Tornado之架构概述图
一、Tornado之架构概述图
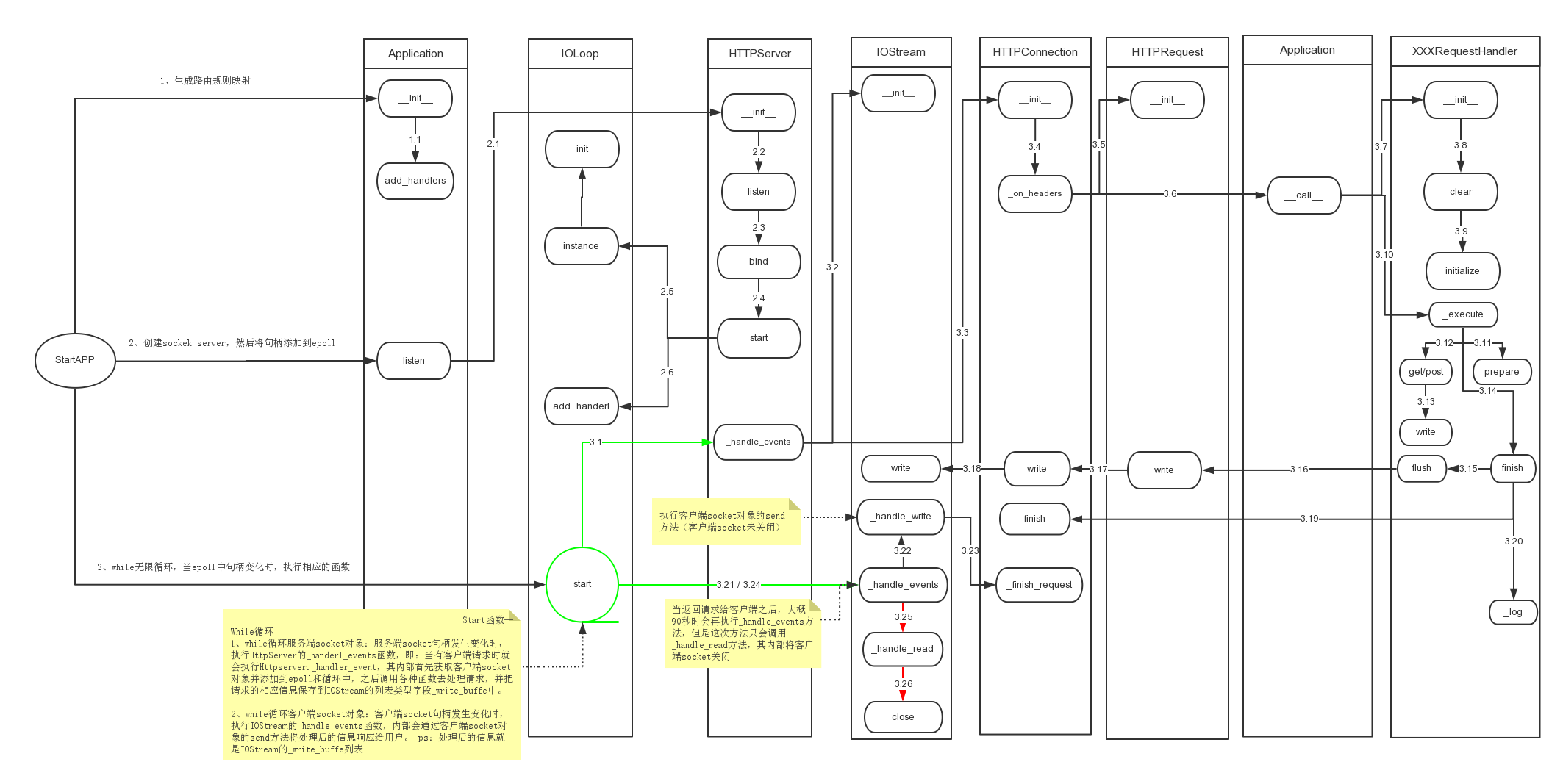
二、Application类详细分析:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf8 -*-
# __Author: "Skiler Hao"
# date: 2017/5/17 11:45 import tornado.web class Application(object):
"""A collection of request handlers that make up a web application.
