深入理解SpringCloud之分布式配置
Spring Cloud Config Server能够统一管理配置,我们绝大多数情况都是基于git或者svn作为其配置仓库,其实SpringCloud还可以把数据库作为配置仓库,今天我们就来了解一下。顺便分析一下其实现原理。
一、PropertySourceLocator接口
1.1、代码分析
这个接口的作用用于定制化引导配置,通过这个接口我们可以通过代码动态的向Environment中添加PropertySource,该接口定义如下:
/*
* Copyright 2013-2014 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.config; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource; /**
* Strategy for locating (possibly remote) property sources for the Environment.
* Implementations should not fail unless they intend to prevent the application from
* starting.
*
* @author Dave Syer
*
*/
public interface PropertySourceLocator { /**
* @param environment the current Environment
* @return a PropertySource or null if there is none
*
* @throws IllegalStateException if there is a fail fast condition
*/
PropertySource<?> locate(Environment environment); }
那么此接口在SpringCloud类引导类PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration里有处理,核心代码如下:
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(PropertySourceBootstrapProperties.class)
public class PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration implements
ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>, Ordered { @Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(
BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.propertySourceLocators);
boolean empty = true;
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = applicationContext.getEnvironment();
for (PropertySourceLocator locator : this.propertySourceLocators) {
PropertySource<?> source = null;
source = locator.locate(environment);
if (source == null) {
continue;
}
logger.info("Located property source: " + source);
composite.addPropertySource(source);
empty = false;
}
if (!empty) {
MutablePropertySources propertySources = environment.getPropertySources();
String logConfig = environment.resolvePlaceholders("${logging.config:}");
LogFile logFile = LogFile.get(environment);
if (propertySources.contains(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME)) {
propertySources.remove(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
}
insertPropertySources(propertySources, composite);
reinitializeLoggingSystem(environment, logConfig, logFile);
setLogLevels(applicationContext, environment);
handleIncludedProfiles(environment);
}
} //..... private void insertPropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources,
CompositePropertySource composite) {
MutablePropertySources incoming = new MutablePropertySources();
incoming.addFirst(composite);
PropertySourceBootstrapProperties remoteProperties = new PropertySourceBootstrapProperties();
new RelaxedDataBinder(remoteProperties, "spring.cloud.config")
.bind(new PropertySourcesPropertyValues(incoming));
if (!remoteProperties.isAllowOverride() || (!remoteProperties.isOverrideNone()
&& remoteProperties.isOverrideSystemProperties())) {
propertySources.addFirst(composite);
return;
}
if (remoteProperties.isOverrideNone()) {
propertySources.addLast(composite);
return;
}
if (propertySources
.contains(StandardEnvironment.SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME)) {
if (!remoteProperties.isOverrideSystemProperties()) {
propertySources.addAfter(
StandardEnvironment.SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME,
composite);
}
else {
propertySources.addBefore(
StandardEnvironment.SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME,
composite);
}
}
else {
propertySources.addLast(composite);
}
} }
在这里我们可以清楚的看到,首先会获取所有的PropertySourceLocator,并调用其locate方法,只有当propertySouceLocator有实现类时,它才会获取当前引导上下文的Environment,并在 insertPropertySources方法里,把PropertySourceLocator的自定义属性值添加到引导上下文的环境当中。
1.2、代码示例
代码目录结构如下:
在这里注意,自定义实现的PropertySourceLocator是我们的引导程序,因此一定不能被主程序componentScan到
MyTestPropertySourceLocator代码如下:
package com.bdqn.lyrk.config.bootstrap; import org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.config.PropertySourceLocator;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.env.MapPropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource; import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map; @Configuration
public class MyTestPropertySourceLocator implements PropertySourceLocator {
@Override
public PropertySource<?> locate(Environment environment) {
