图解Leetcode组合总和系列——回溯(剪枝优化)+动态规划
Leetcode组合总和系列——回溯(剪枝优化)+动态规划
组合总和 I
给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
说明:
所有数字(包括 target)都是正整数。
解集不能包含重复的组合。示例 1:
输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7,
所求解集为:
[
[7],
[2,2,3]
]来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum
此题要求解出所有可能的解,则需要用回溯法去回溯尝试求解,我们可以画一棵解空间树:
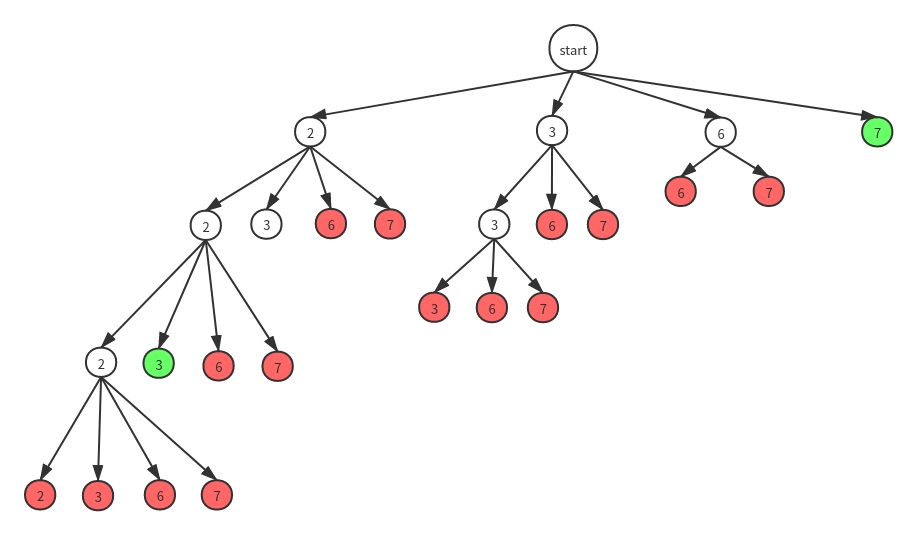
图中绿色节点表示找到了一种可行解,而红色的节点表示到这个节点的时候组合总和的值已经大于target了,无需继续向下尝试,直接返回即可。
因为题目要求解集无重复,即2,2,3和3,2,2应该算作同一种解,所以我们在回溯的时候应该先对candidates数组排序,然后每次只向下回溯大于等于自己的节点。
观察解空间树我们发现:当某一层中第一次出现红色节点或绿色节点后,后面的节点将全变为红色,因为数组是经过排序的,任意节点后面的节点都是大于此节点的(candidates数组无重复元素),所以当出现一个红/绿色节点后,后面的节点不必再继续检查,直接剪枝即可。
剪枝后的解空间树如下:
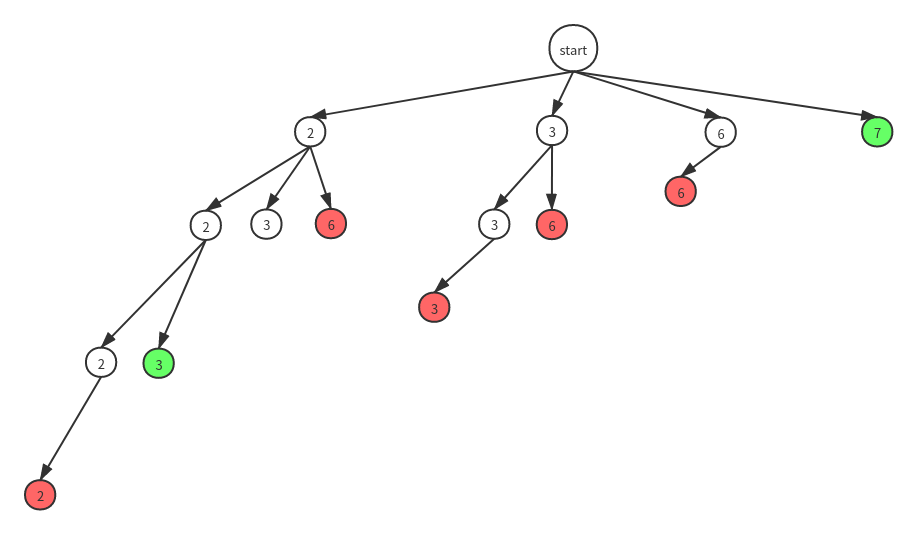
这样看整棵解空间树就小多了,下面直接上代码:
Java版本的回溯解法代码
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
dfs(candidates,target,0,new ArrayList());
return result;
}
public void dfs (int[] candidates, int target, int currSum, List<Integer> res) {
if (currSum == target) {
result.add (new ArrayList(res));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (currSum + candidates[i] > target) {
return;
}
int size = res.size();
if (size==0 || candidates[i] >= res.get(size-1)) {
