Fragment的创建与通信
由于这里涉及到接口回调的问题,所以先来看一看什么是接口回调:
这就好比老板和员工的微妙关系,老板需要员工去工作,员工挣钱了以后还要告诉老板自己挣了多少钱,然后由老板来处理这些钱。
首先创建一个接口:
package com.fitsoft;
public interface CallBack {
void collectMoney(String name, int money);
}
由于员工挣完钱了以后,钱由老板来处理,因此接口也是由老板来实现
创建老板类:
package com.fitsoft;
/**
* @author Joker
* @since 2019/9/20 0020 18:49
*/
public class Boss implements CallBack {
void makeMoney(){
String name = "小三";
System.out.println(name+"快去工作!");
Staff staff = new Staff(name, this);
staff.doWork();
}
public void collectMoney(String name, int money) {
System.out.println(name+"帮我挣了"+money+"元");
}
}
这里有两个方法,一个是叫员工去赚钱,在makeMoney()方法中创建一个员工,让员工去doWork(),另一个是员工赚完钱以后回调给老板,由老板来打印输出(花钱)。
看一看员工类:
package com.fitsoft;
/**
* @author Joker
* @since 2019/9/20 0020 18:35
*/
class Staff {
private String myName;
private CallBack callBack;
Staff(String name, CallBack callBack){
this.myName = name;
this.callBack = callBack;
}
void doWork(){
System.out.println(myName + " make money ing...");
callBack.collectMoney(myName, 500);
}
}
在构造函数中初始化名字和接口,在doWork()方法中(由老板来调用的方法),输出我正在赚钱,赚完钱之后,执行老板的collectMoney()方法,告诉老板:这钱是我给你的,你可以收了,然后老板就执行了:
public void collectMoney(String name, int money) {
System.out.println(name+"帮我挣了"+money+"元");
}
总的流程大致是这样,接下来创建测试类:
package com.fitsoft;
/**
* @author Joker
* @since 2019/9/20 0020 18:47
*/
public class Test {
@org.junit.Test
public void test(){
new Boss().makeMoney();
}
}
直接调用老板类中的赚钱方法(赚钱是不可能赚钱的,这辈子都不可能去赚钱的,只有让员工去赚钱这样子才能维持生活...)。
看一看输出:
小三快去工作!
小三 make money ing...
小三帮我挣了500元
以上大致是接口回调的内容,接下来才是主题:Fragment
首先创建布局activity_main.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.fitsoft.MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/fragment_add"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="8dp"
android:layout_marginTop="24dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="8dp"
android:layout_marginRight="8dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="8dp"
android:text="add"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.498"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.0" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/fragment_remove"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="8dp"
android:layout_marginTop="32dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="8dp"
android:layout_marginRight="8dp"
android:text="remove"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.498"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/fragment_add" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/fragment_modify"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="8dp"
android:layout_marginTop="32dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="8dp"
android:layout_marginRight="8dp"
android:text="modify"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.498"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/fragment_remove" />
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/main_fragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="8dp"
android:layout_marginTop="8dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="8dp"
android:layout_marginRight="8dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="8dp"
android:orientation="vertical"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="1.0"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.666" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_in_activity"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="8dp"
android:layout_marginTop="8dp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/main_fragment" />
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
界面大致是这样子的:

