Python实现自动化监控远程服务器
最近发现Python课器做很多事情,在监控服务器有其独特的优势,耗费资源少,开发周期短。
首先我们做一个定时或者实时脚本timedtask.py,让其定时监控目标服务器,两种方式:
第一种:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2017/11/27 15:59
# @Desc : 定时任务,以需要的时间间隔执行某个命令
# @File : timedtask.py
# @Software: PyCharm import time, os
from monitorserver import alltask def roll_back(cmd, inc = 60):
while True:
#执行方法,函数
alltask()
time.sleep(inc) roll_back("echo %time%", 5)
第二种:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2017/11/27 15:59
# @Desc : 定时任务,以需要的时间间隔执行某个命令
# @File : timedtask.py
# @Software: PyCharm import time, os def roll_back(cmd, inc = 60):
while True:
#监控代码文件所在位置
os.system('python /home/../monitorserver.py');
time.sleep(inc) roll_back("echo %time%", 5)
做过监控应该都知道,我们主要监控服务器,负载均衡、磁盘、内存、CPU、网络接口(流量)、端口代码,主要针对这些,我做了以下远程监控,第一种和第二种监控代码一样,代码monitorserver.py如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2017/11/27 15:59
# @Desc : 服务器监控代码
# @File : monitorserver.py
# @Software: PyCharm import pexpect
import re import time
import threading """
主方法
127.0.0.1#远程服务器ip地址
"""
def ssh_command(user, host, password, command):
ssh_new_key = 'Are you sure you want to continue connecting'
child = pexpect.spawn('ssh -l %s %s %s' % (user, host, command))
i = child.expect([pexpect.TIMEOUT, ssh_new_key, 'password: '])
if i == 0:
print 'ERROR!'
print 'SSH could not login. Here is what SSH said:'
print child.before, child.after
return None
if i == 1:
child.sendline('yes')
child.expect('password: ')
i = child.expect([pexpect.TIMEOUT, 'password: '])
if i == 0:
print 'ERROR!'
print 'SSH could not login. Here is what SSH said:'
print child.before, child.after
return None
child.sendline(password)
return child """
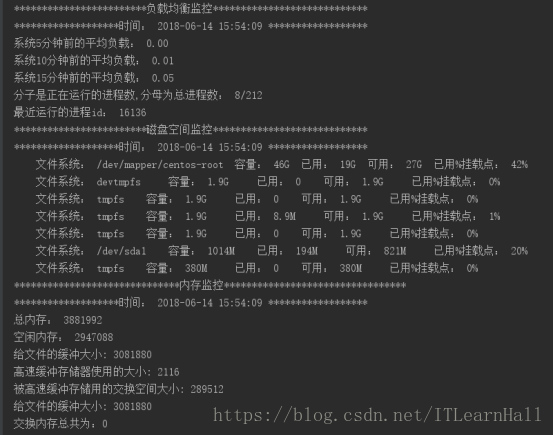
内存监控
"""
def mem_info(): child = ssh_command("远程服务器用户名", "127.0.0.1", "远程服务器密码", "cat /proc/meminfo")
child.expect(pexpect.EOF)
mem = child.before
mem_values = re.findall("(\d+)\ kB", mem)
MemTotal = mem_values[0]
MemFree = mem_values[1]
Buffers = mem_values[2]
Cached = mem_values[3]
SwapCached=mem_values[4]
SwapTotal = mem_values[13]
SwapFree = mem_values[14]
print '******************************内存监控*********************************'
print "*******************时间:", time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime()), "******************"
print "总内存:",MemTotal
print "空闲内存:", MemFree
print "给文件的缓冲大小:",Buffers
print "高速缓冲存储器使用的大小:", Cached
print "被高速缓冲存储用的交换空间大小:", SwapCached
print "给文件的缓冲大小:", Buffers
if int(SwapTotal) == 0:
print u"交换内存总共为:0"
else:
Rate_Swap = 100 - 100*int(SwapFree)/float(SwapTotal)
print u"交换内存利用率:", Rate_Swap
