rabbitmq五种模式详解(含实现代码)
一、五种模式详解
1.简单模式(Queue模式)
当生产端发送消息到交换机,交换机根据消息属性发送到队列,消费者监听绑定队列实现消息的接收和消费逻辑编写.简单模式下,强调的一个队列queue只被一个消费者监听消费.
1.1 结构

- 生产者:生成消息,发送到交换机
- 交换机:根据消息属性,将消息发送给队列
- 消费者:监听这个队列,发现消息后,获取消息执行消费逻辑
1.2应用场景
常见的应用场景就是一发,一接的结构
例如:
- 手机短信
- 邮件单发
2.争抢模式(Work模式)
强调的也是后端队列与消费者绑定的结构
2.1结构

- 生产者:发送消息到交换机
- 交换机:根据消息属性将消息发送给队列
- 消费者:多个消费者,同时绑定监听一个队列,之间形成了争抢消息的效果
2.2应用场景
- 抢红包
- 资源分配系统
3.路由模式(Route模式 Direct定向)
从路由模式开始,关心的就是消息如何到达的队列,路由模式需要使用的交换机类型就是路由交换机(direct)
3.1 结构

- 生产端:发送消息,在消息中处理消息内容,携带一个routingkey
- 交换机:接收消息,根据消息的routingkey去计算匹配后端队列的routingkey
- 队列:存储交换机发送的消息
- 消费端:简单模式 工作争抢
3.2应用场景
- 短信
- 聊天工具
- 邮箱。。
手机号/邮箱地址,都可以是路由key
4.发布订阅模式(Pulish/Subscribe模式 Fanout广播)
不计算路由的一种特殊交换机
4.1结构

4.2应用场景
- 消息推送
- 广告
5.主题模式(Topics模式 Tpoic通配符)
路由key值是一种多级路径。中国.四川.成都.武侯区
5.1结构

生产端:携带路由key,发送消息到交换机
队列:绑定交换机和路由不一样,不是一个具体的路由key,而可以使用*和#代替一个范围
| * | 字符串,只能表示一级 |
| --- | --- |
| # | 多级字符串 |交换机:根据匹配规则,将路由key对应发送到队列
消息路由key:
- 北京市.朝阳区.酒仙桥
- 北京市.#: 匹配true
- 上海市.浦东区.*: 没匹配false
- 新疆.乌鲁木齐.#
5.2 应用场景
- 做物流分拣的多级传递.
6.完整结构

二、代码实现
1.创建SpringBoot工程
1.1 工程基本信息

1.2 依赖信息

1.3 配置文件applicasion.properties
# 应用名称
spring.application.name=springboot-demo
# Actuator Web 访问端口
management.server.port=8801
management.endpoints.jmx.exposure.include=*
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
management.endpoint.health.show-details=always
# 应用服务 WEB 访问端口
server.port=8801
######################### RabbitMQ配置 ########################
# RabbitMQ主机
spring.rabbitmq.host=127.0.0.1
# RabbitMQ虚拟主机
spring.rabbitmq.virtual-host=demo
# RabbitMQ服务端口
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
# RabbitMQ服务用户名
spring.rabbitmq.username=admin
# RabbitMQ服务密码
spring.rabbitmq.password=admin
# RabbitMQ服务发布确认属性配置
## NONE值是禁用发布确认模式,是默认值
## CORRELATED值是发布消息成功到交换器后会触发回调方法
## SIMPLE值经测试有两种效果,其一效果和CORRELATED值一样会触发回调方法,其二在发布消息成功后使用rabbitTemplate调用waitForConfirms或waitForConfirmsOrDie方法等待broker节点返回发送结果,根据返回结果来判定下一步的逻辑,要注意的点是waitForConfirmsOrDie方法如果返回false则会关闭channel,则接下来无法发送消息到broker;
spring.rabbitmq.publisher-confirm-type=simple
# RabbitMQ服务开启消息发送确认
spring.rabbitmq.publisher-returns=true
######################### simple模式配置 ########################
# RabbitMQ服务 消息接收确认模式
## NONE:不确认
## AUTO:自动确认
## MANUAL:手动确认
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.acknowledge-mode=manual
# 指定最小的消费者数量
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.concurrency=1
# 指定最大的消费者数量
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.max-concurrency=1
# 开启支持重试
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.retry.enabled=true
2.简单模式
2.1 创建SimpleQueueConfig 简单队列配置类
package com.gmtgo.demo.simple;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Configuration
public class SimpleQueueConfig {
/**
* 定义简单队列名.
*/
private final String simpleQueue = "queue_simple";
@Bean
public Queue simpleQueue() {
return new Queue(simpleQueue);
}
}
2.2 编写生产者
package com.gmtgo.demo.simple;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class SimpleProducer {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sendMessage() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
String message = "简单消息" + i;
log.info("我是生产信息:{}", message);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend( "queue_simple", message);
}
}
}
2.3 编写消费者
package com.gmtgo.demo.simple;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class SimpleConsumers {
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue_simple")
public void readMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
log.info("我是消费信息:{}", new String(message.getBody()));
}
}
2.4 编写访问类
package com.gmtgo.demo.simple;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/rabbitMq")
public class SimpleRabbitMqController {
@Autowired
private SimpleProducer simpleProducer;
@RequestMapping(value = "/simpleQueueTest")
public String simpleQueueTest() {
simpleProducer.sendMessage();
return "success";
}
}
2.5 测试启动项目访问 simpleQueueTest

