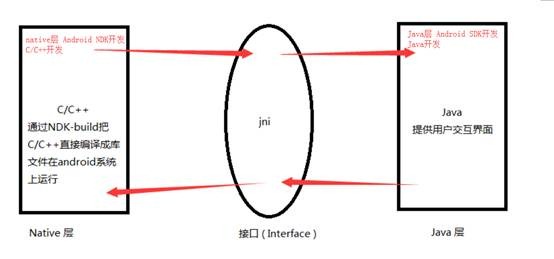
Native层和so接口和Java层
一、Java层加载so文件
Android在Java层加载so的接口是System.loadLibrary()逐级调用的过程:
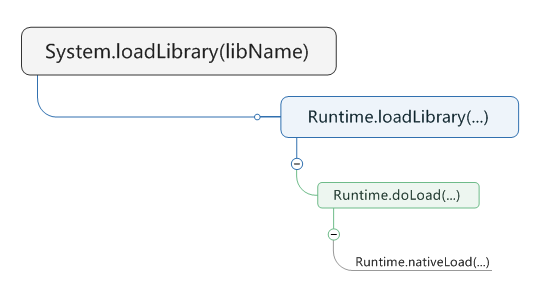
System.loadLibrary()系统源码:
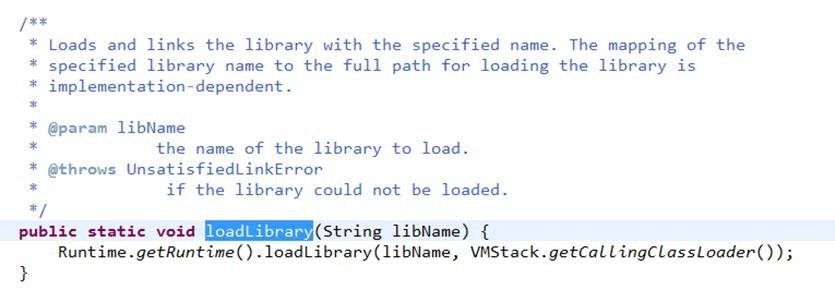
987 public static void loadLibrary(String libName) {
988 Runtime.getRuntime().loadLibrary(libName, VMStack.getCallingClassLoader());
989 }
例程 System.loadLibrary(“xxx”) [xxx:libname名称]
Ctrl+左键Loadlibrary跟踪(如果不显示代码,添加SDK目录下\sources\android-18文件夹)
Ctrl+左键 Runtime.getRuntime().loadLibrary() 中的 loadLibrary跟踪

系统重载了loadLibrary()函数察看重载的 loadLibrary()
其中String libraryName参数为so文件的绝对路径
* Searches for and loads the given shared library using the given ClassLoader.
*/
void loadLibrary(String libraryName, ClassLoader loader) {
if (loader != null) {
String filename = loader.findLibrary(libraryName);
if (filename == null) {
// It's not necessarily true that the ClassLoader used
// System.mapLibraryName, but the default setup does, and it's
// misleading to say we didn't find "libMyLibrary.so" when we
// actually searched for "liblibMyLibrary.so.so".
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError(loader + " couldn't find \"" +
System.mapLibraryName(libraryName) + "\"");
}
String error = doLoad(filename, loader);
if (error != null) {
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError(error);
}
return;
} String filename = System.mapLibraryName(libraryName);
List<String> candidates = new ArrayList<String>();
String lastError = null;
for (String directory : mLibPaths) {
String candidate = directory + filename;
candidates.add(candidate); if (IoUtils.canOpenReadOnly(candidate)) {
String error = doLoad(candidate, loader);
if (error == null) {
return; // We successfully loaded the library. Job done.
}
lastError = error;
}
} if (lastError != null) {
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError(lastError);
}
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError("Library " + libraryName + " not found; tried " + candidates);
}
loadLibrary()
其中doLoad()为加载函数,源码:
private String doLoad(String name, ClassLoader loader) {
// Android apps are forked from the zygote, so they can't have a custom LD_LIBRARY_PATH,
// which means that by default an app's shared library directory isn't on LD_LIBRARY_PATH.
// The PathClassLoader set up by frameworks/base knows the appropriate path, so we can load
// libraries with no dependencies just fine, but an app that has multiple libraries that
// depend on each other needed to load them in most-dependent-first order.
// We added API to Android's dynamic linker so we can update the library path used for
// the currently-running process. We pull the desired path out of the ClassLoader here
// and pass it to nativeLoad so that it can call the private dynamic linker API.
// We didn't just change frameworks/base to update the LD_LIBRARY_PATH once at the
// beginning because multiple apks can run in the same process and third party code can
// use its own BaseDexClassLoader.
// We didn't just add a dlopen_with_custom_LD_LIBRARY_PATH call because we wanted any
// dlopen(3) calls made from a .so's JNI_OnLoad to work too.
// So, find out what the native library search path is for the ClassLoader in question...
String ldLibraryPath = null;
if (loader != null && loader instanceof BaseDexClassLoader) {
ldLibraryPath = ((BaseDexClassLoader) loader).getLdLibraryPath();
}
// nativeLoad should be synchronized so there's only one LD_LIBRARY_PATH in use regardless
// of how many ClassLoaders are in the system, but dalvik doesn't support synchronized
// internal natives.
synchronized (this) {
return nativeLoad(name, loader, ldLibraryPath);
}
}
doLoad()
nativeLoad()用来加载name指向的so文件,nativeLoad()是Runtime类的一个native函数,在native层对应Runtime_nativeLoad()。
至此Java层的so文件加载跟踪完。根据nativeLoad进入Native层跟踪
二、nativeload开始 Native层的调用
Nativeload函数分析图
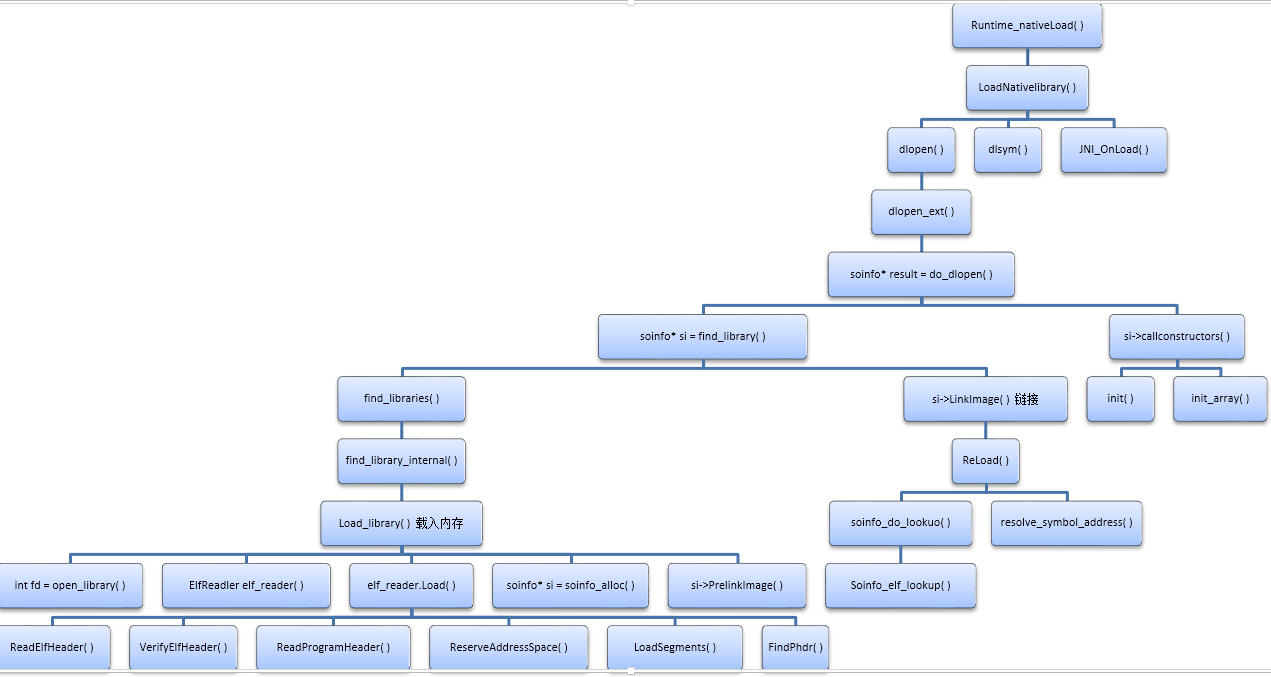
分三个阶段:
1. so文件加载
在java_lang_Runtime.cc文件中
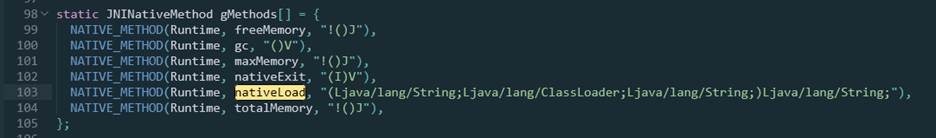
可知Java层的nativeLoad对应Native层的Runtime_nativeLoad()
46static jstring Runtime_nativeLoad(JNIEnv* env, jclass, jstring javaFilename, jobject javaLoader, jstring javaLdLibraryPath) {
ScopedUtfChars filename(env, javaFilename);
if (filename.c_str() == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
if (javaLdLibraryPath != NULL) {
ScopedUtfChars ldLibraryPath(env, javaLdLibraryPath);
if (ldLibraryPath.c_str() == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
void* sym = dlsym(RTLD_DEFAULT, "android_update_LD_LIBRARY_PATH");
if (sym != NULL) {
typedef void (*Fn)(const char*);
Fn android_update_LD_LIBRARY_PATH = reinterpret_cast<Fn>(sym);
(*android_update_LD_LIBRARY_PATH)(ldLibraryPath.c_str());
} else {
LOG(ERROR) << "android_update_LD_LIBRARY_PATH not found; .so dependencies will not work!";
}
}
std::string detail;
{
ScopedObjectAccess soa(env);
StackHandleScope<> hs(soa.Self());
Handle<mirror::ClassLoader> classLoader(
hs.NewHandle(soa.Decode<mirror::ClassLoader*>(javaLoader)));
JavaVMExt* vm = Runtime::Current()->GetJavaVM();
// 调用JavaVMExt类的LoadNativeLibrary()加载so文件,detail用于存储加载过程中的Log信息
bool success = vm->LoadNativeLibrary(filename.c_str(), classLoader, &detail);
if (success) {
return nullptr;
}
}
// Don't let a pending exception from JNI_OnLoad cause a CheckJNI issue with NewStringUTF.