Free_Mem = int(MemFree) + int(Buffers) + int(Cached)
Used_Mem = int(MemTotal) - Free_Mem
Rate_Mem = 100*Used_Mem/float(MemTotal)
print u"内存利用率:", str("%.2f" % Rate_Mem), "%" """
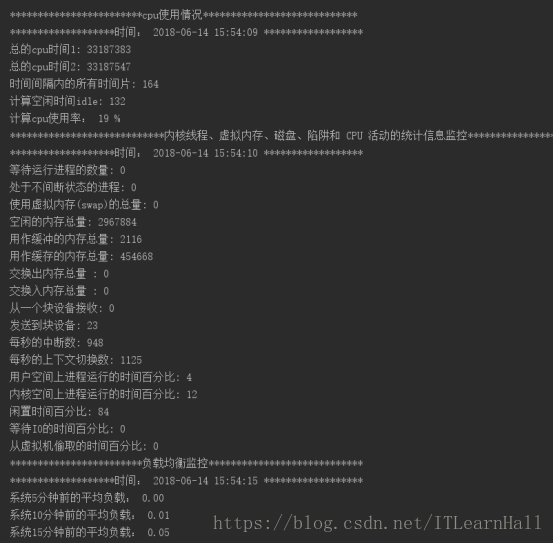
内核线程、虚拟内存、磁盘、陷阱和 CPU 活动的统计信息
"""
def vm_stat_info():
child = ssh_command("远程服务器用户名", "127.0.0.1", "远程服务器密码", "vmstat 1 2 | tail -n 1")
child.expect(pexpect.EOF)
vmstat_info = child.before.strip().split()
processes_waiting = vmstat_info[0]
processes_sleep = vmstat_info[1]
swpd = vmstat_info[2]
free = vmstat_info[3]
buff = vmstat_info[4]
cache = vmstat_info[5]
si = vmstat_info[6]
so = vmstat_info[7]
io_bi = vmstat_info[8]
io_bo = vmstat_info[9]
system_interrupt = vmstat_info[10]
system_context_switch = vmstat_info[11]
cpu_user = vmstat_info[12]
cpu_sys = vmstat_info[13]
cpu_idle = vmstat_info[14]
cpu_wait = vmstat_info[15]
st=vmstat_info[16]
print '****************************内核线程、虚拟内存、磁盘、陷阱和 CPU 活动的统计信息监控****************************'
print "*******************时间:", time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime()), "******************"
print "等待运行进程的数量:", processes_waiting
print "处于不间断状态的进程:", processes_sleep
print "使用虚拟内存(swap)的总量:", swpd
print "空闲的内存总量:", free
print "用作缓冲的内存总量:", buff
print "用作缓存的内存总量:", cache
print "交换出内存总量 :", si
print "交换入内存总量 :", so
print "从一个块设备接收:", io_bi
print "发送到块设备:", io_bo
print "每秒的中断数:", system_interrupt
print "每秒的上下文切换数:", system_context_switch
print "用户空间上进程运行的时间百分比:", cpu_user
print "内核空间上进程运行的时间百分比:", cpu_sys
print "闲置时间百分比:", cpu_idle
print "等待IO的时间百分比:", cpu_wait
print "从虚拟机偷取的时间百分比:", st '''
cpu监控
'''
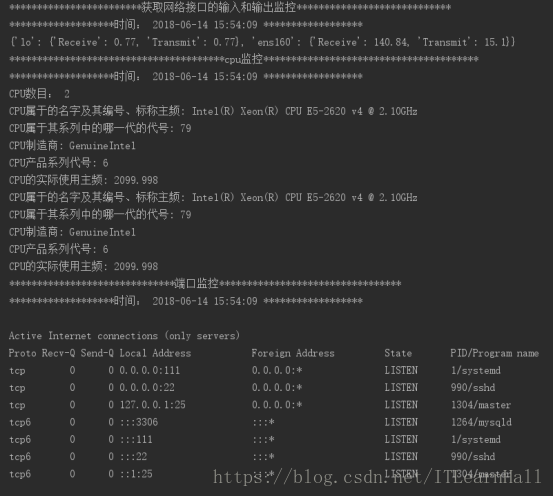
def cpu_info():
child = ssh_command("远程服务器用户名", "127.0.0.1", "远程服务器密码", "cat /proc/cpuinfo")
child.expect(pexpect.EOF)
cpuinfo = child.before
cpu_num = re.findall('processor.*?(\d+)', cpuinfo)[-1]
cpu_num = str(int(cpu_num) + 1)
print '***************************************cpu监控***************************************'
print "*******************时间:", time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime()), "******************"
print u"CPU数目:", cpu_num
li = cpuinfo.replace('\t', '').split('\r')
CPUinfo = {}
procinfo = {}
nprocs = 0
for line in li:
if line.find("processor") > -1:
CPUinfo['CPU%s' % nprocs] = procinfo
nprocs = nprocs + 1
else:
if len(line.split(':')) == 2:
procinfo[line.split(':')[0].strip()] = line.split(':')[1].strip()
else:
procinfo[line.split(':')[0].strip()] = ''
for processor in CPUinfo.keys():
print "CPU属于的名字及其编号、标称主频:",CPUinfo[processor]['model name']
print "CPU属于其系列中的哪一代的代号:", CPUinfo[processor]['model']
