/etc/profile、~/.bash_profile等几个文件的执行过程
分类: LINUX
2012-04-26 17:44:55

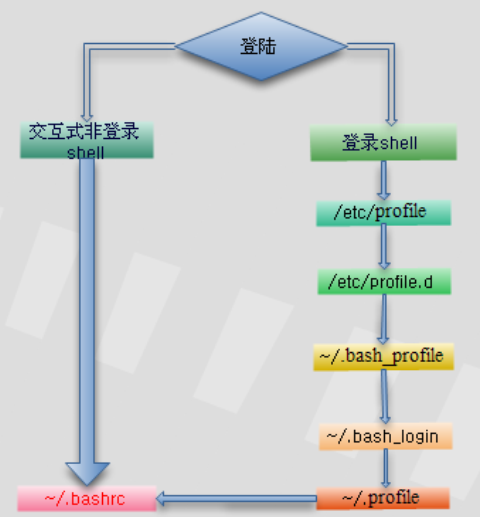
关于登录linux时,/etc/profile、~/.bash_profile等几个文件的执行过程。
在登录Linux时要执行文件的过程如下:
在 刚登录Linux时,首先启动 /etc/profile 文件,然后再启动用户目录下的 ~/.bash_profile、 ~/.bash_login或 ~/.profile文件中的其中一个,执行的顺序为:~/.bash_profile、 ~/.bash_login、 ~/.profile。如果 ~/.bash_profile文件存在的话,一般还会执行 ~/.bashrc文件。因为在 ~/.bash_profile文件中一般会有下面的代码:
if [ -f ~/.bashrc ] ; then
. ./bashrc
fi
~/.bashrc中,一般还会有以下代码:
if [ -f /etc/bashrc ] ; then
. /etc/bashrc
fi
所以,~/.bashrc会调用 /etc/bashrc文件。最后,在退出shell时,还会执行 ~/.bash_logout文件。
执 行顺序为:/etc/profile -> (~/.bash_profile | ~/.bash_login | ~/.profile) -> ~/.bashrc ->/etc/bashrc -> ~/.bash_logout
关于各个文件的作用域,在网上找到了以下说明:
(1)/etc/profile: 此文件为系统的每个用户设置环境信息,当用户第一次登录时,该文件被执行. 并从/etc/profile.d目录的配置文件中搜集shell的设置。
(2)/etc/bashrc: 为每一个运行bash shell的用户执行此文件.当bash shell被打开时,该文件被读取。
(3)~/.bash_profile: 每个用户都可使用该文件输入专用于自己使用的shell信息,当用户登录时,该文件仅仅执行一次!默认情况下,他设置一些环境变量,执行用户的.bashrc文件。
(4)~/.bashrc: 该文件包含专用于你的bash shell的bash信息,当登录时以及每次打开新的shell时,该该文件被读取。
(5)~/.bash_logout: 当每次退出系统(退出bash shell)时,执行该文件. 另外,/etc/profile中设定的变量(全局)的可以作用于任何用户,而~/.bashrc等中设定的变量(局部)只能继承/etc /profile中的变量,他们是"父子"关系。
(6)~/.bash_profile 是交互式、login 方式进入 bash 运行的~/.bashrc 是交互式 non-login 方式进入 bash 运行的通常二者设置大致相同,所以通常前者会调用后者。
我 做了个实验,在/etc/profile,/etc/bashrc,~/.bashrc和~/.bash_profile文件的最后追加同一个变量分别赋 予不同的值,实验结果表明变量最后的值为~/.bash_profile里的值。(4个文件都没有修改其他设置,都是安装系统后的默认值。)
再有就是4个文件都追加一个值到同一个文件,开机后查看该文件内容的顺序为:
/etc/profile
~/.bash_profile
~/.bashrc
/etc/bashrc
----------------------
其他文章:
redhat bash 初始化设置
先说明三个概念
登录shell
正常登录程序启动的shell.既登录成功后紧接着给登录用户启动的shell.
非登录交互式shell
这个shell的工作方式是交互式的,等用户输入,然后执行,再等用户输入。显然登录shell就是一个交互式shell。
如下,我们可获得一个交互式非登录shell:
[root@localhost ~]# bash
[root@localhost ~]# pwd
/root
非交互式shell
为运行一个shell脚本启动的shell.
