Django-rest-framework源码分析----认证
目录
- Django rest framework(1)----认证
- Django rest framework(2)----权限
- Django rest framework(3)----节流
- Django rest framework(4)----版本
- Django rest framework(5)----解析器
- Django rest framework(6)----序列化
- Django rest framework(7)----分页
一、基础
1.1.安装
两种方式:
- github
- pip直接安装
pip install djangorestframework
1.2.需要先了解的一些知识
理解下面两个知识点非常重要,django-rest-framework源码中到处都是基于CBV和面向对象的封装
(1)面向对象封装的两大特性
把同一类方法封装到类中 将数据封装到对象中
(2)CBV
基于反射实现根据请求方式不同,执行不同的方法
原理:url-->view方法-->dispatch方法(反射执行其它方法:GET/POST/PUT/DELETE等等)
二、简单实例
2.1.settings
先创建一个project和一个app(我这里命名为API)
首先要在settings的app中添加
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'rest_framework',
]
2.2.url
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from API.views import AuthView urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('api/v1/auth/',AuthView.as_view()),
]
2.3.models
一个保存用户的信息
一个保存用户登录成功后的token
from django.db import models class UserInfo(models.Model):
USER_TYPE = (
(1,'普通用户'),
(2,'VIP'),
(3,'SVIP')
) user_type = models.IntegerField(choices=USER_TYPE)
username = models.CharField(max_length=32)
password = models.CharField(max_length=64) class UserToken(models.Model):
user = models.OneToOneField(UserInfo,on_delete=models.CASCADE)
token = models.CharField(max_length=64)
2.4.views
用户登录(返回token并保存到数据库)
from django.shortcuts import render
from django.http import JsonResponse
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from API import models def md5(user):
import hashlib
import time
#当前时间,相当于生成一个随机的字符串
ctime = str(time.time())
m = hashlib.md5(bytes(user,encoding='utf-8'))
m.update(bytes(ctime,encoding='utf-8'))
return m.hexdigest() class AuthView(object):
def post(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
ret = {'code':1000,'msg':None}
try:
user = request._request.POST.get('username')
pwd = request._request.POST.get('password')
obj = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(username=user,password=pwd).first()
if not obj:
ret['code'] = 1001
ret['msg'] = '用户名或密码错误'
#为用户创建token
token = md5(user)
#存在就更新,不存在就创建
models.UserToken.objects.update_or_create(user=obj,defaults={'token':token})
ret['token'] = token
