hadoop2 作业执行过程之作业提交
hadoop2.2.0、centos6.5
hadoop任务的提交常用的两种,一种是测试常用的IDE远程提交,另一种就是生产上用的客户端命令行提交
通用的任务程序提交步骤为:
1.将程序打成jar包;
2.将jar包上传到HDFS上;
3.用命令行提交HDFS上的任务程序。
跟着提交步骤从命令行提交开始
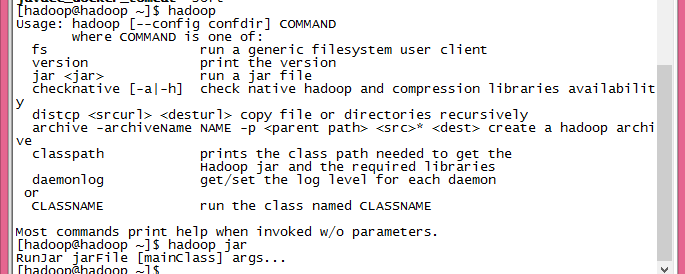
最简单的提交命令应该如:
hadoop jar /home/hadoop/hadoop-2.2.0/hadoop-examples.jar wordcount inputPath outputPath
在名为hadoop的shell 命令文件中当参数为jar时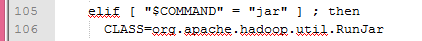
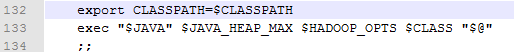
确定了要运行的CLASS文件和环境变量后最后执行了了exec命令来运行
看org.apache.hadoop.util.RunJar类的main方法
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
String usage = "RunJar jarFile [mainClass] args...";
//验证提交的参数数量
if (args.length < 1) {
System.err.println(usage);
System.exit(-1);
}
//验证jar文件是否存在
int firstArg = 0;
String fileName = args[firstArg++];
File file = new File(fileName);
if (!file.exists() || !file.isFile()) {
System.err.println("Not a valid JAR: " + file.getCanonicalPath());
System.exit(-1);
}
String mainClassName = null;
JarFile jarFile;
try {
jarFile = new JarFile(fileName);
} catch(IOException io) {
throw new IOException("Error opening job jar: " + fileName)
.initCause(io);
}
//验证是否存在main方法
Manifest manifest = jarFile.getManifest();
if (manifest != null) {
mainClassName = manifest.getMainAttributes().getValue("Main-Class");
}
jarFile.close();
if (mainClassName == null) {
if (args.length < 2) {
System.err.println(usage);
System.exit(-1);
}
mainClassName = args[firstArg++];
}
mainClassName = mainClassName.replaceAll("/", ".");
//设置临时目录并验证
File tmpDir = new File(new Configuration().get("hadoop.tmp.dir"));
ensureDirectory(tmpDir);
final File workDir;
try {
workDir = File.createTempFile("hadoop-unjar", "", tmpDir);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
// If user has insufficient perms to write to tmpDir, default
// "Permission denied" message doesn't specify a filename.