3.Work队列
3.1 编写工作配置
package com.gmtgo.demo.work;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Configuration
public class WorkQueueConfig {
/**
* 队列名.
*/
private final String work = "work_queue";
@Bean
public Queue workQueue() {
return new Queue(work);
}
}
3.2 编写生产者
package com.gmtgo.demo.work;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class WorkProducer {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sendMessage() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
String message = "工作消息" + i;
log.info("我是生产信息:{}", message);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("work_queue", message);
}
}
}
3.3 编写消费者1
package com.gmtgo.demo.work;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class WorkConsumers1 {
@RabbitListener(queues = "work_queue")
public void readMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
log.info("我是消费信息1:{}", new String(message.getBody()));
}
}
3.4 编写消费者2
package com.gmtgo.demo.work;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class WorkConsumers2 {
@RabbitListener(queues = "work_queue")
public void readMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
log.info("我是消费信息2:{}", new String(message.getBody()));
}
}
3.5 编写测试方法
package com.gmtgo.demo.work;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "rabbitMq")
public class WorkRabbitMqController {
@Autowired
private WorkProducer workProducer;
@RequestMapping(value = "workQueueTest")
public String workQueueTest() {
workProducer.sendMessage();
return "success";
}
}
3.6 测试启动项目访问 workQueueTest

控制台打印,发现10条消息 偶数条消费者1获取,奇数条消费者2获取,并且平均分配。
当然通过代码实现按需分配,即谁的性能强,谁优先原则,实现负载均衡。
配置可控分配数
4. 发布订阅模式(Publish/Subscibe模式)
订阅模式–多个消费者监听不同的队列,但队列都绑定同一个交换机
4.1 编写订阅配置类
package com.gmtgo.demo.fanout;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Configuration
public class FanoutQueueConfig {
/**
* 声明队列名.
*/
private final String fanout1 = "fanout_queue_1";
private final String fanout2 = "fanout_queue_2";
/**
* 声明交换机的名字.
*/
private final String fanoutExchange = "fanoutExchange";
/**
* 声明队列.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueue1() {
return new Queue(fanout1);
}
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueue2() {
return new Queue(fanout2);
}
/**
* 声明交换机.
*/
@Bean
public FanoutExchange exchange() {
return new FanoutExchange(fanoutExchange);
}
/**
* 队列绑定交换机,也可在可视化工具中进行绑定.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Binding bindingFanoutQueue1(Queue fanoutQueue1, FanoutExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue1).to(exchange);
}
@Bean
public Binding bindingFanoutQueue2(Queue fanoutQueue2, FanoutExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue2).to(exchange);
}
}
4.2 编写订阅生产者
package com.gmtgo.demo.fanout;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class FanoutProducer {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sendMessage() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
String message = "订阅模式消息" + i;
log.info("我是生产信息:{}", message);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("fanoutExchange", "", message);
}
}
}
4.3 编写订阅消费者1
package com.gmtgo.demo.fanout;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class FanoutConsumers1 {
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout_queue_1")
public void readMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
log.info("我是消费信息1:{}", new String(message.getBody()));
}
}
4.4 编写订阅消费者2
package com.gmtgo.demo.fanout;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class FanoutConsumers2 {
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout_queue_2")
public void readMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
log.info("我是消费信息2:{}", new String(message.getBody()));
}
}
4.5 编写测试方法
package com.gmtgo.demo.fanout;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "rabbitMq")
public class FanoutRabbitMqController {
@Autowired
private FanoutProducer fanoutProducer;
@RequestMapping(value = "fanoutQueueTest")
public String fanoutQueueTest() {
fanoutProducer.sendMessage();
return "success";
}
}
3.6 测试启动项目访问 fanoutQueueTest

