Vlan间通讯,动态路由
Vlan间通讯,动态路由
1 案例1:三层交换vlan间通信
1.1 问题
VLAN实现了广播域的隔离,同时也将VLAN间的通信隔离了。三层交换技术使得VLAN间可以通信。
- 通过三层交换实现VLAN间通信
1.2 方案
为了解决了传统路由器低速、复杂所造成的网络瓶颈问题,引入了三层交换技术。它根据实际应用时的情况,灵活地在网络第二层或者第三层进行网络分段。具有三层交换功能的设备是一个带有第三层路由功能的第二层交换机。
简单地说,三层交换技术就是:二层交换技术+三层转发技术。
三层交换实现的拓扑如图-1所示:
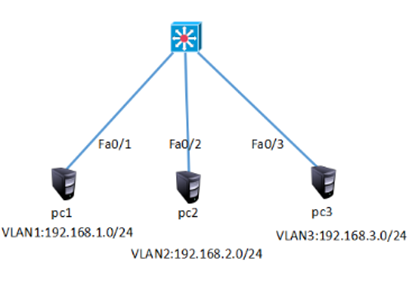
图-1
1.3 步骤
实现此案例需要按照如下步骤进行。
步骤一:在连接PC的交换机上划分3个VLAN,并按图-1把PC机加入相应VLAN
- tarenasw-3L (config)#vlan 2 //vlan1是默认VLAN,不需创建
- tarenasw-3L (config-vlan)#vlan 3
- tarenasw-3L (config-vlan)#exit
- tarenasw-3L (config)#interface f0/1
- tarenasw-3L (config-if)#switchport mode access
- tarenasw-3L (config-if)#switchport access vlan 1
- tarenasw-3L (config-if)#interface f0/2
- tarenasw-3L (config-if)#switchport mode access
- tarenasw-3L (config-if)#switchport access vlan 2
- tarenasw-3L (config-if)#interface f0/3
- tarenasw-3L (config-if)#switchport mode access
- tarenasw-3L (config-if)#switchport access vlan 3
步骤二:查看划分完的VLAN信息
VLAN1是默认VLAN,不需单独创建,也不能改名。所有端口默认都在VLAN1中。
- tarenasw-2L#show vlan
- VLAN Name Status Ports
- ---- ----------------------- --------- ---------------------
- 1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/4, Fa0/5, Fa0/6
- Fa0/7, Fa0/8, Fa0/9, Fa0/10
- Fa0/11, Fa0/12, Fa0/13, Fa0/14
- Fa0/15, Fa0/16, Fa0/17, Fa0/18
- Fa0/19, Fa0/20, Fa0/21, Fa0/22
- Fa0/23, Fa0/24, Gig1/1, Gig1/2
- 2 vlan0002 active Fa0/2
- 3 vlan0003 active Fa0/3
步骤三:为vlan1、vlan2、vlan3分别设置管理IP并开启三层交换机路由功能
- tarenasw-3L #enable
- tarenasw-3L #configure terminal
- tarenasw-3L (config)#ip routing //开启三层交换机路由功能
- tarenasw-3L (config)#interface vlan 1
- tarenasw-3L (config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.254 255.255.255.0
- tarenasw-3L (config-if)#no shutdown
- tarenasw-3L (config-if)#exit
- tarenasw-3L (config)#interface vlan 2
- tarenasw-3L (config-if)#ip address 192.168.2.254 255.255.255.0
- tarenasw-3L (config-if)#no shutdown
- tarenasw-3L (config-if)#exit
- tarenasw-3L (config)#interface vlan 3
- tarenasw-3L (config-if)#ip address 192.168.3.254 255.255.255.0
- tarenasw-3L (config-if)#no shutdown
步骤四:给客户端配置IP地址并测试网络连通性如图-2图-3所示
图-2

图-3
在PC1三上测试网络连通性
- PC1>ping 192.168.3.1
- Pinging 192.168.3.1 with 32 bytes of data:
- Reply from 192.168.3.1: bytes=32 time=11ms TTL=128
- Reply from 192.168.3.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=128
- Reply from 192.168.3.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=128
- Reply from 192.168.3.1: bytes=32 time=4ms TTL=128
- Ping statistics for 192.168.3.1:
- Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
- Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
- Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 11ms, Average = 4ms
2 案例2:多交换机vlan间通信
2.1 问题
三层交换机将接入层交换机汇聚到一起后还需实现了多交换机间不同VLAN的通信。
2.2 方案
三层交换机连接其他交换机的链路需配置为中继链路,三层交换机接口配置trunk模式需先封装,sw1规划vlan1、vlan2、vlan3,Sw2规划vlan4、vlan5并按图-4给相应vlan配置对应网段的IP。
网络的拓扑结构如图-4所示:

图-4
2.3 步骤
实现此案例需要按照如下步骤进行。
步骤一:配置三层交换机
1)三层交换机创建vlan并配置vlan的虚端口IP并开启路由功能
- Switch>enable
- Switch#configure terminal
- Switch(config)#vlan 2
- Switch(config-vlan)#vlan 3
- Switch(config-vlan)#vlan 4
- Switch(config-vlan)#vlan 5
- Switch(config)#interface vlan 1
- Switch(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.254 255.255.255.0
- Switch(config-if)#no shutdown
- Switch(config)#interface vlan 2
- Switch(config-if)#ip address 192.168.2.254 255.255.255.0
- Switch(config-if)#no shutdown
