OpenGL ES 3.0之VertexAttributes,Vertex Arrays,and Buffer Objects(九)
顶点数据,也称为顶点属性,指每一个顶点数据。指能被用来描述每个顶点的数据,或能被所有顶点使用的常量值。例如你想绘制一个具有颜色的立方体三角形。你指定一个恒定的值用于三角形的所有三个顶点颜色。但三角形的三个顶点位置是不同的,你需要指定一个顶点矩阵存储三个位置值。
指定顶点属性数据
顶点属性数据可以使用顶点数组或常量值指定每个顶点数据,OpenGL ES 3.0 必须至少支持16 个顶点属性。应用应该能够查询编译器支持的确切属性数。下面的程序指出如何查询。
GLint maxVertexAttribs; // n will be >= 8
glGetIntegerv(GL_MAX_VERTEX_ATTRIBS, &maxVertexAttribs);
常量顶点属性
常量顶点属性是指基元的所有顶点属性是相同的,因此仅仅对基元的所有顶点仅仅需要指定一个值。顶点属性常量使用下面的函数指定:
void glVertexAttriblf(GLuint index, GLfloat x);
void glVertexAttrib2f(GLuint index, GLfloat x, GLfloat y);
void glVertexAttrib3f( GLuint index, GLfloat x, GLfloat y,
GLfloat z);
void glVertexAttrib4f( GLuint index, GLfloat x, GLfloat y,
GLfloat z, GLfloat w);
void glVertexAttriblfv(GLuint index, const GLfloat *values);
void glVertexAttrib2fv(GLuint index, const GLfloat *values);
void glVertexAttrib3fv(GLuint index, const GLfloat *values);
void glVertexAttrib4fv(GLuint index, const GLfloat *values);
glVertexAttrib*通过索引来装在一般顶点属性,glVertexAttriblf和glVertexAttriblfv加载(x, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)到顶点属性,glVertexAttrib2f and glVertexAttrib2fv 装载(x, y, 0.0, 1.0),glVertexAttrib3f 和glVertexAttrib3fv 装载(x, y, z, 1.0),glVertexAttrib4f and
glVertexAttrib4fv 装载(x, y, z, w)
顶点数组
顶点数组指定每个顶点的属性数据即存储在应用程序地址空间(OpenGL ES 叫clientspace)缓冲区的数据。它们提供有效的和灵活的方法指定顶点属性数据。顶点数组使用glVertexAttribPointer 或glVertexAttribIPointer函数指定:

存储所有的顶点属性在一个缓冲区中,这种存储顶点属性的方法叫结构数组,这种方法描述每个顶点的所有属性。存储每个顶点属性到分开的缓冲区,这种存储顶点属性的方法叫数组结构每个顶点有四个属性—位置、法线、两个贴图坐标,这些属性被存储在一个缓冲区中,被所有顶点分享。顶点位置属性是三个浮点数(x, y, z)的矢量。法线也是三个浮点数的矢量,每个贴图坐标是两个浮点数的矢量。
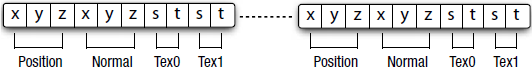
结构数组代码示例
#define VERTEX_POS_SIZE 3 // x, y, and z
#define VERTEX_NORMAL_SIZE 3 // x, y, and z
#define VERTEX_TEXCOORD0_SIZE 2 // s and t
#define VERTEX_TEXCOORDl_SIZE 2 // s and t
#define VERTEX_POS_INDX 0
#define VERTEX_NORMAL_INDX 1
#define VERTEX_TEXCOORD0_INDX 2
#define VERTEX_TEXCOORDl_INDX 3
// the following 4 defines are used to determine the locations
// of various attributes if vertex data are stored as an array
// of structures
#define VERTEX_POS_OFFSET 0
#define VERTEX_NORMAL_OFFSET 3
#define VERTEX_TEXCOORD0_OFFSET 6
#define VERTEX_TEXC00RD1_0FFSET 8
#define VERTEX_ATTRIB_SIZE (VERTEX_POS_SIZE + \
VERTEX_NORMAL_SIZE + \
VERTEX_TEXCOORD0_SIZE + \
VERTEX_TEXC00RD1_SIZE)
float *p = (float*) malloc(numVertices * VERTEX_ATTRIB_SIZE
* sizeof(float));
// position is vertex attribute 0
glVertexAttribPointer(VERTEX_POS_INDX, VERTEX_POS_SIZE,
GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE,
VERTEX_ATTRIB_SIZE * sizeof(float),
p);
// normal is vertex attribute 1
glVertexAttribPointer(VERTEX_NORMAL_INDX, VERTEX_NORMAL_SIZE,
GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE,
VERTEX_ATTRIB_SIZE * sizeof(float),
(p + VERTEX_NORMAL_OFFSET));
// texture coordinate 0 is vertex attribute 2
glVertexAttribPointer(VERTEX_TEXCOORDO_INDX,
VERTEX_TEXCOORD0_SIZE,
GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE,
VERTEX_ATTRIB_SIZE * sizeof(float),
(p + VERTEX_TEXCOORD0_OFFSET));
// texture coordinate 1 is vertex attribute 3
glVertexAttribPointer(VERTEX_TEXCOORDl_INDX,
VERTEX_TEXC00RD1_SIZE,
GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE,
VERTEX_ATTRIB_SIZE * sizeof(float),
(p + VERTEX_TEXC00RD1_0FFSET));
数组结构示例代码
float *position = (float*) malloc(numVertices *
VERTEX_POS_SIZE * sizeof(float));
float *normal = (float*) malloc(numVertices *
