手写Spring Config,最终一战,来瞅瞅撒!

上一篇说到了手写Spring AOP,来进行功能的增强,下面本篇内容主要是手写Spring Config。通过配置的方式来使用Spring
前面内容链接:
我自横刀向天笑,手写Spring IOC容器,快来Look Look!
配置分析
为什么要提供配置的方式呢,之前的内容中我们测试的时候都是通过代码来进行的:
GeneralBeanDefinition bd = new GeneralBeanDefinition();
bd.setBeanClass(Lad.class);
List<Object> args = new ArrayList<>();
args.add("sunwukong");
args.add(new BeanReference("magicGril"));
bd.setConstructorArgumentValues(args);
bf.registerBeanDefinition("swk", bd);
bd = new GeneralBeanDefinition();
bd.setBeanClass(MagicGril.class);
args = new ArrayList<>();
args.add("baigujing");
bd.setConstructorArgumentValues(args);
bf.registerBeanDefinition("magicGril", bd);
下面看下平时使用的时候,通过配置是什么样的:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="girl" class="di.MagicGirl"
init-method="start" destroy-method="end">
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="girl"></constructor-arg>
<property name="friend" ref="boy"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="boy" class="di.Lad">
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="boy"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg type="di.MagicGirl" value="girl"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
可以看出,提供配置的方式的优点:
- 实用简单,改动起来比较灵活
- 而且不需要改动代码
常用的配置方式,就是XML和注解的形式,它们的工作过程如下:
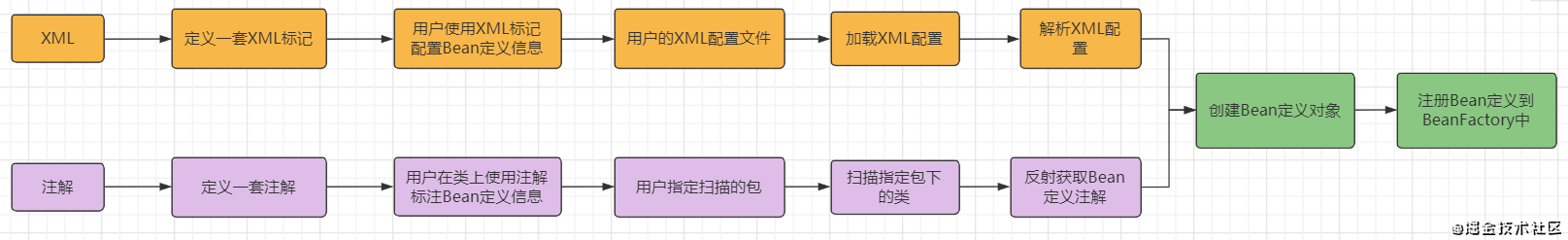