env->ExceptionClear();
return env->NewStringUTF(detail.c_str());
}
Runtime_nativeLoad()
根据代码加载so的分析,查看LoadNativeLibrary()源代码
3225bool JavaVMExt::LoadNativeLibrary(const std::string& path,
Handle<mirror::ClassLoader> class_loader,
std::string* detail) {
detail->clear(); // 是否加载过该so文件,如果是就不需要再次加载
SharedLibrary* library;
Thread* self = Thread::Current();
{
// TODO: move the locking (and more of this logic) into Libraries.
MutexLock mu(self, libraries_lock);
library = libraries->Get(path);
}
if (library != nullptr) {
if (library->GetClassLoader() != class_loader.Get()) {
// The library will be associated with class_loader. The JNI
// spec says we can't load the same library into more than one
// class loader.
StringAppendF(detail, "Shared library \"%s\" already opened by "
"ClassLoader %p; can't open in ClassLoader %p",
path.c_str(), library->GetClassLoader(), class_loader.Get());
LOG(WARNING) << detail;
return false;
}
VLOG(jni) << "[Shared library \"" << path << "\" already loaded in "
<< "ClassLoader " << class_loader.Get() << "]";
if (!library->CheckOnLoadResult()) {
StringAppendF(detail, "JNI_OnLoad failed on a previous attempt "
"to load \"%s\"", path.c_str());
return false;
}
return true;
} // 没有加载过该so,需要加载
self->TransitionFromRunnableToSuspended(kWaitingForJniOnLoad);
const char* path_str = path.empty() ? nullptr : path.c_str();
// 调用dlopen()加载so文件
void* handle = dlopen(path_str, RTLD_LAZY);
bool needs_native_bridge = false;
if (handle == nullptr) {
if (android::NativeBridgeIsSupported(path_str)) {
handle = android::NativeBridgeLoadLibrary(path_str, RTLD_LAZY);
needs_native_bridge = true;
}
}
self->TransitionFromSuspendedToRunnable(); VLOG(jni) << "[Call to dlopen(\"" << path << "\", RTLD_LAZY) returned " << handle << "]"; if (handle == nullptr) {
*detail = dlerror();
LOG(ERROR) << "dlopen(\"" << path << "\", RTLD_LAZY) failed: " << *detail;
return false;
} // Create a new entry.
// TODO: move the locking (and more of this logic) into Libraries.
bool created_library = false;
{
MutexLock mu(self, libraries_lock);
library = libraries->Get(path);
if (library == nullptr) { // 加载完后,新建SharedLibrary对象,并将path存入libraries
library = new SharedLibrary(path, handle, class_loader.Get());
libraries->Put(path, library);
created_library = true;
}
}
if (!created_library) {
LOG(INFO) << "WOW: we lost a race to add shared library: "
<< "\"" << path << "\" ClassLoader=" << class_loader.Get();
return library->CheckOnLoadResult();
} VLOG(jni) << "[Added shared library \"" << path << "\" for ClassLoader " << class_loader.Get()
<< "]"; bool was_successful = false;
void* sym = nullptr;
if (UNLIKELY(needs_native_bridge)) {
library->SetNeedsNativeBridge();
sym = library->FindSymbolWithNativeBridge("JNI_OnLoad", nullptr);
} else {
sym = dlsym(handle, "JNI_OnLoad");// 找到JNI_OnLoad()
} if (sym == nullptr) {
VLOG(jni) << "[No JNI_OnLoad found in \"" << path << "\"]";
was_successful = true;
} else {
// Call JNI_OnLoad. We have to override the current class
// loader, which will always be "null" since the stuff at the
// top of the stack is around Runtime.loadLibrary(). (See
// the comments in the JNI FindClass function.)
typedef int (*JNI_OnLoadFn)(JavaVM*, void*);
JNI_OnLoadFn jni_on_load = reinterpret_cast<JNI_OnLoadFn>(sym);
StackHandleScope<> hs(self);
Handle<mirror::ClassLoader> old_class_loader(hs.NewHandle(self->GetClassLoaderOverride()));
self->SetClassLoaderOverride(class_loader.Get()); int version = ;
{
ScopedThreadStateChange tsc(self, kNative);
VLOG(jni) << "[Calling JNI_OnLoad in \"" << path << "\"]";
// 调用JNI_Onload()
version = (*jni_on_load)(this, nullptr);
} if (runtime->GetTargetSdkVersion() != && runtime->GetTargetSdkVersion() <= ) {
fault_manager.EnsureArtActionInFrontOfSignalChain();
}
self->SetClassLoaderOverride(old_class_loader.Get()); if (version == JNI_ERR) {
StringAppendF(detail, "JNI_ERR returned from JNI_OnLoad in \"%s\"", path.c_str());
} else if (IsBadJniVersion(version)) {
StringAppendF(detail, "Bad JNI version returned from JNI_OnLoad in \"%s\": %d",
path.c_str(), version);
// It's unwise to call dlclose() here, but we can mark it
// as bad and ensure that future load attempts will fail.
// We don't know how far JNI_OnLoad got, so there could
// be some partially-initialized stuff accessible through
// newly-registered native method calls. We could try to
// unregister them, but that doesn't seem worthwhile.
} else {
was_successful = true;
}
VLOG(jni) << "[Returned " << (was_successful ? "successfully" : "failure")
<< " from JNI_OnLoad in \"" << path << "\"]";
} library->SetResult(was_successful);
return was_successful;
}
LoadNativeLibrary()
LoadNativeLibrary()函数执行过程:
1. 判断so文件是否已经加载,若已经加载判断与class_Loader是否重复
2. 如果so文件没有被加载,dlopen()打开so文件加载
3. 调用dlsym() 加载 “JNI_OnLoad”函数地址
4. 调用JNI_OnLoad()函数
至此Native层so文件加载完成,根据分析结果追踪dlopen()
dlopen()源码: /bionic/linker/dlfcn.cpp
82void* dlopen(const char* filename, int flags) {
83 return dlopen_ext(filename, flags, nullptr);
84}
跟踪dlopen_ext()
68static void* dlopen_ext(const char* filename, int flags, const android_dlextinfo* extinfo) {
ScopedPthreadMutexLocker locker(&g_dl_mutex);
soinfo* result = do_dlopen(filename, flags, extinfo);
if (result == nullptr) {
__bionic_format_dlerror("dlopen failed", linker_get_error_buffer());
return nullptr;
}
return result;
}
dlopen_ext()
根据代码filename指向的 .so文件,返回值为soinfo*,指向so文件指针,所以dlopen_ext()返回的指针指向 soinfo对象
跟踪 do_dlopen():/bionic/linker/linker.cpp
1041soinfo* do_dlopen(const char* name, int flags, const android_dlextinfo* extinfo) {
if ((flags & ~(RTLD_NOW|RTLD_LAZY|RTLD_LOCAL|RTLD_GLOBAL|RTLD_NOLOAD)) != ) {
DL_ERR("invalid flags to dlopen: %x", flags);
return nullptr;
}
if (extinfo != nullptr) {
if ((extinfo->flags & ~(ANDROID_DLEXT_VALID_FLAG_BITS)) != ) {
DL_ERR("invalid extended flags to android_dlopen_ext: 0x%" PRIx64, extinfo->flags);
return nullptr;
}
if ((extinfo->flags & ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_LIBRARY_FD) == &&
(extinfo->flags & ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_LIBRARY_FD_OFFSET) != ) {
DL_ERR("invalid extended flag combination (ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_LIBRARY_FD_OFFSET without ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_LIBRARY_FD): 0x%" PRIx64, extinfo->flags);
return nullptr;
}
}
// extinfo为null
protect_data(PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE);
soinfo* si = find_library(name, flags, extinfo);
if (si != nullptr) {
// 初始化
si->CallConstructors();
}
protect_data(PROT_READ);
return si;
}
do_dlopen()
find_library()得到soinfo对象,分析源码需要跟踪find_library()和CallConstructors(),根据代码顺序继续分析
do_dlopen()总共两部分
do_dlopen()的第一部分:
find_library():
968static soinfo* find_library(const char* name, int dlflags, const android_dlextinfo* extinfo) {
if (name == nullptr) {
somain->ref_count++;
return somain;
}
soinfo* si;
if (!find_libraries(&name, , &si, nullptr, , dlflags, extinfo)) {
return nullptr;
}
return si;
}
find_library()
根据代码跟踪 find_libraries()的参数:/bionic/linker/linker.cpp
find_libraries()参数:
const char* const library_names[], //so文件名的数组
soinfo* soinfos[], //指向soinfos数组的指针,将library_names中so的结果存入soinfos数组中
soinfo* ld_preloads[], //ld_preloads = NULL
size_t ld_preloads_size, //ld_preloads_size = 0
int dlflags,
const android_dlextinfo* extinfo //extinfo = NULL
896static bool find_libraries(const char* const library_names[], size_t library_names_size, soinfo* soinfos[],
soinfo* ld_preloads[], size_t ld_preloads_size, int dlflags, const android_dlextinfo* extinfo) {
// Step 1: prepare.