- Switch(config)#interface vlan 3
- Switch(config-if)#ip address 192.168.3.254 255.255.255.0
- Switch(config-if)#no shutdown
- Switch(config)#interface vlan 4
- Switch(config-if)#ip address 192.168.4.254 255.255.255.0
- Switch(config-if)#no shutdown
- Switch(config)#interface vlan 5
- Switch(config-if)#ip address 192.168.5.254 255.255.255.0
- Switch(config-if)#no shutdown
- Switch(config)#ip routing //开启路由功能
2)三层交换的Fa0/23、Fa0/24设置为中继链路模式
- Switch(config)#interface range f0/23-24
- Switch (config-if-range)#switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
- Switch (config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk
步骤二:配置二层交换机
1)Sw1创建vlan2、 vlan3并将端口加入vlan
- Sw1(config)#vlan 2
- Sw1(config-vlan)#vlan 3
- Sw1(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/2
- Sw1(config-if)#switchport access vlan 2
- Sw1(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/3
- Sw1(config-if)#switchport access vlan 3
- Sw1(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/5
- Sw1(config-if)#switchport mode trunk //连接三层交换机的接口配置为trunk模式
2)Sw2创建vlan4、 vlan5并将端口加入vlan
- Sw2(config)#vlan 4
- Sw2(config-vlan)#vlan 5
- Sw2(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/1
- Sw2(config-if)#switchport access vlan 4
- Sw2(config)#interface f0/2
- Sw2(config-if)#switchport access vlan 5
步骤三:按图-4配置IP并测试网络的连通性
- PC>ipconfig
- FastEthernet0 Connection:(default port)
- Link-local IPv6 Address.........: FE80::2D0:D3FF:FE2E:5D25
- IP Address......................: 192.168.1.1
- Subnet Mask.....................: 255.255.255.0
- Default Gateway.................: 192.168.1.254
- PC>ping 192.168.4.1
- Pinging 192.168.4.1 with 32 bytes of data:
- Reply from 192.168.4.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=127
- Reply from 192.168.4.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=127
- Reply from 192.168.4.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=127
- Reply from 192.168.4.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=127
- Ping statistics for 192.168.4.1:
- Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 3, Lost = 1 (25% loss),
- Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
- Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
- PC>ping 192.168.5.1
- Pinging 192.168.5.1 with 32 bytes of data:
- Reply from 192.168.5.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=127
- Reply from 192.168.5.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=127
- Reply from 192.168.5.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=127
- Reply from 192.168.5.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=127
- Ping statistics for 192.168.5.1:
- Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 3, Lost = 1 (25% loss),
- Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
- Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
3 案例3:三层交换配置路由
3.1 问题
三层交换机实现了VLAN间互通后,还要与其他网络进行通信,这样就需要有相关的路由机制。
- 交换接口配置为三层接口实现路由间通信
3.2 方案
三层交换机既然具有三层功能,也就可以实现与路由器相似的配置。既可以把交换接口配置为三层接口,也可以在其上配置静态、动态路由。通过对三层交换机的路由配置,实现VLAN与其他网络的互通。
网络的拓扑结构如图-5所示:
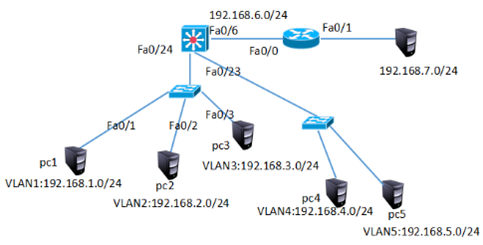
图-5
3.3 步骤
实现此案例需要按照如下步骤进行。
步骤一:多交换机vlan通信与案例2完全一致,不再赘述
步骤二:将三层交换的Fa0/6口配置为三层路由端口,并配置IP地址
三层交换机的物理端口默认是二层端口,只具有二层特性,不能配置IP地址。把二层端口配置为三层端口后,该端口就具备路由功能了,可以配置IP地址,但同时也就关闭了其二层特性,比如不能把三层端口加入VLAN。