VERTEX_NORMAL_SIZE * sizeof(float));
float *texcoordO = (float*) malloc(numVertices *
VERTEX_TEXCOORD0_SIZE * sizeof(float));
float *texcoordl = (float*) malloc(numVertices *
VERTEX_TEXC00RD1_SIZE * sizeof(float));
// position is vertex attribute 0
glVertexAttribPointer(VERTEX_POS_INDX, VERTEX_POS_SIZE,
GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE,
VERTEX_POS_SIZE * sizeof(float),
position);
// normal is vertex attribute 1
glVertexAttribPointer(VERTEX_NORMAL_INDX, VERTEX_NORMAL_SIZE,
GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE,
VERTEX_NORMAL_SIZE * sizeof(float),
normal);
// texture coordinate 0 is vertex attribute 2
glVertexAttribPointer(VERTEX_TEXCOORDO_INDX,
VERTEX_TEXCOORD0_SIZE,
GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE,
VERTEX_TEXCOORD0_SIZE *
sizeof(float), texcoordO);
// texture coordinate 1 is vertex attribute 3
glVertexAttribPointer(VERTEX_TEXCOORDl_INDX,
VERTEX_TEXC00RD1_SIZE,
GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE,
VERTEX_TEXC00RD1_SIZE * sizeof(float),
texcoordl);
性能提示
1.如何存储不同的顶点属性。
使用结构数组要比使用数组结构性能更有优,原因是每个顶点的属性数据能够被连续的读出,这种内存结构更有效。但使用array of structures 不好的是当我们想去修改指定的属性时。如果一个顶点属性需要被修改(像贴图坐标),这将必须更新顶点缓冲区。当顶点缓冲区作为缓冲区对象时,整个
顶点属性缓冲区将需要更新加载,
2.顶点属性使用哪种数据格式
顶点属性数据格式 通过调用glVertexAttribPointer 函数的参数type指定,这样做不但影响顶点属性的绘图数据的存储要求,也影响全部的执行工作,它是渲染帧时的内存带宽的要求。数据量越小,对带宽要求越低。OpenGL ES 3支持16位浮点顶点格式命名gl_half_float,建议尽量使用gl_half_float,Texture coordinates, normals, binormals, tangent vectors都适合使用gl_half_float来存储,颜色使用四个GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE来存储每个顶点颜色,顶点位置应该存储为GL_FLOAT。
3.如何标准化glVertexAttribPointer 工作
顶点属性在被顶点着色器使用前,作为单一精度的浮点值被存储在内存中。如果顶点属性的数据类型不是浮点数,那么它们的值将在着色器使用前转变为浮点值。normalized标志指示非浮点顶点属性数据转化为单一精度的浮点值。如果normalized符为false,顶点数值被直接转化为浮点值,转化非浮点变量为浮点类型是相似的
GLfloat f;
GLbyte b;
f = (GLfloat)b; // f represents values in the range [-128.0,
// 127.0]
如果normalized为true,顶点数据类型如果是GL_BYTE, GL_SHORT 或 GL_FIXED 被匹配到[-1.0,1.0],数据类型如果是GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE or GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT 被匹配到[0.0,1.0]。下面描述非浮点值数据类型normalized转换过程

也有可能访问整数顶点属性数据为整数的顶点着色器,而不将它们转换为浮点数。在这种情况下,glvertexattribipointer功能应使用顶点属性应该被声明为一个整数类型的顶点着色。
4.在常量顶点属性和顶点数组之间选择


int Init ( ESContext *esContext )
{
UserData *userData = (UserData*) esContext->userData;
const char vShaderStr[] =
"#version 300 es \n"
"layout(location = 0) in vec4 a_color; \n"
"layout(location = 1) in vec4 a_position; \n"
"out vec4 v_color; \n"
"void main() \n"
"{ \n"
" v_color = a_color; \n"
" gl_Position = a_position; \n"
"}";
const char fShaderStr[] =
"#version 300 es \n"
"precision mediump float; \n"
"in vec4 v_color; \n"
"out vec4 o_fragColor; \n"
"void main() \n"
"{ \n"
" o_fragColor = v_color; \n"
"}" ;
GLuint programObject;
// Create the program object
programObject = esLoadProgram ( vShaderStr, fShaderStr );
if ( programObject == )
return GL_FALSE;
// Store the program object
userData->programObject = programObject;
glClearColor ( 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f );
return GL_TRUE;
}
void Draw ( ESContext *esContext )
{
UserData *userData = (UserData*) esContext->userData;
GLfloat color[] = { 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f };
// 3 vertices, with (x, y, z) per-vertex
GLfloat vertexPos[ * ] =
{
0.0f, 0.5f, 0.0f, // v0
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // v1
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f // v2