Map<String, Object> propertySource = new HashMap<>();
propertySource.put("student.name", "admin");
MapPropertySource mapPropertySource = new MapPropertySource("customer", propertySource); return mapPropertySource;
}
}
spring.factories文件:
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration=\
com.bdqn.lyrk.config.bootstrap.MyTestPropertySourceLocator
ConfigServer:
package com.bdqn.lyrk.config.server; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.EnableConfigServer;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; @SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigServer
public class ConfigServer { public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext = SpringApplication.run(ConfigServer.class, args);
Environment environment = applicationContext.getBean(Environment.class);
System.out.println(environment);
System.out.println(environment.getProperty("student.name"));
}
}
运行结果如下:
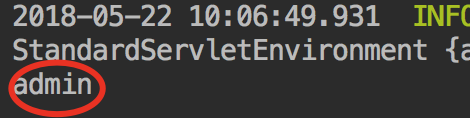
我们可以看到,当我们把自定义的PropertySourceLocator作为引导程序配置时,该接口的locate方法返回值会添加到Environment当中
二、ConfigServer
ConfigServer是配置中心的服务端,它负责统一管理配置,当我们以http://地址:端口号/{application}-{profile}.properties发送请求时会被EnvironmentController处理,我们来看一下EnvironmentController的源码:
@RestController
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, path = "${spring.cloud.config.server.prefix:}")
public class EnvironmentController { public EnvironmentController(EnvironmentRepository repository) {
this(repository, new ObjectMapper());
} public EnvironmentController(EnvironmentRepository repository,
ObjectMapper objectMapper) {
this.repository = repository;
this.objectMapper = objectMapper;
} @RequestMapping("/{name}/{profiles}/{label:.*}")
public Environment labelled(@PathVariable String name, @PathVariable String profiles,
@PathVariable String label) {
if (name != null && name.contains("(_)")) {
// "(_)" is uncommon in a git repo name, but "/" cannot be matched
// by Spring MVC
name = name.replace("(_)", "/");
}
if (label != null && label.contains("(_)")) {
// "(_)" is uncommon in a git branch name, but "/" cannot be matched
// by Spring MVC
label = label.replace("(_)", "/");
}
Environment environment = this.repository.findOne(name, profiles, label);
return environment;
} @RequestMapping("/{name}-{profiles}.properties")
public ResponseEntity<String> properties(@PathVariable String name,
@PathVariable String profiles,
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "true") boolean resolvePlaceholders)
throws IOException {
return labelledProperties(name, profiles, null, resolvePlaceholders);
} @RequestMapping("/{label}/{name}-{profiles}.properties")
public ResponseEntity<String> labelledProperties(@PathVariable String name,
@PathVariable String profiles, @PathVariable String label,
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "true") boolean resolvePlaceholders)
throws IOException {
validateProfiles(profiles);
Environment environment = labelled(name, profiles, label);
Map<String, Object> properties = convertToProperties(environment);
String propertiesString = getPropertiesString(properties);
if (resolvePlaceholders) {
propertiesString = resolvePlaceholders(prepareEnvironment(environment),
propertiesString);
}
return getSuccess(propertiesString);
} // .....省略其他代码
}
在这里的核心代码是labelled,该方法首先会解析(_)将其替换为/ ,然后调用的EnvironmentRepository的findOne方法。
/*
* Copyright 2013-2015 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.cloud.config.server.environment; import org.springframework.cloud.config.environment.Environment; /**
* @author Dave Syer
* @author Roy Clarkson
*/
public interface EnvironmentRepository { Environment findOne(String application, String profile, String label); }
此接口主要是根据application profiles label这三个参数拿到对应的Environment 注意这里的Environment不是Springframework下的Environment接口:
/*
* Copyright 2013-2015 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.cloud.config.environment; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonCreator;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty; /**
* Simple plain text serializable encapsulation of a list of property sources. Basically a
* DTO for {@link org.springframework.core.env.Environment}, but also applicable outside
* the domain of a Spring application.