配置的工作过程
定义XML标记和注解
需要定义什么样的XML标记和注解呢?通过之前的内容知道,配置的内容就是Bean定义信息,那么Bean定义的内容就是需要配置的内容
首先来看下Bean定义接口中有哪些信息:
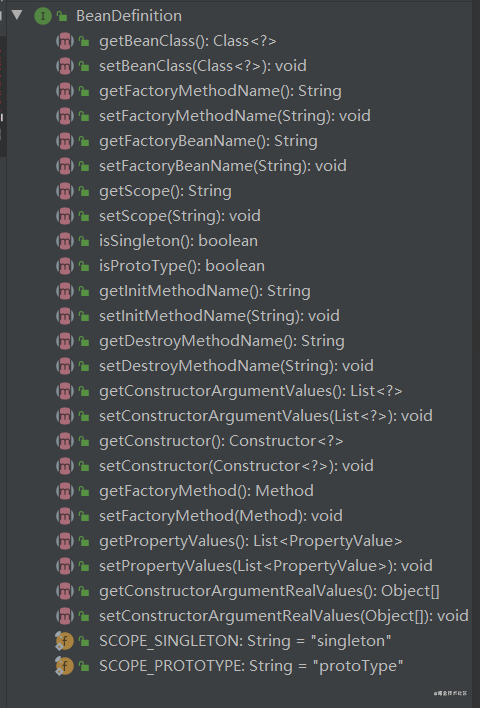
XML配置的方式,首先需要定义一个DTD或者XSD文档,来定义一套标记信息,去指定Bean定义
<bean id="girl" class="di.MagicGirl"
init-method="start" destroy-method="end">
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="girl"></constructor-arg>
<property name="friend" ref="boy"></property>
</bean>
可以看出,bean的配置指定的内容就是Bean定义接口中的信息
注解的方式,需要定义一套注解,那么需要哪些注解呢,也是Bean定义接口中的内容:
- 指定类、指定BeanName、指定scope、指定工厂方法、指定工厂Bean、指定init method、指定destroy method,这些在我们使用Spring的时候是通过@Component来实现的
- 指定构造参数的依赖:@Autowired、@Qualifier
- 指定属性依赖:@Value
Bean配置的解析
Bean配置的解析过程,需要单独的接口来实现,而不是在BeanFactory中来做,要做到单一职责原则,所以需要定义单独的接口来解析Bean配置,然后再向BeanFactory注册Bean定义
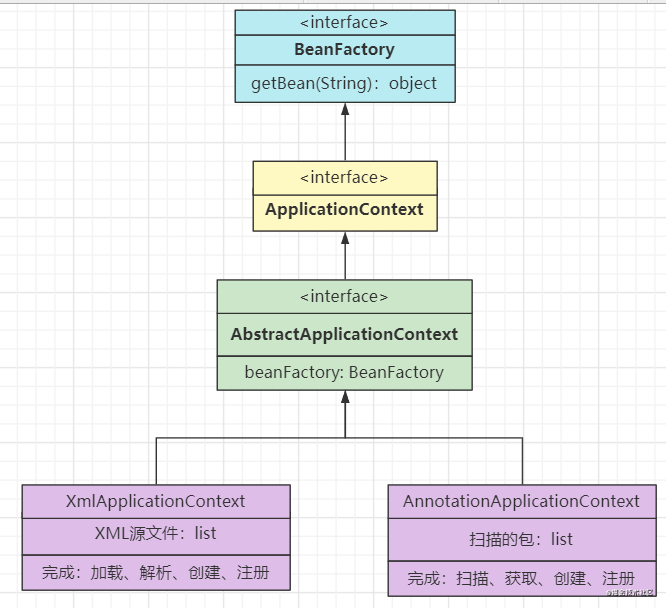
ApplicationContext接口
ApplicationContext这个接口就是用来完成Bean配置解析的,上面说到实现配置的方式有XML和注解,所以会有两个实现类来实现ApplicationContext接口
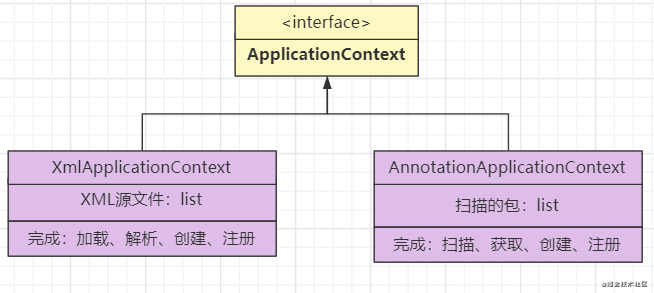
- XML方式的实现:
- XML文件可能存在多个,所以这里使用了list
- 需要完成:加载xml、解析xml、创建Bean定义、注册Bean定义的任务
- 注解方式的实现
- 扫描的包也会存在多个,这里也使用list
- 需要完成:扫描包、获取注解、创建Bean定义、注册Bean定义的任务
因为需要创建和注册Bean定义,所以会使用到BeanFactory和BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,那么这部分代码在子类中分别实现的话就会重复,所以抽象出来放在父类中:
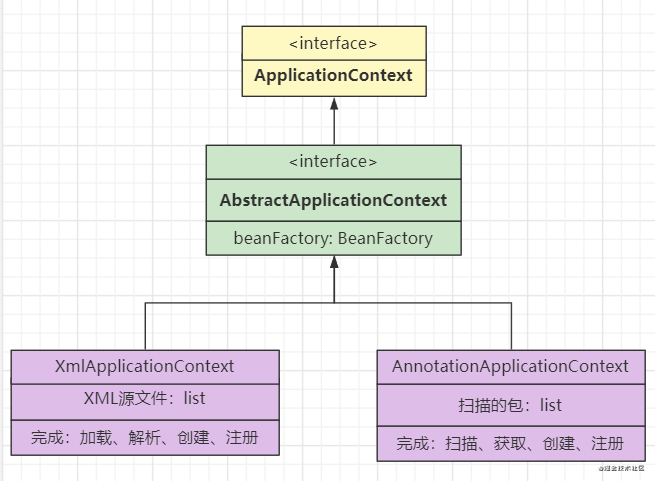
用户在使用的使用需要知道哪些接口和类呢?
