Codeforces Round #242 (Div. 2) A~C
A. Squats
time limit per test:1 second
memory limit per test:256 megabytes
input:standard input
output:standard output
Pasha has many hamsters and he makes them work out. Today, n hamsters (n is even) came to work out. The hamsters lined up and each hamster either sat down or stood up.
For another exercise, Pasha needs exactly  hamsters to stand up and the other hamsters to sit down. In one minute, Pasha can make some hamster ether sit down or stand up. How many minutes will he need to get what he wants if he acts optimally well?
hamsters to stand up and the other hamsters to sit down. In one minute, Pasha can make some hamster ether sit down or stand up. How many minutes will he need to get what he wants if he acts optimally well?
The first line contains integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 200; n is even). The next line contains n characters without spaces. These characters describe the hamsters' position: the i-th character equals 'X', if the i-th hamster in the row is standing, and 'x', if he is sitting.
In the first line, print a single integer — the minimum required number of minutes. In the second line, print a string that describes the hamsters' position after Pasha makes the required changes. If there are multiple optimal positions, print any of them.
4
xxXx
1
XxXx
2
XX
1
xX
6
xXXxXx
0
xXXxXx
题意 : X代表站着,x代表蹲着,要求n只中正好有一半是蹲着一半是站着,让一只仓鼠由蹲变为站或由站变为蹲需要1分钟,问最少需要多少分钟能够达到要求。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream> using namespace std ;
char sh[] ;
int main()
{
int n ;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
scanf("%s",sh) ;
int cnt = ;
for(int i = ; i < n ; i++)
if(sh[i] == 'X')
cnt++ ;
if(cnt == n/)
{
printf("0\n%s\n",sh) ;
}
else if(cnt > n/)
{
printf("%d\n",cnt-n/) ;
for(int i = ,k = ; i < n && k < cnt-n/ ; i++)
if(sh[i] == 'X')
{
sh[i] = 'x';
k++ ;
}
printf("%s\n",sh) ;
}
else if(cnt < n/)
{
printf("%d\n",n/-cnt) ;
for(int i = ,k = ; i < n && k < n/-cnt ; i++)
if(sh[i] == 'x')
{
sh[i] = 'X';
k++ ;
}
printf("%s\n",sh) ;
}
}
return ;
}
B. Megacity
time limit per test:1 second
memory limit per test:256 megabytes
input:standard input
output:standard output
The administration of the Tomsk Region firmly believes that it's time to become a megacity (that is, get population of one million). Instead of improving the demographic situation, they decided to achieve its goal by expanding the boundaries of the city.
The city of Tomsk can be represented as point on the plane with coordinates (0; 0). The city is surrounded with n other locations, the i-th one has coordinates (xi, yi) with the population of ki people. You can widen the city boundaries to a circle of radius r. In such case all locations inside the circle and on its border are included into the city.
Your goal is to write a program that will determine the minimum radius r, to which is necessary to expand the boundaries of Tomsk, so that it becomes a megacity.
The first line of the input contains two integers n and s (1 ≤ n ≤ 103; 1 ≤ s < 106) — the number of locatons around Tomsk city and the population of the city. Then n lines follow. The i-th line contains three integers — the xi and yi coordinate values of the i-th location and the number ki of people in it (1 ≤ ki < 106). Each coordinate is an integer and doesn't exceed 104 in its absolute value.
It is guaranteed that no two locations are at the same point and no location is at point (0; 0).
In the output, print "-1" (without the quotes), if Tomsk won't be able to become a megacity. Otherwise, in the first line print a single real number — the minimum radius of the circle that the city needs to expand to in order to become a megacity.
The answer is considered correct if the absolute or relative error don't exceed 10 - 6.