except Exception as e:
ret['code'] = 1002
ret['msg'] = '请求异常'
return JsonResponse(ret)
2.5.利用postman发请求
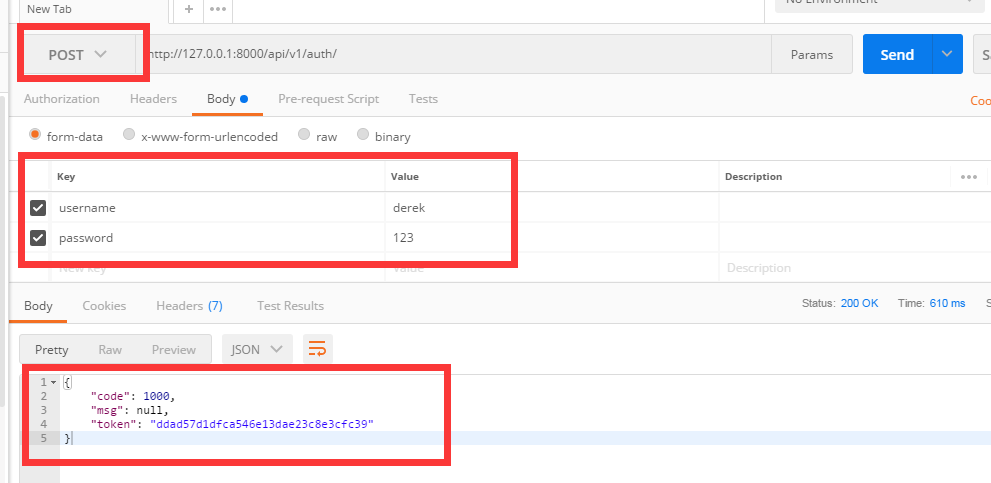
如果用户名和密码正确的话 会生成token值,下次该用户再登录时,token的值就会更新
数据库中可以看到token的值
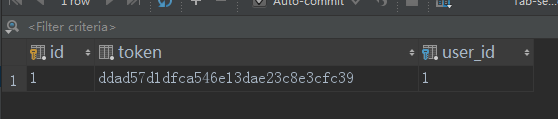
当用户名或密码错误时,抛出异常
三、添加认证
基于上面的例子,添加一个认证的类
3.1.url
path('api/v1/order/',OrderView.as_view()),
3.2.views
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
from django.http import JsonResponse
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from API import models
from rest_framework.request import Request
from rest_framework import exceptions
from rest_framework.authentication import BasicAuthentication ORDER_DICT = {
1:{
'name':'apple',
'price':15
},
2:{
'name':'dog',
'price':100
}
} def md5(user):
import hashlib
import time
#当前时间,相当于生成一个随机的字符串
ctime = str(time.time())
m = hashlib.md5(bytes(user,encoding='utf-8'))
m.update(bytes(ctime,encoding='utf-8'))
return m.hexdigest() class AuthView(object):
'''用于用户登录验证'''
def post(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
ret = {'code':1000,'msg':None}
try:
user = request._request.POST.get('username')
pwd = request._request.POST.get('password')
obj = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(username=user,password=pwd).first()
if not obj:
ret['code'] = 1001
ret['msg'] = '用户名或密码错误'
#为用户创建token
token = md5(user)
#存在就更新,不存在就创建
models.UserToken.objects.update_or_create(user=obj,defaults={'token':token})
ret['token'] = token
except Exception as e:
ret['code'] = 1002
ret['msg'] = '请求异常'
return JsonResponse(ret) class Authentication(APIView):
'''认证'''
def authenticate(self,request):
token = request._request.GET.get('token')
token_obj = models.UserToken.objects.filter(token=token).first()
if not token_obj:
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed('用户认证失败')
#在rest framework内部会将这两个字段赋值给request,以供后续操作使用
return (token_obj.user,token_obj) def authenticate_header(self, request):
pass class OrderView(APIView):
'''订单相关业务''' authentication_classes = [Authentication,] #添加认证
def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
#request.user
#request.auth
ret = {'code':1000,'msg':None,'data':None}
try:
