codeforces 592B/C
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/592/problem/B
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Ari the monster always wakes up very early with the first ray of the sun and the first thing she does is feeding her squirrel.
Ari draws a regular convex polygon on the floor and numbers it's vertices 1, 2, ..., n in clockwise order. Then starting from the vertex 1she draws a ray in the direction of each other vertex. The ray stops when it reaches a vertex or intersects with another ray drawn before. Ari repeats this process for vertex 2, 3, ..., n (in this particular order). And then she puts a walnut in each region inside the polygon.
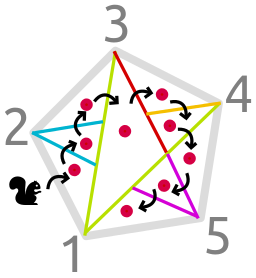
Ada the squirrel wants to collect all the walnuts, but she is not allowed to step on the lines drawn by Ari. That means Ada have to perform a small jump if she wants to go from one region to another. Ada can jump from one region P to another region Q if and only if P and Q share a side or a corner.
Assuming that Ada starts from outside of the picture, what is the minimum number of jumps she has to perform in order to collect all the walnuts?
The first and only line of the input contains a single integer n (3 ≤ n ≤ 54321) - the number of vertices of the regular polygon drawn by Ari.
Print the minimum number of jumps Ada should make to collect all the walnuts. Note, that she doesn't need to leave the polygon after.
5
9
3
1
One of the possible solutions for the first sample is shown on the picture above.
找规律。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
long long n;
cin>>n;
cout<<(n-)*(n-)<<endl;
}
─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/592/problem/C
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Vector Willman and Array Bolt are the two most famous athletes of Byteforces. They are going to compete in a race with a distance of Lmeters today.
Willman and Bolt have exactly the same speed, so when they compete the result is always a tie. That is a problem for the organizers because they want a winner.
While watching previous races the organizers have noticed that Willman can perform only steps of length equal to w meters, and Bolt can perform only steps of length equal to b meters. Organizers decided to slightly change the rules of the race. Now, at the end of the racetrack there will be an abyss, and the winner will be declared the athlete, who manages to run farther from the starting point of the the racetrack (which is not the subject to change by any of the athletes).
Note that none of the athletes can run infinitely far, as they both will at some moment of time face the point, such that only one step further will cause them to fall in the abyss. In other words, the athlete will not fall into the abyss if the total length of all his steps will be less or equal to the chosen distance L.
Since the organizers are very fair, the are going to set the length of the racetrack as an integer chosen randomly and uniformly in range from 1 to t (both are included). What is the probability that Willman and Bolt tie again today?
The first line of the input contains three integers t, w and b (1 ≤ t, w, b ≤ 5·1018) — the maximum possible length of the racetrack, the length of Willman's steps and the length of Bolt's steps respectively.
Print the answer to the problem as an irreducible fraction  . Follow the format of the samples output.
. Follow the format of the samples output.
The fraction  (p and q are integers, and both p ≥ 0 and q > 0 holds) is called irreducible, if there is no such integer d > 1, that both pand q are divisible by d.
(p and q are integers, and both p ≥ 0 and q > 0 holds) is called irreducible, if there is no such integer d > 1, that both pand q are divisible by d.
10 3 2
3/10
7 1 2
3/7
In the first sample Willman and Bolt will tie in case 1, 6 or 7 are chosen as the length of the racetrack.
题意:
两个人跑步比赛,一个人一步只能走w米,一个人一步只能走b米;
终点位置可以在整数1~t里面随便选择一个;
终点之后都是陷阱,两个人比赛但两个人都不想死,所以不能越过终点,在这种情况下,谁走的远,就算谁赢;
然后问你选择平局的概率是多少。
题解:
算算样例,可以看出所有最小公倍数情况的终点都能产生平局;
我们设tail=min(w,b)-1,可以看出,1~tail位置的终点也产生平局,每个最小公倍数终点后面tail个位置也能产生平局;
那么我们就围绕这个进行计算,可以按照1~t里有多少个lcm(w,b)整数倍终点进行分类考虑;
不过有一个错误点就是lcm(w,b)超过unsigned long long范围的情况,
这样一来,因为t的范围限制,lcm(w,b)必然大于t了,只需要在前面特判一下lcm(w,b)>t的情况即可,
具体怎么特判,lcm(w,b) = (w*b) / gcd(w,b) > t,两边取对数进行比较即可。
AC代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long llu;
inline llu gcd(llu m,llu n){return n?gcd(n,m%n):m;}
llu lcm(llu m,llu n){return m/gcd(m,n)*n;}
void output(llu p,llu q)
{
llu pq_gcd=gcd(p,q);
cout<<p/pq_gcd<<"/"<<q/pq_gcd<<endl;
}
bool check(llu t,llu w,llu b)
{
return log(w*1.0)+log(b*1.0)-log(gcd(w,b)*1.0)>log(t*1.0);
}
int main()
{
llu t,w,b;
cin>>t>>w>>b; llu tail=min(w,b)-;//tail>=0 if(check(t,w,b))//判断lcm(w,b)>t?