- 指定配置相关:xml、注解
- 获取bean相关:BeanFactory
那么可以使用外观模式,让用户只需要知道ApplicationContext和其子类就行了,ApplicationContext可以继承BeanFactory,继而把两个接口合在一起:
ApplicationContext接口:
/**
* @className: ApplicationContext
* 用来构建整个应用环境的接口,用来完成Bean的配置和解析
* 1:为了减少用户对框架类接口的依赖,扩展了BeanFactory接口,
* Bean的配置和Bean的获取都可以通过ApplicationContext接口来完成
* 2:配置资源的方式有xml和注解,所以存在xml和注解两种子类的实现
* 3. Bean配置解析首先需要加载,所以实现了配置资源Resource的加载接口ResourceLoader
* @author: TR
*/
public interface ApplicationContext extends ResourceLoader,BeanFactory {
}
ApplicationContext的抽象类实现
/**
* @className: AbstractApplicationContext
* @description: ApplicationContext的抽象类实现
* @author: TR
*/
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext implements ApplicationContext {
/** 用组合的方式来持有BeanFactory,完成BeanFactory接口的方法 */
protected BeanFactory beanFactory;
public AbstractApplicationContext() {
super();
this.beanFactory = new PreBuildBeanFactory();
}
public AbstractApplicationContext(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
super();
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
@Override
public Object getBean(String beanName) throws Exception {
return this.beanFactory.getBean(beanName);
}
@Override
public void registerBeanPostProcessor(BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor) {
this.beanFactory.registerBeanPostProcessor(beanPostProcessor);
}
}
xml配置方式的ApplicationContext实现类
/**
* @className: XmlApplicationContext
* @description: xml配置方式的ApplicationContext实现类
* @author: TR
*/
public class XmlApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext {
}
注解配置方式的ApplicationContext实现类
/**
* @className: AnnotationApplicationContext
* @description: 注解配置方式的ApplicationContext实现类
* @author: TR
*/
public class AnnotationApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext {
}
配置的实现
XML方式
XML文件来源的处理
xml配置文件的来源会有多种,比如:
不同来源的XML文件,它的加载方式是不一样的,但是在解析的过程中,最后都希望获取到InputStream
这里也需要设计一套接口,对于不同来源的XML文件分别进行处理
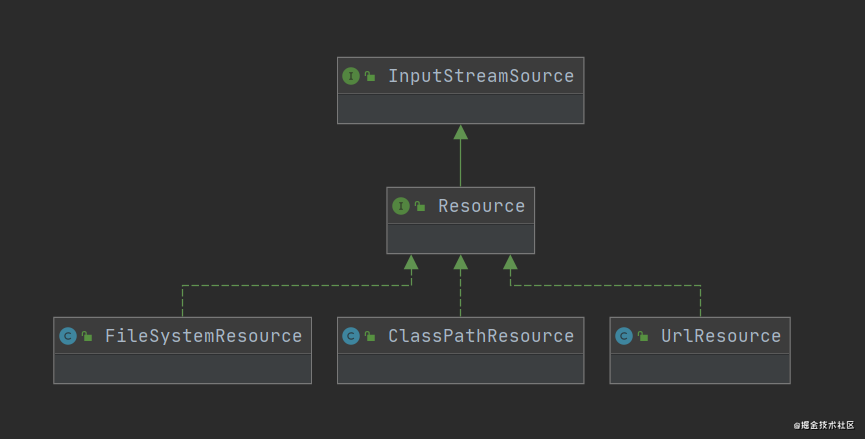
InputStreamSource接口
/**
* @className: InputStreamSource
* @description: 配置方式的最终统一接口
* @author: TR
*/
public interface InputStreamSource {
/**
* 最终要获取的就是输入流
* @return: java.io.InputStream
**/
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
}
Resource接口
/**
* @className: Resource
* @description: 输入流的资源扩展接口
* @author: TR
*/
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {
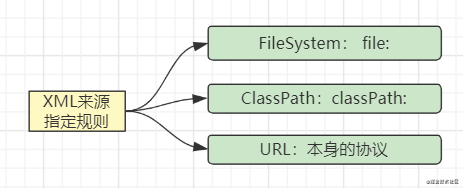
//classpath形式的xml配置文件
String CLASS_PATH_PREFIX = "classpath:";
//系统文件形式的xml配置文件
String File_SYSTEM_PREFIX = "file:";
/**
* 判断资源是否存在
* @return: boolean
**/
boolean exists();
/**
* 是否可读
* @return: boolean
**/
boolean isReadable();
/**
* 是否打开
* @return: boolean
**/
boolean isOpen();
/**
* 获取资源文件
* @return: java.io.File
**/
File getFile();
}
InputStreamSource接口的实现类
FileSystemResource实现类:
/**
* @className: FileSystemResource
* @description: 系统文件类型的资源实现类
* @author: TR
*/
public class FileSystemResource implements Resource {
/** 文件资源对象 */
private File file;
public FileSystemResource(String fileName) {
super();
this.file = new File(fileName);
}
public FileSystemResource(File file) {
super();
this.file = file;
}
@Override
public boolean exists() {
return this.file == null ? false : this.file.exists();
}
@Override
public boolean isReadable() {
return this.file == null ? false : this.file.canRead();
}
@Override