// a.宽度优先搜索的栈,父节点的依赖库为其子节点,根节点是代加载的.so文件
LoadTaskList load_tasks;
// b.初始化
for (size_t i = ; i < library_names_size; ++i) {
const char* name = library_names[i];
load_tasks.push_back(LoadTask::create(name, nullptr));
} // c.该so文件和其它所有依赖库的列表
SoinfoLinkedList found_libs;
size_t soinfos_size = ; auto failure_guard = make_scope_guard([&]() {
// Housekeeping
load_tasks.for_each([] (LoadTask* t) {
LoadTask::deleter(t);
}); for (size_t i = ; i<soinfos_size; ++i) {
soinfo_unload(soinfos[i]);
}
}); // Step 2:
// 优先搜索加载该.so文件和其依赖库 for (LoadTask::unique_ptr task(load_tasks.pop_front()); task.get() != nullptr; task.reset(load_tasks.pop_front())) {
// 加载so文件
soinfo* si = find_library_internal(load_tasks, task->get_name(), dlflags, extinfo);// extinfo == null
if (si == nullptr) {
return false;
}
// needed_by依赖于si
soinfo* needed_by = task->get_needed_by(); if (is_recursive(si, needed_by)) {
// 判断是否有递归依赖关系
return false;
}
// si引用计数
si->ref_count++;
if (needed_by != nullptr) {
needed_by->add_child(si);
}
found_libs.push_front(si); // When ld_preloads is not null first
// ld_preloads_size libs are in fact ld_preloads.
if (ld_preloads != nullptr && soinfos_size < ld_preloads_size) {
ld_preloads[soinfos_size] = si;
} if (soinfos_size<library_names_size) {
// 只将library_names中对应的soinfos存入soinfos
soinfos[soinfos_size++] = si;
}
} // Step 3:
// 链接加载库
soinfo* si;
while ((si = found_libs.pop_front()) != nullptr) {
if ((si->flags & FLAG_LINKED) == ) {
// 如果si没有链接,对si进行链接
if (!si->LinkImage(extinfo)) {
// extinfo == null
return false;
}
si->flags |= FLAG_LINKED;
}
} // All is well - found_libs and load_tasks are empty at this point
// and all libs are successfully linked.
failure_guard.disable();
return true;
}
find_libraries()
find_libraries()对library_names[ ]中的so文件加载到内存,进行链接
find_libraries()分三步骤:
第一步:初始化:
a) 加载的so可能以来其他库,采用优先搜索依次加载方式。搜索树中父节点的依赖库为其子节点。根节点是so文件
b) 初始化
c) found_libs是so文件和其依赖库的列表
第二步:宽度优先搜索加载so:
d) find_library_internal()将so载入内存
第三步:对加载的so进行链接:
根据上述分析,查看
find_library_internal()函数源码,用于加载so /bionic/linker/linker.cpp
865static soinfo* find_library_internal(LoadTaskList& load_tasks, const char* name, int dlflags, const android_dlextinfo* extinfo) {// extinfo==null
// 检查是否被加载过
soinfo* si = find_loaded_library_by_name(name);
// 加载过直接返回si,否则调用load_library
if (si == nullptr) {
TRACE("[ '%s' has not been found by name. Trying harder...]", name);
si = load_library(load_tasks, name, dlflags, extinfo);
}
return si;
}
find_library_internal()
跟进查看load_library()源码:
777static soinfo* load_library(LoadTaskList& load_tasks, const char* name, int dlflags, const android_dlextinfo* extinfo) {// extinfo == null
int fd = -; // so文件描述符
off64_t file_offset = ;
ScopedFd file_guard(-);
// 第一部分:
if (extinfo != nullptr && (extinfo->flags & ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_LIBRARY_FD) != ) {
fd = extinfo->library_fd;
if ((extinfo->flags & ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_LIBRARY_FD_OFFSET) != ) {
file_offset = extinfo->library_fd_offset;
}
} else {
// 打开so文件
fd = open_library(name);
if (fd == -) {
DL_ERR("library \"%s\" not found", name);
return nullptr;
}
file_guard.reset(fd);
}
// 文件偏移必须是PAGE_SIZE的整数倍,这里file_offset == 0
if ((file_offset % PAGE_SIZE) != ) {
DL_ERR("file offset for the library \"%s\" is not page-aligned: %" PRId64, name, file_offset);
return nullptr;
}
struct stat file_stat;
if (TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(fstat(fd, &file_stat)) != ) {
// 获取so文件的状态
DL_ERR("unable to stat file for the library \"%s\": %s", name, strerror(errno));
return nullptr;
}
// 因为Linux下可以生成文件的链接文件,这里检查so文件是否以不同名字加载
for (soinfo* si = solist; si != nullptr; si = si->next) {
if (si->get_st_dev() != &&
si->get_st_ino() != &&
si->get_st_dev() == file_stat.st_dev &&
si->get_st_ino() == file_stat.st_ino &&
si->get_file_offset() == file_offset) {
TRACE("library \"%s\" is already loaded under different name/path \"%s\" - will return existing soinfo", name, si->name);
return si;
}
}
if ((dlflags & RTLD_NOLOAD) != ) {
DL_ERR("library \"%s\" wasn't loaded and RTLD_NOLOAD prevented it", name);
return nullptr;
}
// 第二部分:
// 读取ELF头,加载段 file_offset == 0
ElfReader elf_reader(name, fd, file_offset);
if (!elf_reader.Load(extinfo)) {
return nullptr;
}
// 第三部分
// 为soinfo分配空间
soinfo* si = soinfo_alloc(SEARCH_NAME(name), &file_stat, file_offset);
if (si == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
// 加载 so 文件时,mmap 得到的空间的首地址
si->base = elf_reader.load_start();
// ReserveAddressSpace 中开辟的内存空间的大小
si->size = elf_reader.load_size();
// 加载段时的基址,load_bias+p_vaddr 为段的实际内存地址
si->load_bias = elf_reader.load_bias();
// program header 的个数
si->phnum = elf_reader.phdr_count();
// program header table 在内存中的起始地址
si->phdr = elf_reader.loaded_phdr();
if (!si->PrelinkImage()) {
// 解析.dynmaic section
soinfo_free(si);
return nullptr;
}
// 将该so文件依赖的库添加到待加载队列中
for_each_dt_needed(si, [&] (const char* name) {
// si依赖于name的库
load_tasks.push_back(LoadTask::create(name, si));
});
return si;
}
static soinfo *find_loaded_library_by_name(const char* name) {
const char* search_name = SEARCH_NAME(name);
for (soinfo* si = solist; si != nullptr; si = si->next) {
if (!strcmp(search_name, si->name)) {
return si;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
load_library()
load_library()分三个部分:
第一部分:打开.so文件,并判断是否已经加载
内存页的大小:PAGE_SIZE为4096
第二部分:加载.so文件的可加载段
用ElfReader类解析ELF头
根据源码Load()的源码:
135bool ElfReader::Load(const android_dlextinfo* extinfo) {
// ReadElfHeader()读取ELF头结果给ElfReader的Elf32_Ehdr header_,成员变量
return ReadElfHeader() &&
VerifyElfHeader() &&
ReadProgramHeader() &&
ReserveAddressSpace(extinfo) &&
LoadSegments() &&
FindPhdr();
}
Load()
根据ElfReader源码,分析return的返回值的函数源码
VerifyElfHeader():检查ELF头某些字段是否合法,根据源码,ELF头中,byte_ident[16]字段的后10位没有进行校验
159bool ElfReader::VerifyElfHeader() {
// 检查magicNum 与 \177ELF
if (memcmp(header_.e_ident, ELFMAG, SELFMAG) != ) {
DL_ERR("\"%s\" has bad ELF magic", name_);
return false;
}
// 检测ELF为数与目前操作系统的为数是否相同(32位或64位)
int elf_class = header_.e_ident[EI_CLASS];
#if defined(__LP64__)
if (elf_class != ELFCLASS64) {
if (elf_class == ELFCLASS32) {
DL_ERR("\"%s\" is 32-bit instead of 64-bit", name_);
} else {
DL_ERR("\"%s\" has unknown ELF class: %d", name_, elf_class);
}
return false;
}
#else
if (elf_class != ELFCLASS32) {
if (elf_class == ELFCLASS64) {
DL_ERR("\"%s\" is 64-bit instead of 32-bit", name_);
} else {
DL_ERR("\"%s\" has unknown ELF class: %d", name_, elf_class);
}
return false;
}
#endif
// 该so文件必须是小端存储
if (header_.e_ident[EI_DATA] != ELFDATA2LSB) {
// EI_DATA=5,ELFDATA2LSB=1
DL_ERR("\"%s\" not little-endian: %d", name_, header_.e_ident[EI_DATA]);
return false;
}
// 该so文件必须共享目标文件
if (header_.e_type != ET_DYN) {
// ET_DYN=3
DL_ERR("\"%s\" has unexpected e_type: %d", name_, header_.e_type);
return false;
}
// 版本号必须为1
if (header_.e_version != EV_CURRENT) {
DL_ERR("\"%s\" has unexpected e_version: %d", name_, header_.e_version);
return false;
}
// 如果目标平台是arm,ELF_TARG_MACH=40
if (header_.e_machine != ELF_TARG_MACH) {
DL_ERR("\"%s\" has unexpected e_machine: %d", name_, header_.e_machine);
return false;
}
return true;
}
VerifyElfHeader()
ReadProgramHeader()将 program header table从.so 文件通过 mmap64 映射到只读私有匿名内存
213bool ElfReader::ReadProgramHeader() {
phdr_num_ = header_.e_phnum;// phdr的数目
// Like the kernel, we only accept program header tables that
// are smaller than 64KiB.