然后创建Fragment中的布局fragment_main.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:background="#4CAF50"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_in_fragment"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="8dp"
android:layout_marginTop="8dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="8dp"
android:layout_marginRight="8dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="8dp"
android:text="这是Fragment界面"
android:textColor="#fff"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.498"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.415" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_in_fragment"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="8dp"
android:layout_marginTop="8dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="8dp"
android:layout_marginRight="8dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="8dp"
android:text="modify"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.498"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/tv_in_fragment"
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.064" />
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
界面是这样的:

首先我们创建Activity的管理类MainActivity:
package com.fitsoft;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentActivity;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentManager;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity {
Button add;
Button remove;
Button modify;
TextView textView;
MainFragment mainFragment;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
textView = findViewById(R.id.tv_in_activity);
mainFragment = new MainFragment();
mainFragment.setOnBtnClickListener(new MainFragment.OnBtnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onBtnClick() {
textView.setText("===这里的值已经被修改了===");
}
});
add = findViewById(R.id.fragment_add);
add.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
FragmentManager fm = getSupportFragmentManager();
//获得fragment的事务
FragmentTransaction ft = fm.beginTransaction();
ft.add(R.id.main_fragment, mainFragment);
ft.commit();
}
});
remove = findViewById(R.id.fragment_remove);
remove.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
FragmentManager fm = getSupportFragmentManager();
//获得fragment的事务
FragmentTransaction ft = fm.beginTransaction();
ft.remove(mainFragment);
ft.commit();
}
});
modify = findViewById(R.id.fragment_modify);
modify.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
mainFragment.modify();
}
});
}
}
然后创建Fragment的管理类MainFragment:
package com.fitsoft;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.annotation.NonNull;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment; //兼容性好
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
/**
* @author Joker
* @since 2019/9/19 0019 20:48
*/
public class MainFragment extends Fragment {
Button button;
View view;
TextView textView;
private OnBtnClickListener onBtnClickListener;
public void setOnBtnClickListener(OnBtnClickListener onBtnClickListener){
this.onBtnClickListener = onBtnClickListener;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_main, container, false);
textView = view.findViewById(R.id.tv_in_fragment);
button = view.findViewById(R.id.btn_in_fragment);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if(onBtnClickListener != null)
onBtnClickListener.onBtnClick();
}
});
return view;
}
public void modify(){
textView.setText("===修改之后的值===");
}
public interface OnBtnClickListener {
void onBtnClick();
}
}
为了兼容性更好这里我用v4包下的Fragment,启动app之后出现如下界面:
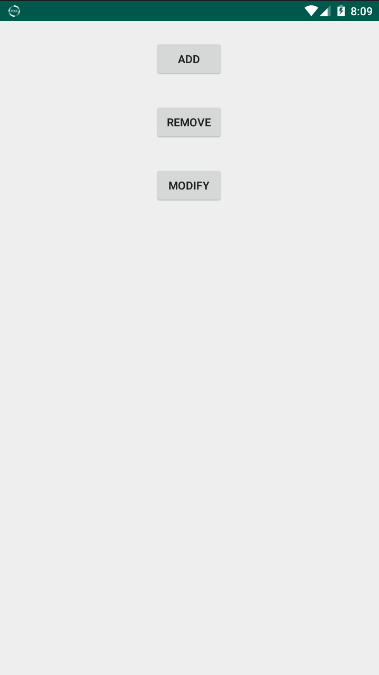
这些就是运行之后我们Activity上面的布局,当我们点击ADD按钮之后,触发事件:
add.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
FragmentManager fm = getSupportFragmentManager();
//获得fragment的事务