ret['data'] = ORDER_DICT
except Exception as e:
pass
return JsonResponse(ret)
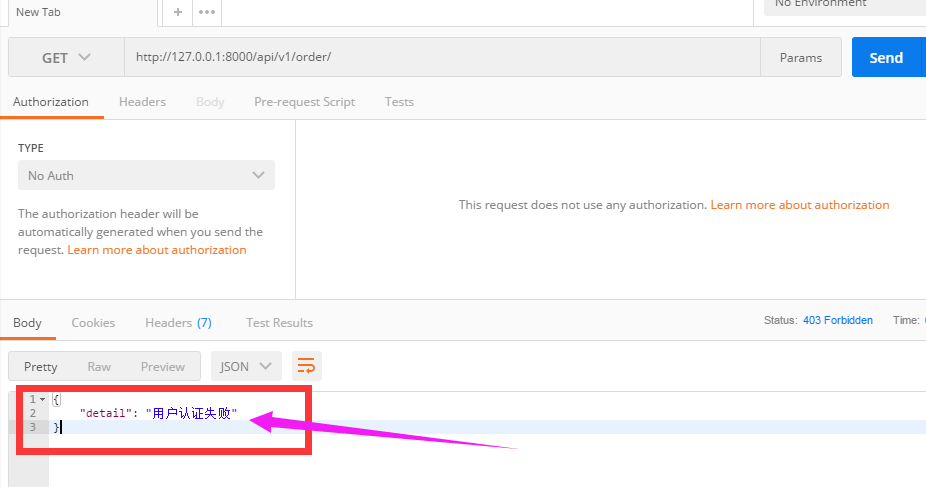
3.3用postman发get请求
请求的时候没有带token,可以看到会显示“用户认证失败”
这样就达到了认证的效果,django-rest-framework的认证是怎么实现的呢,下面基于这个例子来剖析drf的源码。
四、drf的认证源码分析
源码流程图
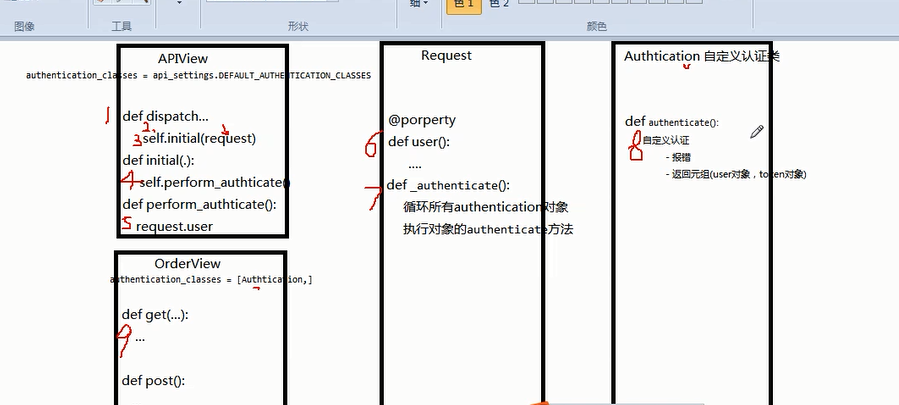
请求先到dispatch
dispatch()主要做了两件事
- 封装request
- 认证
具体看我写的代码里面的注释
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
`.dispatch()` is pretty much the same as Django's regular dispatch,
but with extra hooks for startup, finalize, and exception handling.
"""
self.args = args
self.kwargs = kwargs
#对原始request进行加工,丰富了一些功能
#Request(
# request,
# parsers=self.get_parsers(),
# authenticators=self.get_authenticators(),
# negotiator=self.get_content_negotiator(),
# parser_context=parser_context
# )
#request(原始request,[BasicAuthentications对象,])
#获取原生request,request._request
#获取认证类的对象,request.authticators
#1.封装request
request = self.initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs)
self.request = request
self.headers = self.default_response_headers # deprecate? try:
#2.认证
self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs) # Get the appropriate handler method
if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names:
handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(),
self.http_method_not_allowed)
else:
handler = self.http_method_not_allowed response = handler(request, *args, **kwargs) except Exception as exc:
response = self.handle_exception(exc) self.response = self.finalize_response(request, response, *args, **kwargs)
return self.response
4.1.reuqest
(1)initialize_request()
可以看到initialize()就是封装原始request
def initialize_request(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Returns the initial request object.
"""
parser_context = self.get_parser_context(request) return Request(
request,
parsers=self.get_parsers(),
authenticators=self.get_authenticators(), #[BasicAuthentication(),],把对象封装到request里面了
negotiator=self.get_content_negotiator(), parser_context=parser_context )
(2)get_authenticators()
通过列表生成式,返回对象的列表
def get_authenticators(self):
"""
Instantiates and returns the list of authenticators that this view can use.