4 999998
1 1 1
2 2 1
3 3 1
2 -2 1
2.8284271
4 999998
1 1 2
2 2 1
3 3 1
2 -2 1
1.4142136
2 1
1 1 999997
2 2 1
-1
题意 : 周围有n个城市,这个城市目前有k个人,这个城市要往外扩充,来让人数达到1000000,以0,0为圆心,问你找一个半径为r的圆,要使r尽量小并且这个城市扩充之后的人数至少为1000000 。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream> using namespace std ; struct node
{
double x,y ;
int num ;
} p[]; int cmp(const node &a,const node &b)
{
if(sqrt(a.x*a.x+a.y*a.y) == sqrt(b.x*b.x+b.y*b.y))
return a.num > b.num ;
return sqrt(a.x*a.x+a.y*a.y) < sqrt(b.x*b.x+b.y*b.y) ;
}
int main()
{
int n , k;
while(~scanf("%d %d",&n,&k))
{
int sum = ;
for(int i = ; i < n ; i++)
{
scanf("%lf %lf %d",&p[i].x,&p[i].y,&p[i].num) ;
sum += p[i].num ;
}
if(sum + k < )
{
printf("-1\n") ;
continue ;
}
sort(p,p+n,cmp) ;
int cnt = -k,j,i ;
for(i = ,j = cnt; i < n && j >= ; i++)
{
if(p[i].num >= j)
break ;
else {
j -= p[i].num ;
} }
printf("%.7lf\n",sqrt(p[i].x*p[i].x+p[i].y*p[i].y)) ;
}
return ;
}
C. Magic Formulas
time limit per test:1 second
memory limit per test:256 megabytes
input:standard input
output:standard output
People in the Tomskaya region like magic formulas very much. You can see some of them below.
Imagine you are given a sequence of positive integer numbers p1, p2, ..., pn. Lets write down some magic formulas:
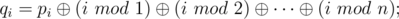
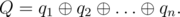
Here, "mod" means the operation of taking the residue after dividing.
The expression 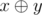 means applying the bitwise xor (excluding "OR") operation to integers x and y. The given operation exists in all modern programming languages. For example, in languages C++ and Java it is represented by "^", in Pascal — by "xor".
means applying the bitwise xor (excluding "OR") operation to integers x and y. The given operation exists in all modern programming languages. For example, in languages C++ and Java it is represented by "^", in Pascal — by "xor".
People in the Tomskaya region like magic formulas very much, but they don't like to calculate them! Therefore you are given the sequence p, calculate the value of Q.
The first line of the input contains the only integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 106). The next line contains n integers: p1, p2, ..., pn (0 ≤ pi ≤ 2·109).
The only line of output should contain a single integer — the value of Q.
3
1 2 3
3
题意 : 给你p1,p2.....pn,根据给定的两个式子,让你求出Q 。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h> using namespace std ; long long a[] ;
long long m ; void table()
{
a[] = ;
a[] = ;
for(int i = ; i < ; i++)
a[i] = a[i-] ^ i ;
} int main()
{
int n ;
table() ;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
long long sum = ;
for(int i = ; i <= n ; i++)
{
scanf("%I64d",&m) ;
sum = sum ^ m ;
}
for(int i = ; i <= n ; i++)
{
int rest = n % i ;
int t = n / i ;
if(t % )
{
sum ^= a[i-] ;
if(rest != )
sum ^= a[rest] ;
}
else
{
if(rest != )
sum ^= a[rest] ;
}
}
printf("%I64d\n",sum) ;
}
return ;
}
这个代码其实有更为简单的写法。。。。。
#include<stdio.h> long long sum,a[],n,m; int main()
{
while(~scanf("%I64d",&n))
{
for(int i = ; i <= n ; i++)
{
a[i] = a[i-] ^ i ;
scanf("%I64d",&m) ;
sum ^= m ^ a[n % i] ^ ( n / i % ? a[i-] : );
}
printf("%I64d\n",sum) ;
}
return ;
}
很神奇有没有。。。。
Codeforces Round #242 (Div. 2) A~C的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #242 (Div. 2) C题
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/424/problem/C, 想来一个小时,就是做不出,都做出来了,悲剧! 分析:我们知道交换异或的顺序不影响答案! 然后就是求t ...
- Codeforces Round #242 (Div. 2) A. Squats
注意题目一次只能改变一个松鼠,Pasha can make some hamster ether sit down or stand up.是单数不是复数 #include <iostream& ...