以FC5的bash为例,跟shell环境配置相关的文件以下几个,
/etc/profile
/etc/profile.d/*.sh
/etc/bashrc
~/.bash_profile
~/.bashrc
有时你会发现定义一个别名,有时好像在任意一个文件里定义都可以起作用,有时好像又不起作用,那是为什么呢?这些配置文件各自互责了什么工作?相互的关系是怎么样的?跟前面介绍的不同种类的shell的关系是如何的呢?下面对每个文件单独进行说明。
/etc/profile
Linux规定,当启动一个登录shell会执行这个脚本. 测试过程如下:
把LIST的定义加到/etc/profile文件的未尾并保存. 如下:
alias LIST='ls -l'
把所有其它shell配置文件或目录改名,这样系统就找不到那些shell脚本了,不会执行,重而避免其它配置文件的干扰。如下:
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /etc/profile.bak
[root@localhost ~]# mv /etc/profile.d/* -t /etc/profile.bak/
[root@localhost ~]# mv /etc/bashrc /etc/bashrc.bak
[root@localhost ~]# mv ~/.bash_profile ~/.bash_profile.bak
[root@localhost ~]# mv ~/.bashrc ~/.bashrc.bak
交互式shell,并测试过程如下:
[root@localhost ~]# bash
bash-3.1# LIST
bash: LIST: command not found
bash-3.1# exit
exit
[root@localhost ~]#
显然启动一个普通交互式shell的时候, shell配置文件/etc/profile不起作用
非交互式shell, 测试过程如下:
为了验证先写一个测试脚本,如下:
#!/bin/bash
LIST
把这个脚本保存为t.sh并加下可执行权限:
[root@localhost ~]# chmod a x t.sh
[root@localhost ~]# ./t.sh
./t.sh: line 2: LIST: command not found
[root@localhost ~]#
显然启动一个非交互式shell时,shell配置文件/etc/profile不起作用
登录shell,并测试过程如下:
Last login: Wed Nov 19 10:22:23 2008 from 192.168.0.97
-bash-3.1# LIST
total 160
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Aug 14 12:24 Desktop
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3211 Nov 6 10:15 Session.vim
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 10 10:58 a
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 126 Nov 12 12:42 a.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 261 Nov 6 15:23 a.zip
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 157 Nov 6 15:23 aa.zip
-rw------- 1 root root 1054 Aug 14 11:59 anaconda-ks.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 691 Nov 18 10:09 b.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 31671 Aug 14 11:58 install.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4155 Aug 14 11:50 install.log.syslog
-rw------- 1 root root 20310 Nov 17 13:51 mbox
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 17 17:22 shell
-rwxrwxrwx 1 root root 65 Nov 19 10:11 t.sh
drwxr-xr-x 14 root root 4096 Nov 5 15:34 test
-bash-3.1#
显然启动一个登录shell时,shell配置文件/etc/profile会起作用
~/.bash_profile
这个文件跟/etc/profile起作用的时机是一样的,都是只在启动一个登录shell的时候才会被source,跟/etc/profile不同的是,这里的配置只影响单个用户,不对其它用户产生影响。
/etc/bashrc与~/.bashrc
从字面上我们可以理解这两个文件应该跟根bash相关,即 只要你启动了一个bash类型的shell这两文件的配置就将发生作用。如果你的shell是sh、csh或是ksh这两个文件将不起作用。按前面的介 绍,可能很会猜测/etc/bashrc与~/.bashrc的关系跟/etc/profile与~/.bash_profile的关系一样,一个是全局 的,一个是针对单个用户的。从结果上看确实是这样的,但实现过程却是不一样的。启动一个bash时直接source ~/.bashrc, 而这~/.bashrc里面会source /etc/bashrc。
/etc/profile.d/*.sh
在fc5下这里的脚本会在/etc/profile里或是~/.bashrc里同时source, 所以这里的设置都是一些不同分类的全局环境设置。
总结在FC5下一个登录bash的环境初始全过程是:
/etc/profile
|
--/etc/profile.d/*
~/.bash_profile
|
--~/.bashrc
|
--/etc/bashrc
|
--/etc/profile.d/*
一个普通交互式bash的初始全过程是:
~/.bashrc
|
--/etc/bashrc
|
--/etc/profile.d/*
对于非交互式bash的初始全过程是:
不重新source 任何新的shell脚本,只继承当前shell的设置.
/etc/profile、~/.bash_profile等几个文件的执行过程的更多相关文章
- linux下系统启动时,几个配置文件 /etc/profile、~/.bash_profile 等几个文件的执行过程,先后顺序
1. 在登录Linux时要执行文件的过程如下: 在刚登录Linux时, 首先启动 /etc/profile 文件, 然后再启动用户目录下的 ~/.bash_profile. ~/.bash_login ...
- 【转】Linux 之 /etc/profile、~/.bash_profile 等几个文件的执行过程
原文网址:http://blog.csdn.net/ithomer/article/details/6322892 在登录Linux时要执行文件的过程如下:在刚登录Linux时,首先启动 /etc/p ...