"""
return [auth() for auth in self.authentication_classes]
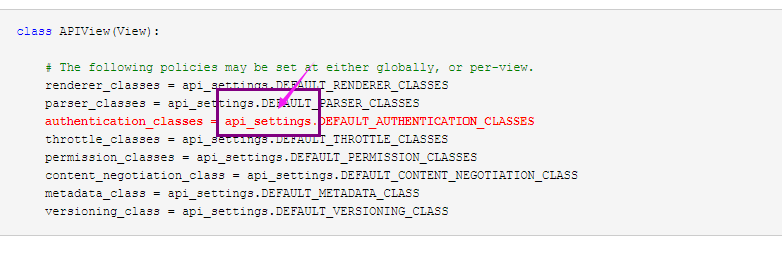
(3)authentication_classes
APIView里面有个 authentication_classes 字段
可以看到默认是去全局的配置文件找(api_settings)
class APIView(View):
# The following policies may be set at either globally, or per-view.
renderer_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES
parser_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_PARSER_CLASSES
authentication_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES
throttle_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES
permission_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES
content_negotiation_class = api_settings.DEFAULT_CONTENT_NEGOTIATION_CLASS
metadata_class = api_settings.DEFAULT_METADATA_CLASS
versioning_class = api_settings.DEFAULT_VERSIONING_CLASS
4.2.认证
self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs)
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
`.dispatch()` is pretty much the same as Django's regular dispatch,
but with extra hooks for startup, finalize, and exception handling.
"""
self.args = args
self.kwargs = kwargs
#对原始request进行加工,丰富了一些功能
#Request(
# request,
# parsers=self.get_parsers(),
# authenticators=self.get_authenticators(),
# negotiator=self.get_content_negotiator(),
# parser_context=parser_context
# )
#request(原始request,[BasicAuthentications对象,])
#获取原生request,request._request
#获取认证类的对象,request.authticators
#1.封装request
request = self.initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs)
self.request = request
self.headers = self.default_response_headers # deprecate? try:
#2.认证
self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs) # Get the appropriate handler method
if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names:
handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(),
self.http_method_not_allowed)
else:
handler = self.http_method_not_allowed response = handler(request, *args, **kwargs) except Exception as exc:
response = self.handle_exception(exc) self.response = self.finalize_response(request, response, *args, **kwargs)
return self.response
(1)initial()
主要看 self.perform_authentication(request),实现认证
def initial(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Runs anything that needs to occur prior to calling the method handler.
"""
self.format_kwarg = self.get_format_suffix(**kwargs) # Perform content negotiation and store the accepted info on the request
neg = self.perform_content_negotiation(request)
request.accepted_renderer, request.accepted_media_type = neg # Determine the API version, if versioning is in use.
version, scheme = self.determine_version(request, *args, **kwargs)
request.version, request.versioning_scheme = version, scheme # Ensure that the incoming request is permitted
#3.实现认证
self.perform_authentication(request)
self.check_permissions(request)
self.check_throttles(request)
(2)perform_authentication()
调用了request.user
def perform_authentication(self, request):
"""
Perform authentication on the incoming request. Note that if you override this and simply 'pass', then authentication
will instead be performed lazily, the first time either
`request.user` or `request.auth` is accessed.
"""
request.user
(3)user
request.user的request的位置

点进去可以看到Request有个user方法,加 @property 表示调用user方法的时候不需要加括号“user()”,可以直接调用:request.user
@property
def user(self):
"""
Returns the user associated with the current request, as authenticated
by the authentication classes provided to the request.
"""
if not hasattr(self, '_user'):
with wrap_attributeerrors():
#获取认证对象,进行一步步的认证
self._authenticate()
return self._user
(4)_authenticate()
循环所有authenticator对象
def _authenticate(self):
"""
Attempt to authenticate the request using each authentication instance
in turn.
"""
#循环认证类的所有对象
#执行对象的authenticate方法
for authenticator in self.authenticators:
try:
#执行认证类的authenticate方法
#这里分三种情况
#1.如果authenticate方法抛出异常,self._not_authenticated()执行
#2.有返回值,必须是元组:(request.user,request.auth)
#3.返回None,表示当前认证不处理,等下一个认证来处理
user_auth_tuple = authenticator.authenticate(self)
except exceptions.APIException:
self._not_authenticated()
raise if user_auth_tuple is not None:
self._authenticator = authenticator
self.user, self.auth = user_auth_tuple
return self._not_authenticated()
返回值就是例子中的:
token_obj.user-->>request.user
token_obj-->>request.auth
#在rest framework内部会将这两个字段赋值给request,以供后续操作使用
return (token_obj.user,token_obj) #例子中的return
当都没有返回值,就执行self._not_authenticated(),相当于匿名用户,没有通过认证
def _not_authenticated(self):
"""
Set authenticator, user & authtoken representing an unauthenticated request. Defaults are None, AnonymousUser & None.