public boolean isOpen() {
return false;
}
@Override
public File getFile() {
return file;
}
@Override
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
return new FileInputStream(this.file);
}
}
ClassPathResource实现类:
/**
* @className: ClassPathResource
* @description: classpath形式的资源实现类
* @author: TR
*/
public class ClassPathResource implements Resource {
//classpath所需要的信息
private String path;
private Class<?> clazz;
private ClassLoader classLoader;
public ClassPathResource(String path) {
this(path, null );
}
public ClassPathResource(String path, Class<?> clazz) {
this(path, clazz, null);
}
public ClassPathResource(String path, Class<?> clazz, ClassLoader classLoader) {
super();
this.path = path;
this.clazz = clazz;
this.classLoader = classLoader;
}
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
public void setPath(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
public Class<?> getClazz() {
return clazz;
}
public void setClazz(Class<?> clazz) {
this.clazz = clazz;
}
public ClassLoader getClassLoader() {
return classLoader;
}
public void setClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.classLoader = classLoader;
}
@Override
public boolean exists() {
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(path)) {
if (this.clazz != null) {
return this.clazz.getResource(path) != null;
}
if (this.classLoader != null) {
return this.classLoader.getResource(path.startsWith("/") ? path.substring(1) : path) != null;
}
return this.getClass().getResource(path) != null;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isReadable() {
return exists();
}
@Override
public boolean isOpen() {
return false;
}
@Override
public File getFile() {
return null;
}
@Override
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(path)) {
if (this.clazz != null) {
return this.clazz.getResourceAsStream(path);
}
if (this.classLoader != null) {
return this.classLoader.getResourceAsStream(path.startsWith("/") ? path.substring(1) : path);
}
return this.getClass().getResourceAsStream(path);
}
return null;
}
}
UrlResource实现类:
/**
* @className: UrlResource
* @description: URL形式的资源实现类
* @author: TR
*/
public class UrlResource implements Resource {
/** url的资源对象 */
private URL url;
public UrlResource(String url) throws IOException {
this.url = new URL(url);
}
public UrlResource(URL url) {
super();
this.url = url;
}
public URL getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(URL url) {
this.url = url;
}
@Override
public boolean exists() {
return this.url != null;
}
@Override
public boolean isReadable() {
return exists();
}
@Override
public boolean isOpen() {
return false;
}
@Override
public File getFile() {
return null;
}
@Override
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
return null;
}
}
XML资源加载器
用户给定资源时是一个字符串,上面有三种资源,那么谁去负责创建这些资源呢
这里需要定义一个资源加载器,去分辨不同的资源,然后进行加载,这部分工作是由ApplicationContext来完成的,所以ApplicationContext需要继承ResourceLoader接口
ResourceLoader接口:
/**
* @className: ResourceLoader
* 配置资源加载接口
* 不同的配置方式,加载过程不一样,所以需要抽象出来一个接口应对变化的部分
* 虽然加载的方式不一样,但是返回的资源结果是一样的,都是Resource
* @author: TR
*/
public interface ResourceLoader {
/**
* 加载资源
* @param location:
* @return: demo.context.Resource
**/
Resource getResource(String location) throws IOException;
}
在这里,还需要区分用户给的字符串代表的是哪种资源,所以需要定义字符串的规则:
注解方式
如何扫描的
扫描的包有哪些呢?