print "CPU制造商:", CPUinfo[processor]['vendor_id']
print "CPU产品系列代号:", CPUinfo[processor]['cpu family']
print "CPU的实际使用主频:", CPUinfo[processor]['cpu MHz'] """
负载均衡
"""
def load_stat():
child = ssh_command("远程服务器用户名", "127.0.0.1", "远程服务器密码", "cat /proc/loadavg")
child.expect(pexpect.EOF)
loadavgs = child.before.strip().split()
print '************************负载均衡监控****************************'
print "*******************时间:",time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime()),"******************"
print "系统5分钟前的平均负载:", loadavgs[0]
print "系统10分钟前的平均负载:", loadavgs[1]
print "系统15分钟前的平均负载:", loadavgs[2]
print "分子是正在运行的进程数,分母为总进程数:",loadavgs[3]
print "最近运行的进程id:", loadavgs[4] """
获取网络接口的输入和输出
"""
def ionetwork():
child = ssh_command("远程服务器用户名", "127.0.0.1", "远程服务器密码", "cat /proc/net/dev")
child.expect(pexpect.EOF)
netdata = child.before
li = netdata.strip().split('\n')
print '************************获取网络接口的输入和输出监控****************************'
print "*******************时间:",time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime()),"******************"
net = {}
for line in li[2:]:
line = line.split(":")
eth_name = line[0].strip()
# if eth_name != 'lo':
net_io = {}
net_io['Receive'] = round(float(line[1].split()[0]) / (1024.0 * 1024.0), 2)
net_io['Transmit'] = round(float(line[1].split()[8]) / (1024.0 * 1024.0), 2)
net[eth_name] = net_io
print net """
磁盘空间监控
"""
def disk_stat():
child = ssh_command("远程服务器用户名", "127.0.0.1", "远程服务器密码", "df -h")
child.expect(pexpect.EOF)
disk = child.before
disklist = disk.strip().split('\n')
disklists=[]
for disk in disklist:
disklists.append(disk.strip().split())
print '************************磁盘空间监控****************************'
print "*******************时间:", time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime()), "******************"
for i in disklists[1:]:
print "\t文件系统:", i[0],
print "\t容量:", i[1],
print "\t已用:", i[2],
print "\t可用:", i[3],
print "\t已用%挂载点:", i[4] """
端口监控
一般是远程服务器用户名用户
"""
def getComStr():
child = ssh_command("远程服务器用户名", "127.0.0.1", "远程服务器密码", "netstat -tpln")
child.expect(pexpect.EOF)
Com = child.before
print '******************************端口监控*********************************'
print "*******************时间:", time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime()), "******************"
print Com """
获取网络接口的输入和输出
"""
def cpu():
child = ssh_command("远程服务器用户名", "127.0.0.1", "远程服务器密码", 'cat /proc/stat | grep "cpu "')
child.expect(pexpect.EOF)
child1 = ssh_command("远程服务器用户名", "127.0.0.1", "远程服务器密码", 'cat /proc/stat | grep "cpu "')