res.add(candidates[i]);
dfs(candidates, target, currSum+candidates[i],res);
res.remove(size);
}
}
}
}
Go版本的回溯解法代码
func combinationSum(candidates []int, target int) (result [][]int) {
sort.Ints(candidates)
var dfs func(res []int, currSum int)
dfs = func(res []int, currSum int) {
if currSum == target {
result = append(result, append([]int(nil), res...))
return
}
for i := 0; i < len(candidates); i++ {
if currSum + candidates[i] > target {
return
}
if len(res) == 0 || candidates[i] >= res[len(res)-1] {
length := len(res)
res = append(res, candidates[i])
dfs(res, currSum+candidates[i])
res = res[:length]
}
}
}
var res []int
dfs(res, 0)
return
}
组合总和 II
给定一个数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
说明:
所有数字(包括目标数)都是正整数。
解集不能包含重复的组合。示例 1:
输入: candidates = [2,5,2,1,2], target = 5,
所求解集为:
[
[1,2,2],
[5]
]
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum-ii
和组合总和I不同的是这个题目中的candidates数组中出现了重复数字,而且每个数字只能使用一次,我们对这个数组进行排序,每次回溯进下一层的时候都从上一层访问的节点的下一个开始访问。画出的解空间树如下:
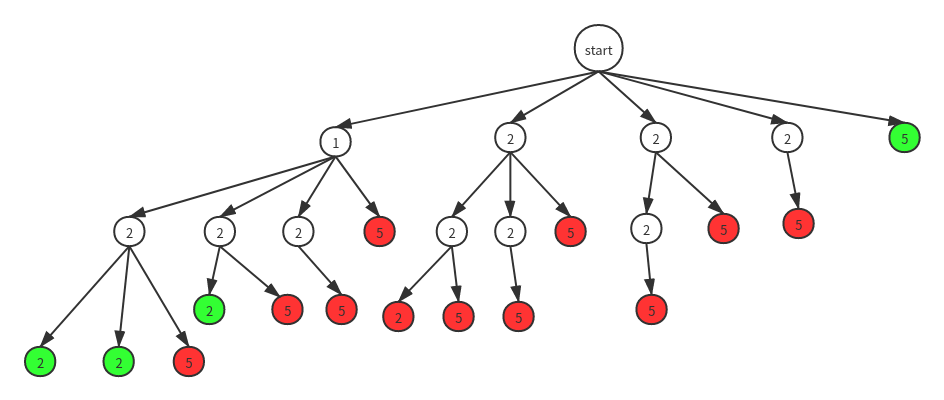
观察解空间树发现还是有重复的解出现,比如1,2,2出现了两次,这种问题我们可以通过两种方法来解决
每次当找到一个可行解后,判断看是否此解已经存在于之前发现的解中了,如果存在就丢弃
剪枝,同一层中同样的节点只能出现一次,这样不但整个解空间树会小很多,而且避免了判断时候的开销,下面是剪枝后的解空间树
