I/O模型(同步、非同步、阻塞、非阻塞)总结
I/O:同步(synchronous)、异步(asynchronous)、阻塞(blocking)、非阻塞(nonblocking)
1、I/O内部机制
出于安全考虑,用户程序(用户态)是没办法直接操作I/O设备进行数据读入或输出的,需要借助操作系统(内核态)提供的API来进行I/O,所以通常我们说I/O其实是通过系统调用来完成的。
程序发起I/O调用时涉及两个阶段,以read为例:
- 等待内核态将数据从外设读入并准备好,进入就绪状态 (Waiting for the data to be ready)。这步是外设与内存间的复制,是耗时操作!
- 将数据从内核复制到进程中即内核态复制到用户态 (Copying the data from the kernel to the process)。这步是内存间的复制,比上步快很多。
通常说的IO时的“阻塞”是指从外设数据到内存时是否阻塞,也就是上述的步骤1。
2、同步异步阻塞非阻塞的区别
阻塞、非阻塞(针对系统调用(内核态)而言?):在于发起的I/O调用是否立即返回。阻塞I/O等I/O完成才返回(即等1、2都结束才返回。1、2均阻塞),非阻塞I/O立即返回,此时I/O还没完成(即1立即返回,若没准备好则循环检测直到就绪,就绪后等阶段2。1不阻塞、2阻塞)。可见,阻塞非阻塞的的区别体现在是否等待耗时步骤1完成。
一个不那么恰当的比喻:假设你在家,要去车站接你朋友,你朋友尚未到车站。你朋友到车站前这段过程、从车站到你家这段过程分别相当于上述阶段1、2。非阻塞就是:你告诉你朋友要去车站接他,让他到车站时跟你说你再去...
同步、异步(针对用户线程(用户态)而言?):在于调用者(线程)在发起I/O调用后能否继续执行之后的代码或工作
阻塞不一定是同步的,非阻塞也不一定是异步的,反之亦然。
- 同步阻塞I/O:如JDK I/O(发起I/O调用不立即返回,调用者在I/O完成前也没法进行之后的操作)
- 同步非阻塞I/O:如JDK NIO(发起I/O调用后立即返回,此后通过循环检查直到I/O就绪才进行I/O操作,操作完了才进行之后的工作,因此是同步的)。
- 异步I/O:如可以写一个带回调参数的方法,该方法根据String content、String filePath参数将conent写入指定文件,方法内启用新线程进行I/O,完成后调用回调函数通知调用者。至于是阻塞还是非阻塞则看新线程内进行的I/O是阻塞还是非阻塞的。一个异步阻塞I/O的示例如下:
public class FileIO {
public void saveStrToFile(String fileName, String str, IFileIOCallback callback) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
File file = getExistsFile(fileName);
writeStrToFile(str, file);
callback.onResult(true);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
callback.onResult(false);
}
}
}).start();
}
}
阻塞非阻塞的区别简述,可参阅:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/bfAYDalNcZpqsnyt_NvIhQ(码农翻身)
3、Unix下的五种I/O模型
(详见 IO同步异步阻塞非阻塞 )
- 阻塞I/O(blocking IO,属于synchronous,阶段1、2皆阻塞)
- 非阻塞I/O(nonblocking IO,属于synchronous,阶段1非阻塞、2阻塞)
- 对单个I/O请求意义不大,但给I/O多路复用提供了条件,使能在一个线程里处理多个I/O,从而提高并发处理IO能力。如对于很多个socket连接,若连接一个就建立新线程阻塞处理则可能导致线程数很多,而可创建的线程数受OS限制,就算采用线程池,每个线程一次仍只能处理一个socket,且多线程切换开销大;此时可采用非阻塞I/O在一个线程里同时处理多个连接,通过轮询看哪个socket数据就绪,这其实就是下面的I/O多路复用。
- I/O多路复用(IO multiplexing,或称event driven IO,属于synchronous,阶段1非阻塞、2阻塞)
- 主要就是利用非阻塞I/O提高并发处理能力:用户进程调用select/epoll(阻塞),select/epoll内部不断轮询所负责的所有socket当某个socket有数据到达了就通知用户进程(非阻塞),户进程再调用read操作(阻塞或非阻塞)。优势在于能处理更多连接,在web server中连接数少的情况下用IO multiplexing性能不一定比multi-threading + blocking IO好。
- 信号驱动I/O(signal driven IO,属于synchronous,阶段1非阻塞、2阻塞)
- 与非阻塞I/O类似,调用立即返回,不过在调用时还注册了信号处理函数,当数据就绪时线程收到SIGIO信号,在信号处理函数中调用I/O操作函数处理数据。
- 异步I/O(asynchronous IO),此模式下,调用的阶段1、2都由内核完成,不需要用户线程参与。