控制台打印 ,发现两个绑定了不同队列的消费者都接受到了同一条消息查看RabbitMq 服务器:



5. 路由模式(Route模式 Direct定向)
5.1 编写路由配置类
package com.gmtgo.demo.direct;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Configuration
public class DirectQueueConfig {
/**
* 声明队列名.
*/
private final String direct1 = "direct_queue_1";
private final String direct2 = "direct_queue_2";
/**
* 声明交换机的名字.
*/
private final String directExchange = "directExchange";
/**
* 声明队列.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Queue directQueue1() {
return new Queue(direct1);
}
@Bean
public Queue directQueue2() {
return new Queue(direct2);
}
/**
* 声明路由交换机.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public DirectExchange directExchange() {
return new DirectExchange(directExchange);
}
/**
* 队列绑定交换机,指定routingKey,也可在可视化工具中进行绑定.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
Binding bindingDirectExchange1(Queue directQueue1, DirectExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue1).to(exchange).with("update");
}
/**
* 队列绑定交换机,指定routingKey,也可在可视化工具中进行绑定.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
Binding bindingDirectExchange2(Queue directQueue2, DirectExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue2).to(exchange).with("add");
}
}
5.2 编写生产者
package com.gmtgo.demo.direct;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class DirectProducer {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sendMessageA() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
String message = "路由模式--routingKey=update消息" + i;
log.info("我是生产信息:{}", message);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("directExchange", "update", message);
}
}
public void sendMessageB() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
String message = "路由模式--routingKey=add消息" + i;
log.info("我是生产信息:{}", message);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("directExchange", "add", message);
}
}
}
5.3 编写消费者1
package com.gmtgo.demo.direct;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class DirectConsumers1 {
@RabbitListener(queues = "direct_queue_1")
public void readMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
log.info("我是消费信息1:{}", new String(message.getBody()));