二层端口(交换机上的端口默认都是二层端口)默认是激活状态,那些没有使用到的端口为了安全应该手工将其禁用(shutdown);而三层端口(路由器上的端口或是三层交换机上被配置成路由端口的端口)默认是禁用状态,在使用之前务必要将其激活(no shutdown)。
- Switch(config)#interface f0/6
- Switch(config-if)#no switchport
- Switch(config-if)#ip address 192.168.6.1 255.255.255.0
- Switch(config-if)#no shutdown
步骤三:配置路由器的端口IP地址
- Switch(config)#interface f0/0
- Switch(config-if)#ip address 192.168.6.2 255.255.255.0
- Switch(config-if)#no shutdown
- Switch(config-if)#interface f0/1
- Switch(config-if)#ip address 192.168.7.254 255.255.255.0
- Switch(config-if)#no shutdown
步骤四:在三层交换机上配置静态路由,以便VLAN内主机可以与外界网络互联
- Switch(config)#ip route 192.168.7.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.6.2
- Switch(config)#exit
- Switch#show ip route
- Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
- D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
- N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
- E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
- i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
- * - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
- P - periodic downloaded static route
- Gateway of last resort is not set
- C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, Vlan1
- C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, Vlan2
- C 192.168.3.0/24 is directly connected, Vlan3
- C 192.168.4.0/24 is directly connected, Vlan4
- C 192.168.5.0/24 is directly connected, Vlan5
- C 192.168.6.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/6
- S 192.168.7.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.6.2
步骤五:在路由器上配置到达三个VLAN网络的静路由
- tarena-rouer(config)#ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.6.1
- tarena-rouer(config)#ip route 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.6.1
- tarena-rouer(config)#ip route 192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.6.1
- tarena-rouer(config)#ip route 192.168.4.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.6.1
- tarena-rouer(config)#ip route 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.6.1
- tarena-rouer(config)#exit
- tarena-rouer#show ip route
- Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
- D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
- N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
- E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
- i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
- * - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
- P - periodic downloaded static route
- Gateway of last resort is not set
- S 192.168.1.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.6.1
- S 192.168.2.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.6.1
- S 192.168.3.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.6.1
- S 192.168.4.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.6.1
- S 192.168.5.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.6.1
- C 192.168.6.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
- C 192.168.7.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
- tarena-rouer#
步骤六:在PC上测试与VLAN的连通性
- PC>ipconfig
- FastEthernet0 Connection:(default port)
- Link-local IPv6 Address.........: FE80::2E0:8FFF:FE14:BB43
- IP Address......................: 192.168.7.1
- Subnet Mask.....................: 255.255.255.0
- Default Gateway.................: 192.168.7.254
- SERVER>ping 192.168.1.1
- Pinging 192.168.1.1 with 32 bytes of data:
- Request timed out.
- Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
- Ping statistics for 192.168.1.1:
- Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 3, Lost = 1 (25% loss),
- Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
- Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms
- SERVER>ping 192.168.2.10
- Pinging 192.168.2.1 with 32 bytes of data:
- Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Ping statistics for 192.168.2.1:
- Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
- Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
- Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
- SERVER>ping 192.168.3.1
- Pinging 192.168.3.1 with 32 bytes of data:
- Reply from 192.168.3.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.3.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.3.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.3.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Ping statistics for 192.168.3.1:
- Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
- Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
- Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms
4 案例4:RIP动态路由配置
4.1 问题
在相对较小而且结构不变的网络中,静态路由是很好的解决方案,它配置简单而且不过多消耗设备资源(动态路由协议在运行时要消耗路由器内部资源,在与其他路由器更新信息时又会消耗网络资源)。
然而在大型网络中,网络非常多,而且很有可能因为某些因素的影响,网络拓扑会有轻微变化。这时如果仍然采用静态路由就非常不方便了。
- 通过RIP实现路由间通信
4.2 方案
动态路由协议配置灵活,路由器会发送自身的路由信息给其他路由器,同时也会接收其他路由器发来的路由信息建立自己的路由表。这样在路由器上就不必像静态路由那样为每个目标地址都配置路由,因为路由器可以通过协议学习这些路由。网络拓扑改变,路由信息也会自动更新,无需管理员干预。
网络拓扑如图-6所示:

图-6
4.3 步骤
实现此案例需要按照如下步骤进行。
步骤一:按图-6配置路由接口IP分别(与以前路由配置接口IP方法一致不再赘述配置)
步骤二:在三台路由上配置RIP路由协议
- tarena-router1(config)#router rip
- tarena-router1(config-router)#version 2
- tarena-router1(config-router)#no auto-summary
- tarena-router1(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0
- tarena-router1(config-router)#network 192.168.2.0
- tarena-router2(config)#router rip
- tarena-router2(config-router)#version 2
- tarena-router2(config-router)#no auto-summary
- tarena-router2(config-router)#network 192.168.3.0
- tarena-router2(config-router)#network 192.168.2.0
- tarena-router3(config)#router rip
- tarena-router3(config-router)#version 2
- tarena-router3(config-router)#no auto-summary
- tarena-router3(config-router)#network 192.168.3.0
- tarena-router3(config-router)#network 192.168.4.0
步骤三:分别在三台路由器上查看路由表
注意以R开头的路由,这些路由表示通过RIP协议从其他运行RIP的路由器学习过来的路由。每条路由都写明了目标网络、下一跳IP地址以及从自己哪个端口发出去。
- tarena-router1#show ip route
- Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
- D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
- N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
- E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
- i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
- * - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
- P - periodic downloaded static route
- Gateway of last resort is not set
- C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
- C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
- R 192.168.3.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:26, FastEthernet0/1
- R 192.168.4.0/24 [120/2] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:26, FastEthernet0/1
- tarena-router2#show ip route
- Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
- D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
- N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
- E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
- i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
- * - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
- P - periodic downloaded static route
- Gateway of last resort is not set
- R 192.168.1.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.2.1, 00:00:04, FastEthernet0/1
- C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
- C 192.168.3.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
- R 192.168.4.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.3.2, 00:00:09, FastEthernet0/0
- tarena-router3#show ip route
- Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
- D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
- N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