System.err.println("Error creating temp dir in hadoop.tmp.dir "
+ tmpDir + " due to " + ioe.getMessage());
System.exit(-1);
return;
}
if (!workDir.delete()) {
System.err.println("Delete failed for " + workDir);
System.exit(-1);
}
ensureDirectory(workDir);
//增加删除工作目录的钩子,任务执行完后要删除
ShutdownHookManager.get().addShutdownHook(
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
FileUtil.fullyDelete(workDir);
}
}, SHUTDOWN_HOOK_PRIORITY);
unJar(file, workDir);
ArrayList<URL> classPath = new ArrayList<URL>();
classPath.add(new File(workDir+"/").toURI().toURL());
classPath.add(file.toURI().toURL());
classPath.add(new File(workDir, "classes/").toURI().toURL());
File[] libs = new File(workDir, "lib").listFiles();
if (libs != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < libs.length; i++) {
classPath.add(libs[i].toURI().toURL());
}
}
//通过反射的方式执行任务程序的main方法,并把剩余的参数作为任务程序main方法的参数
ClassLoader loader =
new URLClassLoader(classPath.toArray(new URL[0]));
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(loader);
Class<?> mainClass = Class.forName(mainClassName, true, loader);
Method main = mainClass.getMethod("main", new Class[] {
Array.newInstance(String.class, 0).getClass()
});
String[] newArgs = Arrays.asList(args)
.subList(firstArg, args.length).toArray(new String[0]);
try {
main.invoke(null, new Object[] { newArgs });
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw e.getTargetException();
}
}
环境设置好后就要开始执行任务程序的main方法了
以WordCount为例:
package org.apache.hadoop.examples; import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.StringTokenizer; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser; public class WordCount { public static class TokenizerMapper
extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable>{ private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text(); public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString());
while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(itr.nextToken());
context.write(word, one);
}
}
} public static class IntSumReducer
extends Reducer<Text,IntWritable,Text,IntWritable> {
private IntWritable result = new IntWritable(); public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,
Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable val : values) {
sum += val.get();
}
result.set(sum);
context.write(key, result);
}
} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args).getRemainingArgs();
if (otherArgs.length != 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: wordcount <in> <out>");
System.exit(2);
}
Job job = new Job(conf, "word count");
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(TokenizerMapper.class);
job.setCombinerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
在程序运行入口main方法中
首先定义配置文件类 Configuration,此类是Hadoop各个模块的公共使用类,用于加载类路径下的各种配置文件,读写其中的配置选项;
第二步中用到了 GenericOptionsParser 类,其目的是将命令行中的后部分参数自动设置到变量conf中,
如果代码提交的时候传入其他参数,比如指定reduce的个数,可以根据 GenericOptionsParser的命令行格式这么写:
bin/hadoop jar MyJob.jar com.xxx.MyJobDriver -Dmapred.reduce.tasks=5,
其规则是 -D 加上MR的配置选项(默认reduce task的个数为1,map的个数也为1);
之后就是 Job 的定义
使用的job类的构造方法为
public Job(Configuration conf, String jobName) throws IOException {
this(conf);
setJobName(jobName);
}
调用了另外一个构造方法,并设置了Job的名字(即WordCount)
public Job(Configuration conf) throws IOException {
this(new JobConf(conf));
}
public JobConf(Configuration conf) {
super(conf);
if (conf instanceof JobConf) {
JobConf that = (JobConf)conf;
credentials = that.credentials;
}
checkAndWarnDeprecation();
}
job 已经根据 配置信息实例化好运行环境了,下面就是加入实体“口食”
依次给job添加Jar包、设置Mapper类、设置合并类、设置Reducer类、设置输出键类型、设置输出值类型
在setJarByClass中
public void setJarByClass(Class<?> cls) {
ensureState(JobState.DEFINE);
conf.setJarByClass(cls);
}
它先判断当前job的状态是否在运行中,接着通过class找到jar文件,将jar路径赋值给mapreduce.jar.jar属性(寻找jar文件的方法使通过ClassUtil类中的findContainingJar方法)
job的提交方法是
job.waitForCompletion(true)
public boolean waitForCompletion(boolean verbose
) throws IOException, InterruptedException,
ClassNotFoundException {
if (state == JobState.DEFINE) {
submit();
}
if (verbose) {
monitorAndPrintJob();
} else {
// get the completion poll interval from the client.