*
* @author Dave Syer
* @author Spencer Gibb
*
*/
public class Environment { private String name; private String[] profiles = new String[0]; private String label; private List<PropertySource> propertySources = new ArrayList<>(); private String version; private String state; public Environment(String name, String... profiles) {
this(name, profiles, "master", null, null);
} /**
* Copies all fields except propertySources
* @param env
*/
public Environment(Environment env) {
this(env.getName(), env.getProfiles(), env.getLabel(), env.getVersion(), env.getState());
} @JsonCreator
public Environment(@JsonProperty("name") String name,
@JsonProperty("profiles") String[] profiles,
@JsonProperty("label") String label,
@JsonProperty("version") String version,
@JsonProperty("state") String state) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.profiles = profiles;
this.label = label;
this.version = version;
this.state = state;
} public void add(PropertySource propertySource) {
this.propertySources.add(propertySource);
} public void addAll(List<PropertySource> propertySources) {
this.propertySources.addAll(propertySources);
} public void addFirst(PropertySource propertySource) {
this.propertySources.add(0, propertySource);
} public List<PropertySource> getPropertySources() {
return propertySources;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public String getLabel() {
return label;
} public void setLabel(String label) {
this.label = label;
} public String[] getProfiles() {
return profiles;
} public void setProfiles(String[] profiles) {
this.profiles = profiles;
} public String getVersion() {
return version;
} public void setVersion(String version) {
this.version = version;
} public String getState() {
return state;
} public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "Environment [name=" + name + ", profiles=" + Arrays.asList(profiles)
+ ", label=" + label + ", propertySources=" + propertySources
+ ", version=" + version
+ ", state=" + state + "]";
} }
SpringCloud中的Environment类与Springframework的Environment接口相仿,前者中的属性终将会添加至后者当中,下面我们可以看一下它是怎么实现的
首先我们下找到spring-cloud-config-server-xxx.jar下的spring.factories文件:
# Bootstrap components
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration=\
org.springframework.cloud.config.server.bootstrap.ConfigServerBootstrapConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.config.server.config.EncryptionAutoConfiguration # Application listeners
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
org.springframework.cloud.config.server.bootstrap.ConfigServerBootstrapApplicationListener # Autoconfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.cloud.config.server.config.ConfigServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.config.server.config.EncryptionAutoConfiguration
我们可以看到,此处配置了引导类有一个叫:ConfigServerBootstrapConfiguration,我们不妨看看这个引导类:
/*
* Copyright 2013-2015 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.cloud.config.server.bootstrap; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.client.ConfigClientProperties;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.config.ConfigServerProperties;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.config.EnvironmentRepositoryConfiguration;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.config.TransportConfiguration;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.environment.EnvironmentRepository;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.environment.EnvironmentRepositoryPropertySourceLocator;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; /**
* Bootstrap configuration to fetch external configuration from a (possibly
* remote) {@link EnvironmentRepository}. Off by default because it can delay
* startup, but can be enabled with
* <code>spring.cloud.config.server.bootstrap=true</code>. This would be useful,
* for example, if the config server were embedded in another app that wanted to
* be configured from the same repository as all the other clients.
*
* @author Dave Syer
* @author Roy Clarkson
*/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnProperty("spring.cloud.config.server.bootstrap")
public class ConfigServerBootstrapConfiguration { @EnableConfigurationProperties(ConfigServerProperties.class)
@Import({ EnvironmentRepositoryConfiguration.class, TransportConfiguration.class })
protected static class LocalPropertySourceLocatorConfiguration { @Autowired
private EnvironmentRepository repository; @Autowired
private ConfigClientProperties client; @Autowired
private ConfigServerProperties server; @Bean
public EnvironmentRepositoryPropertySourceLocator environmentRepositoryPropertySourceLocator() {
return new EnvironmentRepositoryPropertySourceLocator(this.repository, this.client.getName(),
this.client.getProfile(), getDefaultLabel());
} private String getDefaultLabel() {
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.client.getLabel())) {
return this.client.getLabel();
} else if (StringUtils.hasText(this.server.getDefaultLabel())) {
return this.server.getDefaultLabel();
}
return null;
} } }
该引导中装配了一个EnvironmentRepositoryPropertySourceLocator的类,我们继续看看这个类:
/*
* Copyright 2013-2014 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.cloud.config.server.environment; import java.util.Map; import org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.config.PropertySourceLocator;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.environment.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.CompositePropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.env.MapPropertySource; /**
* A PropertySourceLocator that reads from an EnvironmentRepository.
