Hibernate的一级缓存和二级缓存
- Fist level cache: This is enabled by default and works in session scope. Read more about hibernate first level cache.
- Second level cache: This is apart from first level cache which is available to be used globally in session factory scope.
一级缓存(不能disable):
- First level cache is associated with “session” object and other session objects in application can not see it.
- The scope of cache objects is of session. Once session is closed, cached objects are gone forever.
- First level cache is enabled by default and you can not disable it.
- When we query an entity first time, it is retrieved from database and stored in first level cache associated with hibernate session.
- If we query same object again with same session object, it will be loaded from cache and no sql query will be executed.
- The loaded entity can be removed from session using evict() method. The next loading of this entity will again make a database call if it has been removed using evict() method.
- The whole session cache can be removed using clear() method. It will remove all the entities stored in cache.
二级缓存默认是disable,需要自己配置
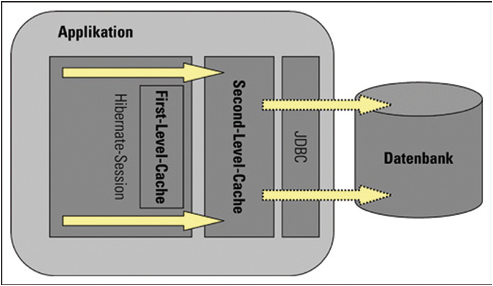
How second level cache works:
Lets write all the facts point by point:
- Whenever hibernate session try to load an entity, the very first place it look for cached copy of entity in first level cache (associated with particular hibernate session).
- If cached copy of entity is present in first level cache, it is returned as result of load method.
- If there is no cached entity in first level cache, then second level cache is looked up for cached entity.
- If second level cache has cached entity, it is returned as result of load method. But, before returning the entity, it is stored in first level cache also so that next invocation to load method for entity will return the entity from first level cache itself, and there will not be need to go to second level cache again.
- If entity is not found in first level cache and second level cache also, then database query is executed and entity is stored in both cache levels, before returning as response of load() method.
- Second level cache validate itself for modified entities, if modification has been done through hibernate session APIs.
- If some user or process make changes directly in database, the there is no way that second level cache update itself until “timeToLiveSeconds” duration has passed for that cache region. In this case, it is good idea to invalidate whole cache and let hibernate build its cache once again. You can use below code snippet to invalidate whole hibernate second level cache.
refer:https://howtodoinjava.com/hibernate/understanding-hibernate-first-level-cache-with-example/
https://howtodoinjava.com/hibernate/how-hibernate-second-level-cache-works/
Hibernate的一级缓存和二级缓存的更多相关文章
- 【转】hibernate缓存:一级缓存和二级缓存
什么是缓存? 缓存是介于物理数据源与应用程序之间,是对数据库中的数据复制一份临时放在内存中的容器,其作用是为了减少应用程序对物理数据源访问的次数,从而提高了应用程序的运行性能.Hibernate在进行 ...
- Hibernate中的一级缓存、二级缓存和懒加载(转)
1.为什么使用缓存 hibernate使用缓存减少对数据库的访问次数,从而提升hibernate的执行效率.hibernate中有两种类型的缓存:一级缓存和二级缓存. 2.一级缓存 Hibenate中 ...
- Hibernate一级缓存与二级缓存的区别
一级缓存: 就是Session级别的缓存.一个Session做了一个查询操作,它会把这个操作的结果放在一级缓存中. 如果短时间内这个session(一定要同一个session)又做了同一个操作,那么h ...
- Hibernate中一级缓存和二级缓存使用详解
一.一级缓存二级缓存的概念解释 (1)一级缓存就是Session级别的缓存,一个Session做了一个查询操作,它会把这个操作的结果放在一级缓存中,如果短时间内这个 session(一定要同一个ses ...
- Hibernate中的一级缓存、二级缓存和懒加载
1.为什么使用缓存 hibernate使用缓存减少对数据库的访问次数,从而提升hibernate的执行效率.hibernate中有两种类型的缓存:一级缓存和二级缓存. 2.一级缓存 Hibenate中 ...