int completionPollIntervalMillis =
Job.getCompletionPollInterval(cluster.getConf());
while (!isComplete()) {
try {
Thread.sleep(completionPollIntervalMillis);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
}
}
}
return isSuccessful();
}
参数 verbose ,如果想在控制台打印当前的任务执行进度,则设为true
public void submit()
throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
ensureState(JobState.DEFINE);
setUseNewAPI();
connect();
final JobSubmitter submitter =
getJobSubmitter(cluster.getFileSystem(), cluster.getClient());
status = ugi.doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<JobStatus>() {
public JobStatus run() throws IOException, InterruptedException,
ClassNotFoundException {
return submitter.submitJobInternal(Job.this, cluster);
}
});
state = JobState.RUNNING;
LOG.info("The url to track the job: " + getTrackingURL());
}
在submit 方法中会把Job提交给对应的Cluster,然后不等待Job执行结束就立刻返回
同时会把Job实例的状态设置为JobState.RUNNING,从而来表示Job正在进行中
然后在Job运行过程中,可以调用getJobState()来获取Job的运行状态
Submit主要进行如下操作
- 检查Job的输入输出是各项参数,获取配置信息和远程主机的地址,生成JobID,确定所需工作目录(也是MRAppMaster.java所在目录),执行期间设置必要的信息
- 拷贝所需要的Jar文件和配置文件信息到HDFS系统上的指定工作目录,以便各个节点调用使用
- 计算并获数去输入分片(Input Split)的数目,以确定map的个数
- 调用YARNRunner类下的submitJob()函数,提交Job,传出相应的所需参数(例如 JobID等)。
- 等待submit()执行返回Job执行状态,最后删除相应的工作目录。
在提交前先链接集群(cluster),通过connect方法
private synchronized void connect()
throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
if (cluster == null) {
cluster =
ugi.doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Cluster>() {
public Cluster run()
throws IOException, InterruptedException,
ClassNotFoundException {
return new Cluster(getConfiguration());
}
});
}
}
这是一个线程保护方法。这个方法中根据配置信息初始化了一个Cluster对象,即代表集群
public Cluster(Configuration conf) throws IOException {
this(null, conf);
}
public Cluster(InetSocketAddress jobTrackAddr, Configuration conf)
throws IOException {
this.conf = conf;
this.ugi = UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser();
initialize(jobTrackAddr, conf);
}
private void initialize(InetSocketAddress jobTrackAddr, Configuration conf)
throws IOException {
synchronized (frameworkLoader) {
for (ClientProtocolProvider provider : frameworkLoader) {
LOG.debug("Trying ClientProtocolProvider : "
+ provider.getClass().getName());
ClientProtocol clientProtocol = null;
try {
if (jobTrackAddr == null) {
//创建YARNRunner对象
clientProtocol = provider.create(conf);
} else {
clientProtocol = provider.create(jobTrackAddr, conf);
}
//初始化Cluster内部成员变量
if (clientProtocol != null) {
clientProtocolProvider = provider;
client = clientProtocol;
LOG.debug("Picked " + provider.getClass().getName()
+ " as the ClientProtocolProvider");
break;
}
else {
LOG.debug("Cannot pick " + provider.getClass().getName()
+ " as the ClientProtocolProvider - returned null protocol");
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
LOG.info("Failed to use " + provider.getClass().getName()
+ " due to error: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
if (null == clientProtocolProvider || null == client) {
throw new IOException(
"Cannot initialize Cluster. Please check your configuration for "
+ MRConfig.FRAMEWORK_NAME
+ " and the correspond server addresses.");
}
}
可以看出创建客户端代理阶段使用了java.util.ServiceLoader,在2.3.0版本中包含LocalClientProtocolProvider(本地作业)和YarnClientProtocolProvider(yarn作业)(hadoop有一个Yarn参数mapreduce.framework.name用来控制你选择的应用框架。在MRv2里,mapreduce.framework.name有两个值:local和yarn),此处会根据mapreduce.framework.name的配置创建相应的客户端