}
}
5.4 编写消费者2
package com.gmtgo.demo.direct;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class DirectConsumers2 {
@RabbitListener(queues = "direct_queue_2")
public void readMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
log.info("我是消费信息2:{}", new String(message.getBody()));
}
}
5.5 编写访问类
package com.gmtgo.demo.direct;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "rabbitMq")
public class DirectRabbitMqController {
@Autowired
private DirectProducer directProducer;
@RequestMapping(value = "directQueueTest1")
public String directQueueTest1() {
directProducer.sendMessageA();
return "success";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "directQueueTest2")
public String directQueueTest2() {
directProducer.sendMessageB();
return "success";
}
}
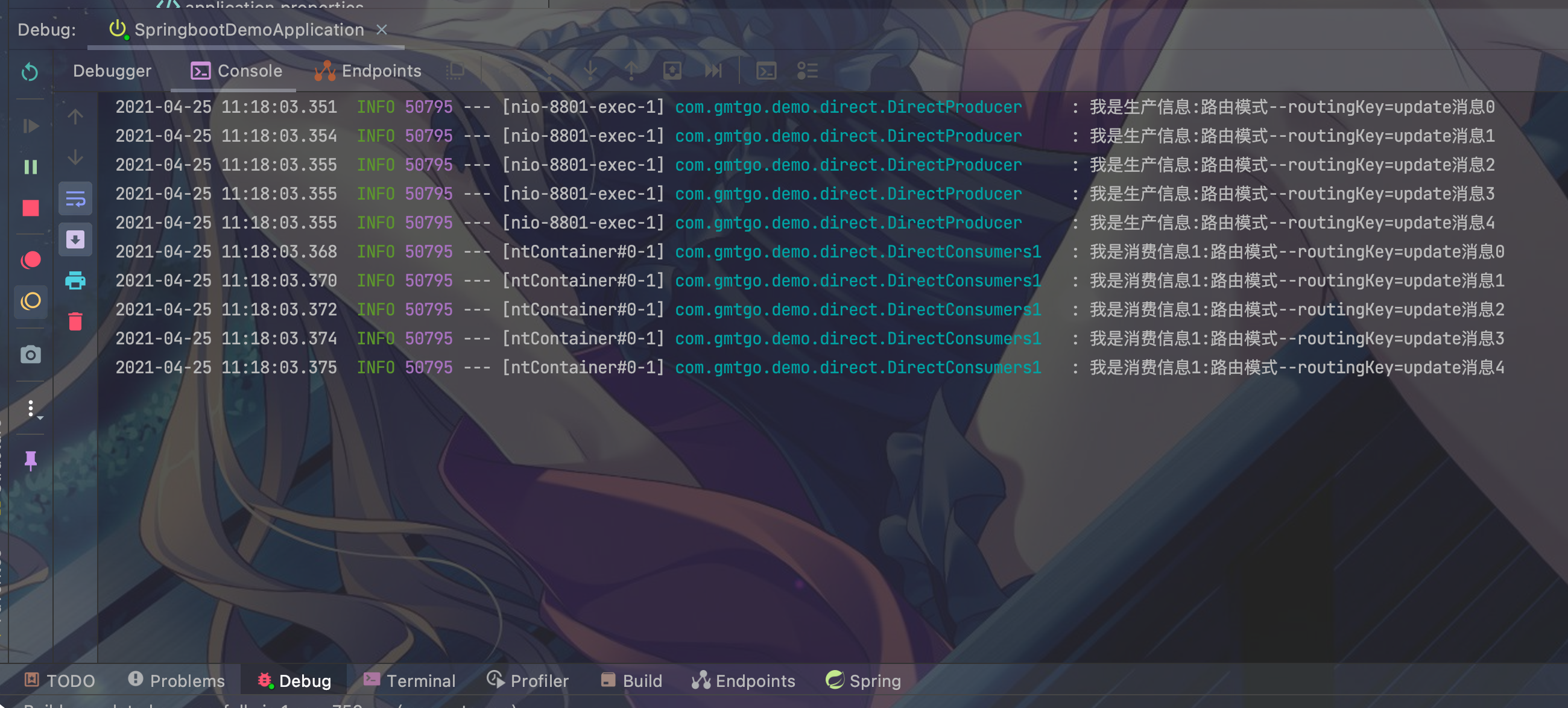
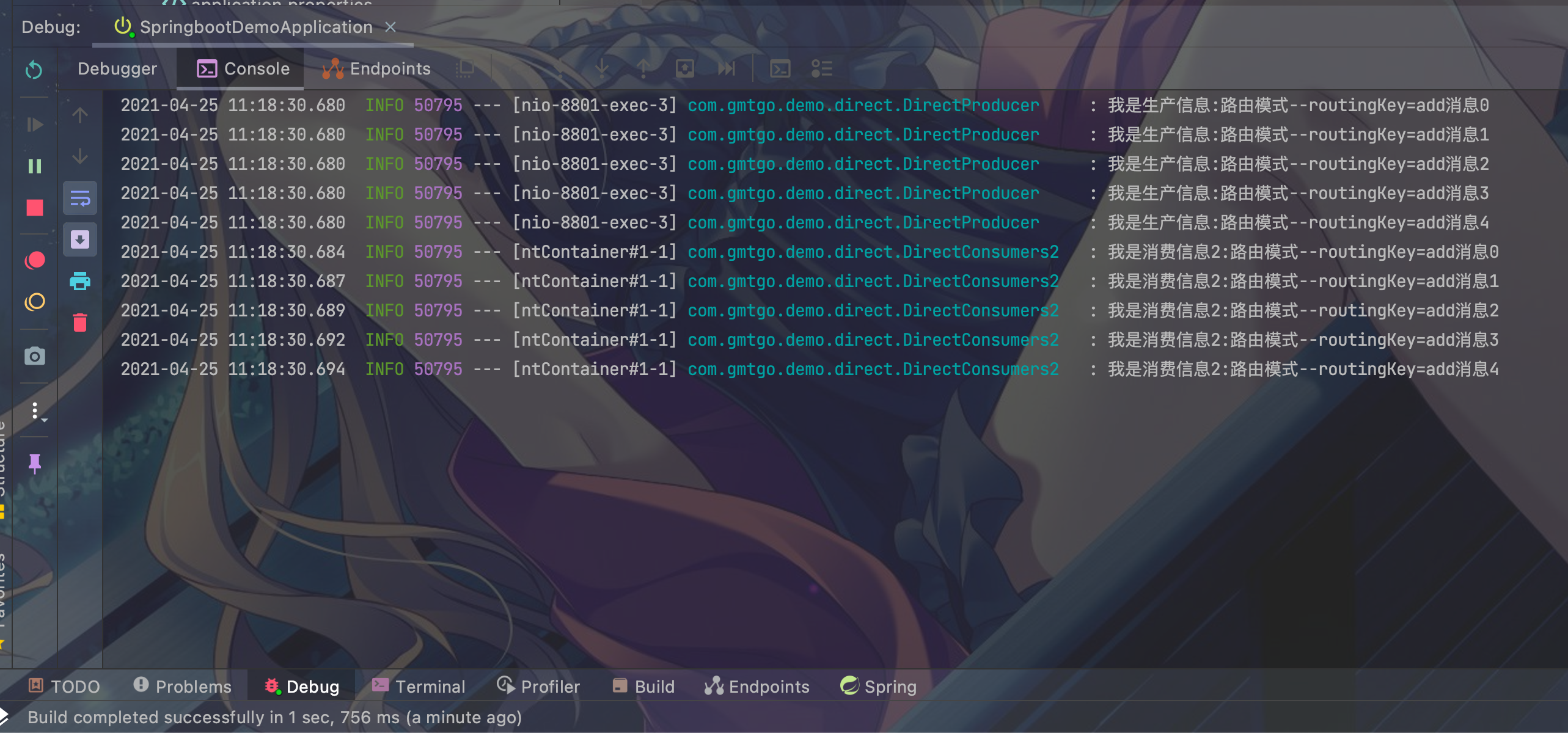
5.6 测试启动项目访问directQueueTest1 , directQueueTest2
- 访问地址http://127.0.0.1:8801/rabbitMq/directQueueTest1
- 访问地址http://127.0.0.1:8801/rabbitMq/directQueueTest2
- 结果:
- directQueueTest1:
- directQueueTest2:
- directQueueTest1:
6. 主题模式(Topics模式 Tpoic通配符)
6.1 编写路由配置类
package com.gmtgo.demo.topic;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Configuration
public class TopicQueueConfig {
/**
* 声明队列名.
*/
private final String topic1 = "topic_queue_1";
private final String topic2 = "topic_queue_2";
/**
* 声明交换机的名字.
*/
private final String topicExchange = "topicExchange";
/**
* 声明队列.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue1() {
return new Queue(topic1);
}
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue2() {
return new Queue(topic2);
}
/**
* 声明路由交换机.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public TopicExchange topicExchange() {
return new TopicExchange(topicExchange);
}
/**
* 队列绑定交换机,指定routingKey,也可在可视化工具中进行绑定.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
Binding bindingTopicExchange1(Queue topicQueue1, TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue1).to(exchange).with("topic.keyA");
}
/**
* 队列绑定交换机,指定routingKey,也可在可视化工具中进行绑定.
* 绑定的routing key 也可以使用通配符:
* *:匹配不多不少一个词
* #:匹配一个或多个词
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