- hibernate缓存:一级缓存和二级缓存
1.什么是缓存? 缓存是介于物理数据源与应用程序之间,是对数据库中的数据复制一份临时放在内存中的容器,其作用是为了减少应用程序对物理数据源访问的次数,从而提高了应用程序的运行性能.Hibernate在 ...
- Hibernate一级缓存和二级缓存深度比较
1.什么是缓存 缓存是介于应用程序和物理数据源之间,其作用是为了降低应用程序对物理数据源访问的频次,从而提高了应用的运行性能.缓存内的数据是对物理数据源中的数据的复制,应用程序在运行时从缓存读写数据, ...
- Hibernate一级缓存和二级缓存详解
(1)一级缓存 是Session级别的缓存,一个Session做了一个查询操作,它会把这个操作的结果放在一级缓存中,如果短时间内这个session(一定要同一个session)又做了同一个操作,那么h ...
- Hibernate之一级缓存和二级缓存
1:Hibernate的一级缓存: 1.1:使用一级缓存的目的是为了减少对数据库的访问次数,从而提升hibernate的执行效率:(当执行一次查询操作的时候,执行第二次查询操作,先检查缓存中是否有数据 ...
- Hibernate 的一级缓存和二级缓存总结
缓存:缓存是什么,解决什么问题? 位于速度相差较大的两种硬件/软件之间的,用于协调两者数据传输速度差异的结构,均可称之为缓存Cache.缓存目的:让数据更接近于应用程序,协调速度不匹配,使访问速度更快 ...
随机推荐
- 【LeetCode】61. 旋转链表
61. 旋转链表 知识点:链表: 题目描述 给你一个链表的头节点 head ,旋转链表,将链表每个节点向右移动 k 个位置. 示例 输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 输出:[4 ...
- 【LeetCode】389.找不同
389.找不同 知识点:哈希表.抵消思想: 题目描述 给定两个字符串 s 和 t,它们只包含小写字母. 字符串 t 由字符串 s 随机重排,然后在随机位置添加一个字母. 请找出在 t 中被添加的字母. ...
- jumpserver 用户,系统用户和管理用户 普通用户和特权用户 区别
前言 现在很多公司都有在用Jumpserver跳板机 有很多人一直对jumpserver的各种用户还不是很了解 当你了解了这几个概念了之后,就能更好的灵活的运用到分配权限当中去. 下面我们一个一个的说 ...
- SpringBoot+Redis 实现消息订阅发布
什么是 Redis Redis 是一个开源的使用 ANSI C语言编写的内存数据库,它以 key-value 键值对的形式存储数据,高性能,读取速度快,也提供了持久化存储机制. Redis 通常在项目 ...
- 第十八篇 -- QTreeWidget应用篇 -- kuwo
效果图: 最近学习QTreeWidget,总想着做些什么,正好学习过一点简单的爬虫,就做了一个简易的"酷我音乐下载器",界面可能不太好看,以后继续优化. ui_kuwo.py # ...
- Pb代理工具之mitmproxy
mitmproxy 一 . mitmproxy介绍 mitmproxy 就是用于 MITM 的 proxy,MITM 即中间人攻击(Man-in-the-middle attack). 不同于 fid ...
- SpringBoot下Schdule的配置与使用
我们在平常项目开发中,经常会用到周期性定时任务,这个时候使用定时任务就能很方便的实现.在SpringBoot中用得最多的就是Schedule. 一.SpringBoot集成Schedule 1.依赖配 ...
- Linux下获取当前程序的绝对路径
在Linux开发应用时,我们常常需要在程序中获取当前程序绝对路径,我们可以通过readlink读取符号链接/proc/self/exe进行获取,这个符号链接代表当前程序,它的源路径就是当前程序的绝对路 ...
- js学习笔记之自调用函数、闭包、原型链
自调用函数 var name = 'world!'; // console.log(typeof name) (function () { console.log(this.name, name, ...
- 使用Python玩转阿里云盘
项目地址: https://github.com/foyoux/aligo 这个项目起源于我的一个简单需求, 我有25000个文件, 已经上传了9000个, 但是现在我把这些文件重新整理了, 最后我不 ...