需要注意的是,与阻塞I/O模型相比,使用非阻塞I/O(或I/O多路复用)模型的主要目的是提高并发处理I/O的能力,后者一般也在I/O请求量大且每个请求读写的数据量较少的场景下才比前者有优势。此外,上述同步I/O模型的阶段2是阻塞的。
总结:

同步非阻塞、IO多路复用的典型应用场景是服务端Socket编程:用一个线程处理所有连接。
4、Java NIO
Java IO:阻塞、Stream(file stream、socket stream)、面向字节
Java NIO:非阻塞、Channel(file channel、socket channel)、面向Buffer
4.1、基本概念
主要概念:Channel、Buffer、Selector(多路复用器)
- Selector:JAVA NIO中的多路复用器,配合SelectionKey使用
- Channel:ServerSocketChannel、SocketChannel、DatagramChannel(UDP)、FileChannel。通道将数据传输给 ByteBuffer 对象或者从 ByteBuffer 对象获取数据进行传输,通道可以是单向( unidirectional)或者双向的( bidirectional)。
- Buffer:ByteBuffer、MappedByteBuffer(内存映射文件)、ShortBuffer、IntBuffer、LongBuffer、FloatBuffer、DoubleBuffer、CharBuffer。前两者有两种分配方式:从直接内存或从Java堆内存分配,前者是为了解决非直接缓冲区(如通过wrap()函数所创建的被包装的缓冲区)的效率问题而引入直接的。
4.2、Buffer
(更多详情参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/leesf456/p/6713741.html)
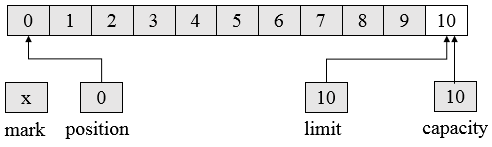
1、Buffer内部含有四个属性:(0 <= mark <= position <= limit <= capacity)
- 容量( Capacity):缓冲区能够容纳的数据元素的最大数量,容量在缓冲区创建时被设定,并且永远不能被改变。
- 上界(Limit):缓冲区现有元素的个数。
- 位置(Position):下一个要被读或写的元素的索引。位置会自动由相应的 get( )和 put( )函数更新。
- 标记(Mark):一个备忘位置。调用 mark( )来设定 mark = postion。调用 reset( )设定 position = mark。标记在设定前是未定义的(undefined)。
初始化一个容量为10的BtyeBuffer,逻辑视图如下(mark未被设定,position初始为0,capacity为10,limit为10):
2、Buffer操作:分配(allocate、allocateDirect、wrap)、read(flip、rewind)、write(clear、compact)、mark(mark、reset)
- 分配:allocate、allocateDirect操作创建一个缓冲区对象并分配一个私有的空间来储存指定容量大小的数据;wrap创建一个缓冲区对象但是不分配任何空间来储存数据元素,使用所提供的数组作为存储空间来储存缓冲区中的数据,因此在缓冲区的操作会改动数组,反之亦然。
- 进入读模式:flip(limit设位position、position设为0,mark失效)——只允许单次读因为limit变了、rewind(假定limit已经被正确设置,position设为0,mark失效)——允许多次重复读,因为limit不变
- 进入写模式:clear(position设为0,limit设为capacity,mark失效)、compact(数据整体移到前面后,limit设为capacity,position设为最后一个元素后面,mark失效)
- 标记:mark(mark设为position)、reset(position设为mark)
由上可见,如果连续两次调用flip()则缓冲区的大小变为0。
示例:
package cn.edu.buaa.nio; import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; /**
* @author zsm
* @date 2017年2月21日 下午3:04:27 Java NIO 有以下Buffer类型:ByteBuffer、MappedByteBuffer(内存映射文件)、ShortBuffer、IntBuffer、LongBuffer、FloatBuffer、DoubleBuffer、CharBuffer。前两者有两种分配方式:从直接内存或从Java堆内存分配
*/ public class T0_BufferDemo {
// read:flip,rewind;
// write:clear,compact
// mark:mark,reset // read from buffer:inChannel.write(buf)、buf.get()
// write into buffer:inChannel.read(buf)、buf.put(..)
