spring 框架提供了构建 Web 应用程序的全功 ...
- spring mvc 工作原理
SpringMVC的工作原理图: SpringMVC流程 1. 用户发送请求至前端控制器DispatcherServlet. 2. DispatcherServlet收到请求调用HandlerMa ...
- 从零开始学spring源码之xml解析(二):默认标签和自定义标签解析
默认标签: 上一篇说到spring的默认标签和自定义标签,发现这里面东西还蛮多的.决定还是拆开来写.今天就来好好聊聊这两块是怎么玩的,首先我们先看看默认标签: private void parseDe ...
- Spring MVC 工作原理和流程、注解
Spring MVC 是实现MVC设计模式的企业级开发框架,是Spring框架的一个子模块,无需整合,开发起来更加便捷. MVC设计模式 MVC是一种设计模式,它将应用程序分为 Controller. ...
- spring mvc 工作流程
Spring Web MVC 处理Http请求的大致过程:一旦Http请求到来,DispatcherSevlet将负责将请求分发.DispatcherServlet可以认为是Spring提供的前端控制 ...
随机推荐
- 混合编程:如何用python11调用C++
摘要:在实际开发过程中,免不了涉及到混合编程,比如,对于python这种脚本语言,性能还是有限的,在一些对性能要求高的情景下面,还是需要使用c/c++来完成. 那怎样做呢?我们能使用pybind11作 ...
- MySQL基础知识:MySQL Connection和Session
在connection的生命里,会一直有一个user thread(以及user thread对应的THD)陪伴它. Connection和Session概念 来自Stackoverflow的一个回答 ...
- TEB 、TIB、PEB--Vista 32
TEB struct TEB typedef struct _TEB { NT_TIB NtTib; PVOID EnvironmentPointer; CLIENT_ID ClientId; PVO ...
- CPython-对象/类型系统
Python中一切皆对象,包括实例对象和类型对象,如整数.浮点数.字符串是实例对象,整数类型.浮点数类型.字符串类型是类型对象. # [Python]>>> n=10 >> ...
- 力扣 - 剑指 Offer 09. 用两个栈实现队列
目录 题目 思路 代码 复杂度分析 题目 剑指 Offer 09. 用两个栈实现队列 思路 刚开始想的是用stack1作为数据存储的地方,stack2用来作为辅助栈,如果添加元素直接push入stac ...
- kubernetes:基于ab的压力测试
基于ab的压力测试 # cat apache-test.yaml ################################################################### ...
- shell的配置文件
1. bash shell 的配置文件 bash shell的配置文件很多,可以分成下面类别 1.1 按生效范围划分两类 全局配置:针对所有用户皆有效 /etc/profile /etc/profil ...
- 基于Hive进行数仓建设的资源元数据信息统计:Spark篇
在数据仓库建设中,元数据管理是非常重要的环节之一.根据Kimball的数据仓库理论,可以将元数据分为这三类: 技术元数据,如表的存储结构结构.文件的路径 业务元数据,如血缘关系.业务的归属 过程元数据 ...
- ICMP主机探测过程
#1from scapy.all import * from random import randint from optparse import OptionParser #2 对用户输入的参数进行 ...
- HarmonyOS三方件开发指南(17)-BottomNavigationBar
目录: 1.引言 2.功能介绍 3.BottomNavigationBar使用指南 4.BottomNavigationBar开发指南 5.<HarmonyOS三方件开发指南>文章合集 引 ...