};
glViewport ( , , esContext->width, esContext->height );
glClear ( GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT );
glUseProgram ( userData->programObject );
glVertexAttrib4fv ( , color );
glVertexAttribPointer ( , , GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, ,
vertexPos );
glEnableVertexAttribArray ( );
glDrawArrays ( GL_TRIANGLES, , );
glDisableVertexAttribArray ( );
}
在顶点着色器中声明顶点属性变量
在顶点着色器中,通过限定符【in】来声明一个变量作为顶点属性。属性变量也可以加【layout】限定符,用于提供属性索引。如下
layout(location = ) in vec4 a_position;
layout(location = ) in vec2 a_texcoord;
layout(location = ) in vec3 a_normal;
【in】限度符支持的数据类型包括float, vec2,vec3, vec4, int, ivec2, ivec3, ivec4, uint, uvec2, uvec3,uvec4, mat2, mat2x2, mat2x3, mat2x4, mat3, mat3x3, mat3x4,=mat4, mat4x2, and mat4x3.它并不支持数组和结构体。下面声明会发生编译错误
in foo_t a_A; // foo_t is a structure
in vec4 a_B[];
声明的顶点属性变量是只读的,不可被修改
顶点缓存对象
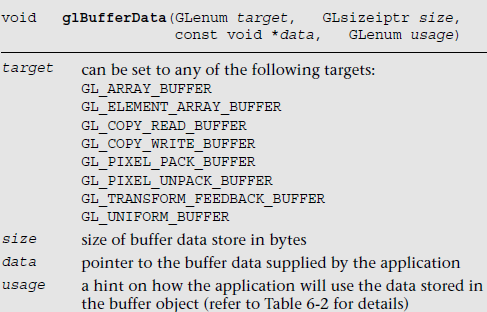
顶点数据通过顶点数组存储在客户端内存中,当使用glDrawArrays or glDrawElements绘制时,此数据必须从客户端内存复制到图形内存。顶点缓存区对象允许应用程序顶点数据分配和缓存在具有高性能的图形内存并渲染。而避免重发数据的每一次图元的绘制。缓存对象支持2种类型,数据缓存对象和元素数组缓存对象,数组缓存对象使用GL_ARRAY_BUFFER令牌来指定,元素数组缓存对象使用GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER来指定,在使用缓冲区对象之前,我们需要分配缓冲对象并将顶点数据和元素索引上传到缓冲对象。
void initVertexBufferObjects(vertex_t *vertexBuffer,
GLushort *indices,
GLuint numVertices,
GLuint numlndices,
GLuint *vboIds)
{
glGenBuffers(, vboIds);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vboIds[]);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, numVertices *
sizeof(vertex_t), vertexBuffer,
GL_STATIC_DRAW);
// bind buffer object for element indices
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, vboIds[]);
glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER,
numIndices * sizeof(GLushort),
indices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
}

glGenBuffers用于创建缓存区对象。N为0的值被系统保留不会分配,所以当使用0时会发生错误。

glBindBuffer函数是一个缓存区对象设置为当前在使用的缓存区对象。glGenBuffers 在被使用glBindBuffer 绑定前,不要求被指定缓冲区对象名,一个应用能指定一个未使用的缓冲区对象名字去绑定。但我们推荐使用glGenBuffers 返回的名字而不是自己指定。
与缓存对象关联的状态有如下


顶点数组数据和元素顶点数组数据被创建和初始化使用glBufferData 函数

#define VERTEX_POS_SIZE 3 // x, y, and z
#define VERTEX_COLOR_SIZE 4 // r, g, b, and a
#define VERTEX_POS_INDX 0
#define VERTEX_COLOR_INDX 1
//
// vertices - pointer to a buffer that contains vertex
// attribute data
// vtxStride - stride of attribute data / vertex in bytes
// numIndices - number of indices that make up primitives
// drawn as triangles
// indices - pointer to element index buffer
//
void DrawPrimitiveWithoutVBOs(GLfloat *vertices,
GLint vtxStride,
GLint numIndices,
GLushort *indices)
{
GLfloat *vtxBuf = vertices;
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, );
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, );
glEnableVertexAttribArray(VERTEX_POS_INDX);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(VERTEX_COLOR_INDX);
glVertexAttribPointer(VERTEX_POS_INDX, VERTEX_POS_SIZE,
GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, vtxStride,
vtxBuf);
vtxBuf += VERTEX_POS_SIZE;
glVertexAttribPointer(VERTEX_COLOR_INDX,
VERTEX_COLOR_SIZE, GL_FLOAT,
GL_FALSE, vtxStride, vtxBuf);
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, numIndices, GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT,
indices);
glDisableVertexAttribArray(VERTEX_POS_INDX);
glDisableVertexAttribArray(VERTEX_COLOR_INDX);
}
void DrawPrimitiveWithVBOs(ESContext *esContext,
GLint numVertices, GLfloat *vtxBuf,