*
* @author Dave Syer
*
*/
public class EnvironmentRepositoryPropertySourceLocator implements PropertySourceLocator { private EnvironmentRepository repository;
private String name;
private String profiles;
private String label; public EnvironmentRepositoryPropertySourceLocator(EnvironmentRepository repository,
String name, String profiles, String label) {
this.repository = repository;
this.name = name;
this.profiles = profiles;
this.label = label;
} @Override
public org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource<?> locate(Environment environment) {
CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource("configService");
for (PropertySource source : repository.findOne(name, profiles, label)
.getPropertySources()) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Map<String, Object> map = (Map<String, Object>) source.getSource();
composite.addPropertySource(new MapPropertySource(source.getName(), map));
}
return composite;
} }
这个类很明显实现了PropertySourceLocator接口,在locate方法里会调用EnvironmentRepository的findOne方法,此时会将SpringCloud的Environment类和Spring中的Environment相关联
三、ConfigClient
当我们添加config-client时,启动时会去服务端请求远程的配置进而加载至当前的Environment当中。我们先看一看它的spring.factories文件:
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.cloud.config.client.ConfigClientAutoConfiguration # Bootstrap components
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration=\
org.springframework.cloud.config.client.ConfigServiceBootstrapConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.config.client.DiscoveryClientConfigServiceBootstrapConfiguration
根据引导配置,我们去追溯一下ConfigServiceBootstrapConfiguration的源代码:
/*
* Copyright 2013-2017 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.cloud.config.client; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment;
import org.springframework.retry.annotation.EnableRetry;
import org.springframework.retry.annotation.Retryable;
import org.springframework.retry.interceptor.RetryInterceptorBuilder;
import org.springframework.retry.interceptor.RetryOperationsInterceptor; /**
* @author Dave Syer
* @author Tristan Hanson
*
*/
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties
public class ConfigServiceBootstrapConfiguration { @Autowired
private ConfigurableEnvironment environment; @Bean
public ConfigClientProperties configClientProperties() {
ConfigClientProperties client = new ConfigClientProperties(this.environment);
return client;
} @Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.cloud.config.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator configServicePropertySource(ConfigClientProperties properties) {
ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator locator = new ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator(
properties);
return locator;
} @ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.cloud.config.failFast", matchIfMissing=false)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Retryable.class, Aspect.class, AopAutoConfiguration.class })
@Configuration
@EnableRetry(proxyTargetClass = true)
@Import(AopAutoConfiguration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(RetryProperties.class)
protected static class RetryConfiguration { @Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "configServerRetryInterceptor")
public RetryOperationsInterceptor configServerRetryInterceptor(
RetryProperties properties) {
return RetryInterceptorBuilder
.stateless()
.backOffOptions(properties.getInitialInterval(),
properties.getMultiplier(), properties.getMaxInterval())
.maxAttempts(properties.getMaxAttempts()).build();
}
} }
与config-server端类似,我们可以发现其装配了一个ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator的Bean,这里我贴出关键代码部分:
@Order(0)
public class ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator implements PropertySourceLocator { private static Log logger = LogFactory
.getLog(ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator.class); private RestTemplate restTemplate;
private ConfigClientProperties defaultProperties; public ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator(ConfigClientProperties defaultProperties) {
this.defaultProperties = defaultProperties;
} @Override
@Retryable(interceptor = "configServerRetryInterceptor")
public org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource<?> locate(
org.springframework.core.env.Environment environment) {
ConfigClientProperties properties = this.defaultProperties.override(environment);
CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource("configService");
RestTemplate restTemplate = this.restTemplate == null ? getSecureRestTemplate(properties)
: this.restTemplate;
Exception error = null;
String errorBody = null;