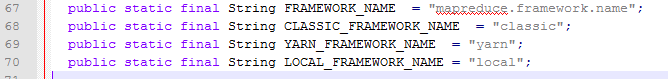
(ServiceLoader是服务加载类,它根据文件配置来在java classpath环境中加载对应接口的实现类)
这里在实际生产中一般都是yarn,所以会创建一个YARNRunner对象(客户端代理类)类进行任务的提交
实例化Cluster后开始真正的任务提交
submitter.submitJobInternal(Job.this, cluster)
JobStatus submitJobInternal(Job job, Cluster cluster)
throws ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException, IOException { //检测输出目录合法性,是否已存在,或未设置
checkSpecs(job); Configuration conf = job.getConfiguration();
addMRFrameworkToDistributedCache(conf);
//获得登录区,用以存放作业执行过程中用到的文件,默认位置/tmp/hadoop-yarn/staging/root/.staging ,可通过yarn.app.mapreduce.am.staging-dir修改
Path jobStagingArea = JobSubmissionFiles.getStagingDir(cluster, conf);
//主机名和地址设置
InetAddress ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
if (ip != null) {
submitHostAddress = ip.getHostAddress();
submitHostName = ip.getHostName();
conf.set(MRJobConfig.JOB_SUBMITHOST,submitHostName);
conf.set(MRJobConfig.JOB_SUBMITHOSTADDR,submitHostAddress);
}
//获取新的JobID,此处需要RPC调用
JobID jobId = submitClient.getNewJobID();
job.setJobID(jobId);
//获取提交目录:/tmp/hadoop-yarn/staging/root/.staging/job_1395778831382_0002
Path submitJobDir = new Path(jobStagingArea, jobId.toString());
JobStatus status = null;
try {
conf.set(MRJobConfig.USER_NAME,
UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser().getShortUserName());
conf.set("hadoop.http.filter.initializers",
"org.apache.hadoop.yarn.server.webproxy.amfilter.AmFilterInitializer");
conf.set(MRJobConfig.MAPREDUCE_JOB_DIR, submitJobDir.toString());
LOG.debug("Configuring job " + jobId + " with " + submitJobDir
+ " as the submit dir");
// get delegation token for the dir
TokenCache.obtainTokensForNamenodes(job.getCredentials(),
new Path[] { submitJobDir }, conf); populateTokenCache(conf, job.getCredentials()); // generate a secret to authenticate shuffle transfers
if (TokenCache.getShuffleSecretKey(job.getCredentials()) == null) {
KeyGenerator keyGen;
try {
keyGen = KeyGenerator.getInstance(SHUFFLE_KEYGEN_ALGORITHM);
keyGen.init(SHUFFLE_KEY_LENGTH);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new IOException("Error generating shuffle secret key", e);
}
SecretKey shuffleKey = keyGen.generateKey();
TokenCache.setShuffleSecretKey(shuffleKey.getEncoded(),
job.getCredentials());
}
//向集群中拷贝所需文件,下面会单独分析(1)
copyAndConfigureFiles(job, submitJobDir);
Path submitJobFile = JobSubmissionFiles.getJobConfPath(submitJobDir); // 写分片文件job.split job.splitmetainfo,具体写入过程与MR1相同,可参考以前文章
LOG.debug("Creating splits at " + jtFs.makeQualified(submitJobDir));
int maps = writeSplits(job, submitJobDir);
conf.setInt(MRJobConfig.NUM_MAPS, maps);
LOG.info("number of splits:" + maps); // write "queue admins of the queue to which job is being submitted"
// to job file.
//设置队列名
String queue = conf.get(MRJobConfig.QUEUE_NAME,
JobConf.DEFAULT_QUEUE_NAME);
AccessControlList acl = submitClient.getQueueAdmins(queue);
conf.set(toFullPropertyName(queue,
QueueACL.ADMINISTER_JOBS.getAclName()), acl.getAclString()); // removing jobtoken referrals before copying the jobconf to HDFS
// as the tasks don't need this setting, actually they may break
// because of it if present as the referral will point to a
// different job.