GLint vtxStride, GLint numIndices,
GLushort *indices)
{
UserData *userData = (UserData*) esContext->userData;
GLuint offset = ;
// vboIds[0] - used to store vertex attribute data
// vboIds[l] - used to store element indices
if ( userData->vboIds[] == && userData->vboIds[] == )
{
// Only allocate on the first draw
glGenBuffers(, userData->vboIds);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, userData->vboIds[]);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vtxStride * numVertices,
vtxBuf, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER,
userData->vboIds[]);
glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER,
sizeof(GLushort) * numIndices,
indices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
}
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, userData->vboIds[]);
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, userData->vboIds[]);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(VERTEX_POS_INDX);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(VERTEX_COLOR_INDX);
glVertexAttribPointer(VERTEX_POS_INDX, VERTEX_POS_SIZE,
GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, vtxStride,
(const void*)offset);
offset += VERTEX_POS_SIZE * sizeof(GLfloat);
glVertexAttribPointer(VERTEX_COLOR_INDX,
VERTEX_COLOR_SIZE,
GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, vtxStride,
(const void*)offset);
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, numIndices, GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT,
0);
glDisableVertexAttribArray(VERTEX_POS_INDX);
glDisableVertexAttribArray(VERTEX_COLOR_INDX);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, );
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, );
}
void Draw ( ESContext *esContext )
{
UserData *userData = (UserData*) esContext->userData;
// 3 vertices, with (x, y, z),(r, g, b, a) per-vertex
GLfloat vertices[ * (VERTEX_POS_SIZE + VERTEX_COLOR_SIZE)] =
{
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, // v0
1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, // c0
-1.0f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // v1
0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, // c1
0.0f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // v2
0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, // c2
};
// index buffer data
GLushort indices[] = { , , };
glViewport ( , , esContext->width, esContext->height );
glClear ( GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT );
glUseProgram ( userData->programObject );
glUniform1f ( userData->offsetLoc, 0.0f );
DrawPrimitiveWithoutVBOs ( vertices,
sizeof(GLfloat) * (VERTEX_POS_SIZE + VERTEX_COLOR_SIZE),
3, indices );
// offset the vertex positions so both can be seen
glUniform1f ( userData->offsetLoc, 1.0f );
DrawPrimitiveWithVBOs ( esContext, , vertices,
sizeof(GLfloat) * (VERTEX_POS_SIZE + VERTEX_COLOR_SIZE),
3, indices );
}
顶点数组对象
OpenGL ES 3.0推出的顶点数组对象。负责单一对象的顶点数组/顶点缓冲区对象转换配置。


#define VERTEX_POS_SIZE 3 // x, y, and z
#define VERTEX_COLOR_SIZE 4 // r, g, b, and a
#define VERTEX_POS_INDX 0
#define VERTEX_COLOR_INDX 1
#define VERTEX_STRIDE ( sizeof(GLfloat) * \
( VERTEX_POS_SIZE + \
VERTEX_COLOR_SIZE ) )
int Init ( ESContext *esContext )
{
UserData *userData = (UserData*) esContext->userData;
const char vShaderStr[] =
"#version 300 es \n"
"layout(location = 0) in vec4 a_position; \n"
"layout(location = 1) in vec4 a_color; \n"
"out vec4 v_color; \n"