logger.info("Fetching config from server at: " + properties.getRawUri());
try {
String[] labels = new String[] { "" };
if (StringUtils.hasText(properties.getLabel())) {
labels = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(properties.getLabel());
} String state = ConfigClientStateHolder.getState(); // Try all the labels until one works
for (String label : labels) {
Environment result = getRemoteEnvironment(restTemplate,
properties, label.trim(), state);
if (result != null) {
logger.info(String.format("Located environment: name=%s, profiles=%s, label=%s, version=%s, state=%s",
result.getName(),
result.getProfiles() == null ? "" : Arrays.asList(result.getProfiles()),
result.getLabel(), result.getVersion(), result.getState())); if (result.getPropertySources() != null) { // result.getPropertySources() can be null if using xml
for (PropertySource source : result.getPropertySources()) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Map<String, Object> map = (Map<String, Object>) source
.getSource();
composite.addPropertySource(new MapPropertySource(source
.getName(), map));
}
} if (StringUtils.hasText(result.getState()) || StringUtils.hasText(result.getVersion())) {
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
putValue(map, "config.client.state", result.getState());
putValue(map, "config.client.version", result.getVersion());
composite.addFirstPropertySource(new MapPropertySource("configClient", map));
}
return composite;
}
}
}
catch (HttpServerErrorException e) {
error = e;
if (MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON.includes(e.getResponseHeaders()
.getContentType())) {
errorBody = e.getResponseBodyAsString();
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
error = e;
}
if (properties.isFailFast()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Could not locate PropertySource and the fail fast property is set, failing",
error);
}
logger.warn("Could not locate PropertySource: "
+ (errorBody == null ? error==null ? "label not found" : error.getMessage() : errorBody));
return null; } private Environment getRemoteEnvironment(RestTemplate restTemplate, ConfigClientProperties properties,
String label, String state) {
String path = "/{name}/{profile}";
String name = properties.getName();
String profile = properties.getProfile();
String token = properties.getToken();
String uri = properties.getRawUri(); Object[] args = new String[] { name, profile };
if (StringUtils.hasText(label)) {
args = new String[] { name, profile, label };
path = path + "/{label}";
}
ResponseEntity<Environment> response = null; try {
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
if (StringUtils.hasText(token)) {
headers.add(TOKEN_HEADER, token);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(state)) { //TODO: opt in to sending state?
headers.add(STATE_HEADER, state);
}
final HttpEntity<Void> entity = new HttpEntity<>((Void) null, headers);
response = restTemplate.exchange(uri + path, HttpMethod.GET,
entity, Environment.class, args);
}
catch (HttpClientErrorException e) {
if (e.getStatusCode() != HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND) {
throw e;
}
} if (response == null || response.getStatusCode() != HttpStatus.OK) {
return null;
}
Environment result = response.getBody();
return result;
} //。。。省略其他代码
}
在这里我们可以发现,当client端启动时,通过RestTemplate请求服务端的EnvironmentController进而添加至当前的Environment
四、使用数据库作为配置中心的仓库
我们先看一下自动装配类:
@Configuration
@Profile("jdbc")
class JdbcRepositoryConfiguration {
@Bean
public JdbcEnvironmentRepository jdbcEnvironmentRepository(JdbcTemplate jdbc) {
return new JdbcEnvironmentRepository(jdbc);
}
}
这里面创建了JdbcEnvironmentRepostiory,紧接着我们在看一下这个类的源码:
/*
* Copyright 2016-2017 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.cloud.config.server.environment; import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.environment.Environment;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.environment.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.ResultSetExtractor;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; /**
* An {@link EnvironmentRepository} that picks up data from a relational database. The
* database should have a table called "PROPERTIES" with columns "APPLICATION", "PROFILE",
* "LABEL" (with the usual {@link Environment} meaning), plus "KEY" and "VALUE" for the
* key and value pairs in {@link Properties} style. Property values behave in the same way
* as they would if they came from Spring Boot properties files named
* <code>{application}-{profile}.properties</code>, including all the encryption and
* decryption, which will be applied as post-processing steps (i.e. not in this repository
* directly).