Application类是request的Handler的集合,组合是一个web应用的组成部分
Instances of this class are callable and can be passed directly to
HTTPServer to serve the application:
Application实例化之后就是可以调用的,也可以直接传递给HTTServer来为Web应用服务
application = web.Application([
(r"/", MainPageHandler),
])
http_server = httpserver.HTTPServer(application)
http_server.listen(8080)
ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start() The constructor for this class takes in a list of URLSpec objects
or (regexp, request_class) tuples. When we receive requests, we
iterate over the list in order and instantiate an instance of the
first request class whose regexp matches the request path.
构造方法接受 URLSpec对象列表 或者 (正则,相应的处理请求的类)的元祖,web服务器收到request请求
接下来会按顺序,如果某个repexp正则匹配成功,就会实例化相应的类
Each tuple can contain an optional third element, which should be a
dictionary if it is present. That dictionary is passed as keyword
arguments to the contructor of the handler. This pattern is used
for the StaticFileHandler below:
每个元祖都可以包含第三个可选的参数,这个第三个参数必须是一个字典,这个字典会作为关键字参数传递给hander的构造器,
下面声明了一个静态文件Handler application = web.Application([
(r"/static/(.*)", web.StaticFileHandler, {"path": "/var/www"}),
])
还支持虚拟主机,通过add_handlers方法,需要把一个主机的正则表达式作为第一个参数
We support virtual hosts with the add_handlers method, which takes in
a host regular expression as the first argument: application.add_handlers(r"www\.myhost\.com", [
(r"/article/([0-9]+)", ArticleHandler),
]) You can serve static files by sending the static_path setting as a
keyword argument. We will serve those files from the /static/ URI
(this is configurable with the static_url_prefix setting),
and we will serve /favicon.ico and /robots.txt from the same directory.
同样可以提供静态文件的访问,需要把静态文件的设置作为关键字参数,我们可以提供/static/文件目录的文件
(在配置中static_url_prefix参数可以配置)
"""
def __init__(self, handlers=None, default_host="", transforms=None,
wsgi=False, **settings):
# 通常的配置都放在settings中
# 设置响应的编码和返回方式,对应的http相应头:Content-Encoding和Transfer-Encoding
# Content-Encoding:gzip 表示对数据进行压缩,然后再返回给用户,从而减少流量的传输。
# Transfer-Encoding:chunck 表示数据的传送方式通过一块一块的传输。
if transforms is None:
self.transforms = []
if settings.get("gzip"):
self.transforms.append(GZipContentEncoding)
self.transforms.append(ChunkedTransferEncoding)
else:
self.transforms = transforms
# 将收到的参数赋值给实例变量,方便调用
self.handlers = []
self.named_handlers = {}
self.default_host = default_host
self.settings = settings
self.ui_modules = {}
self.ui_methods = {}
self._wsgi = wsgi
# 获取获取用户自定义的ui_modules和ui_methods
self._load_ui_modules(settings.get("ui_modules", {}))
self._load_ui_methods(settings.get("ui_methods", {})) # 设置静态文件路径,设置方式则是通过正则表达式匹配url,让StaticFileHandler来处理匹配的url
if self.settings.get("static_path"):
# 检查settings是否有static_path
path = self.settings["static_path"]
# 传递的参数是否有handlers,有的话转化成列表,没有的话是空列表
handlers = list(handlers or [])
# 检查是否有static_url_prefix配置,没有的话使用默认/static/
static_url_prefix = settings.get("static_url_prefix",
"/static/")
# 在handlers追加上静态文件的handlers
handlers = [
(re.escape(static_url_prefix) + r"(.*)", StaticFileHandler,
dict(path=path)),
(r"/(favicon\.ico)", StaticFileHandler, dict(path=path)),
(r"/(robots\.txt)", StaticFileHandler, dict(path=path)),
] + handlers
# 此时,handlers是一个列表,其中的每个元素都是一个对应关系,即:url正则表达式和处理匹配该正则的url的Handler
# 执行Application类的add_handlers ,将 handlers加入进去
if handlers: self.add_handlers(".*$", handlers) # Automatically reload modified modules
# 如果setting设置了debug模式,自动加载重新启动
if self.settings.get("debug") and not wsgi:
import autoreload
autoreload.start() def listen(self, port, address="", **kwargs):
"""Starts an HTTP server for this application on the given port.