"void main() \n"
"{ \n"
" v_color = a_color; \n"
" gl_Position = a_position; \n"
"}";
const char fShaderStr[] =
"#version 300 es \n"
"precision mediump float; \n"
"in vec4 v_color; \n"
"out vec4 o_fragColor; \n"
"void main() \n"
"{ \n"
" o_fragColor = v_color; \n"
"}" ;
GLuint programObject;
// 3 vertices, with (x, y, z),(r, g, b, a) per-vertex
GLfloat vertices[ * (VERTEX_POS_SIZE + VERTEX_COLOR_SIZE)] =
{
0.0f, 0.5f, 0.0f, // v0
1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, // c0
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // v1
0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, // c1
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // v2
0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, // c2
};
GLushort indices[] = { , , };
// Create the program object
programObject = esLoadProgram ( vShaderStr, fShaderStr );
if ( programObject == )
return GL_FALSE;
// Store the program object
userData->programObject = programObject;
// Generate VBO Ids and load the VBOs with data
glGenBuffers ( , userData->vboIds );
glBindBuffer ( GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, userData->vboIds[] );
glBufferData ( GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices),
vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer ( GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, userData->vboIds[]);
glBufferData ( GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof ( indices ),
indices, GL_STATIC_DRAW );
// Generate VAO ID
glGenVertexArrays ( , &userData->vaoId );
// Bind the VAO and then set up the vertex
// attributes
glBindVertexArray ( userData->vaoId );
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, userData->vboIds[]);
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, userData->vboIds[]);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(VERTEX_POS_INDX);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(VERTEX_COLOR_INDX);
glVertexAttribPointer ( VERTEX_POS_INDX, VERTEX_POS_SIZE,
GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, VERTEX_STRIDE, (const void*) );
glVertexAttribPointer ( VERTEX_COLOR_INDX, VERTEX_COLOR_SIZE,
GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, VERTEX_STRIDE,
(const void*) ( VERTEX_POS_SIZE * sizeof(GLfloat) ) );
// Reset to the default VAO
glBindVertexArray ( );
glClearColor ( 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f );
return GL_TRUE;
}
void Draw ( ESContext *esContext )
{
UserData *userData = (UserData*) esContext->userData;
glViewport ( , , esContext->width, esContext->height );
glClear ( GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT );
glUseProgram ( userData->programObject );
// Bind the VAO
glBindVertexArray ( userData->vaoId );
// Draw with the VAO settings
glDrawElements ( GL_TRIANGLES, , GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT,
(const void*) );
// Return to the default VAO
glBindVertexArray ( );
}

OpenGL ES 3.0之VertexAttributes,Vertex Arrays,and Buffer Objects(九)的更多相关文章
- OpenGL ES 3.0 Graphics Pipeline
一:OpenGL ES 3.0 Graphics Pipeline 渲染管道如下图 1.Vertex Buffer/Arrays Objects的数据由应用程序传进来 2.由上图可以看到Textur ...
- OpenGL ES 2.0 渲染管线 学习笔记
图中展示整个OpenGL ES 2.0可编程管线 图中Vertex Shader和Fragment Shader 是可编程管线: Vertex Array/Buffer objects 顶点数据来源, ...
- 【Android 应用开发】OpenGL ES 2.0 -- 制作 3D 彩色旋转三角形 - 顶点着色器 片元着色器 使用详解
最近开始关注OpenGL ES 2.0 这是真正意义上的理解的第一个3D程序 , 从零开始学习 . 案例下载地址 : http://download.csdn.net/detail/han120201 ...