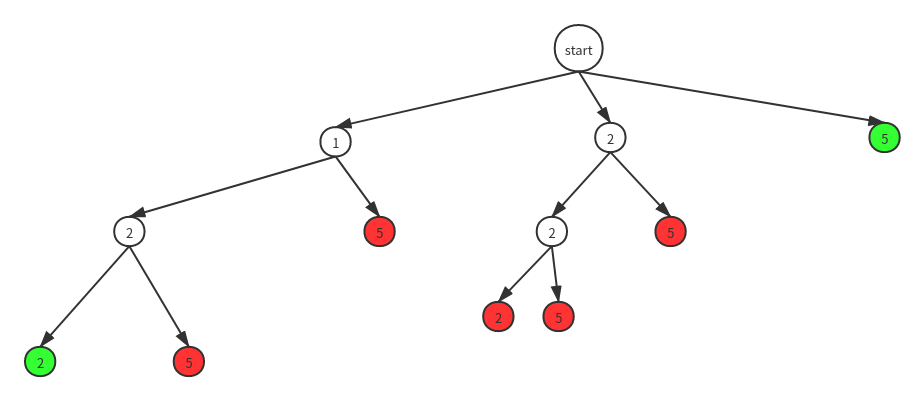
具体剪枝的方法我们可以通过增加一个visit集合,记录同一层是否出现过相同节点,如果出现过就不再次访问此节点。
我对两种解法做了对比,执行的时间效率对比如下:第一种对应上面的结果,第二种解法对应下面的结果
下面贴出第二种解法的代码:
Java版本的回溯解法代码
class Solution {
public static void trace(List<List<Integer>> result, List<Integer> res, int[] candidates, int target, int curr, int index) {
if (curr == target) {
//得到预期目标
result.add(new ArrayList<>(res));
}
Set<Integer> visit = new HashSet<>();
for (int j = index+1; j < candidates.length; j++) {
if (visit.contains(candidates[j])) {
continue;
} else {
visit.add(candidates[j]);
}
if (curr + candidates[j] > target){
//此路不通,后路肯定也不通
break;
} else {
//继续试
res.add(candidates[j]);
int len = res.size();
trace(result, res,candidates,target,curr+candidates[j],j);
res.remove(len-1);
}
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
int curr = 0;
Arrays.sort(candidates);
trace(result, res,candidates,target,curr,-1);
return result;
}
}
Go版本的回溯解法代码
func combinationSum2(candidates []int, target int) (result [][]int) {
sort.Ints(candidates)
var dfs func(res []int, currSum, index int)
dfs = func(res []int, currSum, index int) {
if currSum == target {
result = append(result, append([]int(nil), res...))