Binding bindingTopicExchange2(Queue topicQueue2, TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue2).to(exchange).with("topic.#");
}
}
6.2 编写生产者
package com.gmtgo.demo.topic;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class TopicProducer {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sendMessageA() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
String message = "通配符模式--routingKey=topic.keyA消息" + i;
log.info("我是生产信息:{}", message);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("topicExchange", "topic.keyA", message);
}
}
public void sendMessageB() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
String message = "通配符模式--routingKey=topic.#消息" + i;
log.info("我是生产信息:{}", message);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("topicExchange", "topic.keyD.keyE", message);
}
}
}
6.3 编写消费者1
package com.gmtgo.demo.topic;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class TopicConsumers1 {
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic_queue_1")
public void readMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
log.info("我是消费信息1:{}",new String(message.getBody()));
}
}
6.4 编写消费者2
package com.gmtgo.demo.topic;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class TopicConsumers2 {
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic_queue_2")
public void readMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
log.info("我是消费信息2:{}",new String(message.getBody()));
}
}
6.5 编写访问类
package com.gmtgo.demo.topic;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "rabbitMq")
public class TopicRabbitMqController {
@Autowired
private TopicProducer topicProducer;
@RequestMapping(value = "topicQueueTest1")
public String topicQueueTest1() {
topicProducer.sendMessageA();
return "success";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "topicQueueTest2")
public String topicQueueTest2() {
topicProducer.sendMessageB();
return "success";
}
}
6.6 测试启动项目访问topicQueueTest1 , topicQueueTest2
- 访问地址http://127.0.0.1:8801/rabbitMq/topicQueueTest1
- 访问地址http://127.0.0.1:8801/rabbitMq/topicQueueTest2
- 结果:
- topicQueueTest1,两个消费者都能消费
- topicQueueTest2,只有消费者2 可以消费