{
output(min(tail,t),t);
return ;
} llu wb_lcm=lcm(w,b);
llu cnt=t/wb_lcm;
if(cnt==)
{
if(t<=tail)
{
cout<<"1/1"<<endl;
return ;
}
else
{
output(tail,t);
return ;
}
}
else if(cnt==)
{
llu ed=min(t%wb_lcm,tail)+;
output(tail+ed,t);
return ;
}
else
{
llu ed=min(t%wb_lcm,tail)+;
output(tail+(cnt-)*(tail+)+ed,t);
return ;
}
}
codeforces 592B/C的更多相关文章
- CodeForces 592B
题目链接: http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/592/B 这个题目没啥说的,画图找规律吧,哈哈哈 程序代码: #include <cstdio&g ...
- codeforces 592B The Monster and the Squirrel
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/592/problem/B 题目分类:数学,找规律 题目分析:重要的是画图找规律 代码: #include<bits/s ...
- Codeforces Round #328(Div2)
CodeForces 592A 题意:在8*8棋盘里,有黑白棋,F1选手(W棋往上-->最后至目标点:第1行)先走,F2选手(B棋往下-->最后至目标点:第8行)其次.棋子数不一定相等,F ...
- python爬虫学习(5) —— 扒一下codeforces题面
上一次我们拿学校的URP做了个小小的demo.... 其实我们还可以把每个学生的证件照爬下来做成一个证件照校花校草评比 另外也可以写一个物理实验自动选课... 但是出于多种原因,,还是绕开这些敏感话题 ...
- 【Codeforces 738D】Sea Battle(贪心)
http://codeforces.com/contest/738/problem/D Galya is playing one-dimensional Sea Battle on a 1 × n g ...
- 【Codeforces 738C】Road to Cinema
http://codeforces.com/contest/738/problem/C Vasya is currently at a car rental service, and he wants ...
- 【Codeforces 738A】Interview with Oleg
http://codeforces.com/contest/738/problem/A Polycarp has interviewed Oleg and has written the interv ...
- CodeForces - 662A Gambling Nim
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/662/A 题目大意: 给定n(n <= 500000)张卡片,每张卡片的两个面都写有数字,每个面都有0.5的概 ...
- CodeForces - 274B Zero Tree
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/274/B 题目大意: 给定你一颗树,每个点上有权值. 现在你每次取出这颗树的一颗子树(即点集和边集均是原图的子集的连 ...
随机推荐
- Struts2_day03讲义_使用Struts2完成对客户查询的优化操作
- Dubbo -- 系统学习 笔记 -- 示例 -- 泛化引用
Dubbo -- 系统学习 笔记 -- 目录 示例 想完整的运行起来,请参见:快速启动,这里只列出各种场景的配置方式 泛化引用 泛接口调用方式主要用于客户端没有API接口及模型类元的情况,参数及返回值 ...
- phpVirtualBox – 用浏览器操作虚拟机
摘自:https://code.google.com phpVirtualBox 一个开源的,VirtualBox的用户界面,用PHP编写的AJAX实现.作为一个现代的Web界面,它允许你远程访问和控 ...
- MinGW 是什么
3.1:MinGW 是什么? MinGW 提供了一套简单方便的Windows下的基于GCC 程序开发环境.MinGW 收集了一系列免费的Windows 使用的头文件和库文件:同时整合了GNU ( ht ...
- dedeCMS解码
var str = 'arrs1[]=99&arrs1[]=102&arrs1[]=103&arrs1[]=95&arrs1[]=100&arrs1[]=98& ...
- Four Ways to Create a Thread
Blaise Pascal Magazine Rerun #5: Four Ways to Create a Thread This article was originally written ...
- informix中的时间计算
今天看SUN服务器是的mail(vi /var/mail/xxxuser),发现定时任务上的一些存储过程执行有错误,其中有一个错误是long transaction,长事务错误,到数据库一查,天哪 ...
- Linux中的邮件发送
这里写出两种常用的邮件发送方式: mail: 需要安装sendmail和postfix两个服务 编辑/etc/mail.rc,在最后添加 set from=scottcho@126.com smtp= ...
- Mac下Intellij IDea发布JavaWeb项目 详解三 (为所有Module配置Tomcat Deployment 并测试web 网页 配置Servlet)
step4 为所有项目配置Deployment 4.1 如图 4.2 [+][Artifact] 4.3 将这里列出的所有内容选中后,点[OK] 4.4 选完是这样,表示,这三个java ee 项目会 ...
- 非static成员函数通过类名::来调用,空指针调用成员方法不出错!
首先来看这一段代码: #include <iostream> using namespace std; class A{ public: int k; void p1(){ cout< ...