return
}
var set []int
for i := index+1; i < len(candidates); i++ {
if isExist(set, candidates[i]) {
continue
} else {
set = append(set, candidates[i])
}
if currSum + candidates[i] > target { //遇到红色节点,直接跳出循环,后面也无需尝试
break
} else {
res = append(res, candidates[i])
dfs(res, currSum+candidates[i], i)
res = res[:len(res)-1]
}
}
}
var res []int
dfs(res, 0, -1)
return
}
func isExist(set []int, x int) bool {
for _, v := range set {
if v == x {
return true
}
}
return false
}
组合总和 III
找出所有相加之和为 n 的 k 个数的组合。组合中只允许含有 1 - 9 的正整数,并且每种组合中不存在重复的数字。
说明:
所有数字都是正整数。
解集不能包含重复的组合。示例 1:
输入: k = 3, n = 7
输出: [[1,2,4]]示例 2:
输入: k = 3, n = 9
输出: [[1,2,6], [1,3,5], [2,3,4]]来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum-iii
此题的candidates数组不再由题目给出,而是由[1,9]区间里的数组成,且每种组合不存在重复的数,则每种数字只能用一次,我们还是继续采用回溯法,不同的是限制了解集中数字的个数。而且每层的回溯都从上一层访问的节点的下一个节点开始。
如果使用暴力法去回溯,将得到下面这样的一棵解空间树(由于树过大,所以右边被省略)
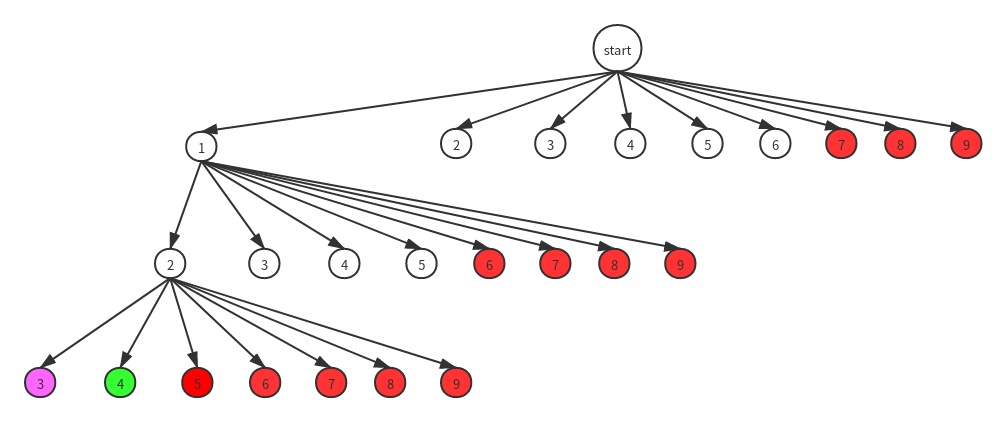
因为题目中规定了树的深度必须是k,红色表示不可能的解,绿色表示可行解,紫色表示到了规定的层数k,但总和小于n的情况。
观察上述的解空间树我们发现了剪枝的方法:
- 对于红色节点之后的节点直接裁剪掉
- 但需要注意紫色的虽然不符合题意,但由于后面可能出现正确解,所以不能剪掉
- 根据树的深度来剪,上面两个题中都没有规定深度,此题还可以根据深度来剪,如果超过规定深度就不继续向下探索
画出剪枝后的解空间树(同样省略了右边的树结构):
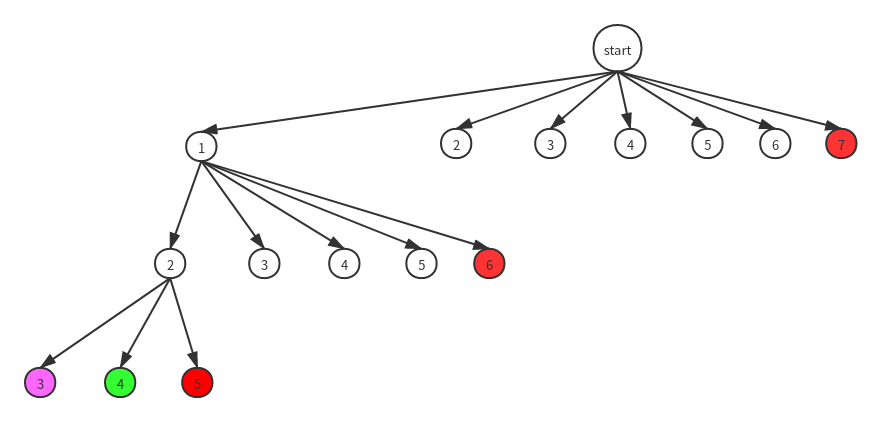
Java版本的回溯解法代码
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
trace(result,res,0,k,n);
return result;
}
public void trace (List<List<Integer>> result, List<Integer> res, int curr, int k, int n) {
if (res.size() == k && curr == n) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(res));
return;
} else if (res.size() < k && curr < n) {
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
int len = res.size();
if (len == 0 || i > res.get(len - 1)) {
res.add(i);
trace(result,res,curr+i,k,n);
res.remove(len);
}
}
} else { //树的深度已经大于规定的k
return;
}
}
}
Go版本的回溯解法代码
func combinationSum3(k int, n int) (result [][]int) {
var dfs func(res []int, currSum int)
dfs = func(res []int, currSum int) {
if len(res) == k && currSum == n {
result = append(result, append([]int(nil), res...))