在指定的端口启动一个HTTPserver应用
This is a convenience alias for creating an HTTPServer object
and calling its listen method. Keyword arguments not
supported by HTTPServer.listen are passed to the HTTPServer
constructor. For advanced uses (e.g. preforking), do not use
this method; create an HTTPServer and call its bind/start
methods directly.
这是一个创建HTTPServer对象的快捷方式,会自动调用HTTPServer的listen方法
HTTPServer不支持关键字参数,listen回传给HTTPServer构造器。但是对于高级的应用(例如:Preforking),请不要使用本方法
可以创建一个HTTTPServer,然后调用它的bind和start方法 Note that after calling this method you still need to call
IOLoop.instance().start() to start the server.
但是注意调用了此方法,还得调用IOLoop.instance().start()去启动服务
"""
# import is here rather than top level because HTTPServer
# is not importable on appengine
# 在此处导入而不是最顶部,是由于HTTPServer在appengine层面不可导入
from tornado.httpserver import HTTPServer # 实例化HTTPServer对象
server = HTTPServer(self, **kwargs)
# 调用HTTPServer的listen方法
server.listen(port, address) def add_handlers(self, host_pattern, host_handlers):
"""Appends the given handlers to our handler list.
追加给定的handlers到handler list中
Note that host patterns are processed sequentially in the
order they were added, and only the first matching pattern is
used. This means that all handlers for a given host must be
added in a single add_handlers call.
注意主机模式的匹配是按加入的顺序依次执行的,只会使用第一次匹配到的模式
所以给定的主机所有handlers,只能通过调用add_handlers来追加
"""
# 如果添加的pattern末尾不是以$结尾,主动加上
if not host_pattern.endswith("$"):
host_pattern += "$"
handlers = []
# The handlers with the wildcard host_pattern are a special
# case - they're added in the constructor but should have lower
# precedence than the more-precise handlers added later.
# If a wildcard handler group exists, it should always be last
# in the list, so insert new groups just before it.
if self.handlers and self.handlers[-1][0].pattern == '.*$':
# 使用.* 这个通配符,还记得上面的init方法不。这些应该有更低的优先级相对于后面使用add_handers添加的
# 所以.* 应该放在新加入的后面,默认.*位置应该总是-1,所以只要insert(-1,)即可在.*前面
self.handlers.insert(-1, (re.compile(host_pattern), handlers))
else:
# 如果没有的话,直接追加就可以,这个else一般木有可能,一般都得先init
self.handlers.append((re.compile(host_pattern), handlers)) # 遍历我们设置的和构造函数中添加的【url->Handler】映射,将url和对应的Handler封装到URLSpec类中(构造函数中会对url进行编译)
# 并将所有的URLSpec对象添加到handlers列表中,而handlers列表和主机名模型组成一个元祖,添加到self.Handlers列表中。
for spec in host_handlers:
# 判断类型是不是元祖
if type(spec) is type(()):
assert len(spec) in (2, 3)
# 断言host_handlers 的长度应该是2或3,例如:(r"/static/(.*)", web.StaticFileHandler, {"path": "/var/www"})
pattern = spec[0]
handler = spec[1]
if len(spec) == 3:
# 将第三个放到kwargs
kwargs = spec[2]
else:
kwargs = {}
# 将数据封装成URLSpec对象
spec = URLSpec(pattern, handler, kwargs)
# 让后将URLSpec对象放在handlers列表里
handlers.append(spec)
# 如果URLSpec对象有名字,则追加到Application实例对象的named_handlers中
if spec.name:
# 如果已经有了,调用logging模块输出多个handlers使用名字~~~,后面的将代替前面的
if spec.name in self.named_handlers:
logging.warning(
"Multiple handlers named %s; replacing previous value",
spec.name)
self.named_handlers[spec.name] = spec def add_transform(self, transform_class):
"""
Adds the given OutputTransform to our transform list.