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
RandomAccessFile aFile = new RandomAccessFile("src/cn/edu/buaa/nio/nio-data.txt", "rw");
FileChannel inChannel = aFile.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(48); // write to buffer
int bytesRead = inChannel.read(buffer);// buffer write manner 1
buffer.put((byte) 'z');// buffer write manner 2
while (bytesRead != -1) {
System.out.println("read " + bytesRead);
// read from buffer
buffer.flip();// 从写buffer模式切换到读buffer模式
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
byte b = buffer.get();// buffer read manner 1
System.out.println((char) b + " " + (0xff & b));
}
buffer.clear();// 进入写模式
inChannel.write(buffer);// buffer read manner 2
bytesRead = inChannel.read(buffer);
}
inChannel.close();
aFile.close();
} }
各种类型的Buffer:
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.wrap(new byte[] { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 'a' });
bb.rewind();
System.out.print("Byte Buffer ");
while (bb.hasRemaining())
System.out.print(bb.position() + " -> " + bb.get() + ", ");
System.out.println();
CharBuffer cb = ((ByteBuffer) bb.rewind()).asCharBuffer();
System.out.print("Char Buffer ");
while (cb.hasRemaining())
System.out.print(cb.position() + " -> " + cb.get() + ", ");
System.out.println();
FloatBuffer fb = ((ByteBuffer) bb.rewind()).asFloatBuffer();
System.out.print("Float Buffer ");
while (fb.hasRemaining())
System.out.print(fb.position() + " -> " + fb.get() + ", ");
System.out.println();
IntBuffer ib = ((ByteBuffer) bb.rewind()).asIntBuffer();
System.out.print("Int Buffer ");
while (ib.hasRemaining())
System.out.print(ib.position() + " -> " + ib.get() + ", ");
System.out.println();
LongBuffer lb = ((ByteBuffer) bb.rewind()).asLongBuffer();
System.out.print("Long Buffer ");
while (lb.hasRemaining())
System.out.print(lb.position() + " -> " + lb.get() + ", ");
System.out.println();
ShortBuffer sb = ((ByteBuffer) bb.rewind()).asShortBuffer();
System.out.print("Short Buffer ");
while (sb.hasRemaining())
System.out.print(sb.position() + " -> " + sb.get() + ", ");
System.out.println();
DoubleBuffer db = ((ByteBuffer) bb.rewind()).asDoubleBuffer();
System.out.print("Double Buffer ");
while (db.hasRemaining())
System.out.print(db.position() + " -> " + db.get() + ", ");
//结果
Byte Buffer 0 -> 0, 1 -> 1, 2 -> 2, 3 -> 3, 4 -> 4, 5 -> 5, 6 -> 6, 7 -> 97,
Char Buffer 0 -> , 1 -> ȃ, 2 -> Ѕ, 3 -> ١,
Float Buffer 0 -> 9.2557E-41, 1 -> 1.5637004E-36,
Int Buffer 0 -> 66051, 1 -> 67438177,
Long Buffer 0 -> 283686952306273,
Short Buffer 0 -> 1, 1 -> 515, 2 -> 1029, 3 -> 1633,
Double Buffer 0 -> 1.401599773079337E-309,
4.3、FileChannel
- File通道不能直接创建,只能通过在一个打开的RandomAccessFile、FileInputStream或FileOutputStream的对象上调用getChannel( )方法来获取,并且getChannel是线程安全的。
- FileChannel 位置position()、大小size()是从底层的文件描述符获得的,channel对position的修改底层文件也能看到,反之亦然。示例如下:
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile("F:/gps data/2016-11-11 18087 60399647/all 0800-0810_576832.txt", "r");
// Set the file position