return
} else if len(res) < k && currSum < n {
i := 1
if len(res) > 0 {
i = res[len(res)-1]+1
}
for ; i < 10; i++ {
res = append(res, i)
dfs(res, currSum+i)
res = res[:len(res)-1]
}
} else { //搜索的深度已经超过了k
return
}
}
var res []int
dfs(res, 0)
return
}
组合总和 IV
给你一个由 不同 整数组成的数组 nums ,和一个目标整数 target 。请你从 nums 中找出并返回总和为 target 的元素组合的个数。
题目数据保证答案符合 32 位整数范围。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3], target = 4
输出:7
解释:
所有可能的组合为:
(1, 1, 1, 1)
(1, 1, 2)
(1, 2, 1)
(1, 3)
(2, 1, 1)
(2, 2)
(3, 1)
请注意,顺序不同的序列被视作不同的组合。示例 2:
输入:nums = [9], target = 3
输出:0来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum-iv
这个道题目并没有像上面一样要求我们找出所有的解集,而是只要求解解的个数,这时如果我们再采用回溯法去求解无疑是造成了很大的浪费,所以考虑使用动态规划,只求解个数而不关注所有解的具体内容。
题目允许数字的重复,且对顺序敏感(即不同顺序视做不同解),这样我们可以通过让每一个nums数组中数num做解集的最后一个数,这样当x作为解集的最后一个数,解集就为num1,num2,num3......x
如果dp数组的dp[x]表示target为x时候的解集个数,那么我们只需要最后求解dp[target]即可。
那么当最后一个数为x时对应的解集个数就为dp[target-x]个,让nums中的每一个数做一次最后一个数,将结果相加就是dp[target]的值,不过需要注意的是dp[0] = 1表示target为0时只有一种解法(即一个数都不要),dp的下标必须为非负数。
下面是状态转移方程(n为nums最后一个元素的下标):
\begin{cases}
1& \text{i=0}\\
\sum_{j=0}^n\ dp[target-nums[j]& \text{i!=0 && target-nums[j] > 0}
\end{cases}
\]
Java版本的动态规划解法代码
class Solution {
public int combinationSum4(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] dp = new int[target+1];
dp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= target; i++) {
for (int num:nums) {
int tmp = i - num;
if (tmp >= 0) {
dp[i] += dp[tmp];
}
}
}
return dp[target];
}
}
Go版本的动态规划解法代码
func combinationSum4(nums []int, target int) int {
dp := make([]int, target+1)
dp[0] = 1
for i := 1; i <= target; i++ {
for _, v := range nums {
tmp := i - v
if tmp >= 0 {
dp[i] += dp[tmp]
}
}
}
return dp[target]
}
图解Leetcode组合总和系列——回溯(剪枝优化)+动态规划的更多相关文章
- Leetcode题目39.组合总和(回溯+剪枝-中等)
题目描述: 给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合. candidates 中的数字可以无 ...
- 34,Leetcode 组合总和I,II -C++ 回溯法
I 题目描述 给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合.candidates 中的数字可以无 ...
- leetcode组合总和 Ⅳ 解题路径
题目: 关于动态规划类题目的思路如何找在上一篇博客 https://www.cnblogs.com/niuyourou/p/11964842.html 讲的非常清楚了,该博客也成为了了leetcode ...
- LeetCode 组合总和(dfs)
题目 给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合. candidates 中的数字可以无限制重 ...