添加OutputTransform到我们的transform列表中
"""
self.transforms.append(transform_class) def _get_host_handlers(self, request):
# 给定一个request可以返回是哪个handlers处理的
host = request.host.lower().split(':')[0]
for pattern, handlers in self.handlers:
if pattern.match(host):
return handlers
# Look for default host if not behind load balancer (for debugging)
if "X-Real-Ip" not in request.headers:
for pattern, handlers in self.handlers:
if pattern.match(self.default_host):
return handlers
return None def _load_ui_methods(self, methods):
"""关于加载ui方法的"""
if type(methods) is types.ModuleType:
self._load_ui_methods(dict((n, getattr(methods, n))
for n in dir(methods)))
elif isinstance(methods, list):
for m in methods: self._load_ui_methods(m)
else:
for name, fn in methods.iteritems():
if not name.startswith("_") and hasattr(fn, "__call__") \
and name[0].lower() == name[0]:
self.ui_methods[name] = fn def _load_ui_modules(self, modules):
"""关于加载ui模块的"""
if type(modules) is types.ModuleType:
self._load_ui_modules(dict((n, getattr(modules, n))
for n in dir(modules)))
elif isinstance(modules, list):
for m in modules: self._load_ui_modules(m)
else:
assert isinstance(modules, dict)
for name, cls in modules.iteritems():
try:
if issubclass(cls, UIModule):
self.ui_modules[name] = cls
except TypeError:
pass def __call__(self, request):
"""
Called by HTTPServer to execute the request.
HTTPServert调用来执行request请求的
"""
transforms = [t(request) for t in self.transforms]
handler = None
args = []
kwargs = {}
handlers = self._get_host_handlers(request)
if not handlers:
handler = RedirectHandler(
self, request, url="http://" + self.default_host + "/")
else:
for spec in handlers:
match = spec.regex.match(request.path)
if match:
# None-safe wrapper around urllib.unquote to handle
# unmatched optional groups correctly
def unquote(s):
if s is None: return s
return urllib.unquote(s)
handler = spec.handler_class(self, request, **spec.kwargs)
# Pass matched groups to the handler. Since
# match.groups() includes both named and unnamed groups,
# we want to use either groups or groupdict but not both.
kwargs = dict((k, unquote(v))
for (k, v) in match.groupdict().iteritems())
if kwargs:
args = []
else:
args = [unquote(s) for s in match.groups()]
break
if not handler:
handler = ErrorHandler(self, request, status_code=404) # In debug mode, re-compile templates and reload static files on every
# request so you don't need to restart to see changes
if self.settings.get("debug"):
if getattr(RequestHandler, "_templates", None):
for loader in RequestHandler._templates.values():
loader.reset()
RequestHandler._static_hashes = {} handler._execute(transforms, *args, **kwargs)
return handler def reverse_url(self, name, *args):
"""Returns a URL path for handler named `name`
给 名字 可以返回其URL路径
The handler must be added to the application as a named URLSpec
"""
if name in self.named_handlers:
"""
self.named_handlers['name'] = URLSpec
URLSpec.reverse()方法,否则抛异常找不到
"""
return self.named_handlers[name].reverse(*args)
raise KeyError("%s not found in named urls" % name) def log_request(self, handler):
"""Writes a completed HTTP request to the logs. By default writes to the python root logger. To change
this behavior either subclass Application and override this method,
or pass a function in the application settings dictionary as
'log_function'.
"""
if "log_function" in self.settings:
self.settings["log_function"](handler)
return
if handler.get_status() < 400:
log_method = logging.info
elif handler.get_status() < 500:
log_method = logging.warning
else:
log_method = logging.error
request_time = 1000.0 * handler.request.request_time()
log_method("%d %s %.2fms", handler.get_status(),
handler._request_summary(), request_time)
Tornado之架构概述图的更多相关文章
- 老李推荐: 第14章2节《MonkeyRunner源码剖析》 HierarchyViewer实现原理-HierarchyViewer架构概述
老李推荐: 第14章2节<MonkeyRunner源码剖析> HierarchyViewer实现原理-HierarchyViewer架构概述 HierarchyViewer库的引入让M ...
- MySQL逻辑架构概述
1.MySQL逻辑架构 MySQL逻辑架构图 MySQL逻辑架构分四层 1.连接层:主要完成一些类似连接处理,授权认证及相关的安全方案. 2.服务层:在 MySQL据库系统处理底层数据之前的所有工作都 ...
- Java生鲜电商平台-微服务架构概述
Java生鲜电商平台-微服务架构概述 单体架构存在的问题 在传统的软件技术架构系统中,基本上将业务功能集中在单一应用内,或者是单一进程中.尽管现代化的软件架构理论以及设计原则已推广多年,但实际技术衍化 ...