child1.expect(pexpect.EOF)
cpus = child.before.strip().split()
cpus1 = child1.before.strip().split()
print '************************cpu使用情况****************************'
print "*******************时间:",time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime()),"******************"
T1=int(cpus[1])+int(cpus[2])+int(cpus[3])+int(cpus[4])+int(cpus[5])+int(cpus[6])+int(cpus[8])+int(cpus[9])
T2=int(cpus1[1]) + int(cpus1[2]) + int(cpus1[3]) + int(cpus1[4] )+ int(cpus1[5] )+int( cpus1[6] )+ int(cpus1[8] )+ int(cpus1[9])
Tol=T2-T1
Idle=int(cpus1[4]) - int(cpus[4])
print '总的cpu时间1:',T1
print '总的cpu时间2:', T2
print '时间间隔内的所有时间片:', Tol
print '计算空闲时间idle:', Idle
print "计算cpu使用率:",100*(Tol-Idle)/Tol,"%" """
第一种执行
"""
def alltask():
try:
threads = []
t1 = threading.Thread(target=mem_info)
threads.append(t1)
t2 = threading.Thread(target=vm_stat_info)
threads.append(t2)
t3 = threading.Thread(target=cpu_info)
threads.append(t3)
t4 = threading.Thread(target=load_stat)
threads.append(t4)
t5 = threading.Thread(target=ionetwork)
threads.append(t5)
t6 = threading.Thread(target=disk_stat)
threads.append(t6)
t7 = threading.Thread(target=getComStr)
threads.append(t7)
t8 = threading.Thread(target=cpu)
threads.append(t8)
for n in range(len(threads)):
threads[n].start()
except Exception, e:
print str(e) """
第二种执行
"""
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
threads = []
t1 = threading.Thread(target=mem_info)
threads.append(t1)
t2 = threading.Thread(target=vm_stat_info)
threads.append(t2)
t3 = threading.Thread(target=cpu_info)
threads.append(t3)
t4 = threading.Thread(target=load_stat)
threads.append(t4)
t5 = threading.Thread(target=ionetwork)
threads.append(t5)
t6 = threading.Thread(target=disk_stat)
threads.append(t6)
t7 = threading.Thread(target=getComStr)
threads.append(t7)
t8 = threading.Thread(target=cpu)
threads.append(t8)
for n in range(len(threads)):
threads[n].start()
except Exception, e:
print str(e)
监控结果如下:
接下来做的是把监控结果可视化,即可,可惜没时间做,就交给各位了!!!
花了两天时间整理的,分享给大家,希望对各位有帮助!!!
Python实现自动化监控远程服务器的更多相关文章
- 通过SSIS监控远程服务器Windows服务并发送邮件报警!
利用SSIS不仅可以做BI项目的ETL,而且还可以做一些系统监控和维护工作,由于之前供应商写的Windows服务是读取ESB的消息进行处理,且通过OA流程与访客系统进行了集成,无论是ESB出现状况,还 ...
- 通过SSIS监控远程服务器磁盘空间并发送邮件报警!
由于之前ESB是供应商部署的,且部署在C盘(C盘空间很小,还添加了很多ESB的windows服务日志在C盘,很容易把C盘空间占满,导致ESB服务运行宕机,几乎每隔几周发生一次事故,需要人工干预处理,不 ...
- 关于nagios监控远程服务器对服务器性能影响的测试
1. Nagios监视远程服务器时,是通过在控制端执行以下命令进行数据收集的: /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_http -I 192.168.16.11 /us ...
- 使用VisualVM监控远程服务器JVM
VisualVM是JDK自带的一款全能型性能监控和故障分析工具,包括对CPU使用.JVM堆内存消耗.线程.类加载的实时监控,内存dump文件分析,垃圾回收运行情况的可视化分析等,对故障排查和性能调优很 ...
