Java学习作业(14.4.21)
前三次作业都是基础语法。真的好水啊。从这次开始记录。
1.编写Java程序,把当前目录下扩展名为txt的文件的扩展名全部更名为back。
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*; public class Home { public void reName(String path, String from, String to) {
File f = new File(path); //声明File对象,用于导入修改路径
File[] fs = f.listFiles(); //声明File对象数组,用于存储f目录下的文件
for (int i = 0; i < fs.length; ++i) {
File f2 = fs[i]; //通过对各个文件的遍历,通过f2 取出各个文件
if (f2.isDirectory()) {
reName(f2.getPath(), from, to); //如果f2 是一个目录,则递归调用reName,更改子目录中的文件
} else {
String name = f2.getName();
if (name.endsWith(from)) { //否则更改该文件下文件
f2.renameTo(new File(f2.getParent() + "/" + name.substring(0, name.indexOf(from)) + to));
}
}
} System.out.print("文件修改成功 \n");
System.out.print("请到文件目录下查看修改:\n");
} public static void main(String[] args) {
Home rf = new Home();
rf.reName("D:\\Desgard_Duan\\作业\\", ".txt", ".back");
}
}
(一开始用eclipse成功运行,但是用控制台一直报“NullPointerError”,在9行后增加了如下代码,成果解决。感谢憨大哥。)
if (fs == null) {
System.out.println("目录中无法获取文件,程序退出。");
System.exit(0);
}
2. 编写程序,用命令行参数实现比较两个文件是否长度和内容完全相同,输出比较结果(用Yes和No表示)。
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*; public class Home2 {
private String file1 = null; //用来存储对比的两个文件名
private String file2 = null; public Home2(String file1, String file2) {
this.file1 = file1;
this.file2 = file2;
} private void cmpFile(String file1, String file2) {
try {
BufferedInputStream inFile1 = new BufferedInputStream(new
FileInputStream(file1));
BufferedInputStream inFile2 = new BufferedInputStream(new
FileInputStream(file2));
//long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //计算毫秒数
if(inFile1.available() == inFile2.available()) {
while(inFile1.read() != -1 && inFile2.read() != -1) { //如果文件没有读取到文件结尾处
if(inFile1.read() != inFile2.read()) {
System.out.println("No");
break;
}
}
System.out.println("Yes");
} else {
System.out.println("No");
}
inFile1.close();
inFile2.close();
System.exit(0);
} catch(IOException error) {
error.printStackTrace();
}
} private static String inputFileName() {
String fileName = null;
BufferedReader buffRead1 = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); //通过缓存方式读取文本,由Reader类扩展而来
try {
fileName = buffRead1.readLine();
} catch(IOException error) {
error.printStackTrace();
}
return fileName;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("please input the two files' full path and name:");
System.out.print("File1:");
String file1 = inputFileName();
System.out.print("File2:");
String file2 = inputFileName();
Home2 fileCompare = new Home2(file1, file2);
fileCompare.cmpFile(file1, file2);
}
}
(此题没有什么难度,只要用学会文件读取,逐个字符进行检查即可。在编写包内类的时候,最好的习惯是给每个成员写入set和get方法,笔者有些偷懒。)
3.编写控制台(字符界面)应用程序,实现文件按字节异或加密。要求输入一字节密钥key和源文件名。建立加密文件,加密文件第1字节为密钥key,以后各字节为源文件各字节与密钥进行异或运算的结果编写另程序实现解密(由加密文件还原源文件)。此题鼓励同学自拟图形界面,综合运用对话框或视窗、文件对话框、多种Component、事件响应来实现加密解密功能。
import java.util.*; import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*; public class Text {
Frame f = new Frame("文件加/解密GUI演示");
MenuBar mb = new MenuBar();
Menu me = new Menu("功能");
NewPanel p = new NewPanel(); Text() {
me.add(new MenuItem("加密"));
me.add(new MenuItem("解密"));
me.add(new MenuItem("-"));
me.add(new MenuItem("退出"));
mb.add(me); f.setMenuBar(mb);
f.add(p);
f.setSize(new Dimension(600, 300));
f.setLocation(400, 200);
f.setVisible(true); me.addActionListener(p);
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
} public static void main(String[] args) {
new Text();
} class NewPanel extends Panel implements ActionListener {
Label la1 = new Label();
Label la2 = new Label();
Label la3 = new Label();
Button bu1 = new Button("打开");
Button bu2 = new Button("打开");
Button bu3 = new Button();
TextField tf = new TextField(4);
Panel p1 = new Panel();
Panel p2 = new Panel();
Panel p3 = new Panel();
File file1 = null, file2 = null; NewPanel() {
p1.add(la1); p1.add(bu1);
p2.add(la2); p2.add(bu2);