randomAccessFile.seek(1000);
// Create a channel from the file
FileChannel fileChannel = randomAccessFile.getChannel();
// This will print "1000"
System.out.println("file pos: " + fileChannel.position());
// Change the position using the RandomAccessFile object
randomAccessFile.seek(500);
// This will print "500"
System.out.println("file pos: " + fileChannel.position());
// Change the position using the FileChannel object
fileChannel.position(200);
// This will print "200"
System.out.println("file pos: " + randomAccessFile.getFilePointer());当channel进行read、write时,position自动更新,若position达到size()则read返回-1,若write时position超过文件大小则扩展文件大小以容纳新数据。若read、write时指定了position,则不会改变当前的文件position,由于通道的状态无需更新,因此绝对的读和写可能会更加有效率,操作请求可以直接传到本地代码;并且多个线程可以并发访问同一个文件而不会相互产生干扰,因为每次调用都是原子性的( atomic),并不依靠调用之间系统所记住的状态。
- FileChannel无法设置为非阻塞模式,它总是运行在阻塞模式下。与Selector一起使用时,Channel必须处于非阻塞模式下,这意味着不能将FileChannel与Selector一起使用。
4.3.1、零拷贝
NIO中的FileChannel拥有transferTo和transferFrom两个方法,可直接把FileChannel中的数据拷贝到另外一个Channel,或直接把另外一个Channel中的数据拷贝到FileChannel。该接口常被用于高效的网络/文件的数据传输和大文件拷贝。在操作系统支持的情况下,通过该方法传输数据并不需要将源数据从内核态拷贝到用户态,再从用户态拷贝到目标通道的内核态,同时也避免了两次用户态和内核态间的上下文切换,也即使用了“零拷贝”,所以其性能一般高于Java IO中提供的方法。
详见 Java零拷贝-MarchOn
4.3.2、内存映射文件
新的 FileChannel 类提供了一个名为 map( )的方法,该方法可以在一个打开的文件和一个特殊类型的 ByteBuffer 之间建立一个虚拟内存映射,由 map( )方法返回的 MappedByteBuffer 对象的行为类似与基于内存的缓冲区,只不过该对象的数据元素存储在磁盘上的文件中。通过内存映射机制来访问一个文件会比使用常规方法读写高效得多,甚至比使用通道的效率都高。
映射方法: buffer = fileChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, fileChannel.size());
- 映射模式:MapMode.READ_WRITE、MapMode.READ_ONLY、MapMode.PRIVATE
- 请求的映射模式将受被调用 map( )方法的 FileChannel 对象的访问权限所限制。如:若通道以只读的权限打开的却请求 MapMode.READ_WRITE 模式,则map( )方法会抛出一个 NonWritableChannelException 异常
- MapMode.PRIVATE模式表示一个写时拷贝( copy-on-write)的映射,这意味着通过 put( )方法所做的任何修改都会导致产生一个私有的数据拷贝并且该拷贝中的数据只有MappedByteBuffer 实例可以看到。该过程不会对底层文件做任何修改,而且一旦缓冲区被施以垃圾收集动作( garbage collected),那些修改都会丢失。
4.4、SocketChannel、ServerSocketChannel
服务端客户端模型演变:阻塞IO(单线程处理所有请求->每个请求创建一个线程处理[1]->线程池处理所有请求[2])->NIO Reactor模式[3]
[1][2][3]优劣:
优势:实现非常简单,在小规模环境中能完美工作;
劣势:在高并发大规模环境下基本无法工作,因为线程的创建和销毁都需要额外的时间开销,另外每创建一个线程都需要一定的系统资源,系统资源有限,不可能无限创建线程,再者,线程数多了之后系统用于上下文切换的时间就会增大;优势:实现比较简单,在一般规模的环境中能够很好地工作;
劣势:在高并发大规模的环境下很可能会因为处理某些任务时需要等待一些外部资源而导致处理时间很长,最终导致整个线程池的所有线程全部繁忙,无法对外提供服务,给用户的感觉就是网站挂了;优势:在高并发大规模环境下也能工作得很好,性能很棒;
劣势:实现比较复杂,Java NIO有该模型的实现
DatagramChannel 和 SocketChannel 实现定义读和写功能的接口而 ServerSocketChannel不实现, ServerSocketChannel 负责监听传入的连接和创建新的 SocketChannel 对象,它本身从不传输数据。
SocketChannel是线程安全的。并发访问时无需特别措施来保护发起访问的多个线程,不过任何时候都只有一个线程的读写操作在进行中。
- Java NIO可以实现阻塞IO的功能,也可以实现非阻塞IO的功能,后者与Selector结合时为Reactor模式(即I/O多路复用模型)
- NIO Channel也可以不结合Selector实现服务端客户端,但当与Selector一起使用时,Channel必须处于非阻塞模式下。这意味着不能将FileChannel与Selector一起使用,因为FileChannel不能切换到非阻塞模式。
SelectionKey包含属性:
- interest集合:SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT、OP_ACCEPT、OP_READ、OP_WRITE
- ready集合:selectionKey.readyOps() ; (isAcceptable()、isConnectable()、isReadable()、isWritable())
- Channel:selectionKey.channel();
- Selector:selectionKey.selector();