if (phdr_num_ < || phdr_num_ > /sizeof(ElfW(Phdr))) {
DL_ERR("\"%s\" has invalid e_phnum: %zd", name_, phdr_num_);
return false;
}
ElfW(Addr) page_min = PAGE_START(header_.e_phoff);//
ElfW(Addr) page_max = PAGE_END(header_.e_phoff + (phdr_num_ * sizeof(ElfW(Phdr))));
// pht在页中的偏移
ElfW(Addr) page_offset = PAGE_OFFSET(header_.e_phoff);
// pht需要的映射内存大小
phdr_size_ = page_max - page_min;
void* mmap_result = mmap64(nullptr, phdr_size_, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE, fd_, file_offset_ + page_min);
if (mmap_result == MAP_FAILED) {
DL_ERR("\"%s\" phdr mmap failed: %s", name_, strerror(errno));
return false;
}
phdr_mmap_ = mmap_result;
phdr_table_ = reinterpret_cast<ElfW(Phdr)*>(reinterpret_cast<char*>(mmap_result) + page_offset);
return true;
}
ReadProgramHeader()
ReserveAddressSpace()通过 mmap 创建足够大的匿名内存空间, 以便能够容纳所有可以加载的段
292bool ElfReader::ReserveAddressSpace(const android_dlextinfo* extinfo) {
ElfW(Addr) min_vaddr;
// 加载所有段所需要的内存空间
load_size_ = phdr_table_get_load_size(phdr_table_, phdr_num_, &min_vaddr);
if (load_size_ == ) {
DL_ERR("\"%s\" has no loadable segments", name_);
return false;
}
uint8_t* addr = reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>(min_vaddr);
void* start;
size_t reserved_size = ;
bool reserved_hint = true;
if (extinfo != nullptr) {
if (extinfo->flags & ANDROID_DLEXT_RESERVED_ADDRESS) {
reserved_size = extinfo->reserved_size;
reserved_hint = false;
} else if (extinfo->flags & ANDROID_DLEXT_RESERVED_ADDRESS_HINT) {
reserved_size = extinfo->reserved_size;
}
}
if (load_size_ > reserved_size) {
if (!reserved_hint) {
DL_ERR("reserved address space %zd smaller than %zd bytes needed for \"%s\"",
reserved_size - load_size_, load_size_, name_);
return false;
}
int mmap_flags = MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS;
// 分配空间
start = mmap(addr, load_size_, PROT_NONE, mmap_flags, -, );
if (start == MAP_FAILED) {
DL_ERR("couldn't reserve %zd bytes of address space for \"%s\"", load_size_, name_);
return false;
}
} else {
start = extinfo->reserved_addr;
}
// 分配匿名内存空间首地址
load_start_ = start;
load_bias_ = reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>(start) - addr;
return true;
}
ReserveAddressSpace()
LoadSegments()函数
335bool ElfReader::LoadSegments() {
for (size_t i = ; i < phdr_num_; ++i) {
const ElfW(Phdr)* phdr = &phdr_table_[i];
// 遍历 program header table 找到可加载段
if (phdr->p_type != PT_LOAD) {
continue;
}
// Segment addresses in memory.
// 段在内存中的起始地址
ElfW(Addr) seg_start = phdr->p_vaddr + load_bias_;
// 段在内存中的结束地址
ElfW(Addr) seg_end = seg_start + phdr->p_memsz;
// seg_start 所在页的起始地址
ElfW(Addr) seg_page_start = PAGE_START(seg_start);
// seg_end 所在页的下一页的起始地址
ElfW(Addr) seg_page_end = PAGE_END(seg_end);
// 文件中段的结束位置在内存中的地址
ElfW(Addr) seg_file_end = seg_start + phdr->p_filesz;
// File offsets.
// 段在文件中的偏移首地址
ElfW(Addr) file_start = phdr->p_offset;
// 段在文件中的结束地址
ElfW(Addr) file_end = file_start + phdr->p_filesz;
// file_start 所在页的起始地址
ElfW(Addr) file_page_start = PAGE_START(file_start);
// 需要映射的文件长度,file_length>=phdr->p_filesz
ElfW(Addr) file_length = file_end - file_page_start;
if (file_length != ) {
// 将文件中的段映射到内存
void* seg_addr = mmap64(reinterpret_cast<void*>(seg_page_start),
file_length,
PFLAGS_TO_PROT(phdr->p_flags),
MAP_FIXED|MAP_PRIVATE,
fd_,
file_offset_ + file_page_start);
if (seg_addr == MAP_FAILED) {
DL_ERR("couldn't map \"%s\" segment %zd: %s", name_, i, strerror(errno));
return false;
}
}
// 将最后一页中,不是段内容的数据置 0
if ((phdr->p_flags & PF_W) != && PAGE_OFFSET(seg_file_end) > ) {
memset(reinterpret_cast<void*>(seg_file_end), , PAGE_SIZE - PAGE_OFFSET(seg_file_end));
}
seg_file_end = PAGE_END(seg_file_end);
// seg_file_end is now the first page address after the file
// content. If seg_end is larger, we need to zero anything
// between them. This is done by using a private anonymous
// map for all extra pages.
if (seg_page_end > seg_file_end) {
void* zeromap = mmap(reinterpret_cast<void*>(seg_file_end),
seg_page_end - seg_file_end,
PFLAGS_TO_PROT(phdr->p_flags),
MAP_FIXED|MAP_ANONYMOUS|MAP_PRIVATE,
-,
);
// 额外的内容置 0
if (zeromap == MAP_FAILED) {
DL_ERR("couldn't zero fill \"%s\" gap: %s", name_, strerror(errno));
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
LoadSegments()
加载完.so 文件后,Load()继续调用 FindPhdr()函数检查可加载段中是否包含 program header table。
728bool ElfReader::FindPhdr() {
const ElfW(Phdr)* phdr_limit = phdr_table_ + phdr_num_;
// 首先检查是否有类型是 PT_PHDR 的段,即 program header table
for (const ElfW(Phdr)* phdr = phdr_table_; phdr < phdr_limit; ++phdr) {
// load_bias_ + phdr->p_vaddr 是 phdr 在内存中的起始地址
if (phdr->p_type == PT_PHDR) {
// 检查是否在内存中
return CheckPhdr(load_bias_ + phdr->p_vaddr);
}
}
// 检查第一个可加载段。如果它在文件中的偏移是 0,那么该段以 ELF 头
// 开始,通过 ELF 头能计算 program header table 的地址
for (const ElfW(Phdr)* phdr = phdr_table_; phdr < phdr_limit; ++phdr) {
if (phdr->p_type == PT_LOAD) {
if (phdr->p_offset == ) {
ElfW(Addr) elf_addr = load_bias_ + phdr->p_vaddr;
const ElfW(Ehdr)* ehdr = reinterpret_cast<const ElfW(Ehdr)*>(elf_addr);
// ehdr->e_phoff 是 pht 在文件中的偏移
ElfW(Addr) offset = ehdr->e_phoff;
// 检查是否在内存中
return CheckPhdr((ElfW(Addr))ehdr + offset);
}
break;
}
}
DL_ERR("can't find loaded phdr for \"%s\"", name_);
return false;
}
FindPhdr()两种方式确定program header table是否在内存,调用CheckPhdr()实现
760bool ElfReader::CheckPhdr(ElfW(Addr) loaded) {
const ElfW(Phdr)* phdr_limit = phdr_table_ + phdr_num_;
// loaded_end 是 pht 在内存中的结束地址
ElfW(Addr) loaded_end = loaded + (phdr_num_ * sizeof(ElfW(Phdr)));
for (ElfW(Phdr)* phdr = phdr_table_; phdr < phdr_limit; ++phdr) {
if (phdr->p_type != PT_LOAD) {
continue;
}
ElfW(Addr) seg_start = phdr->p_vaddr + load_bias_;
ElfW(Addr) seg_end = phdr->p_filesz + seg_start;
if (seg_start <= loaded && loaded_end <= seg_end) {
// 遍历每一个可加载段,检查 pht 的地址范围是否在可加载段中
loaded_phdr_ = reinterpret_cast<const ElfW(Phdr)*>(loaded);
return true;
}
}
DL_ERR("\"%s\" loaded phdr %p not in loadable segment", name_, reinterpret_cast<void*>(loaded));
return false;
}
FindPhdr()
ElfReader.Load()加载so的过程:
1. ReadElfHeader():从.so 文件中读取 ELF 头;
2. VerifyElfHeader():校验 ELF 头;
3. ReadProgramHeader():将.so 文件的 program header table 映射到内存;
4. ReserveAddressSpace():开辟匿名内存空间;
5. LoadSegments():将可加载段加载到 ReserveAddressSpace 开辟的空间中;
6. FindPhdr():校验 program header table 是否在内存中。
第三部分:创建soinfo对象,解析.dynmaic section,并将该.so文件的依赖库添加到待加载的队列中。
Load_library()中PrelinkImage()解析so文件的dynamic setction
dynamic section的定义
// Dynamic table entry for ELF64.