- Codeforces Round #242 (Div. 2) B. Megacity
按照半径排序,然后累加人数直到超过百万 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #inc ...
- Codeforces Round #242 (Div. 2) C. Magic Formulas
解题思路是: Q=q1^q2.......^qn = p1^p2......^pn^((1%1)^....(1%n))^((2%1)^......(2%n))^.... 故Q的求解过程分成两部分 第一 ...
- Codeforces Round #242 (Div. 2) C. Magic Formulas (位异或性质 找规律)
题目 比赛的时候找出规律了,但是找的有点慢了,写代码的时候出了问题,也没交对,还掉分了.... 还是先总结一下位移或的性质吧: 1. 交换律 a ^ b = b ^ a 2. 结合律 (a^b) ^ ...
- Codeforces Round #242 (Div. 2) <A-D>
CF424 A. Squats 题目意思: 有n(n为偶数)个x和X,求最少的变换次数,使得X的个数为n/2,输出变换后的序列. 解题思路: 统计X的个数ans,和n/2比較,少了的话,须要把n/2- ...
- Codeforces Round #242 (Div. 2)C(找规律,异或运算)
一看就是找规律的题.只要熟悉异或的性质,可以秒杀. 为了防止忘记异或的规则,可以把异或理解为半加运算:其运算法则相当于不带进位的二进制加法. 一些性质如下: 交换律: 结合律: 恒等律: 归零律: 典 ...
- Codeforces Round #258 (Div. 2)[ABCD]
Codeforces Round #258 (Div. 2)[ABCD] ACM 题目地址:Codeforces Round #258 (Div. 2) A - Game With Sticks 题意 ...
- Codeforces Round #257 (Div. 1)A~C(DIV.2-C~E)题解
今天老师(orz sansirowaltz)让我们做了很久之前的一场Codeforces Round #257 (Div. 1),这里给出A~C的题解,对应DIV2的C~E. A.Jzzhu and ...
随机推荐
- Swift构造器(Initializer)与析构器(Deinitializer)
为了初始化结构体和类等类型的实例属性. 默认构造器 struct Fahrenheit { var temperature: Doubleinit(){ temperature = 32.0 } } ...
- 开放封闭原则(OCP)
开放封闭原则 转:http://baike.baidu.com/view/2493421.htm转:http://dev.csdn.net/article/38/38826.shtm 开放封闭原则(O ...
- WF4.0 基础篇 (十八) Flowchar
本节主要介绍WF4 中 Flowchart的使用 本文例子下载: http://files.cnblogs.com/foundation/FlowcharSample.rar 本文例子说明 Flowc ...
- 一种简单的权限管理ER图设计
权限管理支持动态地管理用户的角色和权限.权限代表用户可以在什么对象上进行什么操作:角色是一组权限的集合. PS:当增加或删除某个用户的角色时,系统自动将该角色对应的权限(角色 -权限关联表)增加或删除 ...
- Centos6.5网络无法连接问题
1. 先进入对应文件夹: cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ 2.获取root权限: su 然后输入root密码 3.修改ifcfg-eth0 vi ifcf ...
- Android 源码编译 步骤
添加资源后编译步骤 1:lunch 112:mmm frameworks/base/core/res/生成Install: out/target/product/hammerhead/system/f ...
- apache和php扩展问题
1.redis扩展: windows下开发用的xampp集成的环境,想装个php-redis扩展,扩展的github地址: https://github.com/nicolasff/phpredis ...
- 静态页面中如何传json数据
首页传递参数组装成json数据,再编码 var param="{type:'"+type+"',text:'"+select_text+"',sele ...
- 用CSS3写的小案例-图片缩放隐藏内容显示
思路分析 (1).搭建界面 (2).鼠标移到图片的时候,放大显示 (3).鼠标移入到当前的li标签里面找到后面的div让其显示出来 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lan ...
- Inside Microsoft SQL Server 2008: T-SQL Querying 读书笔记1
(5)SELECT (5-2) DISTINCT (5-3)TOP(<top_specifications>) (5-1)<select_list> (1)FRO ...