"""
self._authenticator = None if api_settings.UNAUTHENTICATED_USER:
self.user = api_settings.UNAUTHENTICATED_USER() #AnonymousUser匿名用户
else:
self.user = None if api_settings.UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN:
self.auth = api_settings.UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN() #None
else:
self.auth = None
面向对象知识:
子类继承 父类,调用方法的时候:
- 优先去自己里面找有没有这个方法,有就执行自己的
- 只有当自己里面没有这个方法的时候才会去父类找
因为authenticate方法我们自己写,所以当执行authenticate()的时候就是执行我们自己写的认证
父类中的authenticate方法
def authenticate(self, request):
return (self.force_user, self.force_token)
我们自己写的
class Authentication(APIView):
'''用于用户登录验证'''
def authenticate(self,request):
token = request._request.GET.get('token')
token_obj = models.UserToken.objects.filter(token=token).first()
if not token_obj:
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed('用户认证失败')
#在rest framework内部会将这两个字段赋值给request,以供后续操作使用
return (token_obj.user,token_obj)
认证的流程就是上面写的,弄懂了原理,再写代码就更容易理解为什么了。
4.3.配置文件
继续解读源码
默认是去全局配置文件中找,所以我们应该在settings.py中配置好路径
api_settings源码
api_settings = APISettings(None, DEFAULTS, IMPORT_STRINGS) def reload_api_settings(*args, **kwargs):
setting = kwargs['setting']
if setting == 'REST_FRAMEWORK':
api_settings.reload()
setting中‘REST_FRAMEWORK’中找
全局配置方法:
API文件夹下面新建文件夹utils,再新建auth.py文件,里面写上认证的类
settings.py
#设置全局认证
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
"DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES":['API.utils.auth.Authentication',] #里面写你的认证的类的路径
}
auth.py
# API/utils/auth.py from rest_framework import exceptions
from API import models class Authentication(object):
'''用于用户登录验证'''
def authenticate(self,request):
token = request._request.GET.get('token')
token_obj = models.UserToken.objects.filter(token=token).first()
if not token_obj:
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed('用户认证失败')
#在rest framework内部会将这两个字段赋值给request,以供后续操作使用
return (token_obj.user,token_obj) def authenticate_header(self, request):
pass
在settings里面设置的全局认证,所有业务都需要经过认证,如果想让某个不需要认证,只需要在其中添加下面的代码:
authentication_classes = [] #里面为空,代表不需要认证
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
from django.http import JsonResponse
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from API import models
from rest_framework.request import Request
from rest_framework import exceptions
from rest_framework.authentication import BasicAuthentication ORDER_DICT = {
1:{
'name':'apple',
'price':15
},
2:{
'name':'dog',
'price':100
}
} def md5(user):
import hashlib
import time
#当前时间,相当于生成一个随机的字符串
ctime = str(time.time())
m = hashlib.md5(bytes(user,encoding='utf-8'))
m.update(bytes(ctime,encoding='utf-8'))
return m.hexdigest() class AuthView(APIView):
'''用于用户登录验证''' authentication_classes = [] #里面为空,代表不需要认证 def post(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
ret = {'code':1000,'msg':None}
try:
user = request._request.POST.get('username')
pwd = request._request.POST.get('password')
obj = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(username=user,password=pwd).first()
if not obj:
ret['code'] = 1001
ret['msg'] = '用户名或密码错误'
#为用户创建token
token = md5(user)
#存在就更新,不存在就创建
models.UserToken.objects.update_or_create(user=obj,defaults={'token':token})
ret['token'] = token
except Exception as e:
ret['code'] = 1002
ret['msg'] = '请求异常'
return JsonResponse(ret) class OrderView(APIView):
'''订单相关业务''' def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
# self.dispatch
#request.user
#request.auth
ret = {'code':1000,'msg':None,'data':None}
try:
ret['data'] = ORDER_DICT
except Exception as e:
pass
return JsonResponse(ret)
API/view.py代码
再测试一下我们的代码
不带token发请求

带token发请求
五、drf的内置认证
rest_framework里面内置了一些认证,我们自己写的认证类都要继承内置认证类 "BaseAuthentication"
4.1.BaseAuthentication源码:
class BaseAuthentication(object):
"""
All authentication classes should extend BaseAuthentication.