- 附加的对象(可选):selectionKey.attach(theObject); Object attachedObj = selectionKey.attachment();
示例:
0、不结合Selector
//服务端
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(true);
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 1234));
while (true) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
if (socketChannel != null) {
System.out.println(socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
} else {
System.out.println("no connect");
}
}
1、简单Reactor模式(一线程处理连接、监听就绪及读写操作)
package cn.edu.buaa.nio; import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Set; /**
* @author zsm
* @date 2017年3月14日 上午10:32:57<br>
*
*/
//Java NIO的选择器允许一个单独的线程同时监视多个通道,可以注册多个通道到同一个选择器上,然后使用一个单独的线程来“选择”已经就绪的通道。这种“选择”机制为一个单独线程管理多个通道提供了可能。
//http://www.jasongj.com/java/nio_reactor/#精典Reactor模式
/**
* 单线程Reactor模式<br>
* 多个Channel可以注册到同一个Selector对象上,实现了一个线程同时监控多个请求状态(Channel)。同时注册时需要指定它所关注的事件,例如上示代码中socketServerChannel对象只注册了OP_ACCEPT事件,而socketChannel对象只注册了OP_READ事件。
*/
public class T3_ReactorDemo1_NIOServer {
// 与Selector一起使用时,Channel必须处于非阻塞模式下。这意味着不能将FileChannel与Selector一起使用,因为FileChannel不能切换到非阻塞模式。而套接字通道都可以。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(1234));
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (selector.select() > 0) {
Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = keys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel acceptServerSocketChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel socketChannel = acceptServerSocketChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
System.out.println("Accept request from " + socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int count = socketChannel.read(buffer);// 内核态数据复制到用户态,阻塞
if (count <= 0) {
socketChannel.close();
key.cancel();
System.out.println("Received invalide data, close the connection");
continue;
}
System.out.println("Received message " + new String(buffer.array()));
}
keys.remove(key);
}
}
}
} class T3_ReactorDemo1_NIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(1234));
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String tmpStr;
while ((tmpStr = scanner.nextLine()) != null) {
buffer.clear();
buffer.put(tmpStr.getBytes());
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
socketChannel.write(buffer);
}
}
}
}
2、多线程Reactor模式(一线程处理连接、监听就绪工作,多线程处理读写操作)
package cn.edu.buaa.nio; import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors; /**
* @author zsm
* @date 2017年3月14日 上午10:45:05
*/
// http://www.jasongj.com/java/nio_reactor/#多工作线程Reactor模式
/**
* 多线程Reactor模式<br>
* 经典Reactor模式中,尽管一个线程可同时监控多个请求(Channel),但是所有读/写请求以及对新连接请求的处理都在同一个线程中处理,无法充分利用多CPU的优势,同时读/写操作也会阻塞对新连接请求的处理。因此可以引入多线程,并行处理多个读/写操作
*/
public class T3_ReactorDemo2_NIOServer {
// 与Selector一起使用时,Channel必须处于非阻塞模式下。这意味着不能将FileChannel与Selector一起使用,因为FileChannel不能切换到非阻塞模式。而套接字通道都可以。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(1234));
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true) {
if (selector.selectNow() < 0) {
continue;
}
Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = keys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel acceptServerSocketChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel socketChannel = acceptServerSocketChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
System.out.println("Accept request from " + socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
SelectionKey readKey = socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
readKey.attach(new Processor1());
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
Processor1 processor = (Processor1) key.attachment();
processor.process(key);
}
}
}
}
} class Processor1 {
private static final ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(16); public void process(SelectionKey selectionKey) {
service.submit(() -> {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
int count = socketChannel.read(buffer);// 内核态数据复制到用户态,阻塞
if (count < 0) {
socketChannel.close();
selectionKey.cancel();
System.out.println(socketChannel + "\t Read ended");
return null;
} else if (count == 0) {
return null;
}
System.out.println(socketChannel + "\t Read message " + new String(buffer.array()));
return null;
});
}
} class T3_ReactorDemo2_NIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(1234));
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String tmpStr;
while ((tmpStr = scanner.nextLine()) != null) {
buffer.clear();
buffer.put(tmpStr.getBytes());
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
socketChannel.write(buffer);
}
}
}
}
3、多Reactor模式(一线程处理连接工作,多线程处理监听就绪及读写操作)
package cn.edu.buaa.nio; import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ClosedChannelException;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.spi.SelectorProvider;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors; /**
* @author zsm
* @date 2017年3月14日 上午10:55:01
*/
//http://www.jasongj.com/java/nio_reactor/#多Reactor
/**
* 多Reactor模式<br>
* Netty中使用的Reactor模式,引入了多Reactor,也即一个主Reactor负责监控所有的连接请求,多个子Reactor负责监控并处理读/写请求,减轻了主Reactor的压力,降低了主Reactor压力太大而造成的延迟。
* 并且每个子Reactor分别属于一个独立的线程,每个成功连接后的Channel的所有操作由同一个线程处理。这样保证了同一请求的所有状态和上下文在同一个线程中,避免了不必要的上下文切换,同时也方便了监控请求响应状态。
*/
public class T3_ReactorDemo3_NIOServer {
// 与Selector一起使用时,Channel必须处于非阻塞模式下。这意味着不能将FileChannel与Selector一起使用,因为FileChannel不能切换到非阻塞模式。而套接字通道都可以。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(1234));
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
int coreNum = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
Processor2[] processors = new Processor2[coreNum];
for (int i = 0; i < processors.length; i++) {
processors[i] = new Processor2();
}
int index = 0;
while (selector.select() > 0) {
Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys();
for (SelectionKey key : keys) {
keys.remove(key);
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel acceptServerSocketChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel socketChannel = acceptServerSocketChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
System.out.println("Accept request from " + socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