- 40. 组合总和 II + 递归 + 回溯 + 记录路径
40. 组合总和 II LeetCode_40 题目描述 题解分析 此题和 39. 组合总和 + 递归 + 回溯 + 存储路径很像,只不过题目修改了一下. 题解的关键是首先将候选数组进行排序,然后记录 ...
- Leetcode之回溯法专题-216. 组合总和 III(Combination Sum III)
Leetcode之回溯法专题-216. 组合总和 III(Combination Sum III) 同类题目: Leetcode之回溯法专题-39. 组合总数(Combination Sum) Lee ...
- Leetcode之回溯法专题-40. 组合总和 II(Combination Sum II)
Leetcode之回溯法专题-40. 组合总和 II(Combination Sum II) 给定一个数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使 ...
- LeetCode刷题笔记-回溯法-组合总和问题
题目描述: <组合总和问题>给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合. cand ...
- [leetcode] 39. 组合总和(Java)(dfs、递归、回溯)
39. 组合总和 直接暴力思路,用dfs+回溯枚举所有可能组合情况.难点在于每个数可取无数次. 我的枚举思路是: 外层枚举答案数组的长度,即枚举解中的数字个数,从1个开始,到target/ min(c ...
随机推荐
- Django框架的forms组件与一些补充
目录 一.多对多的三种创建方式 1. 全自动 2. 纯手撸(了解) 3. 半自动(强烈推荐) 二.forms组件 1. 如何使用forms组件 2. 使用forms组件校验数据 3. 使用forms组 ...
- PVE连接Wi-Fi
连接wifi参考文章: https://lzxz1234.cn/archives/417 services看不全信息 connmanctl> services 之后信息太多,看不到上面的怎么办? ...
- Azure Functions(三)集成 Azure Queue Storage 存储消息
一,引言 接着上一篇文章继续介绍 Azure Functions,今天我们将尝试绑定 Queue Storage,将消息存储到 Queue 中,并且学会适用于 Azure Functions 的 Az ...
- C#类中的成员
@ 目录 字段 属性 方法 构造函数 类和对象的简单解释 创建类和对象 类中成员的归属问题 字段 字段的声明与声明变量类似,可以添加访问修饰符,通常情况下字段设置为私有的,然后定义属性对字段的读写进行 ...
- 浅谈Dotnet的数据定位和匹配
Dotnet里,数据定位和匹配的相关编程现在变得很舒服. 最近项目紧,还要不停出差. 所以,写个短点的.最近经常用到的内容:数据定位和匹配. 数据定位 假设我们有这样一个数组: var arr ...
- MySQL入门(2)——存储引擎
MySQL入门(2)--存储引擎 查询MySQL支持的存储引擎 查询全部支持的引擎: show engines; ";"可以使用"\g"等价替换,而使用&quo ...
- 20个最有用的Python数据科学库
核心库与统计 1. NumPy(提交:17911,贡献者:641) 一般我们会将科学领域的库作为清单打头,NumPy 是该领域的主要软件库之一.它旨在处理大型的多维数组和矩阵,并提供了很多高级的数学函 ...
- 前端学习 node 快速入门 系列 —— 服务端渲染
其他章节请看: 前端学习 node 快速入门 系列 服务端渲染 在简易版 Apache一文中,我们用 node 做了一个简单的服务器,能提供静态资源访问的能力. 对于真正的网站,页面中的数据应该来自服 ...
- Get和Post区别(转载)
转载自:https://www.cnblogs.com/logsharing/p/8448446.html GET和POST是HTTP请求的两种基本方法,要说它们的区别,接触过WEB开发的人都能说出一 ...
- 文本相似性计算--MinHash和LSH算法
给定N个集合,从中找到相似的集合对,如何实现呢?直观的方法是比较任意两个集合.那么可以十分精确的找到每一对相似的集合,但是时间复杂度是O(n2).此外,假如,N个集合中只有少数几对集合相似,绝大多数集 ...