- HDFS(Hadoop Distributed File System)的组件架构概述
1.hadoop1.x和hadoop2.x区别 2.组件介绍 HDFS架构概述1)NameNode(nn): 存储文件的元数据,如文件名,文件目录结构,文件属性(生成时间,副本数,文件权限),以及每个 ...
- netty系列之:netty架构概述
目录 简介 netty架构图 丰富的Buffer数据机构 零拷贝 统一的API 事件驱动 其他优秀的特性 总结 简介 Netty为什么这么优秀,它在JDK本身的NIO基础上又做了什么改进呢?它的架构和 ...
- UML精粹5 - 状态图,活动图,通信图,组合结构,组件图,协作,交互概述图,时间图
状态机图state machine diagram 下面是状态图的一个例子(一个城堡中的秘密保险箱的控制面板). 转换transition包括3个部分:trigger-signature [guard ...
- Scrapy架构概述
Scrapy架构概述 1, 从最初自己编写的spiders,获取到start_url,并且封装成Request对象. 2,通过engine(引擎)调度给SCHEDULER(Requests管理调度器) ...
- Python设计模式 - UML - 交互概述图(Interaction Overview Diagram)
简介 交互概述图是将不同交互图衔接在一起的图,属于UML2.0的新增图.交互概述图并没有引入新的建模元素,其主要元素来自于活动图和时序图.交互概述图侧重从整体上概览交互过程中的控制流,包括交互图之间的 ...
- 大型互联网架构概述 关于架构的架构目标 典型实现 DNS CDN LB WEB APP SOA MQ CACHE STORAGE
大型互联网架构概述 目录 架构目标 典型实现 DNS CDN LB WEB APP SOA MQ CACHE STORAGE 本文旨在简单介绍大型互联网的架构和核心组件实现原理. 理论上讲,从安装配置 ...
随机推荐
- LeetCode第[98]题(Java):Validate Binary Search Tree(验证二叉搜索树)
题目:验证二叉搜索树 难度:Medium 题目内容: Given a binary tree, determine if it is a valid binary search tree (BST). ...
- 【性能测试】服务器性能监控、数据采集工具nmon安装使用详解
nmon nmon是一种在AIX与各种Linux操作系统上广泛使用的监控与分析工具,它能在系统运行过程中实时地捕捉系统资源的使用情况,并且能输出结果到文件中,然后通过nmon_analyzer工具产生 ...
- idea 2018注册码
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/zhw0596/article/details/81394870 (最新的看后面!!! 转载的请附上原文链接 搜索不易!)百度的,上一个没用 ...
- WebAPI项目 IHttpActionResult不识别解决办法
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/nnnnnbody/article/details/16945253 使用ASP.NET Web API构造基于restful风格web service ...
- MVC后台的几种跳转方法
//当服务器执行到Response.Redirect语句时,会立即中断页面的生命周期,直接向客户端返回信息,让客户端进行重定向操作.302(暂时重定向) Response.Redirect(" ...
- 1-18 编译安装内核支持ntfs文件系统
大纲: 源码编译Linux内核 使用Linux内核模块 实战:编译一个NTFS内核模块,实现Linux挂载NTFS文件系统并实现读写功能 =============================== ...
- H3C Huawei 交换机 IPv6环境配置
# 使能IPv6报文转发功能. <Sysname> system-view [Sysname] ipv6 # 使能DHCPv6服务器功能. <Sysname> system-v ...
- lspci能看到ifconfig -a看不到网卡
随着宽带技术的快速发展,服务器使用万兆网卡的概率越来越高.最近装了几台服务器都用的万兆网卡,为了图便宜,网卡和模块都是淘宝上买的,这部还真遇到不少问题. 我的服务器都是centos6.4 64位的,网 ...
- 008PHP基础知识——运算符(一)
<?php /** * 运算符(一) */ /*PHP中的运算符: * 1.算术运算符: * 2.递增/递减运算符 * 3.比较运算符 * 4.逻辑运算符 * 5.位运算符 * 6.其他运算符 ...
- Java进阶4表达式中的陷阱
Java进阶4表达式中的陷阱 20131103 表达式是Java中最基本的组成单元,各种表达式是Java程序员最司空见惯的内容,Java中的表达式并不是十分的复杂,但是也有一些陷阱.例如当程序中使用算 ...