p3.add(la3); p3.add(tf); p3.add(bu3); this.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
this.add("North", p1); p1.setVisible(false);
this.add("Center", p2); p2.setVisible(false);
this.add("South", p3); p3.setVisible(false); bu1.addActionListener(this);
bu2.addActionListener(this);
bu3.addActionListener(this);
} public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (e.getSource() == bu1) {
FileDialog fd = new FileDialog(f, "打开文件");
fd.setVisible(true);
if (fd.getFile() != null) {
file1 = new File(fd.getDirectory() + fd.getFile());
la1.setText("第一个文件:" + file1.getAbsolutePath());
}
} else if (e.getSource() == bu2) {
FileDialog fd = new FileDialog(f, "打开文件");
fd.setVisible(true);
if (fd.getFile() != null) {
file2 = new File(fd.getDirectory() + fd.getFile());
la2.setText("第二个文件:" + file2.getAbsolutePath());
}
} else if (e.getSource() == bu3 && e.getActionCommand() == "加密") {
try {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream(file1));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream(file2)); // write key
int key = Integer.parseInt(tf.getText());
bos.write(key);
for (int _; (_ = bis.read()) >= 0; ) bos.write(_^key);
bis.close();
bos.close();
la3.setText("加密成功");
tf.setVisible(false);
bu3.setVisible(false);
p3.setVisible(true);
} catch (IOException _) {
}
} else if (e.getSource() == bu3 && e.getActionCommand() == "解密") {
try {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream(file1));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream(file2)); int key = bis.read();
if (key < 0) {
} else {
for (int _; (_ = bis.read()) >= 0; ) bos.write(_^key);
} bis.close();
bos.close();
la3.setText("解密成功");
la3.setVisible(true);
tf.setVisible(false);
bu3.setVisible(false);
p3.setVisible(true);
} catch (IOException _) {
}
} else if (e.getActionCommand() == "加密") {
la1.setText("选择需加密文件:");
p1.setVisible(true);
la2.setText("选择加密到文件:");
p2.setVisible(true);
la3.setText("请输入密匙(1~255):");
la3.setVisible(true);
tf.setVisible(true);
bu3.setLabel("加密");
bu3.setVisible(true);
p3.setVisible(true);
} else if (e.getActionCommand() == "解密") {
la1.setText("选择需解密文件:");
p1.setVisible(true);
la2.setText("选择解密到文件:");
p2.setVisible(true);
la3.setText("请输入密匙(1~255):");
bu3.setLabel("解密");
bu3.setVisible(true);
la3.setVisible(false);
tf.setVisible(false);
p3.setVisible(true);
} else if (e.getActionCommand() == "退出") {
System.exit(0);
} // 可以重排所有组件
f.setVisible(false);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
}
(憨大哥大代码直接抄来了。最近要准备其他事情。唉。。)
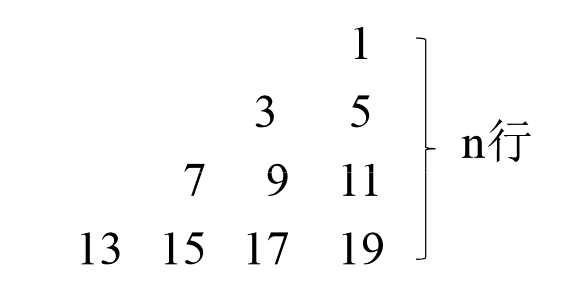
4. 输入打印行数n,打印如下字符图形到屏幕上和字符文件abc.txt中。
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*; public class Home4 {
public static void WriteStringToFile(String filePath, String text) {
try {
File file = new File(filePath);
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
ps.println(text);
} catch (FileNotFoundException error) {
error.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = in.nextInt();
String text = "";
int num = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n - i; j++) {
System.out.print("\t");
text += "\t";
}
for(int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(num + "\t");
text += String.valueOf(num);
text += "\t";
num += 2;
}
System.out.println();
text += "\r\n";
}
WriteStringToFile("abc.txt", text); } }
(最简单的一道作业题目,不多说。)
5. 已知学生类含有实例属性(姓名、学号、成绩),实例方法(构造方法、getter方法)。建立字符文件a.txt,第一行为一个整数(表示学生人数),第二行开始,每行提供一个学生所需的实例属性值。编写程序1,从a.txt输入学生人数和学生信息,建立学生数组。将所有学生数组各元素写入二进制文件a.dat(a.dat的开头4字节为表示学生数的整数)。编写程序2,从a.dat读出学生数据输出为字符文件b.txt(输入出格式同a.txt)。编写程序3读入a.dat数据,用随机文件方式删除成绩<60分的学生记录并存回a.dat。(程序2用于检查程序1和程序2的结果是否正确)。
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.text.*; public class Text {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
fun_1();
//fun_2();
//fun_3();
} public static void fun_1() throws IOException {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(new File("a.txt"));