需要到指定的包目录下找出所有的类文件,而且要包含子孙包下的
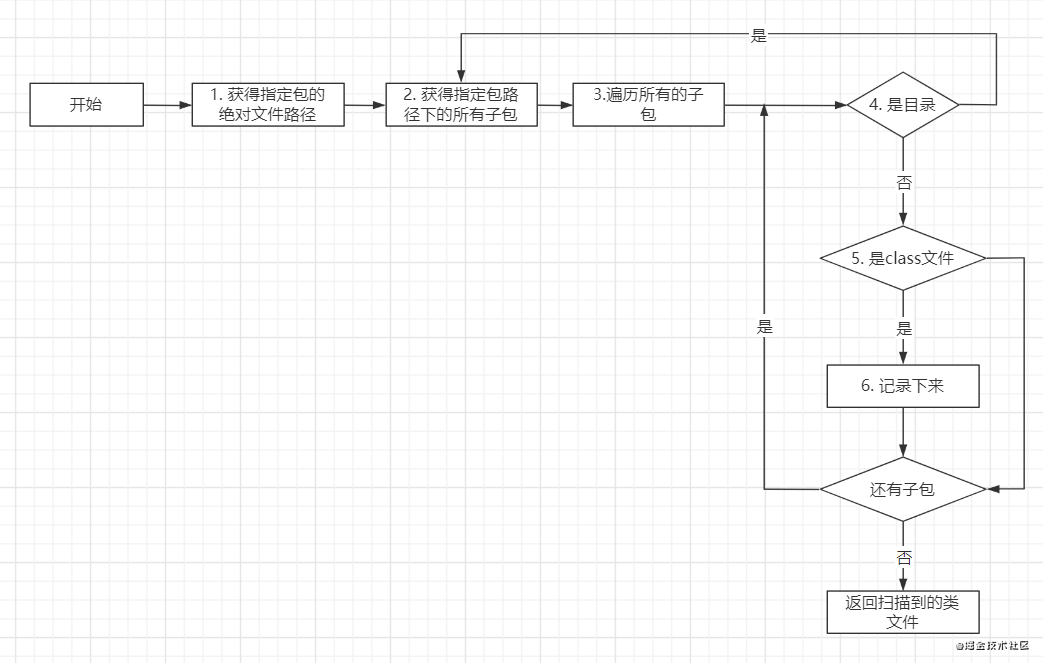
需要定义一个资源路径的匹配行为
扫描的结果
扫描到了包下的class文件后,需要的是类名,而且扫描的是class文件,直接使用上面的FileResource即可
扫描的类ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
/**
* @className: ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
* @description: 扫描class文件
* @author: TR
*/
public class ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner {
private static Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner.class);
private BeanDefinitionRegistry registry;
private BeanDefinitionReader reader;
private PathMatcher pathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
private String resourcePatter = "**/*.class";
public ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
super();
this.registry = registry;
this.reader = new AnnotationBeanDefinitionReader(registry);
}
/**
* 扫描包的方法
* @param basePackages:
* @return: void
**/
public void scan(String... basePackages) throws Throwable {
if (basePackages != null && basePackages.length > 0) {
for (String b : basePackages) {
this.reader.loadBeanDefintions(doScan(b));
}
}
}
/**
* 将扫描的class转为Resource
* @param basePackage:
* @return: demo.context.Resource[]
**/
private Resource[] doScan(String basePackage) throws IOException {
// 扫描包下的类
// 构造初步匹配模式串,= 给入的包串 + / + **/*.class,替换里面的.为/
String pathPattern = StringUtils.replace(basePackage, ".", "/") + "/" + this.resourcePatter;
if (pathPattern.charAt(0) != '/') {
pathPattern = "/" + pathPattern;
}
// 找出模式的根包路径
String rootPath = this.determineRootDir(pathPattern);
// 得到文件名匹配的绝对路径模式
String fullPattern = this.getClass().getResource("/").toString() + pathPattern;
// 根据根包理解得到根包对应的目录
File rootDir = new File(this.getClass().getResource(rootPath).toString());
// 存放找到的类文件的resource集合
Set<Resource> scanedClassFileResources = new HashSet<>();
// 调用doRetrieveMatchingFiles来扫描class文件
this.doRetrieveMatchingFiles(fullPattern, rootDir, scanedClassFileResources);
return (Resource[]) scanedClassFileResources.toArray();
}
private String determineRootDir(String location) {
int rootDirEnd = location.length();
rootDirEnd = location.indexOf('*');
int zi = location.indexOf('?');
if (zi != -1 && zi < rootDirEnd) {
rootDirEnd = location.lastIndexOf('/', zi);
}
if (rootDirEnd != -1) {
return location.substring(0, rootDirEnd);
} else {
return location;
}
}
/**
* 递归找指定目录下的所有类,匹配模式的加入到结果中。
*
* @param fullPattern
* @param dir
* @param result
* @throws IOException
*/
protected void doRetrieveMatchingFiles(String fullPattern, File dir, Set<Resource> result) throws IOException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Searching directory [" + dir.getAbsolutePath() + "] for files matching pattern ["
+ fullPattern + "]");
}
for (File content : listDirectory(dir)) {
String currPath = StringUtils.replace(content.getAbsolutePath(), File.separator, "/");
if (content.isDirectory() && getPathMatcher().matchStart(fullPattern, currPath + "/")) {
if (!content.canRead()) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping subdirectory [" + dir.getAbsolutePath()
+ "] because the application is not allowed to read the directory");
}
} else {
doRetrieveMatchingFiles(fullPattern, content, result);
}
}
if (getPathMatcher().match(fullPattern, currPath)) {
result.add(new FileSystemResource(content));
}
}
}
protected File[] listDirectory(File dir) {
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
if (files == null) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Could not retrieve contents of directory [" + dir.getAbsolutePath() + "]");
}
return new File[0];
}
Arrays.sort(files, Comparator.comparing(File::getName));
return files;
}
public BeanDefinitionRegistry getRegistry() {
return registry;
}
public void setRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
this.registry = registry;
}
public BeanDefinitionReader getReader() {