*
* @author Dave Syer
*
*/
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.cloud.config.server.jdbc")
public class JdbcEnvironmentRepository implements EnvironmentRepository, Ordered { private static final String DEFAULT_SQL = "SELECT KEY, VALUE from PROPERTIES where APPLICATION=? and PROFILE=? and LABEL=?";
private int order = Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 10;
private final JdbcTemplate jdbc;
private String sql = DEFAULT_SQL;
private final PropertiesResultSetExtractor extractor = new PropertiesResultSetExtractor(); public JdbcEnvironmentRepository(JdbcTemplate jdbc) {
this.jdbc = jdbc;
} public void setSql(String sql) {
this.sql = sql;
} public String getSql() {
return this.sql;
} @Override
public Environment findOne(String application, String profile, String label) {
String config = application;
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(label)) {
label = "master";
}
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(profile)) {
profile = "default";
}
if (!profile.startsWith("default")) {
profile = "default," + profile;
}
String[] profiles = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(profile);
Environment environment = new Environment(application, profiles, label, null,
null);
if (!config.startsWith("application")) {
config = "application," + config;
}
List<String> applications = new ArrayList<String>(new LinkedHashSet<>(
Arrays.asList(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(config))));
List<String> envs = new ArrayList<String>(new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(profiles)));
Collections.reverse(applications);
Collections.reverse(envs);
for (String app : applications) {
for (String env : envs) {
Map<String, String> next = (Map<String, String>) jdbc.query(this.sql,
new Object[] { app, env, label }, this.extractor);
if (!next.isEmpty()) {
environment.add(new PropertySource(app + "-" + env, next));
}
}
}
return environment;
} @Override
public int getOrder() {
return order;
} public void setOrder(int order) {
this.order = order;