Processor2 processor = processors[(index++) / coreNum];
processor.addChannel(socketChannel);
}
}
}
}
} class Processor2 {
private static final ExecutorService service = Executors
.newFixedThreadPool(2 * Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
private Selector selector; public Processor2() throws IOException {
this.selector = SelectorProvider.provider().openSelector();
start();
} public void addChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws ClosedChannelException {
socketChannel.register(this.selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} public void start() {
service.submit(() -> {
while (true) {
if (selector.selectNow() <= 0) {
continue;
}
Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = keys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
if (key.isReadable()) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
int count = socketChannel.read(buffer);// 内核态数据复制到用户态,阻塞
if (count < 0) {
socketChannel.close();
key.cancel();
System.out.println(socketChannel + "\t Read ended");
continue;
} else if (count == 0) {
System.out.println(socketChannel + "\t Message size is 0");
continue;
} else {
System.out.println(socketChannel + "\t Read message" + new String(buffer.array()));
}
}
}
}
});
}
} class T3_ReactorDemo3_NIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(1234));
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String tmpStr;
while ((tmpStr = scanner.nextLine()) != null) {
buffer.clear();
buffer.put(tmpStr.getBytes());
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
socketChannel.write(buffer);
}
}
}
}
总结:
JAVA NIO使能用一个(或几个)单线程管理多个通道(网络连接或文件),但付出的代价是解析数据可能会比从一个阻塞流中读取数据更复杂,且提供的API使用起来略复杂,实际项目中不建议直接使用它们进行开发,而是用Netty等第三方库。
5、Netty
Netty是JBOSS针对网络开发的一套应用框架,它也是在NIO的基础上发展起来的。netty基于异步的事件驱动,具有高性能、高扩展性等特性,它提供了统一的底层协议接口,使得开发者从底层的网络协议(比如 TCP/IP、UDP)中解脱出来。
详见: Netty使用示例
6、参考资料
1、http://blog.csdn.net/historyasamirror/article/details/5778378 ——阻塞非阻塞同步异步
2、https://my.oschina.net/andylucc/blog/614295 ——阻塞非阻塞同步异步
3、http://www.jasongj.com/java/nio_reactor/ ——Java NIO Server/Client
4、http://www.iteye.com/magazines/132-Java-NIO ——Java NIO API较详细介绍
5、http://www.cnblogs.com/leesf456/p/6713741.html——Buffer
6、http://www.cnblogs.com/leesf456/p/6715740.html——Channel
I/O模型(同步、非同步、阻塞、非阻塞)总结的更多相关文章
- 简明网络I/O模型---同步异步阻塞非阻塞之惑
转自:http://www.jianshu.com/p/55eb83d60ab1 网络I/O模型 人多了,就会有问题.web刚出现的时候,光顾的人很少.近年来网络应用规模逐渐扩大,应用的架构也需要随之 ...
- Windows I/O模型、同步/异步、阻塞/非阻塞
转载自:http://www.cppblog.com/tx7do/articles/5954.html 同步 所谓同步,就是在发出一个功能调用时,在没有得到结果之前,该调用就不返回.按照这个定义,其实 ...
- Python番外之 阻塞非阻塞,同步与异步,i/o模型
1. 概念理解 在进行网络编程时,我们常常见到同步(Sync)/异步(Async),阻塞(Block)/非阻塞(Unblock)四种调用方式: 同步/异步主要针对C端: 同步: 所谓同步,就 ...
- 网络I/O模型---同步异步阻塞非阻塞之惑
网络I/O模型 人多了,就会有问题.web刚出现的时候,光顾的人很少.近年来网络应用规模逐渐扩大,应用的架构也需要随之改变.C10k的问题,让工程师们需要思考服务的性能与应用的并发能力. 网络应用需要 ...
- linux基础编程:IO模型:阻塞/非阻塞/IO复用 同步/异步 Select/Epoll/AIO(转载)
IO概念 Linux的内核将所有外部设备都可以看做一个文件来操作.那么我们对与外部设备的操作都可以看做对文件进行操作.我们对一个文件的读写,都通过调用内核提供的系统调用:内核给我们返回一个file ...