- E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
- i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
- * - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
- P - periodic downloaded static route
- Gateway of last resort is not set
- R 192.168.1.0/24 [120/2] via 192.168.3.1, 00:00:20, FastEthernet0/0
- R 192.168.2.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.3.1, 00:00:20, FastEthernet0/0
- C 192.168.3.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
- C 192.168.4.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
步骤四:在PC上测试到主机的通信
- PC>ping 192.168.4.1
- Pinging 192.168.4.1 with 32 bytes of data:
- Reply from 192.168.4.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=125
- Reply from 192.168.4.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=125
- Reply from 192.168.4.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=125
- Reply from 192.168.4.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=125
- Ping statistics for 192.168.4.1:
- Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
- Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
- Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
5 案例5:三层交换配置RIP动态路由
5.1 问题
在三层交换机上配置RIP路由协议,以三层交换机代替路由器。
- 通过RIP实现路由间通信
5.2 方案
动态路由协议配置灵活,路由器会发送自身的路由信息给其他路由器,同时也会接收其他路由器发来的路由信息建立自己的路由表。这样在路由器上就不必像静态路由那样为每个目标地址都配置路由,因为路由器可以通过协议学习这些路由。网络拓扑改变,路由信息也会自动更新,无需管理员干预。
网络拓扑如图-7所示:
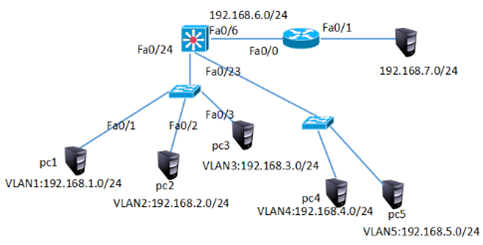
图-7
5.3 步骤
实现此案例需要按照如下步骤进行。
步骤一:VLAN以及端口配置与上面3三层交换配置路由完全一致,不再赘述配置
步骤二:将上面【案例3:在三层交换机与路由器上配置路由】中的静态路由删除
- tarenasw-3L (config)#no ip route 192.168.7.0 192.168.6.2
- tarena-router(config)#no ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.6.1
- tarena-router(config)#no ip route 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.6.1
- tarena-router(config)#no ip route 192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.6.1
- tarena-router(config)#no ip route 192.168.4.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.6.1
- tarena-router(config)#no ip route 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.6.1
步骤三:分别在三层交换机和路由器上配置RIP路由协议
RIP路由协议在配置network时,只需要配置该路由器所直连的主类网络,不与该路由器直连的网络不需要包含在network中。
RIP默认工作在第一版本下,但是RIP-V1是有类路由协议,而且通过广播的方式进行路由更新,无论是功能上还是效率上都有一些缺陷,这些缺陷RIP-V2可以弥补。在使用时建议采用RIP-V2而不是RIP-V1。
- tarenasw-3L(config)#router rip
- tarenasw-3L(config-router)#version 2
- tarenasw-3L(config-router)#no auto-summary
- tarenasw-3L(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0
- tarenasw-3L(config-router)#network 192.168.2.0
- tarenasw-3L(config-router)#network 192.168.3.0
- tarenasw-3L(config-router)#network 192.168.4.0
- tarenasw-3L(config-router)#network 192.168.5.0
- tarenasw-3L(config-router)#network 192.168.6.0
- tarena-router(config)#router rip
- tarena-router(config-router)#version 2
- tarenasw-3L(config-router)#no auto-summary
- tarena-router(config-router)#network 192.168.6.0
- tarena-router(config-router)#network 192.168.7.0
步骤四:分别在三层交换机和路由器上查看路由表
注意以R开头的路由,这些路由表示通过RIP协议从其他运行RIP的路由器学习过来的路由。每条路由都写明了目标网络、下一跳IP地址以及从自己哪个端口发出去。
- tarenasw-3L#show ip route
- Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
- D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
- N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
- E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
- i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
- * - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
- P - periodic downloaded static route
- Gateway of last resort is not set
- C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, Vlan1
- C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, Vlan2
- C 192.168.3.0/24 is directly connected, Vlan3
- C 192.168.4.0/24 is directly connected, Vlan4
- C 192.168.5.0/24 is directly connected, Vlan5
- C 192.168.6.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/6
- R 192.168.7.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.6.2, 00:00:12, FastEthernet0/6 0
- Router#show ip route
- Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
- D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