TokenCache.cleanUpTokenReferral(conf); if (conf.getBoolean(
MRJobConfig.JOB_TOKEN_TRACKING_IDS_ENABLED,
MRJobConfig.DEFAULT_JOB_TOKEN_TRACKING_IDS_ENABLED)) {
// Add HDFS tracking ids
ArrayList<String> trackingIds = new ArrayList<String>();
for (Token<? extends TokenIdentifier> t :
job.getCredentials().getAllTokens()) {
trackingIds.add(t.decodeIdentifier().getTrackingId());
}
conf.setStrings(MRJobConfig.JOB_TOKEN_TRACKING_IDS,
trackingIds.toArray(new String[trackingIds.size()]));
} // Write job file to submit dir
//写入job.xml
writeConf(conf, submitJobFile); //
// Now, actually submit the job (using the submit name)
//这里才开始真正提交,见下面分析(2)
printTokens(jobId, job.getCredentials());
status = submitClient.submitJob(
jobId, submitJobDir.toString(), job.getCredentials());
if (status != null) {
return status;
} else {
throw new IOException("Could not launch job");
}
} finally {
if (status == null) {
LOG.info("Cleaning up the staging area " + submitJobDir);
if (jtFs != null && submitJobDir != null)
jtFs.delete(submitJobDir, true); }
}
}
洋洋洒洒一百余行
(这个可谓任务提交的核心部分,前面的都是铺垫)
关于split的分片:http://www.cnblogs.com/admln/p/hadoop-mapper-numbers-question.html
status = submitClient.submitJob( jobId, submitJobDir.toString(), job.getCredentials());
这里就涉及到YarnClient和RresourceManager的RPC通信了。包括获取applicationId、进行状态检查、网络通信等
这里的submitClient其实就是 YARNRunner的实体类了;
monitorAndPrintJob();
这只是粗略的job提交,详细的还有从在yarn上的RPC通信、在datanode上从文件的输入到map的执行、经过shuffle过程、reduce的执行最后结果的写文件
MR任务的提交大多是任务环境的初始化过程,任务的执行则大多涉及到任务的调度
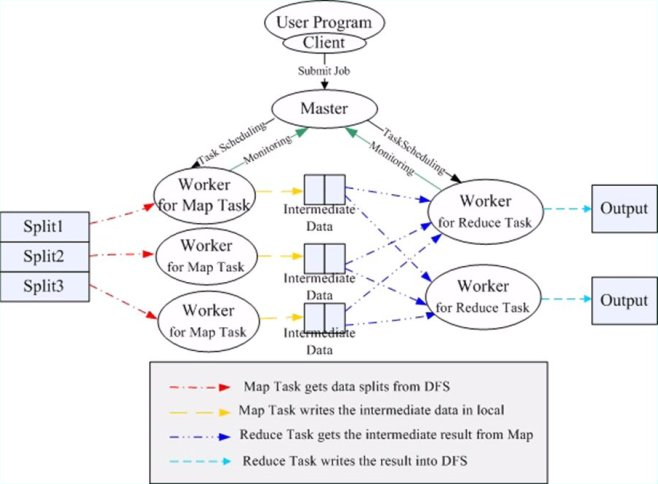
hadoop2 作业执行过程之作业提交的更多相关文章
- hadoop2 作业执行过程之map过程
在执行MAP任务之前,先了解一下它的容器和它容器的领导:container和nodemanager NodeManager NodeManager(NM)是YARN中每个节点上的代理,它管理Hadoo ...
- hadoop2 作业执行过程之yarn调度执行
YARN是hadoop系统上的资源统一管理平台,其主要作用是实现集群资源的统一管理和调度(目前还不完善,只支持粗粒度的CPU和内存的的调配): 它的基本思想是将Mapreduce的jobtracker ...
- hadoop2 作业执行过程之reduce过程
reduce阶段就是处理map的输出数据,大部分过程和map差不多 //ReduceTask.run方法开始和MapTask类似,包括initialize()初始化,根据情况看是否调用runJobCl ...
- MapReduce调度与执行原理之作业提交
前言 :本文旨在理清在Hadoop中一个MapReduce作业(Job)在提交到框架后的整个生命周期过程,权作总结和日后参考,如有问题,请不吝赐教.本文不涉及Hadoop的架构设计,如有兴趣请参考相关 ...