} } class PropertiesResultSetExtractor implements ResultSetExtractor<Map<String, String>> { @Override
public Map<String, String> extractData(ResultSet rs)
throws SQLException, DataAccessException {
Map<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
while (rs.next()) {
map.put(rs.getString(1), rs.getString(2));
}
return map;
} }
我们可以看到该类实现了EnvironmentRepository接口,在findone方法里通过JDBCTemplate来获取数据库中的配置信息。
下面我们来修改config-server端代码
4.1、gradle配置
dependencies {
compile('org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-config-server')
compile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-jdbc')
compile group: 'mysql', name: 'mysql-connector-java'
}
4.2、bootstrap.yml
spring:
profiles:
active: jdbc
application:
name: config-server
cloud:
config:
server:
jdbc:
sql: SELECT `KEY`,`VALUE` FROM PROPERTIES where APPLICATION=? and PROFILE=? and LABEL=?
profile: local
label: master
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/MySchool?characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: root
server:
port: 8888
3、DDL脚本
create table PROPERTIES
(
ID int auto_increment
primary key,
`KEY` varchar(32) null,
VALUE varchar(32) null,
APPLICATION varchar(64) null,
PROFILE varchar(32) null,
LABEL varchar(16) null,
CREATE_DATE datetime null
) CHARSET='utf8'
;
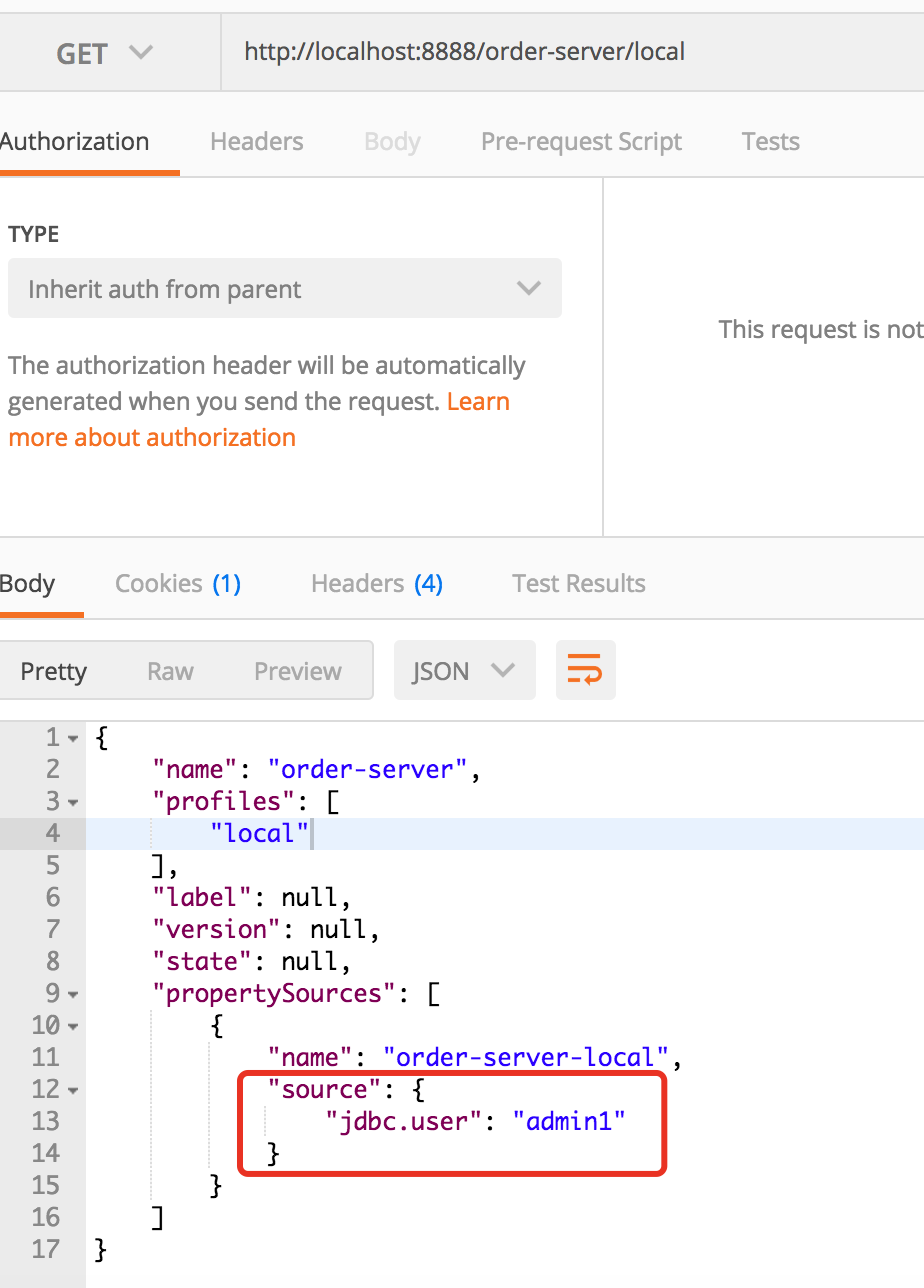
4、验证结果
五、总结
1.ConfigServer利用了SpringCloud引导机制,当主程序启动时,通过PropertySourceLocator的方法把相关配置读到当前的Environment中,同时提供了EnvironmentController使外界能够根据不同的请求获取不同格式的配置结果,由于是引导程序是核心,因此务必使用bootstrap.yml(properties)进行配置操作。
2.SpringCloud的客户端同样利用引导,通过实现PropertySourceLocator接口在程序启动前利用RestTemplate访问ConfigServer获取到配置并加载到当前Environment中
深入理解SpringCloud之分布式配置的更多相关文章
- SpringCloud的分布式配置及消息总线
1.在搭建分布式配置时,我们大概看下分布式配置的流程 如图所示: 当一个系统中的配置文件发生改变的时候,我们需要重新启动该服务,才能使得新的配置文件生效,spring cloud config可以实现 ...
- springcloud的分布式配置Config
1.为什么要统一配置管理? 微服务由多个服务构成,多个服务多个配置,则对这些配置需要集中管理.不同环境不同配置,运行期间动态调整,自动刷新. 统一管理微服务的配置:分布式配置管理的一些组件: zook ...
- SpringCloud学习笔记(九):SpringCloud Config 分布式配置中心
概述 分布式系统面临的-配置问题 微服务意味着要将单体应用中的业务拆分成一个个子服务,每个服务的粒度相对较小,因此系统中会出现大量的服务.由于每个服务都需要必要的配置信息才能运行,所以一套集中式的.动 ...