FragmentTransaction ft = fm.beginTransaction();
ft.add(R.id.main_fragment, mainFragment);
ft.commit();
}
});
在这里将我们的Fragment添加在LinearLayout布局中,就是这个:
点击之后看到Fragment已经生成了:
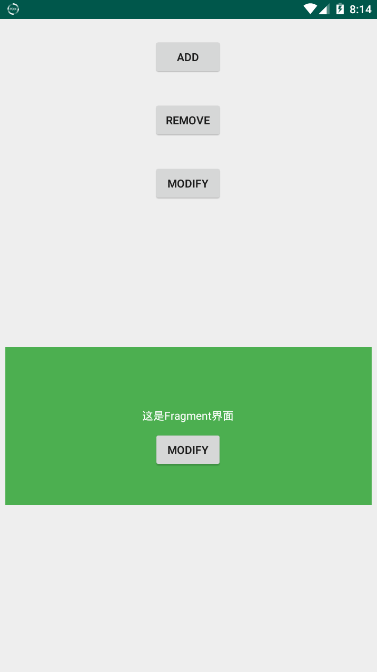
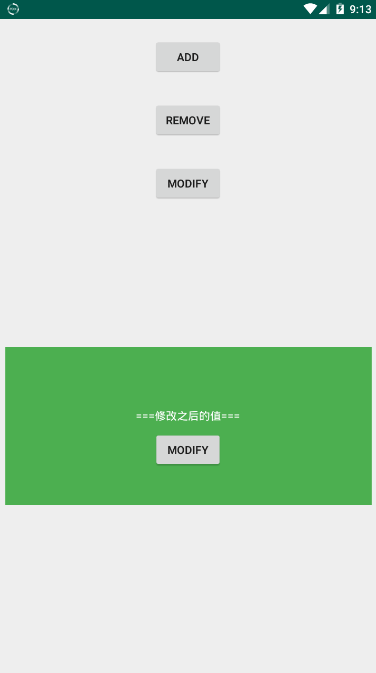
然后我们点击Activity中的MODIFY按钮,在Activity中修改Fragment中的文本值:
modify = findViewById(R.id.fragment_modify);
modify.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
mainFragment.modify();
}
});
在MainFragment中是这么写的:
public void modify(){
textView.setText("===修改之后的值===");
}
将Fragment中的TextView的值进行了修改,修改之后:
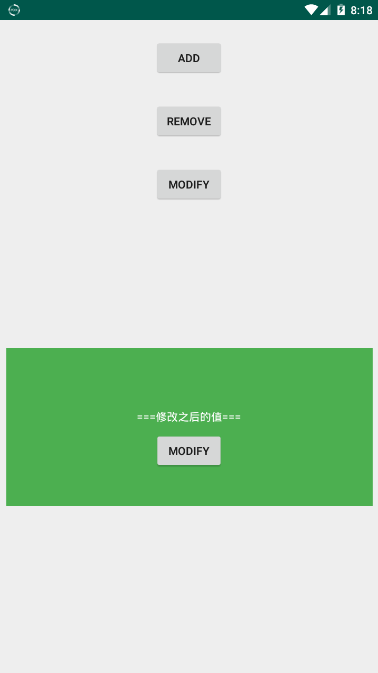
上面我们在Activity中修改Fragment,那么如何在Fragment中调用Activity中的方法呢,当然方法有很多,这里我们使用回调函数的方式进行通信:
在MainFragment中定义接口:
public interface OnBtnClickListener {
void onBtnClick();
}
然后在MainFragment中定义方法,将接口提供给调用者:
public void setOnBtnClickListener(OnBtnClickListener onBtnClickListener){
this.onBtnClickListener = onBtnClickListener;
}
这里MainActivity中使用匿名内部类的方式实现了接口的方法:
mainFragment = new MainFragment();
mainFragment.setOnBtnClickListener(new MainFragment.OnBtnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onBtnClick() {
textView.setText("===这里的值已经被修改了===");
}
});
为什么要set呢?这是为了让两个类中的接口保持一致,原来的MainFragment中的onBtnClickListener是null,而在MainActiviy中却已经写好了方法,就等着你去调用
然后Fragment按钮的点击事件中就调用了接口中的onBtnClick()方法,这跟普通的调用方法还有点不一样,它更像是调用实体类中的方法,只不过没有实例化:
button = view.findViewById(R.id.btn_in_fragment);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if(onBtnClickListener != null)
onBtnClickListener.onBtnClick();
}
});
这里还需要注意,据我分析(如果没有错的话):
onBtnClickListener.onBtnClick();
这行代码算不上调用,更像是执行,因为此时的onBtnClickListener已经不为null了,它只是执行了里面的onBtnClick()方法,
@Override
public void onBtnClick() {
textView.setText("===这里的值已经被修改了===");
}
而真正要被执行的方法应该是已经早早的在set方法中被传递了过来。
然后看看回调之后的效果:
最后还有一个移除Fragment的按钮:
remove = findViewById(R.id.fragment_remove);
remove.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
FragmentManager fm = getSupportFragmentManager();
//获得fragment的事务
FragmentTransaction ft = fm.beginTransaction();
ft.remove(mainFragment);
ft.commit();
}
});
整个过程大致是这样:

然后会有小伙伴发问了,这里和开头举的例子的回调方法不一样啊。。。
好,那我改成一致的...
MainActivity:
package com.fitsoft;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentActivity;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentManager;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity implements OnBtnClickListener{
Button add;
Button remove;
Button modify;
TextView textView;
MainFragment mainFragment;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
textView = findViewById(R.id.tv_in_activity);
mainFragment = new MainFragment();
mainFragment.setOnBtnClickListener(this);
add = findViewById(R.id.fragment_add);
add.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
FragmentManager fm = getSupportFragmentManager();
//获得fragment的事务
FragmentTransaction ft = fm.beginTransaction();
ft.add(R.id.main_fragment, mainFragment);
ft.commit();
}
});
remove = findViewById(R.id.fragment_remove);
remove.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
FragmentManager fm = getSupportFragmentManager();
//获得fragment的事务
FragmentTransaction ft = fm.beginTransaction();
ft.remove(mainFragment);
ft.commit();
}
});
modify = findViewById(R.id.fragment_modify);
modify.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
mainFragment.modify();
}
});
}
@Override
public void onBtnClick() {
textView.setText("===这里的值已经被修改了===");
}
}
其实理解应该不难,毕竟点击事件的触发不也是这样的嘛...
modify.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
mainFragment.modify();
}
});
也可以使类实现View.OnClickListener接口....
Fragment的创建与通信的更多相关文章
- fragment 数据传递,通信
Fragment之间的通信 在本节中,你会学到 1.定义接口 2.实现接口 3.将消息传递给fragment 为了重用Fragment UI 组件,在设计中你应该通过定义每一个fragemnt自己 ...