- linux环境变量设置 以及 source命令 Linux 之 /etc/profile、~/.bash_profile 等几个文件的执行过程 Linux 设置环境变量
定制环境变量 环境变量是和Shell紧密相关的,用户登录系统后就启动了一个Shell.对于Linux来说一般是bash,但也可以重新设定或切换到其它的Shell.环境变量文件:/etc/profil ...
- /etc/profile ~/.bash_profile ~/.bashrc 等文件的执行过程 和 区别
/etc/profile :系统的所有用户共享 ~/.bash_profile:仅针对当前用户有效 我的电脑只用于开发,因此全部配置/etc/profile 参考链接: https://blog.cs ...
- 一个 java 文件的执行过程详解
平时我们都使用 idea.eclipse 等软件来编写代码,在编写完之后直接点击运行就可以启动程序了,那么这个过程是怎么样的? 总体过程 我们编写的 java 文件在由编译器编译后会生成对应的 cla ...
- linux下 /etc/profile、~/.bash_profile ~/.profile的执行过程
关于登录linux时,/etc/profile.~/.bash_profile等几个文件的执行过程. 在登录Linux时要执行文件的过程如下: 在刚登录Linux时,首先启动 /etc/profile ...
- [转] linux下 /etc/profile、~/.bash_profile ~/.profile的执行过程
分类: linux 2015-03-13 16:24 1572人阅读 评论(0) 收藏 举报linuxprofile关于登录linux时,/etc/profile.~/.bash_profile等几个 ...
- 【总结】/etc/rc.d/rc.local 与 /etc/profile .bash_profile .bashrc 文件执行顺序
登陆shell与交互式非登陆shell的区别 登录shell 所谓登录shell,指的是当用户登录系统时所取的那个 shell.登录shell属于交互式shell. 登录shell将查找4个不同的启动 ...
- Linux系统profile、bashrc、bash_profile等环境设置文件的使用
一.前言 关于bash的环境设置文件,分为系统设置和个人设置,一般来说建议用户直接修改个人的设置. 本文测试环境为:centos6.5. 二.系统设置值 1. /etc/sysconfig/i18n ...
随机推荐
- 老司机带带我,FIFO不简单
FIFO,没有想象的那么简单! 根据一般的原则,FIFO这件事情啊,如果能用IP先别自己手写.可以通过FPGA厂家的的IP生成工具生成相应的FIFO. FIFO中的格雷码: 格雷码应用于异步FIFO的 ...
- bzoj4598: [Sdoi2016]模式字符串
Description 给出n个结点的树结构T,其中每一个结点上有一个字符,这里我们所说的字符只考虑大写字母A到Z,再给出长度为m 的模式串s,其中每一位仍然是A到z的大写字母.Alice希望知道,有 ...
- 004:MySQL数据库体系结构
目录 一. MySQL数据库体系结构 1.MySQL数据库体系结构介绍 1 数据库定义 2 数据库实例 2. MySQL体系结构 1 单进程多线程结构 2 存储引擎的概念 3 体系结构图 4 逻辑存储 ...
- node的socket.io的之事件篇
socket.io类库不但可以相互发送消息,而且还可以通过socket端口对象的emit方法互相发送事件. emit在之前的事件上说过现在一句话带过:emit是用来手动触发事件的. socket.em ...
- node中express的中间件之methodOverride
methodOverride中间件必须结合bodyParser中间件一起使用,为bodyParser中间件提供伪HTTP方法支持. index.html代码: <!DOCTYPE html> ...
- libvirt- Virsh 所有命令详单
help 打印帮助 attach-device 从一个XML文件附加装置 attach-disk 附加磁盘设备 attach-interface 获 ...
- Django组件—forms组件
forms组件: 校验字段功能: 针对一个实例:注册用户. 模型:models.py class UserInfo(models.Model): name=models.CharField(max_l ...
- Tkinter Menu(菜单)
Tkinter Menu: 这个小工具的目标是,让我们来创建我们的应用程序,可以通过使用各种菜单.核心功能,提供的方式来创建三个菜单类型:弹出式,顶层,和下拉 这个小工具的目标是,让我们来创建 ...
- Spring定时器Quartz的使用
在JavaEE系统中,我们会经常用到定时任务,比如每天凌晨生成前天报表,每一小时生成汇总数据等等,定时更新某某操作……. 我们可以使用java.util.Timer结合java.util.TimerT ...
- Git(三):Git 使用规范流程
转:http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2015/08/git-use-process.html 团队开发中,遵循一个合理.清晰的Git使用流程,是非常重要的. 否则,每个人 ...