- topicQueueTest1,两个消费者都能消费
至此,五种队列的实现已结束!
7. 实现生产者消息确认
7.1 配置文件
######################### RabbitMQ配置 ########################
# RabbitMQ主机
spring.rabbitmq.host=127.0.0.1
# RabbitMQ虚拟主机
spring.rabbitmq.virtual-host=demo
# RabbitMQ服务端口
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
# RabbitMQ服务用户名
spring.rabbitmq.username=admin
# RabbitMQ服务密码
spring.rabbitmq.password=admin
# RabbitMQ服务发布确认属性配置
## NONE值是禁用发布确认模式,是默认值
## CORRELATED值是发布消息成功到交换器后会触发回调方法
## SIMPLE值经测试有两种效果,其一效果和CORRELATED值一样会触发回调方法,其二在发布消息成功后使用rabbitTemplate调用waitForConfirms或waitForConfirmsOrDie方法等待broker节点返回发送结果,根据返回结果来判定下一步的逻辑,要注意的点是waitForConfirmsOrDie方法如果返回false则会关闭channel,则接下来无法发送消息到broker;
spring.rabbitmq.publisher-confirm-type=simple
# 连接超时时间
spring.rabbitmq.connection-timeout=20000
# RabbitMQ服务开启消息发送确认
spring.rabbitmq.publisher-returns=true
######################### simple模式配置 ########################
# RabbitMQ服务 消息接收确认模式
## NONE:不确认
## AUTO:自动确认
## MANUAL:手动确认
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.acknowledge-mode=manual
# 指定最小的消费者数量
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.concurrency=1
# 指定最大的消费者数量
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.max-concurrency=1
# 每次只消费一个消息
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.prefetch=1
# 开启支持重试
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.retry.enabled=true
# 启用强制信息,默认为false
spring.rabbitmq.template.mandatory=true
7.2 编写消息发送确认类 RabbitConfirmCallback
package com.gmtgo.demo.config;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.CorrelationData;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
public class RabbitConfirmCallback implements RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback {
@Override
public void confirm(CorrelationData correlationData, boolean ack, String cause) {
log.info("=======ConfirmCallback=========");
log.info("correlationData {} " , correlationData);
log.info("ack = {}" , ack);
log.info("cause = {}" , cause);
log.info("=======ConfirmCallback=========");
}
}
7.3 编写消息发送交换机返回机制RabbitConfirmReturnCallBack
package com.gmtgo.demo.config;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Slf4j
public class RabbitConfirmReturnCallBack implements RabbitTemplate.ReturnCallback {
@Override
public void returnedMessage(Message message, int replyCode, String replyText, String exchange, String routingKey) {
log.info("--------------ReturnCallback----------------");
log.info("message = " + message);
log.info("replyCode = {}", replyCode);
log.info("replyText = {}", replyText);
log.info("exchange = {}", exchange);
log.info("routingKey = {}", routingKey);
log.info("--------------ReturnCallback----------------");
}
}
7.4 RabbitMQ配置
在我们的rabbit队列配置类里设置RabbitTemplate
举例:
package com.gmtgo.demo.topic;
import com.gmtgo.demo.config.RabbitConfirmCallback;
import com.gmtgo.demo.config.RabbitConfirmReturnCallBack;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.TopicExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
/**
* @author 大帅
*/
@Configuration
public class TopicQueueConfig {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@PostConstruct
public void initRabbitTemplate() {
// 设置生产者消息确认
rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback(new RabbitConfirmCallback());
rabbitTemplate.setReturnCallback(new RabbitConfirmReturnCallBack());
}
/**
* 声明队列名.
*/
private final String topic1 = "topic_queue_1";
private final String topic2 = "topic_queue_2";
/**
* 声明交换机的名字.
*/
private final String topicExchange = "topicExchange";
/**
* 声明队列.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue1() {
return new Queue(topic1);
}
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue2() {
return new Queue(topic2);
}
/**
* 声明路由交换机.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public TopicExchange topicExchange() {
return new TopicExchange(topicExchange);
}
/**
* 队列绑定交换机,指定routingKey,也可在可视化工具中进行绑定.
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
Binding bindingTopicExchange1(Queue topicQueue1, TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue1).to(exchange).with("topic.keyA");
}
/**
* 队列绑定交换机,指定routingKey,也可在可视化工具中进行绑定.
* 绑定的routing key 也可以使用通配符:
* *:匹配不多不少一个词
* #:匹配一个或多个词
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
Binding bindingTopicExchange2(Queue topicQueue2, TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue2).to(exchange).with("topic.#");
}
}
启动项目发送消息,消息被正常消费,confim回调返回ack=true如果我们将exchange修改,发送到一个不存在的exchange中,会怎么样呢?
会发现confirm回调为false,打印出结果为不存在topicExchange1111的交换机