- N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
- E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
- i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
- * - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
- P - periodic downloaded static route
- Gateway of last resort is not set
- R 192.168.1.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.6.1, 00:00:25, FastEthernet0/0
- R 192.168.2.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.6.1, 00:00:25, FastEthernet0/0
- R 192.168.3.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.6.1, 00:00:25, FastEthernet0/0
- R 192.168.4.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.6.1, 00:00:25, FastEthernet0/0
- R 192.168.5.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.6.1, 00:00:25, FastEthernet0/0
- C 192.168.6.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
- C 192.168.7.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
步骤五:在PC上测试到五个VLAN中主机的通信
- PC>ipconfig
- FastEthernet0 Connection:(default port)
- Link-local IPv6 Address.........: FE80::2E0:8FFF:FE14:BB43
- IP Address......................: 192.168.7.1
- Subnet Mask.....................: 255.255.255.0
- Default Gateway.................: 192.168.7.254
- SERVER>ping 192.168.1.1
- Pinging 192.168.1.10 with 32 bytes of data:
- Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
- Ping statistics for 192.168.1.1:
- Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 3, Lost = 1 (25% loss),
- Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
- Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms
- PC >ping 192.168.2.10
- Pinging 192.168.2.10 with 32 bytes of data:
- Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Ping statistics for 192.168.2.1:
- Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
- Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
- Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
- PC >ping 192.168.3.1
- Pinging 192.168.3.10 with 32 bytes of data:
- Reply from 192.168.3.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.3.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.3.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.3.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Ping statistics for 192.168.3.1:
- Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
- Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
- Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms
- PC >
- 31% /misc/nfsdir SERVER>ping 192.168.3.10
- Pinging 192.168.3.10 with 32 bytes of data:
- Reply from 192.168.4.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.4.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.4.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.4.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Ping statistics for 192.168.4.1:
- Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
- Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
- Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms
- PC>
- 31% /misc/nfsdir
- SERVER>ping 192.168.5.1
- Pinging 192.168.5.1 with 32 bytes of data:
- Reply from 192.168.5.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.5.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.5.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Reply from 192.168.5.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
- Ping statistics for 192.168.5.1:
- Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
- Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
- Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms
- 31% /misc/nfsdir
Vlan间通讯,动态路由的更多相关文章
- Huawei vlan 配置及vlan 间通讯
Huawei Vlan配置及vlan 间通讯实例 组网需求:汇聚层交换机做为 PC 电脑的网关, PC3直连 SW2 属于 vlan 2,网关为 vlanif 2 接口地址192.168.2.1/24 ...
- VLAN间单臂路由访问
实验书上的拓朴图: 注意TRUNK端口和路由器子端口设置,可以承载不同的VLAN标签. 交换机(用2691加交换模块实现的): Building configuration... Current co ...
- 2.2-VLAN间路由
2.2-VLAN间路由 第一代LAN间的通信: 不支持VLAN的交换机:由一个路由器和几个交换机组成,每个交换机的所有端口都同属于一个网段/LAN:在路由器上有几个网段就有几个与之相对 ...
- HCNA Routing&Switching之VLAN间路由
前文我们了解了二层交换技术vlan相关话题,回顾请参考https://www.cnblogs.com/qiuhom-1874/p/15091491.html:今天我们来聊一聊不同VLAN间通信相关话题 ...