int N = cin.nextInt();
Student[] stu = new Student[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
stu[i] = new Student(cin.next(), cin.next(), cin.nextFloat());
} ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(
new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("a.dat"))); oos.write(Chg.toByte(N));
for (Student _ : stu) {
oos.writeObject(_);
} cin.close();
oos.close();
} public static void fun_2() throws Exception {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream("a.dat")));
byte[] b = new byte[4];
ois.read(b);
int N = Chg.toInt(b); PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(
new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("b.txt"))); pw.printf("%d\r\n", N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
Student stu = (Student)ois.readObject();
DecimalFormat fmt= new DecimalFormat("###.##");
pw.println(stu.getName() + " " + stu.getNumber() + " " + fmt.format(stu.getScore()));
}
ois.close();
pw.close();
} public static void fun_3() throws Exception {
// 重写a.dat
Scanner cin = new Scanner(new File("a.txt"));
// RandAccessFile只有"rw"和"r",没有"w"
RandomAccessFile oos = new RandomAccessFile("a.dat", "rw"); int N = cin.nextInt();
oos.writeInt(N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
String name = cin.next();
String number = cin.next();
float score = cin.nextFloat(); oos.writeUTF(name);
oos.writeUTF(number);
oos.writeFloat(score);
} cin.close();
oos.close(); //开始删除
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("a.dat", "rw");
N = raf.readInt();
int M = 0; for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
String name = raf.readUTF();
String number = raf.readUTF();
float score = raf.readFloat(); if (score < 60) continue;
++M;
} long r = 0, w = 0;
raf.seek(0);
raf.readInt();
r = raf.getFilePointer();
raf.seek(0);
raf.writeInt(M);
w = raf.getFilePointer(); for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
raf.seek(r);
String name = raf.readUTF();
String number = raf.readUTF();
float score = raf.readFloat();
r = raf.getFilePointer(); if (score < 60) continue;
raf.seek(w);
raf.writeUTF(name);
raf.writeUTF(number);
raf.writeFloat(score);
w = raf.getFilePointer();
}
raf.setLength(w);
raf.close(); //转换到"b.txt"
RandomAccessFile ois = new RandomAccessFile("a.dat", "r");
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(
new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("b.txt"))); N = ois.readInt();
pw.printf("%d\r\n", N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
String name = ois.readUTF();
String number = ois.readUTF();
Float score = ois.readFloat(); DecimalFormat fmt= new DecimalFormat("###.##");
pw.println(name + " " + number + " " + fmt.format(score));
}
ois.close();
pw.close();
}
} class Student implements Serializable {
private String name;
private String number;
private float score; Student() {
}
Student(String _name, String _number, float _score) {
name = _name;
number = _number;
score = _score;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getNumber() {
return number;
}
public float getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setName(String _name) {
name = _name;
}
public void setNumber(String _number) {
number = _number;
}
public void setScore(float _score) {
score = _score;
}
} class Chg {
public static byte[] toByte(int x) {
byte[] b = new byte[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
b[i] = (byte)(x&0xff);
x >>= 8;
}
return b;
} public static int toInt(byte[] b) {
int x = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <b.length; ++i)
x |= (b[i]&0xff)<<(i*8);
return x;
}
}
收获:通过独立完成java课堂题目,了解了java的基本文件的方法,熟悉了处理文件十分基础的API。希望自身不断提高,争取熟练掌握文件控制。
Desgard_Duan 写于2014.4.27
Java学习作业(14.4.21)的更多相关文章
- Java 学习(14):接口 & 包(设置 CLASSPATH 系统变量)
Java 接口(英文:Interface) 定义:在JAVA编程语言中,接口是一个抽象类型,是抽象方法的集合,接口通常以 interface 来声明. 一个类通过继承接口的方式,从而来继承接口的抽象方 ...