如果我们在消费端处理逻辑时出错会怎么样呢?修改消费端代码我们在消费时让它报错

confirm回调为true,但是在rabbitmq的web界面会发现存在5条没有消费的消息

如果我们把
channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(),false,false);
中最后一个参数改为false呢,会发现在web管理界面没有未被消费的消息,说明这条消息已经被摒弃。
实际开发中,到底是打回到队列呢还是摒弃,要看自己的需求,但是打回队列应该有次数限制,不然会陷入死循环。
继续测试,将routingKey修改为一个没有的key,
7.5 结论
- 如果消息没有到exchange,则confirm回调,ack=false
- 如果消息到达exchange,则confirm回调,ack=true
- exchange到queue成功,则不回调return
- exchange到queue失败,则回调return
8. 项目示例代码:
下载地址:springboot-rabbitmq-demo_1619322789961
rabbitmq五种模式详解(含实现代码)的更多相关文章
- redis 五种数据结构详解(string,list,set,zset,hash)
redis 五种数据结构详解(string,list,set,zset,hash) Redis不仅仅支持简单的key-value类型的数据,同时还提供list,set,zset,hash等数据结构的存 ...
- 【Redis】redis 五种数据结构详解(string,list,set,zset,hash)
redis 五种数据结构详解(string,list,set,zset,hash) Redis不仅仅支持简单的key-value类型的数据,同时还提供list,set,zset,hash等数据结构的存 ...
- redis 五种数据结构详解(string,list,set,zset,hash),各种问题综合
redis 五种数据结构详解(string,list,set,zset,hash) https://www.cnblogs.com/sdgf/p/6244937.html redis 与 spring ...
- 分布式事务 Seata Saga 模式首秀以及三种模式详解 | Meetup#3 回顾
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/67NvEVljnU-0-6rb7MWpGw 分布式事务 Seata Saga 模式首秀以及三种模式详解 | Meetup#3 回顾 原创 蚂蚁金 ...
- Android特效 五种Toast详解
Toast是Android中用来显示显示信息的一种机制,和Dialog不一样的是,Toast是没有焦点的,而且Toast显示的时间有限,过一定的时间就会自动消失.而且Toast主要用于向用户显示提示消 ...
- 转 XMLHttpRequest().readyState的五种状态详解
转 http://javathinker.blog.ccidnet.com/blog-htm-itemid-1262479-do-showone-type-blog-uid-36384.html 在& ...
- Odoo中的五种Action详解
转载请注明原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/ygj0930/p/10826232.html Odoo中的五种action都是继承自ir.actions.actions模型实现的 ...