- Fragment基础----创建
1,Fragment的目的及应用场景 fragment 是3.0后引入的类,其字面翻译为“碎片”. 目的是将activity划分成许多单元再进行组合,可以根据不同分辨率屏幕,在不同状态下,灵活创建优化 ...
- android studio 2.2.2下fragment的创建和跳转
一,首先,Fragment是android应用中十分重要的一个功能,十分轻量化,也类似于activity一样,是一个个布局,可以相互跳转和传递参数.但是,它运行起来十分流畅,而且易于管理,下面是在学习 ...
- android开发(2):多页面的实现 | Fragment的创建与使用
APP中出现多个页面再常见不过了.使用activity与fragment都能实现多页面,这里使用fragment来实现.延续“知音”这个APP的开发,之前已经创建了底部导航条与mainactivity ...
- C# Socket系列二 简单的创建 socket 通信
看了系列一 我们开启了对socket tcp的监听状态,那么这一章我们来讲解怎么创建socket的通信代码 我新建一个类 TSocketBase public abstract class TSock ...
- Android(Fragment和Activity之间通信)
Fragment的使用可以让我们的应用更灵活的适配各种型号的安卓设备,但是对于Fragment和Activity之间的通信,很多朋友应该比较陌生,下面我们就通过一个实例来看一看如何实现. 一.Acti ...
- android中fragment与activity之间通信原理以及例子
参考文章 http://blog.csdn.net/guozh/article/details/25327685#comments Activity和fragment通信方式一般有3种方法 1.在fr ...
- Android笔记之Fragment中创建ViewModel的正确方式
之前一直都是这么写的 pageViewModel = ViewModelProviders.of(this).get(PageViewModel.class); //参数this是当前fragment ...
- Fragment的创建以及与activity的参数传递
点击下面不同的TextView变化不同的Fragment avtivity与Fragment之间传递消息不能使用构造器传递,用bunder传递 首先写一个含有FrameLayout(这个布局最佳),里 ...
随机推荐
- SpringBoot:处理跨域请求
一.跨域背景 1.1 何为跨域? Url的一般格式: 协议 + 域名(子域名 + 主域名) + 端口号 + 资源地址 示例: https://www.dustyblog.cn:8080/say/Hel ...
- 搭建SFTP服务器,允许一个或多个用户拥有一个或多个目录的rwx权限
1.引言 sftp可以为传输文件提供一种安全的网络的加密方法.sftp 与 ftp 有着几乎一样的语法和功能.SFTP 为 SSH的其中一部分,是一种传输档案至 Blogger 伺服器的安全方式.其实 ...
- JVM内存机制与垃圾收集器总结
本文目录 1. JVM内存组成结构 2. JVM内存回收 3. 垃圾收集器与算法 4. jdk1.6中class文件结构 5. jdk1.6 1.7 1.8比较 1. JVM内存组成结构 JVM栈由堆 ...
- 简单易懂的banner图滚动源代码
banner图左右滚动简单易懂源代码 1 样式展示 css代码: * { padding: 0px; margin: 0px; } .banner { width: 100%; height: 450 ...
- Java网络编程之URL和URI
Java网络编程之URL与URI 一.URL与URI简介 URI = Universal Resource Identifier 统一资源标志符 URL = Universal Resource Lo ...
- 六大设计原则(C#)
为什么要有设计原则,我觉得一张图片就可以解释这一切 一.单一职责原则(SRP) 对于一个类而言,应该只有一个发生变化的原因.(单一职责不仅仅是指类) 如果一个模块需要修改,它肯定是有原因的,除此原因之 ...
- VS code 进行 flutter 调试时启动后就停止,无法调试的问题
在编写flutter时,更新需要按 r 或着 R,这就有点麻烦,当然强大的VS code给我们提供了自动更新的功能,那就是调试功能. 首先需要给VS code安装Flutter与Dart插件. 在VS ...
- 配置springboot项目使用外部tomcat
配置springboot项目使用外部tomcat 1.在pom文件中添加依赖 <!--使用自带的tomcat--> <dependency> <groupId>or ...
- HTML(五)列表,区块,布局,表单和输入
HTML 列表 无序列表 Coffee Tea Milk 默认是圆点,也可以 圆圈 正方形 有序列表 Coffee Tea Milk Coffee Tea Milk 默认是用数字排序 大写字母 小写字 ...
- FEL,项目实装记录
FEL,即Fast EL ,版本0.8,具体内容我就不贴了,自行百度 实装遇到的问题: Spring Boot 打包后无法进行表达式编译. 根据百度以及源码,确定这东西是在用JavaCompiler将 ...