1632struct Elf64_Dyn
{
Elf64_Sxword d_tag; // Type of dynamic table entry.
union
{
Elf64_Xword d_val; // Integer value of entry.
Elf64_Addr d_ptr; // Pointer value of entry.
} d_un;
};
dynamic section
PrelinkImage()解析的源码
1858bool soinfo::PrelinkImage() {
/* Extract dynamic section */
ElfW(Word) dynamic_flags = ;
// 根据 program header table 找到.dynamic section
phdr_table_get_dynamic_section(phdr, phnum, load_bias, &dynamic, &dynamic_flags);
/* We can't log anything until the linker is relocated */
bool relocating_linker = (flags & FLAG_LINKER) != ;
if (!relocating_linker) {
INFO("[ linking %s ]", name);
DEBUG("si->base = %p si->flags = 0x%08x", reinterpret_cast<void*>(base), flags);
}
if (dynamic == nullptr) {
if (!relocating_linker) {
DL_ERR("missing PT_DYNAMIC in \"%s\"", name);
}
return false;
} else {
if (!relocating_linker) {
DEBUG("dynamic = %p", dynamic);
}
}
// 找到.ARM.exidx sectioin 在内存中的地址
#if defined(__arm__)
(void) phdr_table_get_arm_exidx(phdr, phnum, load_bias,
&ARM_exidx, &ARM_exidx_count);
#endif
// 该so依赖库的个数
uint32_t needed_count = ;
// 遍历.dynamic
for (ElfW(Dyn)* d = dynamic; d->d_tag != DT_NULL; ++d) {
DEBUG("d = %p, d[0](tag) = %p d[1](val) = %p",
d, reinterpret_cast<void*>(d->d_tag), reinterpret_cast<void*>(d->d_un.d_val));
switch (d->d_tag) {
case DT_SONAME:
// TODO: glibc dynamic linker uses this name for
// initial library lookup; consider doing the same here.
break;
// hash 表相关信息
case DT_HASH:
nbucket = reinterpret_cast<uint32_t*>(load_bias + d->d_un.d_ptr)[];
nchain = reinterpret_cast<uint32_t*>(load_bias + d->d_un.d_ptr)[];
bucket = reinterpret_cast<uint32_t*>(load_bias + d->d_un.d_ptr + );
chain = reinterpret_cast<uint32_t*>(load_bias + d->d_un.d_ptr + + nbucket * );
break;
// 字符串表的偏移,与.dynstr section 对应,d_un.d_ptr 与 s_addr 相等
case DT_STRTAB:
strtab = reinterpret_cast<const char*>(load_bias + d->d_un.d_ptr);
break;
// 字符串表的大小(字节)
case DT_STRSZ:
strtab_size = d->d_un.d_val;
break;
// 符号表的偏移
case DT_SYMTAB:
symtab = reinterpret_cast<ElfW(Sym)*>(load_bias + d->d_un.d_ptr);
break;
// 符号表项的大小(字节)
case DT_SYMENT:
if (d->d_un.d_val != sizeof(ElfW(Sym))) {
DL_ERR("invalid DT_SYMENT: %zd", static_cast<size_t>(d->d_un.d_val));
return false;
}
break;
case DT_PLTREL:
#if defined(USE_RELA)
if (d->d_un.d_val != DT_RELA) {
DL_ERR("unsupported DT_PLTREL in \"%s\"; expected DT_RELA", name);
return false;
}
#else
if (d->d_un.d_val != DT_REL) {
DL_ERR("unsupported DT_PLTREL in \"%s\"; expected DT_REL", name);
return false;
}
#endif
break;
// 与过程链接表相关的重定位表的偏移,与.rel.plt section 对应
case DT_JMPREL:
#if defined(USE_RELA)
plt_rela = reinterpret_cast<ElfW(Rela)*>(load_bias + d->d_un.d_ptr);
#else
plt_rel = reinterpret_cast<ElfW(Rel)*>(load_bias + d->d_un.d_ptr);
#endif
break;
case DT_PLTRELSZ:
#if defined(USE_RELA)
plt_rela_count = d->d_un.d_val / sizeof(ElfW(Rela));
#else
plt_rel_count = d->d_un.d_val / sizeof(ElfW(Rel));
#endif
break;
// 与过程链接表相关的重定位表的大小(字节)
case DT_PLTGOT:
#if defined(__mips__)
// Used by mips and mips64.
plt_got = reinterpret_cast<ElfW(Addr)**>(load_bias + d->d_un.d_ptr);
#endif
// Ignore for other platforms... (because RTLD_LAZY is not supported)
break;
case DT_DEBUG:
// Set the DT_DEBUG entry to the address of _r_debug for GDB
// if the dynamic table is writable
// FIXME: not working currently for N64
// The flags for the LOAD and DYNAMIC program headers do not agree.
// The LOAD section containing the dynamic table has been mapped as
// read-only, but the DYNAMIC header claims it is writable.
#if !(defined(__mips__) && defined(__LP64__))
if ((dynamic_flags & PF_W) != ) {
d->d_un.d_val = reinterpret_cast<uintptr_t>(&_r_debug);
}
break;
#endif
#if defined(USE_RELA)
case DT_RELA:
rela = reinterpret_cast<ElfW(Rela)*>(load_bias + d->d_un.d_ptr);
break;
case DT_RELASZ:
rela_count = d->d_un.d_val / sizeof(ElfW(Rela));
break;
case DT_RELAENT:
if (d->d_un.d_val != sizeof(ElfW(Rela))) {
DL_ERR("invalid DT_RELAENT: %zd", static_cast<size_t>(d->d_un.d_val));
return false;
}
break;
// ignored (see DT_RELCOUNT comments for details)
case DT_RELACOUNT:
break;
case DT_REL:
DL_ERR("unsupported DT_REL in \"%s\"", name);
return false;
case DT_RELSZ:
DL_ERR("unsupported DT_RELSZ in \"%s\"", name);
return false;
#else
// 重定位表的偏移,与.rel.dyn section 对应
case DT_REL:
rel = reinterpret_cast<ElfW(Rel)*>(load_bias + d->d_un.d_ptr);
break;
// 重定位表的总大小(字节)
case DT_RELSZ:
rel_count = d->d_un.d_val / sizeof(ElfW(Rel));
break;
// 重定位表项的大小(字节)
case DT_RELENT:
if (d->d_un.d_val != sizeof(ElfW(Rel))) {
DL_ERR("invalid DT_RELENT: %zd", static_cast<size_t>(d->d_un.d_val));
return false;
}
break;
// "Indicates that all RELATIVE relocations have been concatenated together,
// and specifies the RELATIVE relocation count."
//
// TODO: Spec also mentions that this can be used to optimize relocation process;
// Not currently used by bionic linker - ignored.
case DT_RELCOUNT:
break;
case DT_RELA:
DL_ERR("unsupported DT_RELA in \"%s\"", name);
return false;
#endif
// 初始化函数 init 的偏移
case DT_INIT:
init_func = reinterpret_cast<linker_function_t>(load_bias + d->d_un.d_ptr);
DEBUG("%s constructors (DT_INIT) found at %p", name, init_func);
break;
// 结束函数的偏移
case DT_FINI:
fini_func = reinterpret_cast<linker_function_t>(load_bias + d->d_un.d_ptr);
DEBUG("%s destructors (DT_FINI) found at %p", name, fini_func);
break;
// 初始化函数数组 init_array 的偏移
case DT_INIT_ARRAY:
init_array = reinterpret_cast<linker_function_t*>(load_bias + d->d_un.d_ptr);
DEBUG("%s constructors (DT_INIT_ARRAY) found at %p", name, init_array);
break;
// init_array 的大小(字节)
case DT_INIT_ARRAYSZ:
init_array_count = ((unsigned)d->d_un.d_val) / sizeof(ElfW(Addr));
break;
case DT_FINI_ARRAY:
fini_array = reinterpret_cast<linker_function_t*>(load_bias + d->d_un.d_ptr);
DEBUG("%s destructors (DT_FINI_ARRAY) found at %p", name, fini_array);
break;
case DT_FINI_ARRAYSZ:
fini_array_count = ((unsigned)d->d_un.d_val) / sizeof(ElfW(Addr));
break;
case DT_PREINIT_ARRAY:
preinit_array = reinterpret_cast<linker_function_t*>(load_bias + d->d_un.d_ptr);
DEBUG("%s constructors (DT_PREINIT_ARRAY) found at %p", name, preinit_array);
break;
case DT_PREINIT_ARRAYSZ:
preinit_array_count = ((unsigned)d->d_un.d_val) / sizeof(ElfW(Addr));
break;
case DT_TEXTREL:
#if defined(__LP64__)
DL_ERR("text relocations (DT_TEXTREL) found in 64-bit ELF file \"%s\"", name);
return false;
#else
has_text_relocations = true;
break;
#endif
case DT_SYMBOLIC:
has_DT_SYMBOLIC = true;
break;
// d->d_un.d_val 是依赖库名字在字符串表中的索引
case DT_NEEDED:
++needed_count;
break;
case DT_FLAGS:
if (d->d_un.d_val & DF_TEXTREL) {
#if defined(__LP64__)
DL_ERR("text relocations (DF_TEXTREL) found in 64-bit ELF file \"%s\"", name);
return false;
#else
has_text_relocations = true;
#endif
}
if (d->d_un.d_val & DF_SYMBOLIC) {
has_DT_SYMBOLIC = true;
}
break;
case DT_FLAGS_1:
if ((d->d_un.d_val & DF_1_GLOBAL) != ) {
rtld_flags |= RTLD_GLOBAL;
}
// TODO: Implement other flags
if ((d->d_un.d_val & ~(DF_1_NOW | DF_1_GLOBAL)) != ) {
DL_WARN("Unsupported flags DT_FLAGS_1=%p", reinterpret_cast<void*>(d->d_un.d_val));
}
break;
#if defined(__mips__)
case DT_MIPS_RLD_MAP:
// Set the DT_MIPS_RLD_MAP entry to the address of _r_debug for GDB.