return reader;
}
public void setReader(BeanDefinitionReader reader) {
this.reader = reader;
}
public PathMatcher getPathMatcher() {
return pathMatcher;
}
public void setPathMatcher(PathMatcher pathMatcher) {
this.pathMatcher = pathMatcher;
}
public String getResourcePatter() {
return resourcePatter;
}
public void setResourcePatter(String resourcePatter) {
this.resourcePatter = resourcePatter;
}
}
解析成Bean定义
XML和注解最终的输出结果都是Resource,在这里还需要把Resource解析成Bean定义信息才行
需要定义接口来进行解析:
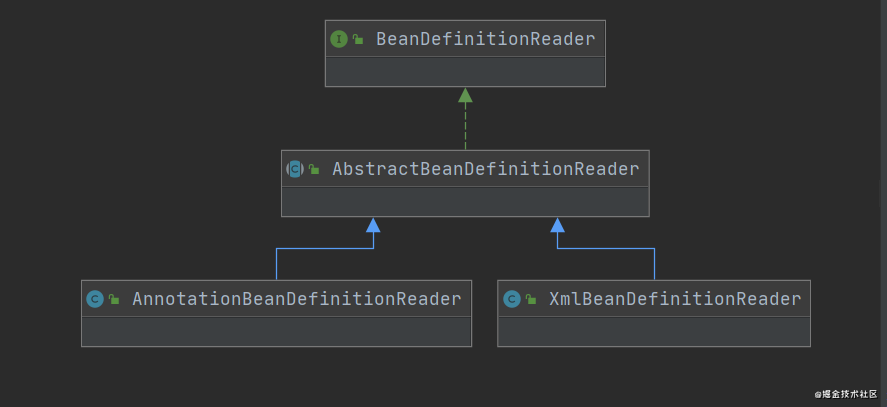
BeanDefinitionReader接口:
/**
* @className: BeanDefinitionReader
* @description: 将Resource资源解析成Bean定义的接口
* @author: TR
*/
public interface BeanDefinitionReader {
/**
* 解析单个资源
* @param resource:
* @return: void
**/
void loadBeanDefintions(Resource resource) throws Throwable;
/**
* 解析多个资源
* @param resource:
* @return: void
**/
void loadBeanDefintions(Resource... resource) throws Throwable;
}
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader抽象类:
/**
* @className: AbstractBeanDefinitionReader
* @description: TODO
* @date: 2021/6/10 15:58
* @author: jinpeng.sun
*/
public abstract class AbstractBeanDefinitionReader implements BeanDefinitionReader {
/** 持有BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,以便完成注册到BeanFactory中 */
protected BeanDefinitionRegistry beanDefinitionRegistry;
public AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry beanDefinitionRegistry) {
super();
this.beanDefinitionRegistry = beanDefinitionRegistry;
}
}
xml配置方式的bean定义解析器:
/**
* @className: XmlBeanDefinitionReader
* @description: xml配置方式的bean定义解析器
* @author: TR
*/
public class XmlBeanDefinitionReader extends AbstractBeanDefinitionReader {
public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry beanDefinitionRegistry) {
super(beanDefinitionRegistry);
}
@Override
public void loadBeanDefintions(Resource resource) throws Throwable {
this.loadBeanDefintions(new Resource[] {resource});
}
@Override
public void loadBeanDefintions(Resource... resource) throws Throwable {
if (resource != null && resource.length > 0) {
for (Resource r : resource) {
this.parseXml(r);
}
}
}
private void parseXml(Resource r) {
//TODO 解析xml文档,获取bean定义,创建bean定义对象,注册到BeanDefinitionRegistry中
}
}
注解配置方式的bean定义解析器:
* @className: AnnotationBeanDefinitionReader
* @description: 注解配置方式的bean定义解析器:
* @author: TR
*/
public class AnnotationBeanDefinitionReader extends AbstractBeanDefinitionReader {
public AnnotationBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry beanDefinitionRegistry) {
super(beanDefinitionRegistry);
}
@Override
public void loadBeanDefintions(Resource resource) throws Throwable {
this.loadBeanDefintions(new Resource[] {resource});
}
@Override
public void loadBeanDefintions(Resource... resource) throws Throwable {
if (resource != null && resource.length > 0) {
for (Resource r : resource) {
this.retriveAndRegistBeanDefinition(r);
}
}
}
private void retriveAndRegistBeanDefinition(Resource resource) {
if(resource != null && resource.getFile() != null) {
String className = getClassNameFormFile(resource.getFile());
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
Component component = clazz.getAnnotation(Component.class);
if (component != null) {
GeneralBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new GeneralBeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setBeanClass(clazz);
beanDefinition.setScope(component.scope());
beanDefinition.setFactoryMethodName(component.factoryMethodName());
beanDefinition.setFactoryBeanName(component.factoryBeanName());
beanDefinition.setInitMethodName(component.initMethodName());
beanDefinition.setDestroyMethodName(component.destroyMethodName());
//获取所有的构造方法,在构造方法上找Autowired注解,如果有的话,将这个构造方法set到bd
this.handleConstructor(clazz, beanDefinition);
//处理工厂方法参数依赖