- SpringCloud与微服务Ⅹ --- SpringCloud Config分布式配置中心
一.SpringCloud Config是什么 分布式系统面临的问题 --- 配置问题 微服务意味着要将单体应用中的业务拆分成一个个子服务,每个服务的粒度相对较小,因此系统中会出现大量的服务.由于每个 ...
- springCloud学习-分布式配置中心(Spring Cloud Config)
1.简介 Spring Cloud Config :分布式配置中心,方便服务配置文件统一管理,它支持配置服务放在配置服务的内存中(即本地),也支持放在远程Git仓库中.在spring cloud co ...
- SpringCloud搭建分布式配置中心(基于git)
1.简介 Spring Cloud Config.它用来为分布式系统中的基础设施和微服务提供集中化的外部配置支持,分为服务端和客户端两个部分. 其中服务端也称为分布式配置中心,他是独立的微服务应用,用 ...
- SpringCloud Config 分布式配置中心
一.分布式系统面临的问题---配置问题 微服务意味着要将单体应用中的业务拆分成一个个子服务,每个服务的粒度相对较小,因此系统中会出现大量服务.由于每个服务都需要必要的配置信息才能运行,所以一套集中式的 ...
- 一起来学Spring Cloud | 第七章:分布式配置中心(Spring Cloud Config)
上一章节,我们讲解了服务网关zuul,本章节我们从git和本地两种存储配置信息的方式来讲解springcloud的分布式配置中心-Spring Cloud Config. 一.Spring Cloud ...
- Springcloud 2.x 版本 分布式配置中心
一.什么是分布式配置中心? 就是为微服务架构中的微服务提供集中化的外部配置支持,配置中心为各个微服务应用的所有环境提供了中心化的外部配置(可能比较难理解,想知道是什么意思就要知道为什么这么配置:这么配 ...
随机推荐
- objective-c中关于类型编码的解释
在某些情况下,我们需要动态的向一个类插入一个实例方法(也可以是一个类方法):这时我们可以用class_addMethod函数来完成: BOOL class_addMethod ( Class cls, ...
- android EventBus详解(三)
post()方法调用流程 我们继续来看EventBus类,的另一个入口方法post() //已省略部分代码 public void post(Object event) { PostingThread ...
- 超高速前端开发工具——Emmet
[由于 CSDN 不支持富文本编辑器写的文章迁移到 Markdown 编辑器中修改,已重发了一个重新排版的版本, 新版链接:http://blog.csdn.net/ys743276112/artic ...
- css选择器语法速查
通用选择器 *{} 类似于通配符,匹配文档中所有元素类型: 类型选择器 h1,h2,p{} 匹配以逗号隔开元素列表中的所有元素 类选择器 .glass{} or p.glass{} id选择器 #id ...
- XSS攻击过滤处理
关于XSS攻击 XSS是一种经常出现在web应用中的计算机安全漏洞,它允许恶意web用户将代码植入到提供给其它用户使用的页面中. XSS漏洞的危害 网络钓鱼,包括盗取各类用户账号: 窃取用户cooki ...
- 学习Selenium遇到的问题和解决方案
问题1:IE驱动位数问题,未安装对应的IE,打不开IE浏览器(已解决20180323) 使用Selenium启动IE浏览器的时候,报错,报错信息如下 org.openqa.selenium.remot ...
- 浏览器调试js
在Google Chrome浏览器出来之前,我一直使用FireFox,因为FireFox的插件非常丰富,更因为FireFox有强大的Firebug,对于前端开发可谓神器. 在Chrome出来的时候,我 ...
- 什么是shell? bash和shell有什么关系?
什么是shell? bash和shell有什么关系? 博客分类: Linux 什么是Shell? shell是你(用户)和Linux(或者更准确的说,是你和Linux内核)之间的接口程序 ...
- DUEditor的诞生
书接上回线上项目py2升级py3的事,除了上篇blog说到的snspy,主要升级的一个包就是DjangoUeditor,由于这个项目的维护人也不维护了,最后所幸自己开了支持Py3且加了一定优化的新版本 ...
- SQL Server Agent Job 多服务器管理