- Java 学习笔记(14)—— 文件操作
java文件操作主要封装在Java.io.File中,而文件读写一般采用的是流的方式,Java流封装在 java.io 包中.Java中流可以理解为一个有序的字符序列,从一端导向到另一端.建立了一个流 ...
- java学习第14天(集合的框架和基本遍历)
今天主要是接触了集合的概念,集合简单意义上来说就是类对象的集合,我们一般用Collection 这个接口来表示,集合主要体系为: Collection |--List |--ArrayList |-- ...
- java学习笔记—HttpServletResponse(21)
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, ...
- Java学习笔记14(面向对象七:final、static)
final:意为最终,不可变,是一个修饰词 有时候一个类地功能被开发好了,不想让子类重写,修改,这里就会用到final关键字 final修饰类: 不可以被继承,但是可以继承其他类 示例: public ...
- Java 学习(13):抽象类& 抽象方法& 封装
目录 --- 抽象类 --- 封装 抽象类: 在面向对象的概念中,所有的对象都是通过类来描绘的,但是反过来,并不是所有的类都是用来描绘对象的,如果一个类中没有包含足够的信息来描绘一个具体的对象,这样的 ...
- Java 学习(15):Java 数据结构
Java 数据结构 Java工具包提供了强大的数据结构.在Java中的数据结构主要包括以下几种接口和类: 枚举(Enumeration) 位集合(BitSet) 向量(Vector) 栈(Stack) ...
- Thinking in Java学习杂记(5-6章)
Java中可以通过访问控制符来控制访问权限.其中包含的类别有:public, "有好的"(无关键字), protected 以及 private.在C++中,访问指示符控制着它后面 ...
- 2018面向对象程序设计(Java)第14周学习指导及要求
2018面向对象程序设计(Java)第14周学习指导及要求(2018.11.29-2018.12.2) 学习目标 (1) 掌握GUI布局管理器用法: (2) 掌握各类Java Swing组件用途及 ...
随机推荐
- [转载]date命令时间转换
Linux时间戳和标准时间的互转 在LINUX系统中,有许多场合都使用时间戳的方式表示时间,即从1970年1月1日起至当前的天数或秒数.如/etc/shadow里的密码更改日期和失效日期,还有代理服务 ...
- Spring 的优秀工具类盘点第 2 部分
特殊字符转义 由于 Web 应用程序需要联合使用到多种语言,每种语言都包含一些特殊的字符,对于动态语言或标签式的语言而言,如果需要动态构造语言的内容时,一个我们经常会碰到的问题就是特殊字符转义的问题. ...
- 总结下java经常犯的错误
编写代码是一种艺术,认识错误是我们代码改进的重要途径之一.以下情况并非大家都能碰到过,但希望提高代码质量的人都引以为戒.以下各种情况,都是初学者经常犯的错误. 1.1 字符串没有判断是否为 ...
- Linux应用开发环境搭建
因为笔者是一名大学生,对Linux内核开发方向非常感兴趣,可是实在是能(ji)力(shu)有(cha)限(jin),仅仅能从Linux应用开发開始,由浅入深,逐步进步,登上人生高峰,因此,昨天搭建了开 ...
- HDU 2074 叠筐
叠筐 Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) Total Submission ...
- Sass函数--颜色函数--RGB颜色函数
RGB颜色函数-RGB()颜色函数 主要分为 RGB , HSL 和 Opacity 三大函数,当然其还包括一些其他的颜色函数,比如说 adjust-color 和 change-color 等.1. ...
- 多种下载文件方式 Response.BinaryWrite(byte[] DocContent);Response.WriteFile(System.IO.FileInfo DownloadFile .FullName);Response.Write(string html2Excel);
通过html给xls赋值,并下载xls文件 一.this.Response.Write(sw.ToString());System.IO.StringWriter sw = new System.IO ...
- WCF相关
1.WCF初探-1:认识WCF(概览)2.WCF初探-2:手动实现WCF程序3.WCF精通系列4.无废话WCF系列教程
- (四)CodeMirror - API
内容相关 cm.getValue() cm.setValue() cm.getRange() editor.getRange({line:1},{line:2}) // 获取内容块字符 cm.repl ...
- hdu1520 第一道树形DP,激动哇咔咔!
A - 树形dp Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:65536KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u Submit Sta ...