""" def authenticate(self, request):
"""
Authenticate the request and return a two-tuple of (user, token).
"""
#内置的认证类,authenticate方法,如果不自己写,默认则抛出异常
raise NotImplementedError(".authenticate() must be overridden.") def authenticate_header(self, request):
"""
Return a string to be used as the value of the `WWW-Authenticate`
header in a `401 Unauthenticated` response, or `None` if the
authentication scheme should return `403 Permission Denied` responses.
"""
#authenticate_header方法,作用是当认证失败的时候,返回的响应头
pass
4.2.修改自己写的认证类
自己写的Authentication必须继承内置认证类BaseAuthentication
# API/utils/auth/py from rest_framework import exceptions
from API import models
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication class Authentication(BaseAuthentication):
'''用于用户登录验证'''
def authenticate(self,request):
token = request._request.GET.get('token')
token_obj = models.UserToken.objects.filter(token=token).first()
if not token_obj:
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed('用户认证失败')
#在rest framework内部会将这两个字段赋值给request,以供后续操作使用
return (token_obj.user,token_obj) def authenticate_header(self, request):
pass
4.3.其它内置认证类
rest_framework里面还内置了其它认证类,我们主要用到的就是BaseAuthentication,剩下的很少用到

六、总结
自己写认证类方法梳理
(1)创建认证类
- 继承BaseAuthentication --->>1.重写authenticate方法;2.authenticate_header方法直接写pass就可以(这个方法必须写)
(2)authenticate()返回值(三种)
- None ----->>>当前认证不管,等下一个认证来执行
- raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed('用户认证失败') # from rest_framework import exceptions
- 有返回值元祖形式:(元素1,元素2) #元素1复制给request.user; 元素2复制给request.auth
(3)局部使用
- authentication_classes = [BaseAuthentication,]
(4)全局使用
#设置全局认证
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
"DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES":['API.utils.auth.Authentication',]
}
源码流程
--->>dispatch
--封装request
---获取定义的认证类(全局/局部),通过列表生成式创建对象
---initial
----peform_authentication
-----request.user (每部循环创建的对象)
Django-rest-framework源码分析----认证的更多相关文章
- Django rest framework源码分析(1)----认证
目录 Django rest framework(1)----认证 Django rest framework(2)----权限 Django rest framework(3)----节流 Djan ...
- Django rest framework 源码分析 (1)----认证
一.基础 django 2.0官方文档 https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.0/ 安装 pip3 install djangorestframework 假如我们想 ...
- Django rest framework源码分析(一) 认证
一.基础 最近正好有机会去写一些可视化的东西,就想着前后端分离,想使用django rest framework写一些,顺便复习一下django rest framework的知识,只是顺便哦,好吧. ...
- Django rest framework源码分析(3)----节流
目录 Django rest framework(1)----认证 Django rest framework(2)----权限 Django rest framework(3)----节流 Djan ...
- Django rest framework源码分析(4)----版本
版本 新建一个工程Myproject和一个app名为api (1)api/models.py from django.db import models class UserInfo(models.Mo ...