{
r_debug** dp = reinterpret_cast<r_debug**>(load_bias + d->d_un.d_ptr);
*dp = &_r_debug;
}
break;
case DT_MIPS_RLD_VERSION:
case DT_MIPS_FLAGS:
case DT_MIPS_BASE_ADDRESS:
case DT_MIPS_UNREFEXTNO:
break;
case DT_MIPS_SYMTABNO:
mips_symtabno = d->d_un.d_val;
break;
case DT_MIPS_LOCAL_GOTNO:
mips_local_gotno = d->d_un.d_val;
break;
case DT_MIPS_GOTSYM:
mips_gotsym = d->d_un.d_val;
break;
#endif
// Ignored: "Its use has been superseded by the DF_BIND_NOW flag"
case DT_BIND_NOW:
break;
// Ignore: bionic does not support symbol versioning...
case DT_VERSYM:
case DT_VERDEF:
case DT_VERDEFNUM:
break;
default:
if (!relocating_linker) {
DL_WARN("%s: unused DT entry: type %p arg %p", name,
reinterpret_cast<void*>(d->d_tag), reinterpret_cast<void*>(d->d_un.d_val));
}
break;
}
}
DEBUG("si->base = %p, si->strtab = %p, si->symtab = %p",
reinterpret_cast<void*>(base), strtab, symtab);
// Sanity checks.
if (relocating_linker && needed_count != ) {
DL_ERR("linker cannot have DT_NEEDED dependencies on other libraries");
return false;
}
if (nbucket == ) {
DL_ERR("empty/missing DT_HASH in \"%s\" (built with --hash-style=gnu?)", name);
return false;
}
if (strtab == ) {
DL_ERR("empty/missing DT_STRTAB in \"%s\"", name);
return false;
}
if (symtab == ) {
DL_ERR("empty/missing DT_SYMTAB in \"%s\"", name);
return false;
}
return true;
}
PrelinkImage()
至此, load_library()函数分析完了find_libraries()分析结束返回上一个函数find_libraries()函数
find_libraries()第三步:
第三步:对加载的so进行链接:调用LinkImage()
LinkImage()源码:
2175bool soinfo::LinkImage(const android_dlextinfo* extinfo) {
#if !defined(__LP64__)
if (has_text_relocations) {
// Make segments writable to allow text relocations to work properly. We will later call
// phdr_table_protect_segments() after all of them are applied and all constructors are run.
DL_WARN("%s has text relocations. This is wasting memory and prevents "
"security hardening. Please fix.", name);
// 使段可读写,通过系统调用 mprotect()来设置
if (phdr_table_unprotect_segments(phdr, phnum, load_bias) < ) {
DL_ERR("can't unprotect loadable segments for \"%s\": %s",
name, strerror(errno));
return false;
}
}
#endif
#if defined(USE_RELA)
if (rela != nullptr) {
DEBUG("[ relocating %s ]", name);
if (Relocate(rela, rela_count)) {
return false;
}
}
if (plt_rela != nullptr) {
DEBUG("[ relocating %s plt ]", name);
if (Relocate(plt_rela, plt_rela_count)) {
return false;
}
}
#else
if (rel != nullptr) {
DEBUG("[ relocating %s ]", name);
// 对重定位表中所指的符号进行重定位
if (Relocate(rel, rel_count)) {
return false;
}
}
// 与调用导入函数相关
if (plt_rel != nullptr) {
DEBUG("[ relocating %s plt ]", name);
// 对重定位表中所指的符号进行重定位
if (Relocate(plt_rel, plt_rel_count)) {
return false;
}
}
#endif
#if defined(__mips__)
if (!mips_relocate_got(this)) {
return false;
}
#endif
DEBUG("[ finished linking %s ]", name);
#if !defined(__LP64__)
if (has_text_relocations) {
// All relocations are done, we can protect our segments back to read-only.
if (phdr_table_protect_segments(phdr, phnum, load_bias) < ) {
DL_ERR("can't protect segments for \"%s\": %s",
name, strerror(errno));
return false;
}
}
#endif
/* We can also turn on GNU RELRO protection */
if (phdr_table_protect_gnu_relro(phdr, phnum, load_bias) < ) {
DL_ERR("can't enable GNU RELRO protection for \"%s\": %s",
name, strerror(errno));
return false;
}
/* Handle serializing/sharing the RELRO segment */
if (extinfo && (extinfo->flags & ANDROID_DLEXT_WRITE_RELRO)) {
if (phdr_table_serialize_gnu_relro(phdr, phnum, load_bias,
extinfo->relro_fd) < ) {
DL_ERR("failed serializing GNU RELRO section for \"%s\": %s",
name, strerror(errno));
return false;
}
} else if (extinfo && (extinfo->flags & ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_RELRO)) {
if (phdr_table_map_gnu_relro(phdr, phnum, load_bias,
extinfo->relro_fd) < ) {
DL_ERR("failed mapping GNU RELRO section for \"%s\": %s",
name, strerror(errno));
return false;
}
}
notify_gdb_of_load(this);
return true;
}
LinkImage()
对rel.dyn 和.rel.plt 两个重定位表都是调用Relocate()来进行重定位的。
#define ELF32_R_SYM(x) ((x) >> 8)
#define ELF32_R_TYPE(x) ((x) & 0xff)
164typedef struct elf32_rel {
Elf32_Addr r_offset;
Elf32_Word r_info;
} Elf32_Rel;
重定位的数据结构
Relocate()源码
1359int soinfo::Relocate(ElfW(Rel)* rel, unsigned count) {
//遍历重定位表
for (size_t idx = ; idx < count; ++idx, ++rel) {
// 重定位类型
unsigned type = ELFW(R_TYPE)(rel->r_info);
// 符号表索引
// 重定位的地址,即 reloc 处的值需要重新计算,对于导入函数来说,地址 reloc 在 got 表中,reloc 处应该是函数的实际地址,代码中函数的地址其实是其在 got 表中的偏移,再从 got 表中跳转到函数的实际地址。
unsigned sym = ELFW(R_SYM)(rel->r_info);
ElfW(Addr) reloc = static_cast<ElfW(Addr)>(rel->r_offset + load_bias);
// 符号的地址
ElfW(Addr) sym_addr = ;
// 符号的名称
const char* sym_name = nullptr;
DEBUG("Processing '%s' relocation at index %zd", name, idx);
if (type == ) { // R_*_NONE
continue;
}
// 该符号在其定义 so 中的记录
ElfW(Sym)* s = nullptr;
// 定义该符号的 so
soinfo* lsi = nullptr;
if (sym != ) {
// 得到符号的名称
sym_name = get_string(symtab[sym].st_name);
// 查找 sym_name 定义在哪个 so
s = soinfo_do_lookup(this, sym_name, &lsi);
if (s == nullptr) {
// 如果该符号没有定义,那么它的绑定类型必须是弱引用
// We only allow an undefined symbol if this is a weak reference...
s = &symtab[sym];
if (ELF_ST_BIND(s->st_info) != STB_WEAK) {
DL_ERR("cannot locate symbol \"%s\" referenced by \"%s\"...", sym_name, name);
return -;
}
/* IHI0044C AAELF 4.5.1.1:
1388
1389 Libraries are not searched to resolve weak references.
1390 It is not an error for a weak reference to remain
1391 unsatisfied.
1392
1393 During linking, the value of an undefined weak reference is:
1394 - Zero if the relocation type is absolute
1395 - The address of the place if the relocation is pc-relative
1396 - The address of nominal base address if the relocation
1397 type is base-relative.
1398 */
switch (type) {
// 没有定义的弱引用,它的 sym_addr 是 0,或者重定位的时候不关心 sym_addr 的值
#if defined(__arm__)
case R_ARM_JUMP_SLOT:
case R_ARM_GLOB_DAT:
case R_ARM_ABS32:
case R_ARM_RELATIVE: /* Don't care. */
// sym_addr was initialized to be zero above or relocation
// code below does not care about value of sym_addr.
// No need to do anything.
break;
#elif defined(__i386__)
case R_386_JMP_SLOT:
case R_386_GLOB_DAT:
case R_386_32:
case R_386_RELATIVE: /* Don't care. */
case R_386_IRELATIVE:
// sym_addr was initialized to be zero above or relocation
// code below does not care about value of sym_addr.
// No need to do anything.
break;
case R_386_PC32:
sym_addr = reloc;
break;
#endif
#if defined(__arm__)
case R_ARM_COPY:
// Fall through. Can't really copy if weak symbol is not found at run-time.