if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(beanDefinition.getFactoryMethodName())) {
this.handleFactoryMethodArgs(clazz, beanDefinition);
}
//处理属性依赖
this.handlePropertyDi(clazz, beanDefinition);
String beanName = "".equals(component.value()) ? component.name() : null;
if (StringUtils.isBlank(beanName)) {
// TODO 应用名称生成规则生成beanName;
// 默认驼峰命名法
beanName = CaseFormat.LOWER_HYPHEN.to(CaseFormat.LOWER_CAMEL, clazz.getSimpleName());
}
// 注册bean定义
this.beanDefinitionRegistry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | BeanDefinitionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void handlePropertyDi(Class<?> clazz, GeneralBeanDefinition bd) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
private void handleFactoryMethodArgs(Class<?> clazz, GeneralBeanDefinition bd) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
private void handleConstructor(Class<?> clazz, GeneralBeanDefinition bd) {
//获取所有的构造方法,在构造方法上找Autowired注解,如果有的话,将这个构造方法set到bd
Constructor<?>[] constructors = clazz.getConstructors();
if (constructors != null && constructors.length > 0) {
for (Constructor c : constructors) {
if (c.getAnnotation(Autowired.class) != null) {
bd.setConstructor(c);
Parameter[] ps = c.getParameters();
//遍历获取参数上的注解,及创建参数依赖
break;
}
}
}
}
private int classPathAbsLength = AnnotationBeanDefinitionReader.class.getResource("/").toString().length();
private String getClassNameFormFile(File file) {
//返回绝对路径名字符串
String absPath = file.getAbsolutePath();
String name = absPath.substring(classPathAbsLength+1, absPath.indexOf("."));
return StringUtils.replace(name, File.separator, ".");
}
}
完善XmlApplicationContext和AnnotationApplicationContext:
public class XmlApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext {
private List<Resource> resources;
private BeanDefinitionReader definitionReader;
public XmlApplicationContext(String... locations) throws Throwable {
super();
load(locations);
//资源解析成BeanDefinition,外派给BeanDefinitionReader接口来实现
this.definitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader((BeanDefinitionRegistry) this.beanFactory);
Resource[] resourceArray = new Resource[resources.size()];
resources.toArray(resourceArray);
//将解析后的BeanDefinition装载到BeanFactory中
definitionReader.loadBeanDefintions(resourceArray);
}
/**
* 根据用户指定的配置文件位置,加载资源信息
* @param locations:
* @return: void
**/
private void load(String[] locations) throws IOException {
if (resources == null) {
resources = new ArrayList<Resource>();
}
//完成加载,创建好Resource
if (locations != null && locations.length > 0) {
for (String lo : locations) {
Resource resource = getResource(lo);
if (resource != null) {
this.resources.add(resource);
}
}
}
}
@Override
public Resource getResource(String location) throws IOException {
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(location)) {
//根据字符串的前缀判断区分,class、系统文件、url三种资源的加载
if (location.startsWith(Resource.CLASS_PATH_PREFIX)) {
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(Resource.CLASS_PATH_PREFIX.length()));
} else if (location.startsWith(Resource.File_SYSTEM_PREFIX)) {
return new FileSystemResource(location.substring(Resource.File_SYSTEM_PREFIX.length()));
} else {
return new UrlResource(location);
}
}
return null;
}
}
public class AnnotationApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext {
private ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner;
public AnnotationApplicationContext(String... locations) throws Throwable {
scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner((BeanDefinitionRegistry) this.beanFactory);
scanner.scan(locations);
}
@Override
public Resource getResource(String location) throws IOException {
return null;
}
}
手写Spring Config,最终一战,来瞅瞅撒!的更多相关文章
- 【Spring】手写Spring MVC
Spring MVC原理 Spring的MVC框架主要由DispatcherServlet.处理器映射.处理器(控制器).视图解析器.视图组成. 完整的Spring MVC处理 流程如下: Sprin ...
- 手写Spring框架,加深对Spring工作机制的理解!