- Django rest framework源码分析(2)----权限
目录 Django rest framework(1)----认证 Django rest framework(2)----权限 Django rest framework(3)----节流 Djan ...
- 3---Django rest framework源码分析(3)----节流
Django rest framework源码分析(3)----节流 目录 添加节流 自定义节流的方法 限制60s内只能访问3次 (1)API文件夹下面新建throttle.py,代码如下: # u ...
- Django之REST framework源码分析
前言: Django REST framework,是1个基于Django搭建 REST风格API的框架: 1.什么是API呢? API就是访问即可获取数据的url地址,下面是一个最简单的 Djang ...
- Django Rest Framework源码剖析(八)-----视图与路由
一.简介 django rest framework 给我们带来了很多组件,除了认证.权限.序列化...其中一个重要组件就是视图,一般视图是和路由配合使用,这种方式给我们提供了更灵活的使用方法,对于使 ...
- Django Rest Framework源码剖析(三)-----频率控制
一.简介 承接上篇文章Django Rest Framework源码剖析(二)-----权限,当服务的接口被频繁调用,导致资源紧张怎么办呢?当然或许有很多解决办法,比如:负载均衡.提高服务器配置.通过 ...
随机推荐
- Type Archive for required library: 'C:/Users/EuphemiaShaw/.m2/repository/org/apache/hadoop/hadoop-hdfs/2.6.5/hadoop-hdfs-2.6.5.jar' in project 'mapreduce' cannot be read or is not a valid ZIP file
error: Description Resource Path Location Type Archive for required library: 'C:/Users/EuphemiaShaw/ ...
- [.Net Core] 简单使用 Mvc 内置的 Ioc(续)
简单使用 Mvc 内置的 Ioc(续) 本文基于 .NET Core 2.0. 上一章<[.Net Core] 简单使用 Mvc 内置的 Ioc>已经对日常 Mvc 中的 Ioc 的简单用 ...
- Hadoop搭建全程
修改配置文件 cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts #进入网络配置目录 dir ifcfg* #找到网卡配置文件 ifc ...
- 功能性AI术语表
算法:一套计算机要遵循的指令.一个算法可以是一个简单的单步程序也可以是一个复杂的神经网络,但是通常被用来指一个模型. 人工智能:这是一个统称.广义上说,软件意味着模仿或取代人类智能的各个方面.人工智能 ...
- 引用第三方dll引发的问题解决
引用的程序集错误 如果引用第三方dll,调试出现引用的程序集出现错误,可以下载dependency,查看这个dll的依赖dll,如果本地电脑没有依赖dll或依赖dll出现问题,则下载或取代依赖dll ...
- windows系统安装jira
主题介绍 JIRA是Atlassian公司出品的项目与事务跟踪工具,被广泛应用于缺陷跟踪.客户服务.需求收集.流程审批.任务跟踪.项目跟踪和敏捷管理等工作领域,其配置灵活.功能全面.部署简单.扩展丰 ...
- git使用.gitignore设置不生效或不起作用的问题
偶然遇到的问题,记录如下: 通常我们在push项目时,会有些配置文件或本地文件不想上传到服务器上 这时候我们会通过设置.gitignore 文件 一般设置成这样: # 20170418 by 51a ...
- 微信小程序开发之--”emplate模板“的应用
第一步:定义模板 ①:新建一个template文件夹用来管理项目中所有的模板(本文案例定义文件夹名为:temp): ②.新建一个wxml文件来定义模板(本文案例定义文件夹名为:temp.wxml): ...
- Sping Boot入门到实战之实战篇(一):实现自定义Spring Boot Starter——阿里云消息队列服务Starter
在 Sping Boot入门到实战之入门篇(四):Spring Boot自动化配置 这篇中,我们知道Spring Boot自动化配置的实现,主要由如下几部分完成: @EnableAutoConfigu ...
- Java中删除第一个集合中以某某开头的元素,删除第二个集合中以某某结尾的元素,并合并成一个集合
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class Test { public static void main(Strin ...