- VisualVM监控远程服务器JVM
VisualVM是JDK自带的一款全能型性能监控和故障分析工具,包括对CPU使用.JVM堆内存消耗.线程.类加载的实时监控,内存dump文件分析,垃圾回收运行情况的可视化分析等,对故障排查和性能调优很 ...
- 【Java】监控远程服务器JVM
今天在用JMeter进行测试的时候,发现线程并发量到50的时候会导致阻塞情况,于是需要监控远程JVM,那么如何监控远程JVM呢? 首先,找到启动计量引擎的sh文件,例如我目前的计量引擎启停文件为str ...
- python利用paramiko连接远程服务器执行命令
python中的paramiko模块是用来实现ssh连接到远程服务器上的库,在进行连接的时候,可以用来执行命令,也可以用来上传文件. 1.得到一个连接的对象 在进行连接的时候,可以使用如下的代码: d ...
- JVM监控远程服务器
1. 首先配置服务器端,进入服务器tomcat的bin目录下,打开catalina.sh配置文件,xxx为服务器配置路径. # cd /xxx/apache-tomcat-/bin # vim cat ...
- 使用WMI和性能计数器监控远程服务器权限设置
应用场景:在web服务器中,通过.NET编码使用WMI查询远程服务器的一些硬件配置信息,使用性能计数器查询远程机器的运行时资源使用情况.在网上没有找到相关的东西,特记录与大家共享. 将web服务器和所 ...
随机推荐
- day 21作业
目录 一.定义一个类:圆形,该类有半径,周长,面积等属性,将半径隐藏起来,将周长与面积开放 二.使用abc模块定义一个phone抽象类 并编写一个具体的实现类 一.定义一个类:圆形,该类有半径,周长, ...
- 一个纯CSS实现的卡片翻转效果
先上代码 <div id="box"> <div class="front">正面</div> <div class= ...
- Java自动化测试框架-02 - TestNG之理论实践 - 纸上得来终觉浅,绝知此事要躬行(详细教程)
理论 TestNG,即Testing, NextGeneration,下一代测试技术,是一套根据JUnit 和NUnit思想而构建的利用注释来强化测试功能的一个测试框架,即可以用来做单元测试,也可以用 ...
- 基于STM32F1与NRF24L01模块的SPI简单通信
一.前言 1.简介: 本文是基于STM32F1,将数据发送至NRF模块的寄存器,并将数据重新读取,通过串口发送出来的简单SPI单通信. 2.SPI简介: 调过STM8的都已经对SPI有所了解,调法都一 ...
- Nmon安装
下载对应系统的nomn工具(我用centos6.5_64位下载的是nmon_linux_14i.tar.gz) mkdir /nmon cd /nmon 导入nmon的tar.gz包解压 tar -z ...
- 手写OOXML文档——导出xlsx格式表格文档
一.准备工作: 2个js库,另外把样式文件抽离出来 require('file-saver'); import JSZip from 'jszip' import {stylesData,theme1 ...
- python学习-流程控制(四)
学习笔记中的源码:传送门 4.2if分支结构 if语句有三种形式: 如果 if 条件为“真”,程序就会执行 i f条件后面的多条语句:否则就会依次判断 elif 条件,如果 elif 条件为“真”,程 ...
- 05jmeter-responses中有多组json数据,提取同一条json数据的两个字段
某接口返回结果如上图,取id和groupNo 1.读取确定的某条json数据:如取第一条,一个JSON Extractor即可实现 2.随机读取某条json数据: 需要两个JSON Extractor ...
- CentOS7使用‘中科大源’
中科大的源质量速度都不错,推荐使用. 这里列出CentOS 7的Base和epel的源. 进入/etc/yum.repos.d/中,将原本的几个repo文件备份,之后新建三个repo文件 内容如下: ...
- vue系列---snabbdom.js使用及源码分析(九)
一:什么是snabbdom? 在学习Vue或React中,我们了解最多的就是虚拟DOM,虚拟DOM可以看作是一颗模拟了DOM的Javascript树,主要是通过vnode实现一个无状态的组件,当组件状 ...