- Cisco基础(二):三层交换vlan间通信、多交换机vlan间通信、三层交换配置路由、RIP动态路由配置、三层交换配置RIP动态路由
一.三层交换vlan间通信 目标: VLAN实现了广播域的隔离,同时也将VLAN间的通信隔离了.三层交换技术使得VLAN间可以通信. 通过三层交换实现VLAN间通信 方案: 为了解决了传统路由器低速. ...
- 利用单臂路由实现vlan间路由
本实验模拟公司场景 通过路由器实现不同vlan部门间通讯,拓扑图如下
- VLAN 间路由的几种方法
方法一:给每个VLAN去分配一个路由器的物理连接第一步,PC设置IP地址和网关192.168.2.2/24 网关是192.168.2.1192.168.3.2/24 网关是192.168.3.1第二步 ...
- 三层交换单臂路由vlan间通信综合实验之降龙要点[转]
单臂路由三层交换机提供vlan间的通信之菜鸟之降龙详解要点: 图示 PC:左到右依次设置IP172.16.10.1, 20.1, 30.1, 40,1 ,50,1 /24 网关10.2 ...
- 三层交换单臂路由vlan间通信综合实验之降龙要点--Lee
单臂路由三层交换机提供vlan间的通信之菜鸟之降龙详解要点: 图示 PC:左到右依次设置IP172.16.10.1, 20.1, 30.1, 40,1 ,50,1 /24 网关10.2 ...
随机推荐
- openwrt 上的 upnp wifi 音频推送 gmediarender
首先是必须启用的模块 Libraries ---> <*> libupnp Sound ---> <*> alsa-utils<*> madplay-a ...
- CSS 权重图
关系图 图片出处我找不到了. 结论 权重从高到低排序 1. !important 2. style 3. #id 4. .class .child-class 5. .class1.class2 6. ...
- 练习div出现的小问题
一.出现图片不显示状况1.class中设定的名字不对2.在高单位后面出现了 “:“ 所以也不显示3.上一个div盒子没有写结束标签 4.在添加背景图,把height的值改成auto后不显示,填上具体数 ...
- 组件/ 外层数据初始化时候,不应该触发 on-change 事件
组件/ 外层数据初始化时候,不应该触发 on-change 事件 watch: { value (value) { this.noOnChange = true // 外层传值 不触发on-chang ...
- 【Weiss】【第03章】练习3.13:桶排序
[练习3.13] 利用社会安全号码对学生记录构成的数组排序.编写一个程序进行这件工作,使用具有1000个桶的基数排序并且分三趟进行. Answer: 首先,对社会安全号码不了解的就把它当成一个不超过9 ...
- HTML每日学习笔记(3)
7.17.2019 XHTML 1.XHTML与HTML的区别: XHTML 元素必须被正确地嵌套. XHTML 元素必须被关闭. 标签名必须用小写字母. XHTML 文档必须拥有根元素.(所有的 X ...
- 矩阵快速幂-QuickPow
矩阵快速幂引入: 1.整数快速幂: 为了引出矩阵的快速幂,以及说明快速幂算法的好处,我们可以先求整数的幂.如果现在要算X^8:则 XXXXXXXX 按照寻常思路,一个一个往上面乘,则乘法运算进行7次. ...
- C++中 string 中的方法的使用详解
string 字符串在所有的语言中都非常重要,c++也不例外,接下来我们将介绍string中的常用方法 1. size() 和 length() 函数 : 他们返回字符串的真实长度,且不会因为空格而截 ...
- Error while importing sbt project:--创建sbt项目导入文件出错
错误截图如下: Error while importing sbt project: List([info] Loading global plugins from C:\Users\RYJ\.sbt ...
- 图解Java设计模式之模板模式
图解Java设计模式之模板模式 豆浆制作问题 模板方法模式基本介绍 模板方法模式原理类图 模板方法模式解决豆浆制作问题 模板方法模式的钩子方法 模板方法模式在Spring框架中的源码分析 模板方法模式 ...