- Redis 五种数据结构详解(string,hash,list,set,zset)
一.五种数据结构: 1. String--字符串 String 数据结构是简单的 key-value 类型,value 不仅可以是 String,也可以是数字(当数字类型用 Long 可以表示的时候e ...
- angular五种服务详解
在这之前angular学习笔记(十五)-module里的'服务'这篇文章里,已经大致讲解了ng中的'服务',在之后的很多地方也用到了服务,但是,所有的服务都是使用app.factory来创建的.但其实 ...
随机推荐
- Docker搭建Hadoop环境
文章目录 Docker搭建Hadoop环境 Docker的安装与使用 拉取镜像 克隆配置脚本 创建网桥 执行脚本 Docker命令补充 更换镜像源 安装vim 启动Hadoop 测试Word Coun ...
- 绿色城市之地下综合管廊3D可视化平台
前言 现阶段,我国绿色城市建设发展正在热火朝天的进行,面对迅速城镇化建设导致的城市病,需要不断寻求足以丰富城市的资源,以此实现城市绿色化智能化发展,比如改造地下管廊.路灯等城市基础设施. 地下综合管廊 ...
- 学习了解使用docker
学习了解使用docker docker是项目开发部署相关工具容器,本文通过官网等资料阅读学习,简单介绍一些基本使用操作: docker是什么 2.docker安装使用 连接进入docker容器 doc ...
- “蚂蚁牙黑”太火,想玩就用ModelArts做一个!
摘要:本文将介绍如何借力一站式 AI 开发平台,"傻瓜式"操作实现生成"蚂蚁牙黑"小视频. 作者:华为云EI专家胡琦 一夜之间,朋友圈都在"蚂蚁牙黑& ...
- MySQL深入研究--学习总结(2)
前言 接上文,继续学习后续章节. 第四章&第五章<深入浅出索引> 这两章节主要介绍的索引结构及其如何合理建立索引,但是我觉得讲的比较简单. 总结回顾下吧,其实在我之前的文章< ...
- 剑指 Offer 32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II + 层次遍历二叉树 + 按层存储
剑指 Offer 32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II Offer_32 题目描述: 题解分析: 这道题我一开始想到的解决方法较粗暴,就是使用两个变量来记录当前层的节点数和下一层的结点数. 以上 ...
- 剑指 Offer 26. 树的子结构
剑指 Offer 26. 树的子结构 Offer 26 题目详情: 题解分析 解法一: 第一种比较容易想到的解法就是查看这两棵树的前序遍历和中序遍历序列是否都匹配. 因为前序遍历和中序遍历可以唯一确定 ...
- JVM 中的StringTable
是什么 字符串常量池是 JVM 中的一个重要结构,用于存储JVM运行时产生的字符串.在JDK7之前在方法区中,存储的是字符串常量.而字符串常量池在 JDK7 开始移入堆中,随之而来的是除了存储字符串常 ...
- 03----python入门----函数相关
一.前期知识储备 函数定义 你可以定义一个由自己想要功能的函数,以下是简单的规则: 函数代码块以 def 关键词开头,后接函数标识符名称和圆括号 () 任何传入参数和自变量必须放在圆括号中间,圆括号 ...
- 计算机二级Python学习笔记(一):温度转换
今天通过一个温度转换的十行代码,理解了一些Python的基本元素. 所谓温度转换,就是摄氏度和华氏度的转换,要求输入摄氏度,可以输出华氏度,反之一样能实现.代码如下: #TempConvert.py ...