- MapReduce调度与执行原理之作业初始化
前言 :本文旨在理清在Hadoop中一个MapReduce作业(Job)在提交到框架后的整个生命周期过程,权作总结和日后参考,如有问题,请不吝赐教.本文不涉及Hadoop的架构设计,如有兴趣请参考相关 ...
- spark作业运行过程之--DAGScheduler
DAGScheduler--stage划分和创建以及stage的提交 本篇,我会从一次spark作业的运行为切入点,将spark运行过程中涉及到的各个步骤,包括DAG图的划分,任务集的创建,资源分配, ...
- Spark作业执行
Spark中一个action触发一个job的执行,在job提交过程中主要涉及Driver和Executor两个节点. Driver主要解决 1. RDD 依赖性分析,生成DAG. 2. 根据RDD D ...
- SQL Server2005作业执行失败的解决办法
数据库:SQL Server 2005,运行环境:Windows Server 2008 在数据库里的所有作业都执行失败,包括自动执行和手动执行.在事件查看器里看到的错误报告如下: 该作业失败. ...
- SQlServer2008 之 定时执行sql语句作业的制定
1.打开[SQL Server Management Studio],在[对象资源管理器]列表中选择[SQL Server 代理]: 2.鼠标右击[SQL Server 代理],选择[启动(S)],如 ...
随机推荐
- [Cocos2d-JS] 安卓机器的几个按钮
cc.eventManager.addListener({ event:cc.EventListener.KEYBOARD, onKeyPressed:function(keycode,event){ ...
- 第二百二十三天 how can I 坚持
今天双十一,过得有点郁闷,昨天鱼死了不说,抢的羽绒服今天才发现是棉服,结果又买了个海澜之家的,搞的今天凌晨买的东西全都写退了,除了小米耳机. 光棍节,好纠结.爱要怎么说出口,你才不会拒绝啊,愁人啊. ...
- 转】Mahout学习路线图
原博文出自于: http://blog.fens.me/hadoop-mahout-roadmap/ 感谢! Mahout学习路线图 Hadoop家族系列文章,主要介绍Hadoop家族产品,常用的项目 ...
- CentOS6.5(带图形安装)在使用过程中遇到的一些网络问题迷惑
比如,经常会遇到这样的问题************************** [root@SourceCompiler local]# pwd/usr/local[root@SourceCompil ...
- Spark的优点
Spark的一站式解决方案,非常之具有吸引力,毕竟啊,任何公司都想用统一的平台去处理遇到的问题,减少开发和维护的人力成本和部署平台的物力成本. 当然,Spark并没有以牺牲性能为代价.相反,在性能方面 ...
- JavaScript面向对象简介
JavaScript面向对象简介 @(编程) [TOC] 1. 命名空间 命名空间是一个容器,它允许开发人员在一个独特的,特定于应用程序的名称下捆绑所有的功能. 在JavaScript中,命名空间只是 ...
- [iOS微博项目 - 2.5] - 封装授权和用户信息读写业务
github: https://github.com/hellovoidworld/HVWWeibo A.封装授权业务 1.把app的授权信息移动到HVWWeibo-Prefix.pch中作为公共 ...
- python scp
scp 0.10.2 Downloads ↓ scp module for paramiko Pure python scp module====================== The scp. ...
- Umbraco中更换IndexSet中的NodeType后,搜索页面没有做出对应更改的效果
在项目开发中,使用ExternalSearcher,有一个ExamineIndex.config文件中存放ExternalIndexSet 开始时是这样的 <!-- Default Indexs ...
- vss使用详解
下面已VSS6.0为主: 一:安装VSS6.0 安装过程中可能会提示 退出,禁止(abort) 重试(retry) 忽略,跳过(Ignore) ,我们选 Ignore 跳过此项, 路径自己选择 ...