在我们的日常工作中,经常会用到Spring.Spring Boot.Spring Cloud.Struts.Mybatis.Hibernate等开源框架,有了这些框架的诞生,平时的开发工作量也是变得越 ...
- 手写Spring+demo+思路
我在学习Spring的时候,感觉Spring是很难的,通过学习后,发现Spring没有那么难,只有你去学习了,你才会发现,你才会进步 1.手写Spring思路: 分为配置.初始化.运行三个阶段如下图 ...
- 手写Spring事务框架
Spring事务基于AOP环绕通知和异常通知 编程事务 声明事务 Spring事务底层使用编程事务+AOP进行包装的 = 声明事务 AOP应用场景: 事务 权限 参数验证 什么是AOP技术 AO ...
- 手写Spring AOP,快来瞧一瞧看一看撒!
目录 AOP分析 Advice实现 定义Advice接口 定义前置.后置.环绕和异常增强接口 Pointcut实现 定义PointCut接口 定义正则表达式的实现类:RegExpressionPoin ...
- 30个类手写Spring核心原理之动态数据源切换(8)
本文节选自<Spring 5核心原理> 阅读本文之前,请先阅读以下内容: 30个类手写Spring核心原理之自定义ORM(上)(6) 30个类手写Spring核心原理之自定义ORM(下)( ...
- 一个老程序员是如何手写Spring MVC的
人见人爱的Spring已然不仅仅只是一个框架了.如今,Spring已然成为了一个生态.但深入了解Spring的却寥寥无几.这里,我带大家一起来看看,我是如何手写Spring的.我将结合对Spring十 ...
- 我是这样手写 Spring 的(麻雀虽小五脏俱全)
人见人爱的 Spring 已然不仅仅只是一个框架了.如今,Spring 已然成为了一个生态.但深入了解 Spring 的却寥寥无几.这里,我带大家一起来看看,我是如何手写 Spring 的.我将结合对 ...
- 《四 spring源码》利用TransactionManager手写spring的aop
事务控制分类 编程式事务控制 自己手动控制事务,就叫做编程式事务控制. Jdbc代码: Conn.setAutoCommite(false); // 设置手动控制事务 Hibern ...
随机推荐
- HDU - 2091 空心三角形 水题,但是有点坑...
空心三角形 Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submi ...
- 【Azure Developer】使用Microsoft Graph API 如何批量创建用户,用户属性中需要包含自定义字段(如:Store_code,Store_name等)
Microsoft Graph 是 Microsoft 365 中通往数据和智能的网关. 它提供统一的可编程模型,可用于访问 Microsoft 365.Windows 10 和企业移动性 + 安全性 ...
- DLL注入技术(输入法注入)
输入法注入原理 IME输入法实际就是一个dll文件(后缀为ime),此dll文件需要导出必要的接口供系统加载输入法时调用.我们可以在此ime文件的DllMain函数的入口通过调用LoadLibrary ...
- .NET Worker Service 如何优雅退出
上一篇文章中我们了解了 .NET Worker Service 的入门知识[1],今天我们接着介绍一下如何优雅地关闭和退出 Worker Service. Worker 类 从上一篇文章中,我们已经知 ...
- 有哪些适合中小企业使用的PaaS平台?
对于中小企业来说,在业务上同样需要工作流.应用平台来进行支持,但是,面对诸如ERP等动辄好几十万的费用来说,完全是在增加运营成本.如何解决中小企业对于业务应用.工作流管理的需求问题呢?使用PaaS低代 ...
- a标签美化
具体选中a标签给予宽高,这样才能在整个a标签范围内才能跳转 但是因为a标签是行内元素,所以要用display:blcok 转化为块状元素 且a标签不继承父元素的color 对a标签设置颜色,要选中a标 ...
- MySQL之数据定义语言(DDL)
写在前面 本文中 [ 内容 ] 代表啊可选项,即可写可不写. SQL语言的基本功能介绍 SQL是一种结构化查询语言,主要有如下几个功能: 数据定义语言(DDL):全称Data Definition L ...
- mybatis-plus批量插入saveBatch太慢?我愿意称rewriteBatchedStatements为神
最近在做项目优化,代码优化之后,测试接口,好家伙.一个定时任务接口执行要10秒左右. 一点点追踪,给每个方法打上执行时间,一点点缩小范围.好家伙,终于让我锁定了目标. 这是mybatis-plus的批 ...
- [bug] org.apache.ibatis.binding.BindingException: Invalid bound statement (not found)
问题 原因不明,按参考文章中的做法,加了空格,clean后解决 参考 http://www.qishunwang.net/news_show_7922.aspx https://www.cnblogs ...
- wps中新罗马字体如何设置Times New Roman
word wps中新罗马字体如何设置Times New Roman ### WPS字体自带 Times New Roman ###