#endif
default:
DL_ERR("unknown weak reloc type %d @ %p (%zu)", type, rel, idx);
return -;
}
} else {
// 找到了符号的定义 so,计算该符号的地址
sym_addr = lsi->resolve_symbol_address(s);
}
count_relocation(kRelocSymbol);
}
switch (type) {
// 根据重定位类型修改 reloc 处的值
#if defined(__arm__)
case R_ARM_JUMP_SLOT:
count_relocation(kRelocAbsolute);
MARK(rel->r_offset);
TRACE_TYPE(RELO, "RELO JMP_SLOT %08x <- %08x %s", reloc, sym_addr, sym_name);
*reinterpret_cast<ElfW(Addr)*>(reloc) = sym_addr;
break;
case R_ARM_GLOB_DAT:
count_relocation(kRelocAbsolute);
MARK(rel->r_offset);
TRACE_TYPE(RELO, "RELO GLOB_DAT %08x <- %08x %s", reloc, sym_addr, sym_name);
*reinterpret_cast<ElfW(Addr)*>(reloc) = sym_addr;
break;
case R_ARM_ABS32:
count_relocation(kRelocAbsolute);
MARK(rel->r_offset);
TRACE_TYPE(RELO, "RELO ABS %08x <- %08x %s", reloc, sym_addr, sym_name);
*reinterpret_cast<ElfW(Addr)*>(reloc) += sym_addr;
break;
case R_ARM_REL32:
count_relocation(kRelocRelative);
MARK(rel->r_offset);
TRACE_TYPE(RELO, "RELO REL32 %08x <- %08x - %08x %s",
reloc, sym_addr, rel->r_offset, sym_name);
*reinterpret_cast<ElfW(Addr)*>(reloc) += sym_addr - rel->r_offset;
break;
case R_ARM_COPY:
/*
1469 * ET_EXEC is not supported so this should not happen.
1470 *
1471 * http://infocenter.arm.com/help/topic/com.arm.doc.ihi0044d/IHI0044D_aaelf.pdf
1472 *
1473 * Section 4.7.1.10 "Dynamic relocations"
1474 * R_ARM_COPY may only appear in executable objects where e_type is
1475 * set to ET_EXEC.
1476 */
DL_ERR("%s R_ARM_COPY relocations are not supported", name);
return -;
#elif defined(__i386__)
case R_386_JMP_SLOT:
count_relocation(kRelocAbsolute);
MARK(rel->r_offset);
TRACE_TYPE(RELO, "RELO JMP_SLOT %08x <- %08x %s", reloc, sym_addr, sym_name);
*reinterpret_cast<ElfW(Addr)*>(reloc) = sym_addr;
break;
case R_386_GLOB_DAT:
count_relocation(kRelocAbsolute);
MARK(rel->r_offset);
TRACE_TYPE(RELO, "RELO GLOB_DAT %08x <- %08x %s", reloc, sym_addr, sym_name);
*reinterpret_cast<ElfW(Addr)*>(reloc) = sym_addr;
break;
case R_386_32:
count_relocation(kRelocRelative);
MARK(rel->r_offset);
TRACE_TYPE(RELO, "RELO R_386_32 %08x <- +%08x %s", reloc, sym_addr, sym_name);
*reinterpret_cast<ElfW(Addr)*>(reloc) += sym_addr;
break;
case R_386_PC32:
count_relocation(kRelocRelative);
MARK(rel->r_offset);
TRACE_TYPE(RELO, "RELO R_386_PC32 %08x <- +%08x (%08x - %08x) %s",
reloc, (sym_addr - reloc), sym_addr, reloc, sym_name);
*reinterpret_cast<ElfW(Addr)*>(reloc) += (sym_addr - reloc);
break;
#elif defined(__mips__)
case R_MIPS_REL32:
#if defined(__LP64__)
// MIPS Elf64_Rel entries contain compound relocations
// We only handle the R_MIPS_NONE|R_MIPS_64|R_MIPS_REL32 case
if (ELF64_R_TYPE2(rel->r_info) != R_MIPS_64 ||
ELF64_R_TYPE3(rel->r_info) != R_MIPS_NONE) {
DL_ERR("Unexpected compound relocation type:%d type2:%d type3:%d @ %p (%zu)",
type, (unsigned)ELF64_R_TYPE2(rel->r_info),
(unsigned)ELF64_R_TYPE3(rel->r_info), rel, idx);
return -;
}
#endif
count_relocation(kRelocAbsolute);
MARK(rel->r_offset);
TRACE_TYPE(RELO, "RELO REL32 %08zx <- %08zx %s", static_cast<size_t>(reloc),
static_cast<size_t>(sym_addr), sym_name ? sym_name : "*SECTIONHDR*");
if (s) {
*reinterpret_cast<ElfW(Addr)*>(reloc) += sym_addr;
} else {
*reinterpret_cast<ElfW(Addr)*>(reloc) += base;
}
break;
#endif
#if defined(__arm__)
case R_ARM_RELATIVE:
#elif defined(__i386__)
case R_386_RELATIVE:
#endif
count_relocation(kRelocRelative);
MARK(rel->r_offset);
if (sym) {
DL_ERR("odd RELATIVE form...");
return -;
}
TRACE_TYPE(RELO, "RELO RELATIVE %p <- +%p",
reinterpret_cast<void*>(reloc), reinterpret_cast<void*>(base));
*reinterpret_cast<ElfW(Addr)*>(reloc) += base;
break;
#if defined(__i386__)
case R_386_IRELATIVE:
count_relocation(kRelocRelative);
MARK(rel->r_offset);
TRACE_TYPE(RELO, "RELO IRELATIVE %p <- %p", reinterpret_cast<void*>(reloc), reinterpret_cast<void*>(base));
*reinterpret_cast<ElfW(Addr)*>(reloc) = call_ifunc_resolver(base + *reinterpret_cast<ElfW(Addr)*>(reloc));
break;
#endif
default:
DL_ERR("unknown reloc type %d @ %p (%zu)", type, rel, idx);
return -;
}
}
return ;
}
Relocate()
soinfo_do_lookup()查找符号的定义 so
soinfo_do_lookup()源码:
482static ElfW(Sym)* soinfo_do_lookup(soinfo* si, const char* name, soinfo** lsi) {
// 计算符号的哈希值
unsigned elf_hash = elfhash(name);
ElfW(Sym)* s = nullptr;
/* "This element's presence in a shared object library alters the dynamic linker's
487 * symbol resolution algorithm for references within the library. Instead of starting
488 * a symbol search with the executable file, the dynamic linker starts from the shared
489 * object itself. If the shared object fails to supply the referenced symbol, the
490 * dynamic linker then searches the executable file and other shared objects as usual."
491 *
492 * http://www.sco.com/developers/gabi/2012-12-31/ch5.dynamic.html
493 *
494 * Note that this is unlikely since static linker avoids generating
495 * relocations for -Bsymbolic linked dynamic executables.
496 */
if (si->has_DT_SYMBOLIC) {
DEBUG("%s: looking up %s in local scope (DT_SYMBOLIC)", si->name, name);
s = soinfo_elf_lookup(si, elf_hash, name);
if (s != nullptr) {
*lsi = si;
}
}
if (s == nullptr && somain != nullptr) {
// 1. Look for it in the main executable unless we already did.
if (si != somain || !si->has_DT_SYMBOLIC) {
DEBUG("%s: looking up %s in executable %s",
si->name, name, somain->name);
s = soinfo_elf_lookup(somain, elf_hash, name);
if (s != nullptr) {
*lsi = somain;
}
}
// 2. Look for it in the ld_preloads
if (s == nullptr) {
for (int i = ; g_ld_preloads[i] != NULL; i++) {
s = soinfo_elf_lookup(g_ld_preloads[i], elf_hash, name);
if (s != nullptr) {
*lsi = g_ld_preloads[i];
break;
}
}
}
}
/* Look for symbols in the local scope (the object who is
529 * searching). This happens with C++ templates on x86 for some
530 * reason.
531 *
532 * Notes on weak symbols:
533 * The ELF specs are ambiguous about treatment of weak definitions in
534 * dynamic linking. Some systems return the first definition found
535 * and some the first non-weak definition. This is system dependent.