- OpenGL ES 2.0 Shader 调试新思路(二): 做一个可用的原型
OpenGL ES 2.0 Shader 调试新思路(二): 做一个可用的原型 目录 背景介绍 请参考前文OpenGL ES 2.0 Shader 调试新思路(一): 改变提问方式 优化 ledCha ...
- OpenGL ES 2.0 Shader 调试新思路(一): 改变提问方式
OpenGL ES 2.0 Shader 调试新思路(一): 改变提问方式 --是什么(答案是具体值) VS 是不是(答案是布尔值) 目录 背景介绍 问题描述 Codea 是 iPad 上的一款很方便 ...
- 《OpenGL® ES™ 3.0 Programming Guide》读书笔记1 ----总览
OpenGL ES 3.0 Graphics Pipeline OpenGL ES 3.0 Vertex Shader Transform feedback: Additionally, OpenGL ...
- OpenGL ES 3.0之Shading Language(八)
每个OpenGL ES 3.0程序要求一个顶点着色器和一个片段着色器去渲染一个图形.着色器概念是API 的中心,本篇将介绍着色器语言部分包含下面几项 1.变量和变量类型 2.矢量和矩阵创建及选择 3. ...
- OpenGL ES 3.0之顶点缓冲
所谓顶点缓冲就是直接将顶点数据存储在gpu的一段缓冲区,不需要从cpu拷贝到gpu.提高了程序的运行效率. 操作步骤 1.创建顶点缓冲对象 GLuint vertexBufferID; 2.分配空间 ...
- OpenGL ES 3.0顶点着色器(一)
OpenGL ES 3.0流程图 1.Vertex Shader(顶点着色器) 顶点着色实现了一种通用的可编程方法操作顶点. 顶点着色器的输入包括以下几个: • Shader program.程序的顶 ...
随机推荐
- sqlserver 2012 IDE中 Windows身份验证连接服务器报错 ,Login failed for user 'xxx\Administrator'. 原因: 找不到与提供的名称匹配的登录名。
问题描述: 本地装了两个实例,一个是SQLEXPRESS,可以正常操作.但是另一个开发常用的实例MSSQLSERVER却连Windows身份验证都报错,报的错误也是很奇葩,怎么会找不到Administ ...
- SQL Server 2012 Always on Availability Groups安装
http://blog.csdn.net/kevinsqlserver/article/details/7886455
- [转载]vs2017与docker
基本需求 系统 win10 vs2017 docker 步骤 1.开启系统的hyper-v 2. 重启电脑 3.安装docker 下载地址:https://docs.docker.com/docker ...
- 基于设备树的TQ2440 DMA学习(2)—— 简单的DMA传输
作者 彭东林 pengdonglin137@163.com 平台 TQ2440 Linux-4.9 概述 上一篇博客分析了DMA控制器的寄存器,循序渐进,下面我们直接操作DMA控制器的寄存器实 ...
- 算法竞赛入门经典+挑战编程+USACO
下面给出的题目共计560道,去掉重复的也有近500题,作为ACMer Training Step1,用1年到1年半年时间完成.打牢基础,厚积薄发. 一.UVaOJ http://uva.onlinej ...
- Linux学习16-CentOS安装gitlab环境
前言 在学习Gitlab的环境搭建之前,首先需要了解Git,Gitlab,GitHub他们三者之间的关系 Git 它是一个源代码版本控制系统,可让您在本地跟踪更改并从远程资源推送或提取更改. GitH ...
- 分析iOS Crash文件,使用命令符号化iOS Crash文件
TBMainClient.ipa改名为TBMainClient.zip并解压得到TBMainClient.app 然后将TBMainClient.app TBMainClient.app.d ...
- Android 4.4 Kitkat Phone工作流程浅析(八)__Phone状态分析
本文来自http://blog.csdn.net/yihongyuelan 转载请务必注明出处 本文代码以MTK平台Android 4.4为分析对象.与Google原生AOSP有些许差异.请读者知悉. ...
- 点击cell动态修改高度动画
点击cell动态修改高度动画 效果 源码 https://github.com/YouXianMing/Animations // // TapCellAnimationController.m // ...
- 灵书妙探第一季/全集Castle迅雷下载
第一季 Castle Season 1 (2009)看点:ABC电视台2009年开播的一部罪案剧,讲述一位罪案小说家Richard Castle帮助纽约警察局凶杀组破案的故事.凶案组女警探Kate B ...