- 阻塞 , 非阻塞 , 同步 ,异步 , I/O模型
•阻塞,非阻塞:进程/线程要访问的数据是否就绪,进程/线程是否需要等待: •同步,异步:访问数据的方式,同步需要主动读写数据,在读写数据的过程中还是会阻塞:异步只需要I/O操作完成的通知,并不主动读写 ...
- (转)同步异步,阻塞非阻塞 和nginx的IO模型
同步异步,阻塞非阻塞 和nginx的IO模型 原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/wxl-dede/p/5134636.html 同步与异步 同步和异步关注的是消息通信机制 (sy ...
- python并发编程之IO模型 同步 异步 阻塞 非阻塞
IO浅谈 首先 我们在谈及IO模型的时候,就必须要引入一个“操作系统”级别的调度者-系统内核(kernel),而阻塞非阻塞是跟进程/线程严密相关的,而进程/线程又是依赖于操作系统存在的,所以自然不能脱 ...
- IO模型对比:同步、异步、阻塞、非阻塞
最近工作接触到了网络服务同步和异步,所以学习了下<UNIX网络编程>,在此作下总结. 一.I/O模型 输入/输出(I/O)是在主存和外部设备(如磁盘驱动器.终端和网络)之间拷贝数据的过程. ...
随机推荐
- php分享二十:mysql优化
1:垂直分割 示例一:在Users表中有一个字段是家庭地址,这个字段是可选字段,相比起,而且你在数据库操作的时候除了个人信息外,你并不需要经常读取或是改写这个字段.那么,为什么不把他放到另外一张表中呢 ...
- Spring Security教程(五):自定义过滤器从数据库从获取资源信息
在之前的几篇security教程中,资源和所对应的权限都是在xml中进行配置的,也就在http标签中配置intercept-url,试想要是配置的对象不多,那还好,但是平常实际开发中都往往是非常多的资 ...
- modelsim编译Xilinx器件库的另一种方法(节省时间)
以前在用modelsim对Xilinx进行器件库编译时,我用的比较多的是直接在ISE中编译器件库,感觉很方便简单,就是编译时间有点长.自从前段时间,在自己电脑装MathType,360杀毒软件将它视为 ...
- [na]二层sw数据交换
1,同vlan下,两台pc配置了GW,arp请求过程. Pc1 ping pc0的时候,触发pc1的arp请求,发给GW后,GW继续发给pc0(同一个vlan),pc0收到后给pc1回复.Pc1发出i ...
- Xcode6中添加pch文件
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/YouXianMing/p/3989155.html 1. 新建工程: 2. 创建pch文件: 3. 在setting里面进行设置: 4. 一切尽在 ...
- lua -- 商店控制器部分
-- 创建商店类,继承了Behavior local UIShopController = class("UIShopController", Behavior); -- 包含并引 ...
- Linux系统Apache服务 - 配置HTTP的默认主页
1.安装HTTPD和httpd-manual软件包 # yum -y install http httpd-manual 2.创建/var/www/html/index.html 内容是 Hello ...
- 深入HBase架构解析(二)【转】
转自:http://www.blogjava.net/DLevin/archive/2015/08/22/426950.html 前言 这是<深入HBase架构解析(一)>的续,不多废话, ...
- java8的新特性以及用法简介
1. 介绍 2 接口的默认方法 2 lambda表达式 2.1 函数式接口 2.2 方法与构造函数引用 2.3 访问局部变量 2.4 访问对象字段与静态变量 3. 内建函数式接口 3.1 Predic ...
- 【C/C++】C语言嵌入式编程修炼·背景篇·软件架构篇·内存操作篇
C 语言嵌入式系统编程修炼之一:背景篇 不同于一般形式的软件编程,嵌入式系统编程建立在特定的硬件平台上,势必要求其编程语言具备较强的硬件直接操作能力.无疑,汇编语言具备这样的特质.但是,归因于汇编语言 ...