536 * Here we return the first definition found for simplicity. */
if (s == nullptr && !si->has_DT_SYMBOLIC) {
// 在其依赖库(子结点)中递归查找符号
DEBUG("%s: looking up %s in local scope", si->name, name);
s = soinfo_elf_lookup(si, elf_hash, name);
if (s != nullptr) {
*lsi = si;
}
}
if (s == nullptr) {
si->get_children().visit([&](soinfo* child) {
DEBUG("%s: looking up %s in %s", si->name, name, child->name);
s = soinfo_elf_lookup(child, elf_hash, name);
if (s != nullptr) {
*lsi = child;
return false;
}
return true;
});
}
if (s != nullptr) {
TRACE_TYPE(LOOKUP, "si %s sym %s s->st_value = %p, "
"found in %s, base = %p, load bias = %p",
si->name, name, reinterpret_cast<void*>(s->st_value),
(*lsi)->name, reinterpret_cast<void*>((*lsi)->base),
reinterpret_cast<void*>((*lsi)->load_bias));
}
return s;
}
soinfo_do_lookup()
soinfo_do_look()分别在其自身、 预加载库和依赖库中查找符号的定义,具体的查找函数是 soinfo_elf_lookup()
soinfo_elf_lookup()源码:
418static ElfW(Sym)* soinfo_elf_lookup(soinfo* si, unsigned hash, const char* name) {
// 符号表
ElfW(Sym)* symtab = si->symtab;
TRACE_TYPE(LOOKUP, "SEARCH %s in %s@%p %x %zd",
name, si->name, reinterpret_cast<void*>(si->base), hash, hash % si->nbucket);
// 通过哈希表在符号表中快速查找 name
for (unsigned n = si->bucket[hash % si->nbucket]; n != ; n = si->chain[n]) {
ElfW(Sym)* s = symtab + n;
// 符号名字需相同
if (strcmp(si->get_string(s->st_name), name)) continue;
// only concern ourselves with global and weak symbol definitions
switch (ELF_ST_BIND(s->st_info)) {
case STB_GLOBAL:
case STB_WEAK:
if (s->st_shndx == SHN_UNDEF) {
// 符号未定义
continue;
}
TRACE_TYPE(LOOKUP, "FOUND %s in %s (%p) %zd",
name, si->name, reinterpret_cast<void*>(s->st_value),
static_cast<size_t>(s->st_size));
// 在 si 中找到符号的定义
return s;
case STB_LOCAL:
continue;
default:
__libc_fatal("ERROR: Unexpected ST_BIND value: %d for '%s' in '%s'",
ELF_ST_BIND(s->st_info), name, si->name);
}
}
TRACE_TYPE(LOOKUP, "NOT FOUND %s in %s@%p %x %zd",
name, si->name, reinterpret_cast<void*>(si->base), hash, hash % si->nbucket);
return nullptr;
}
soinfo_elf_lookup()
Relocate()函数,在找到符号后,调用resolve_symbol_address() 来计算符号的地址 。
resolve_symbol_address() 源码
如果符号的类型不是 STT_GNU_IFUNC(GNU indirect function),如STT_FUNC(可执行代码,如函数)、 STT_OBJECT(数据对象,如变量)等, 直接返回符号的地址,即 s->st_value + load_bias, 否者调用 call_ifunc_resolver()计算符号的地址
call_ifunc_resolver()源码:
1072static ElfW(Addr) call_ifunc_resolver(ElfW(Addr) resolver_addr) {
typedef ElfW(Addr) (*ifunc_resolver_t)(void);
// 将 resolver_addr 转为函数指针
ifunc_resolver_t ifunc_resolver = reinterpret_cast<ifunc_resolver_t>(resolver_addr);
// 执行 resoler_addr 处的函数
ElfW(Addr) ifunc_addr = ifunc_resolver();
TRACE_TYPE(RELO, "Called ifunc_resolver@%p. The result is %p", ifunc_resolver, reinterpret_cast<void*>(ifunc_addr));
return ifunc_addr;
}
call_ifunc_resolver()
重定位类型与重定位值的计算方式对应表
|
重定位类型 |
reloc 处的值 |
|
R_ARM_JUMP_SLOT |
*reloc = sym_addr |
|
R_ARM_GLOB_DAT |
*reloc = sym_addr |
|
R_ARM_ABS32 |
*reloc += sym_addr |
|
R_ARM_REL32 |
*reloc+= sym_addr - rel->r_offset |
|
R_ARM_RELATIVE |
*reloc += base |
至此,find_libraries()的第三部分分析完了。
总结:遍历重定位表,根据重定项的 r_info 获得重定位类型和重定位项对应的符号在符号表中的索引;然后利用 so 中的 hash 表,根据符号名快速地查找符号在哪个 so中定义; 当找到了符号的定义,计算符号的地址 sym_addr;最后根据符号的重定位类型,结合 sym_addr 计算重定位值。
so 文件加载到内存,并链接完成后,就开始调用 so 中的初始化函数。回到 do_dlopen()继续分析。
do_dlopen()的第二部分:
CallConstructors()进行初始化操作
CallConstructors()源码
1656void soinfo::CallConstructors() {
if (constructors_called) {
return;
}
// We set constructors_called before actually calling the constructors, otherwise it doesn't
// protect against recursive constructor calls. One simple example of constructor recursion
// is the libc debug malloc, which is implemented in libc_malloc_debug_leak.so:
// 1. The program depends on libc, so libc's constructor is called here.
// 2. The libc constructor calls dlopen() to load libc_malloc_debug_leak.so.
// 3. dlopen() calls the constructors on the newly created
// soinfo for libc_malloc_debug_leak.so.
// 4. The debug .so depends on libc, so CallConstructors is
// called again with the libc soinfo. If it doesn't trigger the early-
// out above, the libc constructor will be called again (recursively!).
constructors_called = true;
if ((flags & FLAG_EXE) == && preinit_array != nullptr) {
// The GNU dynamic linker silently ignores these, but we warn the developer.
PRINT("\"%s\": ignoring %zd-entry DT_PREINIT_ARRAY in shared library!",
name, preinit_array_count);
}
get_children().for_each([] (soinfo* si) {
si->CallConstructors();
});
TRACE("\"%s\": calling constructors", name);
// DT_INIT should be called before DT_INIT_ARRAY if both are present.
// 调用 init_func 函数
CallFunction("DT_INIT", init_func);
// 调用 init_array 数组中的函数
CallArray("DT_INIT_ARRAY", init_array, init_array_count, false);
}
CallConstructors()
init_func 和init_array,这两个变量是在 PrelinkImage()中解析 dynamic section 时赋值的。 通常加壳逻辑就放在 init_func 或 init_array 中,它们先于 jni_onLoad 执行。
Native层和so接口和Java层的更多相关文章
- JNI通过线程c回调java层的函数
1.参看博客:http://www.jianshu.com/p/e576c7e1c403 Android JNI 篇 - JNI回调的三种方法(精华篇) 2.参看博客: JNI层线程回调Java函数关 ...
- (转)java 层调用Jni(Ndk) 持久化c c++ 对象
对于Jni(Ndk) 很多人应该都有印象,Android的ndk接触到的机会相对会比较多,本例子以android平台为例,pc端的话就以简单的windows为例, 编码完用vs 或是 gcc进行编译成 ...
- Android native进程间通信实例-binder篇之——HAL层访问JAVA层的服务
有一天在群里聊天的时候,有人提出一个问题,怎样才能做到HAL层访问JAVA层的接口?刚好我不会,所以做了一点研究. 之前的文章末尾部分说过了service call 可以用来调试系统的binder服务 ...
- Android Java层,Native层,Lib层打印Log简介【转】
本文转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/AndroidMage/article/details/52225068 说明: 这里我根据个人工作情况说明在各个层打印log.如有问题欢迎拍砖 ...
- Andrdoid中相应用程序的行为拦截实现方式之----从Java层进行拦截
致谢: 感谢 简行之旅的这篇blog:http://blog.csdn.net/l173864930/article/details/38455951,这篇文章是參考这篇blog的进行一步一步操作的, ...
- cocos2d-x 通过JNI实现c/c++和Android的java层函数互调
文章摘要: 本文主要实现两个功能: (1)通过Android sdk的API得到应用程序的包名(PackageName),然后传递给c++层函数. (2)通过c++函数调用Android的java层函 ...
- Android Multimedia框架总结(四)MediaPlayer中从Java层到C++层类关系及prepare及之后其他过程
转载请把头部出处链接和尾部二维码一起转载,本文出自:http://blog.csdn.net/hejjunlin/article/details/52420803 前言:在上篇中,分析了MediaPl ...
- Android消息机制1-Handler(Java层)(转)
转自:http://gityuan.com/2015/12/26/handler-message-framework/ 相关源码 framework/base/core/java/andorid/os ...
- Andrdoid中对应用程序的行为拦截实现方式之----从Java层进行拦截
致谢: 感谢 简行之旅的这篇blog:http://blog.csdn.net/l173864930/article/details/38455951,这篇文章是参考这篇blog的进行一步一步操作的, ...
随机推荐
- Python控制流程
if elif else的用法 三目运算符的用法 while 和 for 两种循环 break 和 continue 的用法 条件判断 if elif else if 和 elif 后面填的判 ...
- TensorFlow Federated:基于分散式数据的机器学习
https://www.tensorflow.org/federated/ TensorFlow Federated (TFF) 是一个开源框架,用于对分散式数据进行机器学习和其他计算.我们开发 TF ...
- c# 第29节 类
本节内容: 1:类是什么 2:声明类 3:类的使用 1:类是什么 2:声明类 在生产上的声明:如下操作 或者快捷操作 ctrl+shift+a 键 出现如下界面: 3:类的使用 using Sys ...
- STL ——map、set、unordered_map、unordered_set
1.map和set map和set底层实现均是红黑树 map支持下标操作,set不支持下标操作. set的迭代器是const的,不允许修改元素的值:map允许修改value,但不允许修改key. se ...
- lua 12 table 的使用
转自:http://www.runoob.com/lua/lua-tables.html table 是 Lua 的一种数据结构用来帮助我们创建不同的数据类型,如:数组.字典等. Lua table ...
- vue项目中常见问题及解决方案
webpack项目中自动引入全局scss变量文件 假设我们有一个公共的scss变量文件variables.scss /*存放所有全局变量*/ $card-title:#C7D200; //首页 卡片标 ...
- CF1207G Indie Album
题目链接 problem 有\(n\)个字符串,对于第\(i\)个字符串通过以下两种方式中的一个给出. \(1\; c\),该字符串只含一个字符\(c\). \(2\ x\ c\),该字符串为第\(x ...
- display Flex 盒子模型布局兼容Android UC
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><meta content= ...
- centos7下安装php-memcached扩展
-> https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_35861664/article/details/72831556 安装扩展进行编译时如果报错,则将 ./configure --w ...
- 基于Django的Rest Framework框架的版本控制
本文目录 一 作用 二 内置的版本控制类 三 局部使用 四 全局使用 五 示例 源码分析 回到目录 一 作用 用于版本的控制 回到目录 二 内置的版本控制类 from rest_framework.v ...
